1996 GMC SIERRA flat tire
[x] Cancel search: flat tirePage 298 of 404

Tires
We don’t make tires. Your new vehicle comes with
high-quality tires made by a leading tire manufacturer.
If you ever have questions about your tire warranty and
where
to obtain service, see your GM Warranty bookJet
for details. Poorly maintained and improperly used tires
are dangerous.
0
0
0 0
Overloading your tires can cause overheating
as a result of too much friction. You could
have an airout and a serious accident. See
“Loading Your Vehicle”
m the Index.
Underinflated tires pose the same danger as
overloaded tires. The resulting accident
could cause serious injury. Check all tires
frequently to maintain the recommended pressure. Tire pressure should be checked
when your tires are cold.
Overinflated tires are more likely to
be
cut, punctured or broken by a sudden
impact
-- such as when you hit a pothole.
Keep tires at the recommended pressure.
Worn, old tires can cause accidents.
If your
tread is badly worn, or if your tires have
been damaged, replace them.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 299 of 404

Inflation -- Tire Pressure
The Certification/Tire label. which is on the rear edge of
the driver's door, or on the incomplete vehicle document
in the cab, shows the correct inflation pressures for your
tires when they're cold. "Cold" means your vehicle has
been sitting for at least three hours or driven no more
than
I mile (I .6 km).
You can operate some vehicles at reduced inflation
pressures
only when you'll be carrying reduced loads.
On those vehicles, the minimum cold inflation pressures
for a typical reduced load are printed on the Improved
Ride Tire Pressure label located
on the driver's door.
Weigh the vehicle to find the load on each tire and see
the label for the
minimum cold inflation pressures for
that load.
1 NOTICE:
~.
1
Don't let anyone tell you that underinflation or
overinflation is
all right. It's not. If your tires
don't have enough air (underinflation), you can
get the following:
NOTICE: (Continued)
NOTICE: (Continued)
Too much flexing
Too much heat
Tire overloading
Bad wear
Bad handling
Bad fuel economy.
if your tires have too much air (overinflation),
you can get the following:
Unusual wear
Bad handling
Rough ride
Needless damage from road hazards.
When
to Check
Check your tires once
a month or more. Also, check the
tire pressure of the spare tire,
6-49
ProCarManuals.com
Page 300 of 404

How to Check
Use a good quality pocket-type gage to check tire
pressure.
You can’t tell if your tires are properly inflated
simply by looking at them. Radial tires may
look
properly inflated even when they’re underinflated.
Be sure
to put the valve caps back on the valve
stems. They help prevent leaks
by keeping out dirt
.and moisture.
Tire Inspection and Rotation
Tires should be inspected every 6,000 to 8,000 miles
(10 000 to 13 000 km) for any signs of unusual wear. If
unusual wear
is present, rotate your tires as soon as
possible and check wheel alignment. Also check for
damaged tires or wheels. See “When It’s Time for New
Tires” and ‘‘Wheel Replacement” later
in this section for
more information.
If your vehicle has dual rear wheels,
also see “Dual ‘Tire Operation” later
in this section.
I
FRT FRT
I
The purpose of regular rotation is to achieve more
uniform wear for all tires on the vehicle. The first
rotation
is the most important. See “Scheduled
Maintenance Services”
in the Index for scheduled
rotation intervals.
If
your vehicle has single rear wheels, always use one of
the correct rotation patterns
shown here when rotating
your tires.
If your vehicle has front [Ires with different load ranges
or tread designs (such as all season vs. on/off road) than
the rear tires, don’t rotate your tires front to rear.
6-50
ProCarManuals.com
Page 301 of 404
rTl
II
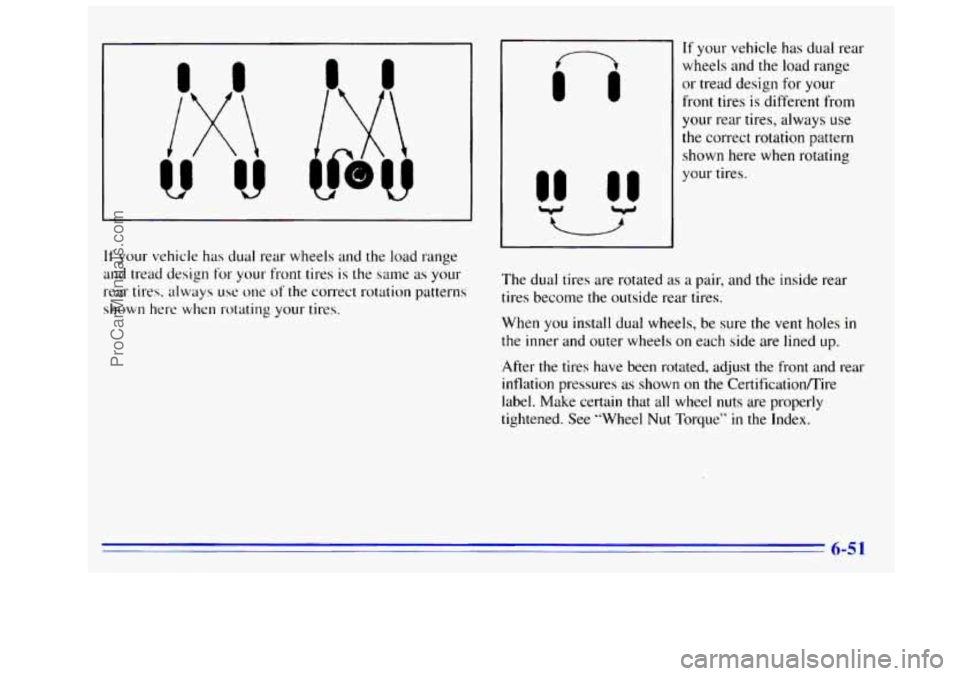
If your vehicle has dual rear wheels and the load range
and tread design for your front tires is the same as your
rear tires. always
use one of the correct rotation patterns
shown here when rotating your tires.
11 If your vehicle has dual rear
Q
wheels and the load range
or tread design for
your
~ front tires is different from
your rear tires, always use
the correct rotation pattern shown here when rotating
your tires.
The dual tires are rotated
as a pair, and the inside rear
tires become the outside rear tires.
When
you install dual wheels, be sure the vent holes in
the inner and outer wheels on each side are lined up.
After the tires have been rotated, adjust the front and rear
inflation pressures as shown on the Certificatiomire
label. Make certain that
all wheel nuts are properly
tightened. See “Wheel
Nut Torque” in the Index.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 302 of 404

When It’s Time for New Tires
Rust or dirt on
a wheel, or on the parts to which
it
is fastened, can make- wheel nuts become loose
.after
a time. The wheel could come off and cause
an accident. When you change
a wheel, remove
any rust or dirt from places where the wheel
attaches to the vehicle. In an emergency, you can
use a cloth or a paper towel to do this; but be
sure to use
a scraper or wire brush later, if you
need to, to get all the rust or dirt
off. (See
“Changing a Flat Tire” in the Index.) One
way to tell when it’s
time for new tires is
to
check the treadwear
indicators, which will
appear when your tires have
only
1/16 inch (1.6 mm) or
less
of tread remaining.
Some commercial truck
tires may not have
treadwear indicators.
Its
You need a new tire if any of the following statemen
are true:
0 You’can see the indicators at three or more places
around the tire.
You can see cord or fabric showing through the tire’s
rubber.
0 The tread or sidewall is cracked, cut or snagged deep
enough to show cord or fabric.
0 The tire has a bump, bulge or split.
0 The tire has a puncture, cut or other damage that ,
can’t be repaired well because of the size or location
of the damage.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 303 of 404

Dual Tire Operation
When the vehicle is new, or whenever a wheel, wheel
bolt or wheel nut is replaced, check the wheel nut torque
after
100, 1,000 and 6,000 miles ( 160, I 600 and IO 000
km) of driving. For proper torque, see "Wheel Nut
Torque" in the Index.
The outer tire on a dual wheel setup generally wears
faster than the inner tire. Your tires will wear more
evenly and last longer
if you rotate the tires periodically.
If you're going to be doing a lot of driving on
high-crown roads,
you can reduce tire wear by adding
5 psi (35 kPa) to the tire pressure in the outer tires. Be
sure to return to the recommended pressures when no
longer driving under those conditions. See "Changing
a
Flat Tire" in the Index for more information.
A CAUTION:
I
If you operate your vehicle with a tire that is
badly underinflated, the tire can overheat. An
overheated tire can lose air suddenly or catch fire.
You or others could be injured. Be sure
all tires
(including the spare, if any) are properly inflated.
Buying New Tires
To find out what kind and size of tires you need, look at
the Certificntion/Tire label.
Tlze tires installed
on your vehicle when it was new had
a Tire Performance Criteria Specification (TPC Spec)
number
on each tire's sidewall. When you get new tires,
get ones
with that same TPC Spec number. That way
your vehicle
will continue to have tires that are designed
to give proper endurance, handling, speed rating,
traction, ride and other things during normal service
on
your vehicle. If your tires have an all-season tread
design,
the TPC number will be followed by an "MS"
(for mud and snow).
If you ever replace your tires with those not having a
TPC
Spec number, make sure they are the same size,
load range, speed rating and construction type
(bias,
bias-belted or radial) as your original tires.
6-53
ProCarManuals.com
Page 305 of 404

Tempera A, B, c
The temperature grades are A (the highest), B, and C,
representing the tire’s resistance to the generation of
heat and its ability
to dissipate heat when tested under
controlled conditions
on a specified indoor laboratory
test wheel. Sustained high temperature can cause the
material of the tire to degenerate and reduce tire life, and
excessive temperature can lead
to sudden tire failure.
The grade
C corresponds to a level of performance
which
all passenger car tires must meet under the
Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard
No. 109. Grades
B and A represent higher levels of performance on the
laboratory test wheel than the minimum required
by law.
--
Warning: The temperature grade for this tire is
established for a tire that is properly inflated and not
overloaded. Excessive speed, underinflation, or
excessive loading, either separately or in combination,
can cause heat buildup and possible tire failure.
Wheel Alignment and Tire Balance
The wheels on your vehicle were aligned and balanced
carefully at the factory
to give you the longest tire life
and best overall performance,
In most cases, you will not need to have your wheels
aligned again. However, if
you notice unusual tire wear
or
your vehicle pulling one way or the other, the
alignment may need
to be reset. If you notice your
vehicle vibrating when driving
on a smooth road, your
wheels may need to be rebalanced.
Wheel Replacement
Replace any wheel that is bent, cracked, or badly rusted
or corroded.
If wheel nuts keep coming loose, the wheel,
wheel bolts and wheel nuts should be replaced.
If the
wheel leaks air, replace it (except some aluminum
wheels, which can sometimes be repaired). See your
GM dealer if any of these conditions exist.
Your dealer will know the kind of wheel you need.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 306 of 404

Each new wheel should have the same load-carrying
capacity, diameter, width, offset and be mounted the same way as the one it replaces.
If you need to replace any
of your wheels, wheel bolts
or wheel nuts, replace them only with new
GM original
equipment parts. This way, you will be sure
to have the
right wheel, wheel bolts and wheel nuts for your vehicle.
CAUTION:
I
Using the wrong replacement wheels, wheel bolts
or wheel nuts on your vehicle can be dangerous.
It could affect the braking and handling of your
vehicle, make your tires lose air and make you
lose. control.
You could have a collision in which
you or others could be injured. Always use the
correct wheel, wheel bolts and wheel nuts for
replacement.
NOTICE:
The wrong wheel can also cause problems with
bearing life, brake cooling, speedometer or
odometer calibration, headlamp aim, bumper
height, vehicle ground clearance and tire or tire
chain clearance to the body and chassis.
7
Whenever a wheel, wheel bolt or wheel nut is replaced
on a dual wheel setup, check the wheel
nut torque after
100,
1,000 and 6,000 miles (160, 1 600 and 10 000 km)
of driving. For proper torque, see “Wheel Nut Torque”
in
the Index.
See “Changing a Flat Tire” in the Index for
more information.
6-56
ProCarManuals.com