1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER charging
[x] Cancel search: chargingPage 658 of 1938
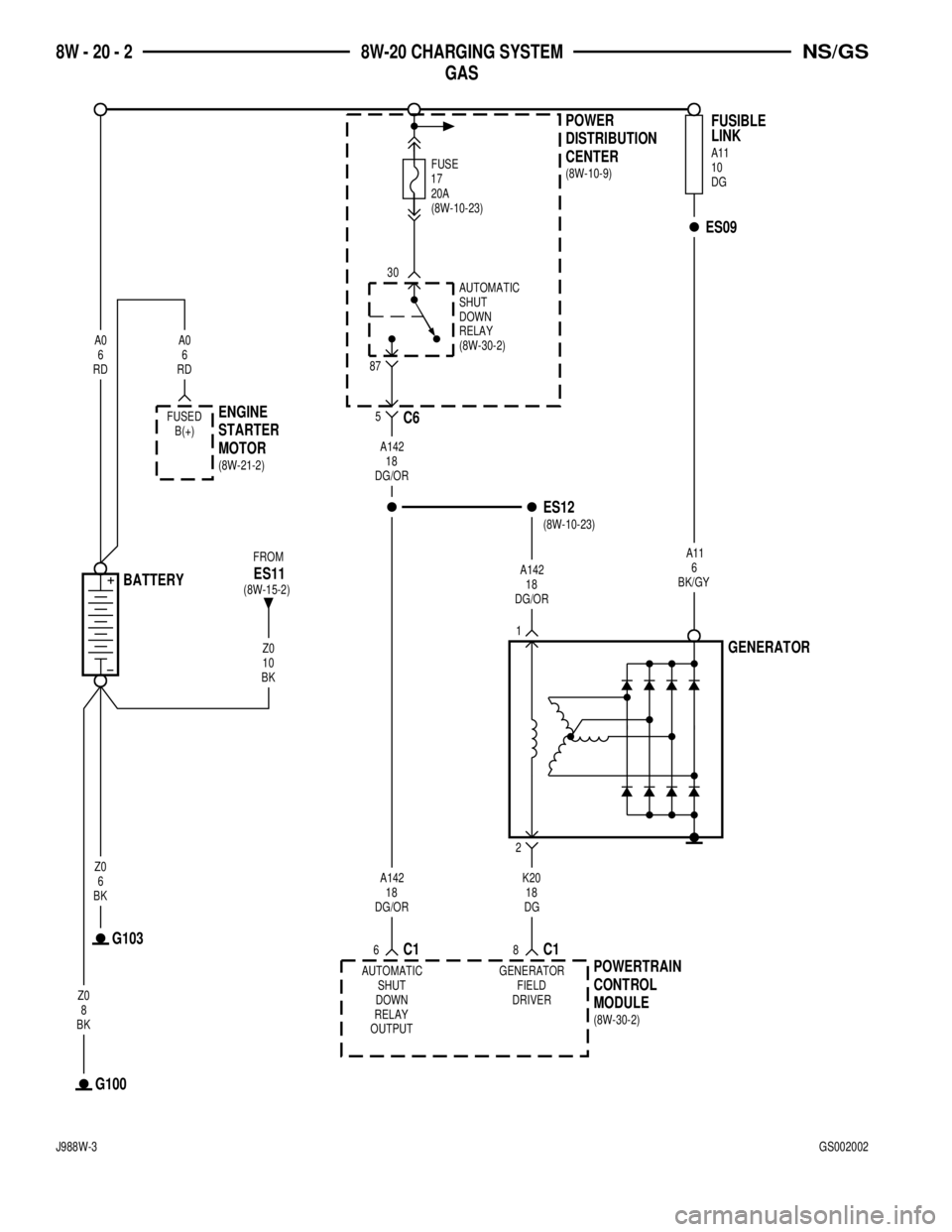
BK/GY6 A11
G103
Z0
6
BKA0
6
RD
87
30
20A
FUSE
17
DG18 K20
8C1
GENERATOR
FIELD
DRIVER
CENTER DISTRIBUTION
POWER
BK8 Z0
G100BATTERY
DG/OR18 A142
GENERATOR
1
2
C16
MODULE CONTROL
POWERTRAIN
AUTOMATIC
SHUT
DOWN
RELAY
5C6
ES12
A142
18
DG/OR
DG/OR18 A142
ES09
DG 10
A11
FUSIBLE
LINK
RD6 A0
ENGINE
STARTER
MOTOR
Z0
10
BK FROM
ES11
OUTPUTRELAYDOWNSHUT AUTOMATIC
FUSED
B(+)(8W-10-23)(8W-10-9)
(8W-30-2) (8W-30-2)
(8W-10-23) (8W-21-2)
(8W-15-2)
8W - 20 - 2 8W-20 CHARGING SYSTEM
GASNS/GS
J988W-3GS002002
Page 659 of 1938

BK/GY6 A11
G103
Z0
2
BK A0
6
RD
87
30
20A
FUSE
17
23
CENTER DISTRIBUTION
POWER
BK8 Z0
G100BATTERY
DG/OR16 A142
GENERATOR
45
MODULE CONTROL
POWERTRAIN
5C6
ES06
A142
18
DG/OR
DG/OR18 A142
ES11
DG 10
A11
FUSIBLE
LINK
ENGINE
STARTER
MOTOR
Z0
10
BK FROM
ES01
OUTPUTRELAY
+VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
1
RELAY PLUG
GLOW
A0
10
RD
FUSIBLE
LINK
A54
16
DB
A54
10
RD
ES26
ES28
A0
2
RD
BS33
A142
16
DG/OR
17E96
B108
A142
18
DG/ORA142
18
DG/OR
DG/OR18 A142DG/OR18 A142
DIESEL
RELAY
OUTPUT
A142
16
DG/OR
68
RELAY
OUTPUT
D+ DFDIESEL
POWER
RELAY
POWER POWERDIESEL
POWERDIESEL(8W-10-25)(8W-10-9)
(8W-30-28) (8W-10-25) (8W-21-3)
(8W-15-3)(8W-30-32)(8W-30-28)
NS/GS8W-20 CHARGING SYSTEM
DIESEL8W - 20 - 3
GS002003J988W-3
Page 736 of 1938

LAMP INDICATOR
VOLTS
CHARGING
SYSTEM
CONTROL INDICATOR
SIGNAL SENSOR COOLANTENGINE 26
C1
TEMPERATURE
TN/BK18 K2
E78 F0211E69
F0912
TN/BK18 K2
2.4L 3.3L/3.8LOTHERS 2.0L
ENGINE
COOLANT
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
2 GAUGE TEMPERATURE
COOLANT
ENGINE ENGINE
COOLANT
TEMPERATURE
CONTROLGAUGE
MODULE
CONTROL
POWERTRAIN PS02 PS01
WT/BK18 D2
VT/BR18D1
(+)
C259
CCD
BUS
(-)
C260
CCD
BUS
1213P18
B23
BS05 BS06
B3327E36
ES13 ES14
D2
18
WT/BKD1
18
VT/BR
CCD
BUS
(-) (+) BUS CCD
BUS CCD
34C2
(-) BUS CCD
3C2
(+)
VT/BR20 D1 D2
20
WT/BK
109
MODULE CONTROL
BODY
D1
20
VT/BRD2
20
WT/BK
RD/WT20 F11
FUSED
IGNITON
(ST-RUN-OFF)
11
C410
INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER
2FUSE10A
ST-RUN-OFF A81
BLOCK JUNCTION
B12 B13
(EATX) (EATX)
PAIR TWISTED
TWISTED
PAIR
D2
20
WT/BKD1
20
VT/BR
D1
(8W-30-10)
(8W-30-16)
(8W-30-24)
(8W-30-4) (8W-30-4) (8W-30-4)
(8W-30-4) (8W-30-4)
(8W-30-4) (8W-30-4)
(8W-45-3) (8W-12-9)(8W-10-16)
(8W-12-2)
8W - 40 - 8 8W-40 INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
GASNS/GS
J988W-3GS004008
Page 737 of 1938

LAMP INDICATOR
VOLTS
CHARGING
SYSTEM
CONTROL INDICATOR
SIGNAL SENSOR COOLANTENGINE 60
C1
TEMPERATURE
B33 E1203
ENGINE
COOLANT
TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
GAUGE TEMPERATURE
COOLANT
ENGINE ENGINE
COOLANT
TEMPERATURE
CONTROLGAUGE
PS02 PS01
CCD
BUS
(-) (+) BUS CCD
BUS CCD
34C2
(-) BUS CCD
3C2
(+)
VT/BR20 D1 D2
20
WT/BK
109
MODULE CONTROL
BODY
D1
20
VT/BRD2
20
WT/BK
FUSED
IGNITION
(ST-RUN-OFF)
INSTRUMENT
CLUSTER
ST-RUN-OFF F11
3
G58
20
BK/YL
BATT M1
B(+) FUSED
PAIR TWISTED
BK/YL20 G58
PK20 D21
61
POWERTRAIN
CONTROL
MODULE
SCI
TRANSMIT
7
3
11
D1
20
VT/BRD2
20
WT/BK
17
B23
P18B17
D21
20
PK
TWISTED
PAIR
TWISTED
PAIR
DATA
LINK
CONNECTOR
TEMPERATUREENGINE
COOLANT
SENSOR
SIGNAL
(8W-30-36)
(8W-30-31) (8W-30-31)
(8W-45-3)
(8W-45-9) (8W-12-9) (8W-10-11)
(8W-30-30)
(8W-30-30)
(8W-30-31)
NS/GS8W-40 INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
DIESEL8W - 40 - 9
GS004009J988W-3
Page 1324 of 1938

THROTTLE BODY....................... 64
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR............ 65
UPSTREAM OXYGEN SENSOR............. 68
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE.............................. 72SPECIAL TOOLS
FUEL................................. 72
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
All engines used in this section have a sequential
Multi-Port Electronic Fuel Injection system. The MPI
system is computer regulated and provides precise
air/fuel ratios for all driving conditions. The Power-
train Control Module (PCM) operates the fuel injec-
tion system.
The PCM regulates:
²Ignition timing
²Air/fuel ratio
²Emission control devices
²Cooling fan
²Charging system
²Idle speed
²Vehicle speed control
Various sensors provide the inputs necessary for
the PCM to correctly operate these systems. In addi-
tion to the sensors, various switches also provide
inputs to the PCM.
All inputs to the PCM are converted into signals.
The PCM can adapt its programming to meet chang-
ing operating conditions.
Fuel is injected into the intake port above the
intake valve in precise metered amounts through
electrically operated injectors. The PCM fires the
injectors in a specific sequence. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the PCM maintains an air fuel ratio
of 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel by constantly adjust-
ing injector pulse width. Injector pulse width is the
length of time the injector is open.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width by opening
and closing the ground path to the injector. Engine
RPM (speed) and manifold absolute pressure (air
density) are the primary inputs that determine injec-
tor pulse width.
MODES OF OPERATION
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to output devices. For example,
the PCM must calculate a different injector pulse
width and ignition timing for idle than it does for
Wide Open Throttle (WOT). There are several differ-
ent modes of operation that determine how the PCM
responds to the various input signals.
There are two different areas of operation, OPEN
LOOP and CLOSED LOOP.
During OPEN LOOP modes the PCM receives
input signals and responds according to preset PCMprogramming. Input from the oxygen (O2S) sensor is
not monitored during OPEN LOOP modes.
During CLOSED LOOP modes the PCM does mon-
itor the O2S sensor input. This input indicates to the
PCM whether or not the calculated injector pulse
width results in the ideal air/fuel ratio of 14.7 parts
air to 1 part fuel. By monitoring the exhaust oxygen
content through the O2S sensor, the PCM can fine
tune the injector pulse width. Fine tuning injector
pulse width allows the PCM to achieve optimum fuel
economy combined with low emissions.
The multi-port fuel injection system has the follow-
ing modes of operation:
²Ignition switch ON (zero RPM)
²Engine start-up
²Engine warm-up
²Cruise (Idle)
²Acceleration
²Deceleration
²Wide Open Throttle
²Ignition switch OFF
The engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up, and
wide open throttle modes are OPEN LOOP modes.
Under most operating conditions, the acceleration,
deceleration, and cruise modes,with the engine at
operating temperatureare CLOSED LOOP modes.
IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE
When the multi-port fuel injection system is acti-
vated by the ignition switch, the following actions
occur:
²The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure
from the MAP sensor input to determine basic fuel
strategy.
²The PCM monitors the coolant temperature sen-
sor and throttle position sensor input. The PCM mod-
ifies fuel strategy based on this input.
When the key is in the ON position and the engine
is not running (zero rpm), the Automatic Shutdown
(ASD) relay and fuel pump relay are not energized.
Therefore battery voltage is not supplied to the fuel
pump, ignition coil, fuel injectors or oxygen sensor
heating element.
ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. The following
actions occur when the starter motor is engaged.
If the PCM receives the camshaft position sensor
and crankshaft position sensor signals, it energizes
the ASD relay and fuel pump relay. These relays sup-
ply battery voltage to the fuel pump, fuel injectors,
14 - 30 FUEL SYSTEMNS
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 1336 of 1938

in the engine compartment next to the battery (Fig.
30). A label affixed to the underside of the PDC cover
identifies the relays and fuses in the PDC.
GENERATOR FIELDÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM regulates the charging system voltage
within a range of 12.9 to 15.0 volts. Refer to Group
8A for Battery system information and 8C for charg-
ing system information.
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
The Automatic Shutdown (ASD) relay supplies bat-
tery voltage to the fuel injectors, electronic ignition
coil and the heating elements in the oxygen sensors.
A buss bar in the Power Distribution Center (PDC)
supplies voltage to the solenoid side and contact side
of the relay. The ASD relay power circuit contains a
25 amp fuse between the buss bar in the PDC and
the relay. The fuse is located in the PDC. Refer to
Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams for circuit information.
The PCM controls the relay by switching the
ground path for the solenoid side of the relay on and
off. The PCM turns the ground path off when the
ignition switch is in the Off position unless the 02
Heater Monitor test is being run. Refer to Group 25,
On-Board Diagnostics. When the ignition switch is in
the On or Crank position, the PCM monitors the
crankshaft position sensor and camshaft position sen-
sor signals to determine engine speed and ignition
timing (coil dwell). If the PCM does not receive the
crankshaft position sensor and camshaft position sen-
sor signals when the ignition switch is in the Run
position, it will de-energize the ASD relay.The ASD relay is located in the PDC (Fig. 30). A
label affixed to the underside of the PDC cover iden-
tifies the relays and fuses in the PDC.
FUEL PUMP RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
The fuel pump relay supplies battery voltage to the
fuel pump. The fuel pump relay power circuit con-
tains a 9 amp fuse. The fuse is located in the PDC.
Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams for circuit infor-
mation.
The PCM controls the fuel pump relay by switch-
ing the ground path for the solenoid side of the relay
on and off. The PCM turns the ground path off when
the ignition switch is in the Off position. When the
ignition switch is in the On position, the PCM ener-
gizes the fuel pump. If the crankshaft position sensor
does not detect engine rotation, the PCM de-ener-
gizes the relay after approximately one second.
The fuel pump relay is located in the PDC (Fig.
30). A label affixed to the underside of the PDC cover
identifies the relays and fuses in the PDC.
STARTER RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
Double Start Override ia a feature that prevents
the starter from operating if the engine is already
running. This feature is accomplished with software
only. There was no hardware added because of this
feature. To incorporate the unique feature of Double
Start Override, it was necessary to use the PCM
(software) to control the starter circuit. To use the
PCM it was necessary to separate the starter relay
coil ground from the park neutral switch. The starter
relay ground is now controlled through Pin 60 of the
PCM. This allows the PCM to interrupt the ground
circuit if other inputs tell it that the engine is turn-
ing. If the starter system is operating properly, it can
be assumed that the override protection is also work-
ing.
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTORÐPCM OUTPUT
The idle air control motor is mounted on the throt-
tle body. The PCM operates the idle air control motor
(Fig. 26) or (Fig. 27) or (Fig. 28). The PCM adjusts
engine idle speed through the idle air control motor
to compensate for engine load or ambient conditions.
The throttle body has an air bypass passage that
provides air for the engine at idle (the throttle blade
is closed). The idle air control motor pintle protrudes
into the air bypass passage and regulates air flow
through it.
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed by moving the
idle air control motor pintle in and out of the bypass
passage. The adjustments are based on inputs the
PCM receives. The inputs are from the throttle posi-
tion sensor, crankshaft position sensor, coolant tem-
perature sensor, and various switch operations
Fig. 30 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
14 - 42 FUEL SYSTEMNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1414 of 1938

The first injector sensor is used only on the fuel
injector for the number±1 cylinder (Fig. 3). It is not
used on the injectors for cylinders number 2, 3, or 4.
FUEL INJECTOR SENSORÐGROUND
Provides a low noise ground for the fuel injector
sensor only.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORÐPCM
INPUT
The 0±5 volt input from this sensor tells the PCM
the temperature of the engine coolant. Based on the
voltage received at the PCM, it will then determine
operation of the fuel timing solenoid, glow plug relay,
electrical vacuum modulator (emission component)
and generator (charging system).
The sensor is located on the side of the #3 cylinder
head near the rear of fuel injection pump (Fig. 4).
ENGINE SPEED SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The engine speed sensor is mounted to the trans-
mission bellhousing at the left/rear side of the engine
block (Fig. 5).
The engine speed sensor produces its own output
signal. If this signal is not received the engine will
not start by the PCM.
The engine speed sensor input is used in conjunc-
tion with the first injector sensor to establish fuel
injection pump timing.
The flywheel has four notches at its outer edge
(Fig. 6). Each notch is spaced equally every 90É. The
notches cause a pulse to be generated when they
pass under the speed sensor (Fig. 6). These pulses
are the input to the PCM. The input from this sensor
determines crankshaft position (in degrees) by moni-
toring the notches.The sensor also generates an rpm signal to the
PCM. This signal is used as an input for the Diesel
relay for control of the generator field, vehicle speed
control, and instrument panel mounted tachometer.
If the engine speed sensor should fail, the system
is unable to compensate for the problem and the car
will stop.
Fig. 3 Fuel Injector Sensor
Fig. 4 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Location
Fig. 5 Engine Speed Sensor Location
14 - 46 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1817 of 1938

HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING
CONTENTS
page page
FRONT HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING
SYSTEM............................... 1REAR HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING
SYSTEM.............................. 41
FRONT HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION......................... 2
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS...... 2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER.............. 2
A/C SERVICE PORTS..................... 2
AIR DISTRIBUTION DUCTS................. 2
COMPRESSOR HIGH-PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE................................ 3
CONDENSATE DRAIN..................... 3
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS . . 3
EVAPORATOR PROBE..................... 3
HANDLING TUBING AND FITTINGS........... 3
HVAC CONTROL MODULE................. 4
REAR BLOWER SPEED SWITCH............ 3
SIDE DOOR HEATER A/C OUTLETS.......... 4
SIDE WINDOW DEMISTER................. 4
SYSTEM AIRFLOW....................... 4
SYSTEM OIL LEVEL...................... 5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
A/C PERFORMANCE TEST................ 12
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER............. 12
ACTUATOR CALIBRATION/DIAGNOSTICS AND
COOLDOWN TEST...................... 6
BLOWER MOTOR AND WHEEL ASSEMBLY.... 13
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL.............. 13
COMPRESSOR NOISE DIAGNOSIS.......... 13
EXPANSION VALVE...................... 13
HEATER PERFORMANCE TEST............ 15
HVAC CONTROL DIAGNOSTIC CONDITIONS . . . 9
SYSTEM CHARGE LEVEL TEST............ 16SERVICE PROCEDURES
CHARGING REFRIGERANT SYSTEM........ 17
EVACUATING REFRIGERANT SYSTEM....... 18
R-134a REFRIGERANT................... 16
STICKING HVAC CONTROL MODULE PUSH
BUTTONS............................ 19
SYSTEM LEAK CHECKING................ 19
THERMOCOUPLE PROBE................. 19
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER............. 20
A/C SERVICE PORTS.................... 20
BLEND-AIR DOOR ACTUATOR............. 20
BLOWER MOTOR AND WHEEL ASSEMBLY.... 21
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR BLOCK........ 21
BLOWER MOTOR WHEEL................. 22
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH/COIL.............. 23
COMPRESSOR......................... 23
CONDENSER ASSEMBLY................. 25
DISCHARGE LINE....................... 26
EVAPORATOR PROBE.................... 27
EXPANSION VALVE...................... 28
FILTER-DRIER ASSEMBLY................. 28
HEATER A/C UNIT HOUSING............... 29
HEATER CORE......................... 30
HEATER HOSES........................ 31
LIQUID LINE........................... 32
MODE DOOR ACTUATOR................. 32
RECIRC DOOR ACTUATOR................ 34
SIDE WINDOW DEMISTER DUCTS.......... 33
SUCTION LINE.......................... 33
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
HEATER A/C UNIT RECONDITION........... 34
NSHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 1