1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 1894 of 1938

INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
Install screws to retain heater core in housing.
Replace heater core tube inlet O-rings. Tighten
heater core tube retaining plate to 361 N´m (276
9 in. lbs.) torque.
HEATER HOSES
REMOVAL
NOTE: Review Safety Precautions and Warnings
before proceeding with this operation.
(1) Drain engine cooling system. Refer to Group 7,
Engine Cooling.
(2) Loosen clamps at each end of heater hose to be
removed (Fig. 38) and (Fig. 39).
CAUTION: When removing hoses from heater core
inlet or outlet nipples, do not use excessive force.
Heater core may become damaged and leak engine
coolant.(3) Carefully rotate hose back and forth while tug-
ging slightly away from connector nipple. If the hose
will not come off, slice the hose at the connector nip-
ple and peel off heater hose. This method will require
heater hose replacement.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
LIQUID LINE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Recover A/C system refrigerant.
(3) Remove ground wire at dash panel.
(4) Remove the nut retaining the refrigerant line
sealing plate to the expansion valve (Fig. 27).
(5) Remove the stud from the expansion valve (Fig.
28).
(6) Remove liquid line from expansion valve.
(7) Cover the openings to prevent contamination.
(8) Disconnect wire connector at pressure trans-
ducer.
(9) Remove liquid line mounting clip at right strut
tower.
(10) Using access slot between radiator crossmem-
ber and grille, loosen liquid line mounting plate at
filter-drier. Remove liquid line from filter-drier.
(11) Remove the old O-rings.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
²Install the stud to the evaporator sealing plate
and tighten 7 to 11 N´m (64 to 96 in. lbs.) torque.
²Install new O-rings.
²Install two-piece line in place of original part.
²Assemble line halves after it is installed on vehi-
cle.
²Evacuate and recharge A/C system.
Fig. 37 Brake Pedal
Fig. 38 Upper Heater Hose
Fig. 39 Lower Heater Hose
24 - 28 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONINGNS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1896 of 1938

(7) Remove suction line mounting nut at compres-
sor (Fig. 10).
(8) Remove suction line mounting bracket.
(9) Remove suction line.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
²Install the stud to the evaporator sealing plate
and tighten 7 to 11 N´m (64 to 96 in. lbs.) torque.
²Install new O-rings.
²Install two-piece line in place of original part.
²Assemble line halves after it is installed on vehi-
cle.
²Evacuate and recharge A/C system.
RECIRC DOOR ACTUATOR
REMOVAL
(1) Pull back on carpeting on the right lower floor.
(2) Remove Recirc. door actuator connector.
(3) Remove (3) mounting screws for Recirc. actua-
tor (Fig. 45).(4) Remove Recirc. actuator.
(5) Disengage actuator linkage at Recirc. door.
(6) Remove actuator from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) For installation, reverse the above procedures.
(2) Perform the HVAC control Calibration Diagnos-
tic and Cooldown test.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
HEATER A/C UNIT RECONDITION
Heater A/C Housing must be removed from vehicle
before performing this operation. Refer to Heater A/C
Unit HousingÐRemoval and Installation.
DISASSEMBLYÐEVAPORATOR HOUSING
(1) Place HVAC unit assembly on workbench.
(2) Remove distribution housing mounting screws
(Fig. 46).
(3) Remove blower motor cover (Fig. 47).
Fig. 44 Right Side Demister Duct
Fig. 45 Recirculation Door Actuator
Fig. 46 Distribution Housing
Fig. 47 Blower Motor Cover
24 - 30 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONINGNS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1906 of 1938

cranking. Whenever the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) sets a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) that
affects vehicle emissions, it illuminates the MIL. If a
problem is detected, the PCM sends a message over
the CCD Bus to the instrument cluster to illuminate
the lamp. The PCM illuminates the MIL only for
DTC's that affect vehicle emissions. The MIL stays
on continuously when the PCM has entered a
Limp-In mode or identified a failed emission compo-
nent or system. The MIL remains on until the DTC
is erased. Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Code
charts in this group for emission related codes.
Also, the MIL either flashes or illuminates contin-
uously when the PCM detects active engine misfire.
Refer to Misfire Monitoring in this section.
Additionally, the PCM may reset (turn off) the MIL
when one of the following occur:
²PCM does not detect the malfunction for 3 con-
secutive trips (except misfire and fuel system moni-
tors).
²PCM does not detect a malfunction while per-
forming three successive engine misfire or fuel sys-
tem tests. The PCM performs these tests while the
engine is operating within6375 RPM of and within
10 % of the load of the operating condition at which
the malfunction was first detected.
STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs to the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) have two recognized states; HIGH and
LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize the
difference between a selected switch position versus
an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective switch.
If the State Display screen shows the change from
HIGH to LOW or LOW to HIGH, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM functions properly. From
the state display screen, access either State Display
Inputs and Outputs or State Display Sensors.
STATE DISPLAY INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link connec-
tor and access the State Display screen. Then access
Inputs and Outputs. The following list contains the
PCM system functions accessible through the Inputs
and Outputs screen.
Park/Neutral Switch
Speed Control Resume
Brake Switch
Speed Control On/Off
Speed Control Set
S/C Vent Solenoid
Actual S/C Vent Sol.
S/C Vacuum Solenoid
Actual S/C Vacuum Sol.
S/C Cancel
S/C Last Cutout
S/C Working Status
S/C Denied Status
A/C Clutch Relay
Actual A/C Clutch Relay
EGR Solenoid
Actual EGR Sol.
Automatic Shutdown Relay
Actual Automatic Shutdown Relay
Automatic Shutdown Relay Sense
Radiator Fan Control Module
Actual Radiator Fan Control Module
Duty Cycle EVAP Purge Solenoid
Actual EVAP Purge Sol.
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
Power Steering Switch
Closed Loop State
Current CMP Edge
Current CKP State
Current Sync State
Fuel Pump Relay
Actual Fuel Pump Relay
Ignition Sense (A21)
Malfunction Lamp
Limp-in Reason
STATE DISPLAY SENSORS
Connect the DRB scan tool to the vehicle and
access the State Display screen. Then access Sensor
Display. The following list contains the PCM system
functions accessible through the Sensor Display
screen.
Battery Temperature
Engine Coolant Temperature
Engine Coolant Temp Sensor
Throttle Position Volts
Minimum Throttle
Knock Sensor Volts
Battery Voltage
MAP Sensor Reading
Idle Air Control Motor Position
Fig. 1 Data Link (Diagnostic) Connector
25 - 2 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1908 of 1938
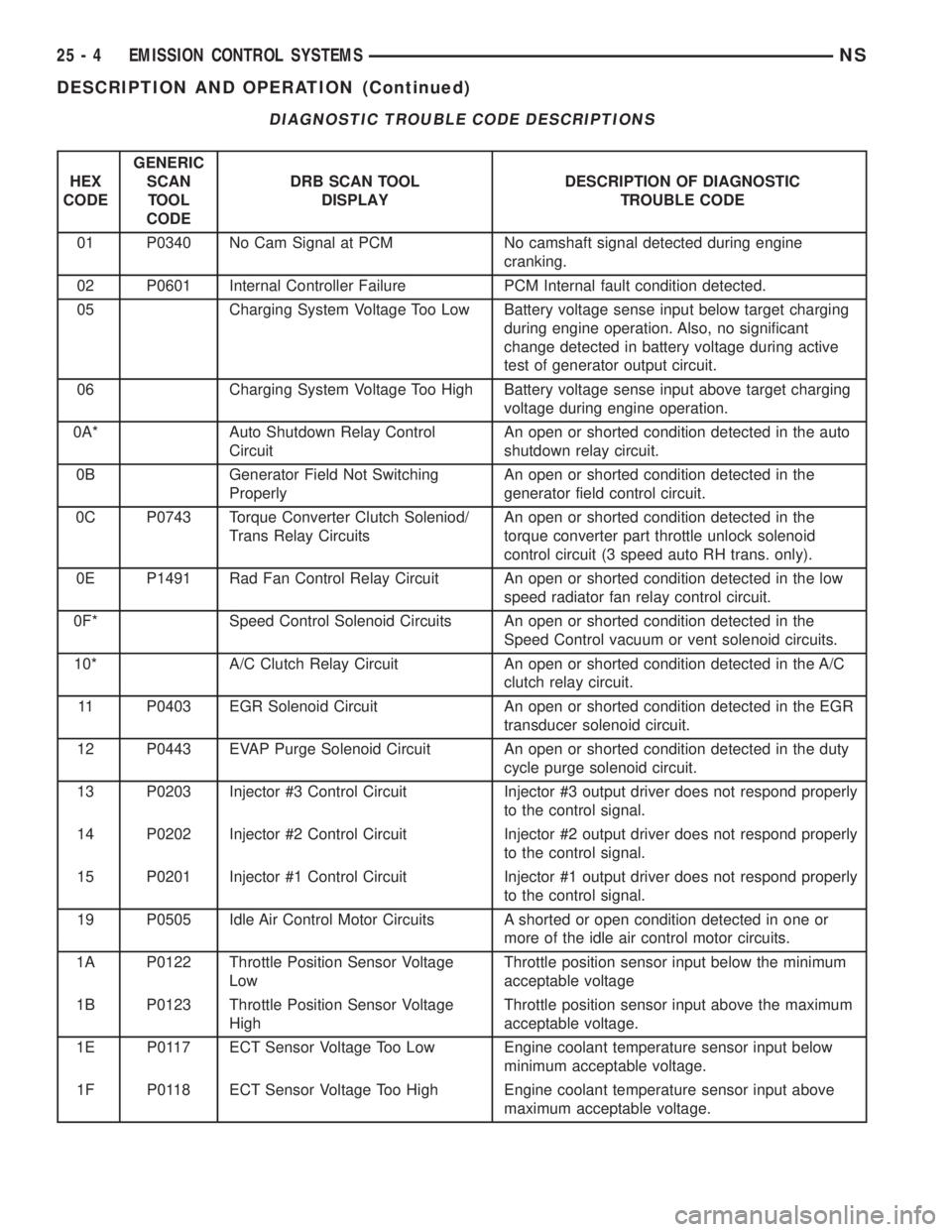
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DESCRIPTIONS
HEX
CODEGENERIC
SCAN
TOOL
CODEDRB SCAN TOOL
DISPLAYDESCRIPTION OF DIAGNOSTIC
TROUBLE CODE
01 P0340 No Cam Signal at PCM No camshaft signal detected during engine
cranking.
02 P0601 Internal Controller Failure PCM Internal fault condition detected.
05 Charging System Voltage Too Low Battery voltage sense input below target charging
during engine operation. Also, no significant
change detected in battery voltage during active
test of generator output circuit.
06 Charging System Voltage Too High Battery voltage sense input above target charging
voltage during engine operation.
0A* Auto Shutdown Relay Control
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the auto
shutdown relay circuit.
0B Generator Field Not Switching
ProperlyAn open or shorted condition detected in the
generator field control circuit.
0C P0743 Torque Converter Clutch Soleniod/
Trans Relay CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the
torque converter part throttle unlock solenoid
control circuit (3 speed auto RH trans. only).
0E P1491 Rad Fan Control Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the low
speed radiator fan relay control circuit.
0F* Speed Control Solenoid Circuits An open or shorted condition detected in the
Speed Control vacuum or vent solenoid circuits.
10* A/C Clutch Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the A/C
clutch relay circuit.
11 P0403 EGR Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the EGR
transducer solenoid circuit.
12 P0443 EVAP Purge Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the duty
cycle purge solenoid circuit.
13 P0203 Injector #3 Control Circuit Injector #3 output driver does not respond properly
to the control signal.
14 P0202 Injector #2 Control Circuit Injector #2 output driver does not respond properly
to the control signal.
15 P0201 Injector #1 Control Circuit Injector #1 output driver does not respond properly
to the control signal.
19 P0505 Idle Air Control Motor Circuits A shorted or open condition detected in one or
more of the idle air control motor circuits.
1A P0122 Throttle Position Sensor Voltage
LowThrottle position sensor input below the minimum
acceptable voltage
1B P0123 Throttle Position Sensor Voltage
HighThrottle position sensor input above the maximum
acceptable voltage.
1E P0117 ECT Sensor Voltage Too Low Engine coolant temperature sensor input below
minimum acceptable voltage.
1F P0118 ECT Sensor Voltage Too High Engine coolant temperature sensor input above
maximum acceptable voltage.
25 - 4 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1911 of 1938
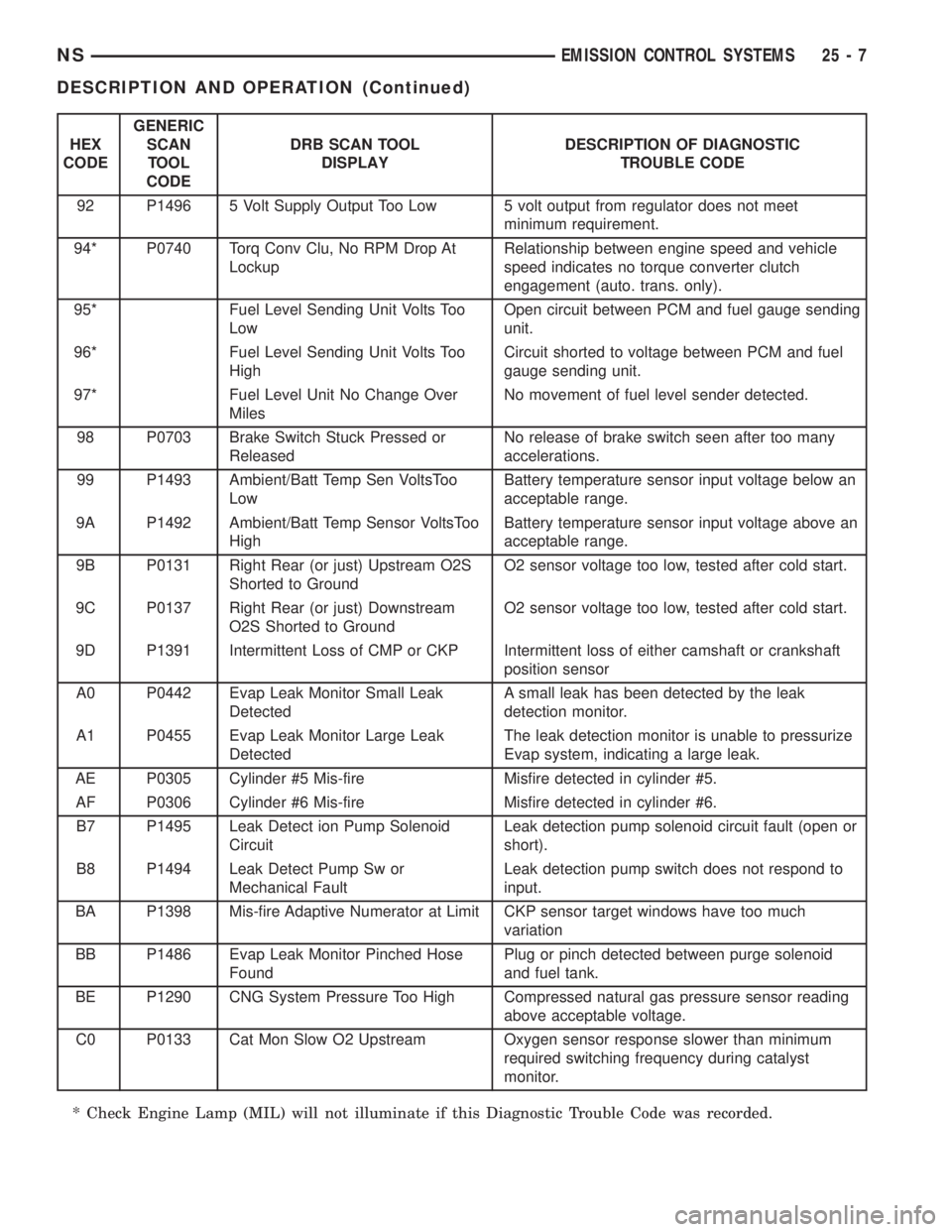
HEX
CODEGENERIC
SCAN
TOOL
CODEDRB SCAN TOOL
DISPLAYDESCRIPTION OF DIAGNOSTIC
TROUBLE CODE
92 P1496 5 Volt Supply Output Too Low 5 volt output from regulator does not meet
minimum requirement.
94* P0740 Torq Conv Clu, No RPM Drop At
LockupRelationship between engine speed and vehicle
speed indicates no torque converter clutch
engagement (auto. trans. only).
95* Fuel Level Sending Unit Volts Too
LowOpen circuit between PCM and fuel gauge sending
unit.
96* Fuel Level Sending Unit Volts Too
HighCircuit shorted to voltage between PCM and fuel
gauge sending unit.
97* Fuel Level Unit No Change Over
MilesNo movement of fuel level sender detected.
98 P0703 Brake Switch Stuck Pressed or
ReleasedNo release of brake switch seen after too many
accelerations.
99 P1493 Ambient/Batt Temp Sen VoltsToo
LowBattery temperature sensor input voltage below an
acceptable range.
9A P1492 Ambient/Batt Temp Sensor VoltsToo
HighBattery temperature sensor input voltage above an
acceptable range.
9B P0131 Right Rear (or just) Upstream O2S
Shorted to GroundO2 sensor voltage too low, tested after cold start.
9C P0137 Right Rear (or just) Downstream
O2S Shorted to GroundO2 sensor voltage too low, tested after cold start.
9D P1391 Intermittent Loss of CMP or CKP Intermittent loss of either camshaft or crankshaft
position sensor
A0 P0442 Evap Leak Monitor Small Leak
DetectedA small leak has been detected by the leak
detection monitor.
A1 P0455 Evap Leak Monitor Large Leak
DetectedThe leak detection monitor is unable to pressurize
Evap system, indicating a large leak.
AE P0305 Cylinder #5 Mis-fire Misfire detected in cylinder #5.
AF P0306 Cylinder #6 Mis-fire Misfire detected in cylinder #6.
B7 P1495 Leak Detect ion Pump Solenoid
CircuitLeak detection pump solenoid circuit fault (open or
short).
B8 P1494 Leak Detect Pump Sw or
Mechanical FaultLeak detection pump switch does not respond to
input.
BA P1398 Mis-fire Adaptive Numerator at Limit CKP sensor target windows have too much
variation
BB P1486 Evap Leak Monitor Pinched Hose
FoundPlug or pinch detected between purge solenoid
and fuel tank.
BE P1290 CNG System Pressure Too High Compressed natural gas pressure sensor reading
above acceptable voltage.
C0 P0133 Cat Mon Slow O2 Upstream Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum
required switching frequency during catalyst
monitor.
* Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will not illuminate if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
NSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1913 of 1938

conditions are met, the EGR is turned off (solenoid
energized) and the O2S compensation control is mon-
itored. Turning off the EGR shifts the air fuel (A/F)
ratio in the lean direction. The O2S data should indi-
cate an increase in the O2 concentration in the com-
bustion chamber when the exhaust gases are no
longer recirculated. While this test does not directly
measure the operation of the EGR system, it can be
inferred from the shift in the O2S data whether the
EGR system is operating correctly. Because the O2S
is being used, the O2S test must pass its test before
the EGR test.
HEX 6A,6B, 6C, 6D, 6E, AE, and AFÐMISFIRE
MONITOR
Excessive engine misfire results in increased cata-
lyst temperature and causes an increase in HC emis-
sions. Severe misfires could cause catalyst damage.
To prevent catalytic convertor damage, the PCM
monitors engine misfire.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
for misfire during most engine operating conditions
(positive torque) by looking at changes in the crank-
shaft speed. If a misfire occurs the speed of the
crankshaft will vary more than normal.
HEX 76, 77, 78, and 79ÐFUEL SYSTEM
MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide. The catalyst works best
when the air fuel (A/F) ratio is at or near the opti-
mum of 14.7 to 1.
The PCM is programmed to maintain the optimum
air/fuel ratio of 14.7 to 1. This is done by making
short term corrections in the fuel injector pulse width
based on the O2S output. The programmed memory
acts as a self calibration tool that the engine control-
ler uses to compensate for variations in engine spec-
ifications, sensor tolerances and engine fatigue over
the life span of the engine. By monitoring the actual
air-fuel ratio with the O2S (short term) and multiply-
ing that with the program long-term (adaptive) mem-
ory and comparing that to the limit, it can be
determined whether it will pass an emissions test. If
a malfunction occurs such that the PCM cannot
maintain the optimum A/F ratio, then the MIL will
be illuminated.
HEX 70, and B4ÐCATALYST MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide.Normal vehicle miles or engine misfire can cause a
catalyst to decay. A meltdown of the ceramic core can
cause a reduction of the exhaust passage. This can
increase vehicle emissions and deteriorate engine
performance, driveability and fuel economy.
The catalyst monitor uses dual oxygen sensors
(O2S's) to monitor the efficiency of the converter. The
dual O2Ss strategy is based on the fact that as a cat-
alyst deteriorates, its oxygen storage capacity and its
efficiency are both reduced. By monitoring the oxy-
gen storage capacity of a catalyst, its efficiency can
be indirectly calculated. The upstream O2S is used to
detect the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas
before the gas enters the catalytic converter. The
PCM calculates the A/F mixture from the output of
the O2S. A low voltage indicates high oxygen content
(lean mixture). A high voltage indicates a low content
of oxygen (rich mixture).
When the upstream O2S detects a lean condition,
there is an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
A functioning converter would store this oxygen so it
can use it for the oxidation of HC and CO. As the
converter absorbs the oxygen, there will be a lack of
oxygen downstream of the converter. The output of
the downstraem O2S will indicate limited activity in
this condition.
As the converter loses the ability to store oxygen,
the condition can be detected from the behavior of
the downstream O2S. When the efficiency drops, no
chemical reaction takes place. This means the con-
centration of oxygen will be the same downstream as
upstream. The output voltage of the downstream
O2S copies the voltage of the upstream sensor. The
only difference is a time lag (seen by the PCM)
between the switching of the O2S's.
To monitor the system, the number of lean-to-rich
switches of upstream and downstream O2S's is
counted. The ratio of downstream switches to
upstream switches is used to determine whether the
catalyst is operating properly. An effective catalyst
will have fewer downstream switches than it has
upstream switches i.e., a ratio closer to zero. For a
totally ineffective catalyst, this ratio will be one-to-
one, indicating that no oxidation occurs in the device.
The system must be monitored so that when cata-
lyst efficiency deteriorates and exhaust emissions
increase to over the legal limit, the MIL (check
engine lamp) will be illuminated.
HEX A0, A1, B7, and B8ÐLEAK DETECTION
PUMP MONITOR
The leak detection assembly incorporates two pri-
mary functions: it must detect a leak in the evapora-
tive system and seal the evaporative system so the
leak detection test can be run.
NSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1921 of 1938
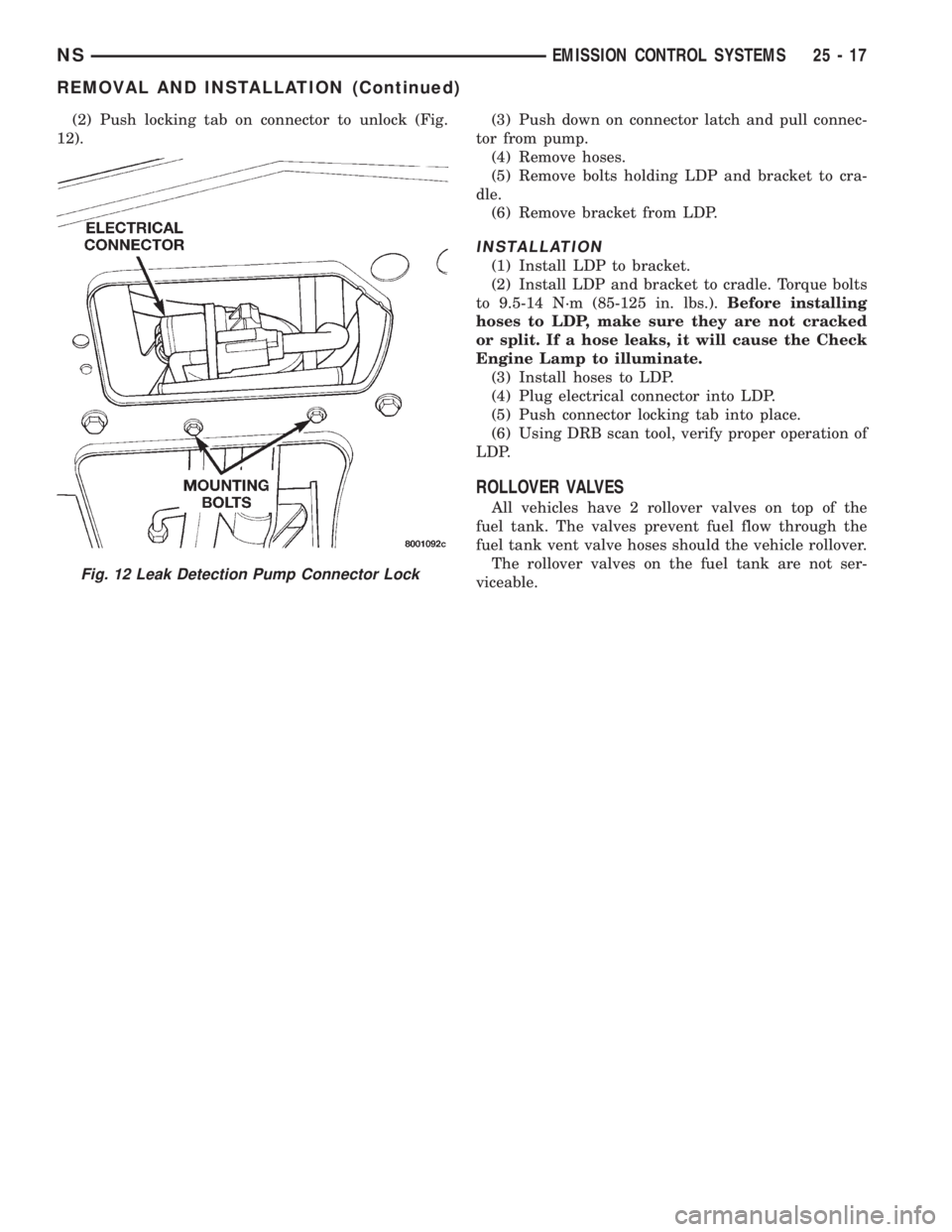
(2) Push locking tab on connector to unlock (Fig.
12).(3) Push down on connector latch and pull connec-
tor from pump.
(4) Remove hoses.
(5) Remove bolts holding LDP and bracket to cra-
dle.
(6) Remove bracket from LDP.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install LDP to bracket.
(2) Install LDP and bracket to cradle. Torque bolts
to 9.5-14 N´m (85-125 in. lbs.).Before installing
hoses to LDP, make sure they are not cracked
or split. If a hose leaks, it will cause the Check
Engine Lamp to illuminate.
(3) Install hoses to LDP.
(4) Plug electrical connector into LDP.
(5) Push connector locking tab into place.
(6) Using DRB scan tool, verify proper operation of
LDP.
ROLLOVER VALVES
All vehicles have 2 rollover valves on top of the
fuel tank. The valves prevent fuel flow through the
fuel tank vent valve hoses should the vehicle rollover.
The rollover valves on the fuel tank are not ser-
viceable.
Fig. 12 Leak Detection Pump Connector Lock
NSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 17
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1925 of 1938

ulated shop air to the metal back- pressure fitting on
the EGR valve.
(6) By hand, open the throttle to the wide open
position. AirSHOULD NOT BE HEARDemitting
from the intake manifold while applying air pressure
at the back-pressure fitting.
(7) If airCAN BE HEARDemitting from the
intake manifold, the poppet valve (Fig. 4) is leaking
at the bottom of the EGR valve. Replace the EGR
valve. Note: The EGR valve, valve control and
attaching hoses are serviced as one assembly. Refer
to EGR Valve Removal/Installation in this group. Do
not attempt clean the old EGR valve.
EGR VALVE CONTROL (TRANSDUCER) TEST
TESTING ELECTRICAL SOLENOID PORTION
OF VALVE
This is not to be used as a complete test of the
EGR system.
Electrical operation of the valve should be checked
with the DRB scan tool. Refer to the appropriate
Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures service manual for
operation of the DRB scan tool. Replace solenoid if
necessary, unit serviced only as an assembly.
TESTING VACUUM TRANSDUCER PORTION
OF VALVE
The first part of this test will determine if the
transducer diaphragm at the back-pressure side of
the valve has ruptured or is leaking. The second part
of the test will determine if engine vacuum (full-man-
ifold) is flowing from the inlet to the outlet side of
the valve. This is not to be used as a complete test of
the EGR system.
(1) Disconnect the rubber back-pressure hose from
the fitting at the bottom of EGR valve (Fig. 4).
(2) Connect a hand-held vacuum pump to this fit-
ting.
(3) Apply 10 inches of vacuum to this fitting.
(4) If vacuum falls off, the valve diaphragm is
leaking.
(5) Replace the EGR valve assembly. Proceed to
next step for further testing.
(6) Remove the rubber hose at the vacuuminlet
fitting (Fig. 4) on the EGR valve.
(7) Connect a vacuum gauge to this disconnected
hose.
(8) Start the engine and bring to operating tem-
perature. Hold engine speed at approximately 1500
rpm.
(9) Check for steady engine vacuum (full-manifold)
at this hose.
(10) If engine vacuum (full-manifold) is not
present, check vacuum line to engine and repair as
necessary before proceeding to next step.(11) Reconnect the rubber hose to the vacuum
inletfitting (Fig. 4) on the EGR valve.
(12) Disconnect the rubber hose at the vacuum
outletfitting (Fig. 4) on the EGR valve.
(13) Connect a vacuum gauge to this fitting.
(14) Disconnect the electrical connector (Fig. 4) at
the valve control. This will simulate an open circuit
(no ground from the PCM) at the valve.
(15) Start the engine and bring to operating tem-
perature.
(16) Hold the engine speed to approximately 2000
rpm while checking for engine vacuum (full-manifold)
at this fitting.To allow full manifold vacuum to
flow through the valve, exhaust back-pressure
must be present at valve. It must be high
enough to hold the bleed valve in the trans-
ducer portion of the valve closed.Have a helper
momentarily (a second or two) hold a rag over the
tailpipe opening to build some exhaust back-pressure
while observing the vacuum gauge. Heavy gloves
should be worn.Do not cover the tailpipe open-
ing for an extended period of time as damage to
components or overheating may result.
(17) As temporary back-pressure is built, full man-
ifold vacuum should be observed at the vacuum out-
let fitting. Without back-pressure, and engine at
approximately 2000 rpm, the gauge reading will be
low. This low reading is normal. At idle speed, the
gauge reading will be erratic. This is also normal.
(18) If full manifold vacuum is not present at the
outlet fitting, but was present at the inlet fitting,
replace the valve. Note: The EGR valve, valve control
and attaching hoses are serviced as one assembly.
Refer to EGR Valve Removal/Installation in this
group.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
EGR VALVE SERVICEÐ3.0L ENGINES
The EGR valve and Electrical EGR Transducer are
serviced as an assembly.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the electric and vacuum connectors
from the electric EGR transducer (Fig. 6).
(2) Remove EGR valve mounting bolts.
(3) Clean all gasket surfaces and discard old gas-
kets. Check for any signs of leakage or cracked sur-
faces. Repair or replace as necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install EGR valve and new gasket on intake
manifold. Tighten mounting bolts to 22 N´m (200 in.
lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect the electrical and vacuum connectors
to the electric EGR transducer.
NSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 21
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)