Page 131 of 2189
Timing Belt
Removal (cont'd)
9. Remove the CKF sensor from the oI pump.
10. Loosen the adjusting bott lgO..to remove tension from theretighten the adjusting bolt.
12 N.m 11.2 kgt.m,8.7 rbf.ftl
Push the tensioner
timing be lt. then
AD.'USNNG BOLT4{ N.m 14.5 kgt m,33 tbtftl
1 1. Remove the timing belt.
6-20
lnstallation
Install the timing belt in the reverse order of removal;Only key points are described here.
l. set rhe timing belt drive pulley so that the No. 1 pis-ton as at top dead center (TDC), Align the groove onthe timing belt drive pulley to the pointer on the oilpump.
TDC MARKPOINTER
I
t
I
TIMING BELTDBIVE PULLEYClean.I
2. Set the camshaft pulley to TDC. Align the TDCmarks on the camshaft pulley to the cylinder headsurface.
Page 133 of 2189
Crankshaft Speed Fluctuation (CKF) Sensor
2.
3.
5.
Replacement
4.
1.
6x1.0mm'12 N.m {1.2 kgt.m,8.7 tbf.ft)
6. Installthe CKF sensor in reverse order of removal.
Remove the cylinder head cover.
NOTE: Refer to page 6-46 when installing.
Remove the crankshaft pulley (see page 6_16),
Remove the upper cover and dipstick/tube {seepage 6-19).
Remove the lower cover and idler pulley bracket(see page 6-19).
Disconnect the CKF sensor connector, then removethe CKF sensor.
CKF SENSORCONNECTOR
6-22
:(
I
Page 254 of 2189
Bt6A2, Dl6Y8 engines:
a. Disconnect the primary HO2S connector then
remove the primary HO2S.
816A2 engine
D16Y8 engine
PRIMARYH02S CONNECTOR
PRIMARY HO2S44 N.m {4.5 kgt'm.33 lbf'ft)
L
2. Install the primary HO2S in reverse order of removal'
Secondsry H02S:
1. Remove the secondary HO2S
Dl6Y5, Dt6Y7 engines:
a. Disconnect the secondary HO2S connector.
then remove the secondary HO2S'
02 SENSOR
816A2, Dt6Y8 ongin6s:
a. Remove the grommet, and pull out the secondary
HO2S connector, then disconnect the secondary
HO25 connector'
SECONOARY H()2S
CONNECTOR
{cont'd)
9-13
Page 255 of 2189
HO2S
Replacement (cont'd)
b, Remove the secondarv HO2S.
02 SENSOR WRENCH
SECONOARY HO2S4,r N.m (4.5 kgf.m, 33 tbf.ft)
Install the secondary HO2S in reverse order ofremovat.
9-14
wa
Page 681 of 2189

Description
The automatic transmission is a 3-element torque converter and a dual-shaft electronically controlled unit which provides
4 soeeds forward and 1 reverse.
Torque Convertel, Geats, and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump, turbine and stator, assembled in a single unit. They are connected to the engine
crankshaft so they turn together as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the torque converter is a ring gear
which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being started. The entire torque converter assembly seryes as a
flywheel while transmiuing power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has two parallel shafts: the mainshaft and the countershaft. The mainshaft is in Iine with the engine
crankshaft. The mainshaft includes the 1st, 2nd and 4th clutches, gears tor 2nd, 4th, reverse and lst (3rd gear is integral
with the mainshaft, while the reverse gear is integral with the 4th gear). The countershaft includes the 3rd clutch, and
gears for 3rd,2nd, 4th, reverse. 1st and park. The gears on the mainshaft are in constant mesh with those on the counter-
shaft. When certain combinations of gears in transmission are engaged by clutches. power is transmitted from the main-
shaft to the countershaft to provide E, ld, E, and E positions.
Electronic Control
The electronic control svstem consists of the Powertrain Control Module {PCM), sensors, a linear solenoid and four
solenojd valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comtonable driving under all conditions. The PCM is
located below the dashboard, under the front lower panel on the passenger's side
Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main vatve body, the secondary valve body, the regulator valve body, the servo body and the
lock-up valve body through the respective separator plates, They are bolted on the torque converter housang
The main valve body contains the manual valve, the 1-2 shift valve. the 2nd orifice control valve, the CPB {Clutch Pressure
Back-up) valve, the modulator valve. the servo control valve, the relief valve, and ATF pump gears The secondary valve
body contains the 2-3 shift valve. the 3-4 shift valve, the 3-4 orifice control valve, the 4th exhaust valve and the CPC (Clutch
pressure Control) valve. The regulator valve body contains the pressure regulator valve, the torque converter check valve,
the cooler relief valve, and the lock-up control valve. The servo body contains the servo valve which is integrated with the
reverse shift fork, and the accumulators. The lock-up valve body contains the lock-up shift valve and the lock-up timing
valve. The linear solenoid and the shift control solenoid valve Ay'B are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing,
and the lock-up control solenoid valve Ay'B is bolted on the outside of the torque converter housing. Fluid from regulator
passes through the manual valve to the various control valves. The clutches receive fluid from their respective teed pipes
or internal hydraulic circuit.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input from various sensors located throughout the car determines which shift control solenoid valve the PCM will activate
Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes a line
to one of the clutches, engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear, The shift control solenoid valves A and B are con-
trolled by the PCM.
Lock-up Mechanism
In ,Dt1 position, in 3rd and 4th. and in E position in 3rd, pressurized fluid is drained from the back of the torque converter
through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held against the torque converter cover. As this takes place, the
mainshaft rotates at the same as the engine crankshaft. Together with hydraulic control, the PCM optimizes the timing of
the lock-up mechanism. The lock-up valves control the range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves A and
B, and linear solenoid. When lock-up control solenoid valves A and B activate, the modulator pressure changes The lock-
up control solenoid valves A and B and the linear solenoid are controlled by the PCM.
(cont'd)
14-3
Page 692 of 2189
Description
Electronic Control System (cont'd)
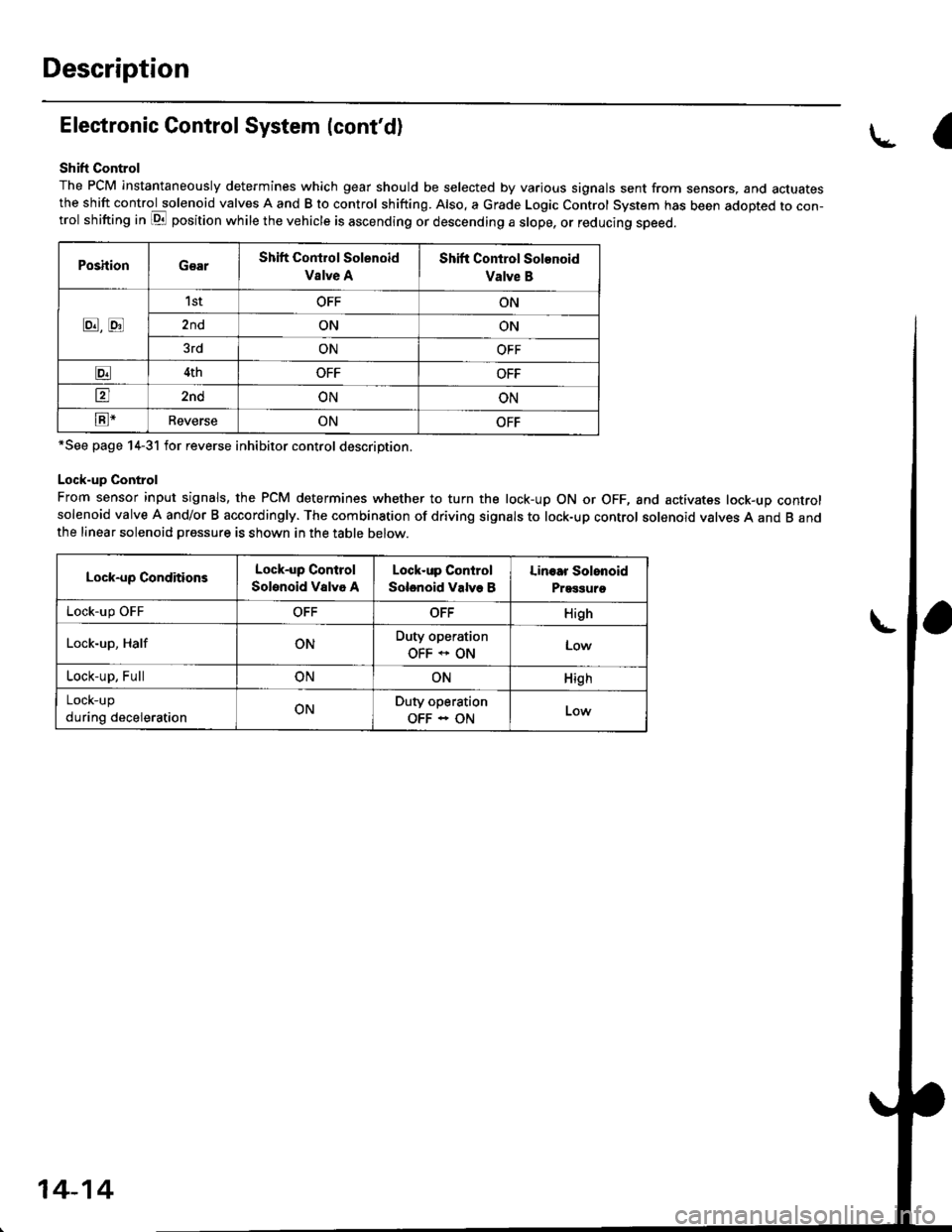
Shift Control
The PCM instantaneously determines which gear should be selected by various signals sent from sensors, and actuatesthe shift control solenoid valves A and B to control shifting. Also. a Grade Logic Control System has been adopted to con-trol shifting in E position while the vehicle is ascending or descending a slope, or reducing speed.
PoshionGearShift Control Solenoid
Vslve A
Shift Control Solenoid
Valve B
8,tr
1stOFFON
2ndONON
3rdONOFF
E4thOFFOFF
tr2ndONON
E-ReverseONOFF
*See page 14-31 for reverse inhibitor control description.
Lock-up Control
From sensor input signals, the PCM determines whether to turn the lock-up ON or OFF, and activates lock-up controlsolenoid valve A and/or B accordingly. The combination of driving signals to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B andthe linear solenoid pressure is shown in the table below.
Lock-up ConditionsLock-up Control
Solenoid Valvo A
Lock-up Control
Solenoid Valve B
Linoar Solonoid
Prggguro
Lock-up OFFOFFOFFHigh
Lock-up, HalfONDuty operation
OFF * ONLow
Lock-up, FullONONHigh
LOCK-Up
during decelerationONDuty operation
OFF - ON
a
14-14
Page 807 of 2189

O LocK WASHER Replace,
O REVERSE SHIFT FORK
O COUNTERSHAFT REVERSE GEAR COLLAR
G) COUNTERSHAFT REVERSE GEAR
@ NEEDLE BEARING
@ REVERSE SELECTOR
O REVERSE SELECTOR HUB
@ COUNTERSHAFT 4TH GEAR
O NEEDLE BEARING
@ DISTANCE GOLLAR, 28 mm Selective part
O COUNTERSHAFT 2ND GEAR
@ THRUST NEEDIE BEARING
@ COUNTERSHAFT 3RD GEAR
@ NEEDLE BEARING
@ COUNTEBSHAFT 3RD GEAR COLLAR
@ THRUST NEEDLE BEAFING
O SPLINED WASHER
@ 3RD CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
@ O-RtNGs Replace.
@ COUNTERSHAFT
@ SNAP RING
@ THRUST WASHER
€) THRUST NEEDTE BEARING
@} MATNSHAFT 4TH GEAR/REVERSE GEAR
@i NEEDLE BEARINGS
@ THRUST NEEDLE EEARING
@) MAINSHAFT 4TH GEAR COLLAR
@ 2ND/4TH CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
@ o-RlNGs Replace.
@ THRUST WASHER,36.5 x 55 mm Sel€ctive part
@ THRUST NEEDLE BEARING
@ MAINSHAFT zND GEAR
@ NEEDLE BEARING
@ THRUST NEEDLE BEARING
@ MAINSHAFI
@ S€ALING RINGS, 35 mm
@ SEALING RING,29 mm
@} NEEDIE BEARING
@ SET RING
@ sHrFT CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE A/B ASSEMSLY
@ HARNESS CLAMP BRACKET
@ SHIFT COI,ITROL SOI"ENOID FILTER/GASKET Replace.
@ CONNECTOR BFACKET
@D TNANSMISSION HANGER
@ BREATHER CAP
@ MAINSHAFT SPEED SENSOR
@ MATNSHAFT SPEED SENSOR WASHER {Dl6Y' ongine}
@ O-RING Replace.
@ SNAP RING
@ MAINSHAFT TRANSMISSION HOUSING BEARING
@ OOUNIERSHAFT TRANSMISSION HOUSING BEARING
@ REVERSE IDLER GEAR SHAFT HOLDER ASSEMBLY
@ NEEDI.E BEARING
@ olL SEAL Replace.
@ SET RING, fll mm Selective part
@ rnANsMrssloN HouslNG
@ REVERSE IDI."ER GEAR
@ DowEL PINS
@ TRANSMISSION HOUSING GASKET Replace.
@ DIFFERENfIAL ASSEMBLY
@ OIL SEAL Replace.
@ TOROUE CONVERTER HOUSING
TOROUE SPECIFICANONS
Boh/Nut No.Torquo valueSizeRomarks
6B
10A
12 N.m {1.2 kgf.m,8.7 lbf.ft)
14 N.m (1.4 kgf'm, 10lbf'ft)
44 N.m (4.5 kgf.m, 33 lbf'ft)
6x1.0mm
6x1.0mm
10 x 1.25 mm
14-129
Page 856 of 2189
Transmission
_\,]ffil
Reassembly (cont'd)
TRANSMISSIONHANGER
MAINSHAFTSUB.ASSEMBLY
*''
Ufln
$*U ./
TRANSMISSION HOUSINGMOUNTING BOLTS10 x 1.25 mm4{ N.m {4.5 kg{.m,33 lbI.ft)
TRANSMISSION HOUSING
REVERSE GEARCOLLAR
REVERSE GEAR
LOCK WASHER
SHIFT FORK
MAINSHAFT SPEEDSENSOR WASHER(D16Y7 engine)
MAINSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFTSUB.ASSEMBLY
OIFFER€NTIALASSEMBLY
SPEED
TRANSMISSIONHOUSING GASKET
TOROUE CONVERTERHOUSING
14-178