1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER tires
[x] Cancel search: tiresPage 1431 of 1938

LOW ASSIST, NO ASSIST, HARD STEERING
POOR RETURN TO CENTER
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
STIFF, HARD TO TURN, SURGES,
MOMENTARY INCREASE IN
EFFORT WHEN TURNING.1. Tires not properly inflated. 1. Inflate tires to specified pressure.
2. Low power steering fluid level. 2. Add power steering fluid as
required to power steering fluid
reservoir to obtain proper level.
Perform leakage diagnosis on power
steering system.
3. Loose power steering pump drive
belt.3. Tighten the power steering pump
drive belt to the specified tension. If
drive belt is defective, replace and
correctly tension.
4. Lack of lubrication in lower control
arm ball joint.4. Replace lower ball joint.
5. Worn lower ball joint. 5. Replace lower ball joint.
6. Low power steering pump
pressure. (Verify using Power
Steering System Test Procedure)6. Verify cause using the Power
Steering System Test Procedure.
Replace the power steering pump if
necessary.
7. High internal leak in steering gear
assembly.7. Check steering system using the
Power Steering System Test
Procedure. If steering gear is
defective replace steering gear.
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
STEERING WHEEL DOES NOT
RETURN TO CENTER POSITION.1. Tires not
inflated to specified pressure.1. Inflate tires to specified pressure.
2. Improper front wheel alignment. 2. Check and adjust as necessary.
3. Steering column U-joints
misaligned.3. Realign steering column U-joints.
4. Mispositioned dash cover. 4. Reposition dash cover.
To evaluate items 6 and 7, disconnect
the intermediate shaft. Turn the
steering wheel and feel or listen for
internal rubbing in steering column.
5. Steering wheel rubbing. 5. Adjust steering column shrouds to
eliminate rubbing condition.
6. Damaged, mis-positioned or
un-lubricated steering column coupler
to dash seal.6. Determine condition which exists
and correct.
7. Binding shaft bearing
in steering column assembly.7. Replace the steering column.Note:
Before replacing steering column,
disconnect intermediate steering
coupler from steering column shaft
and remove steering wheel,
clockspring and shrouds from
steering column. This must be done
to verify a binding shaft bearing in
the steering column before
replacing the steering column.
8. Excessive friction in steering
column coupler.8. Replace steering column coupler.
9. Excessive friction in steering gear. 9. Replace steering gear.
10. Excessive friction in front strut
mount bearing10. Replace the strut mount or strut
mount pivot bearing.
NSSTEERING 19 - 5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1433 of 1938
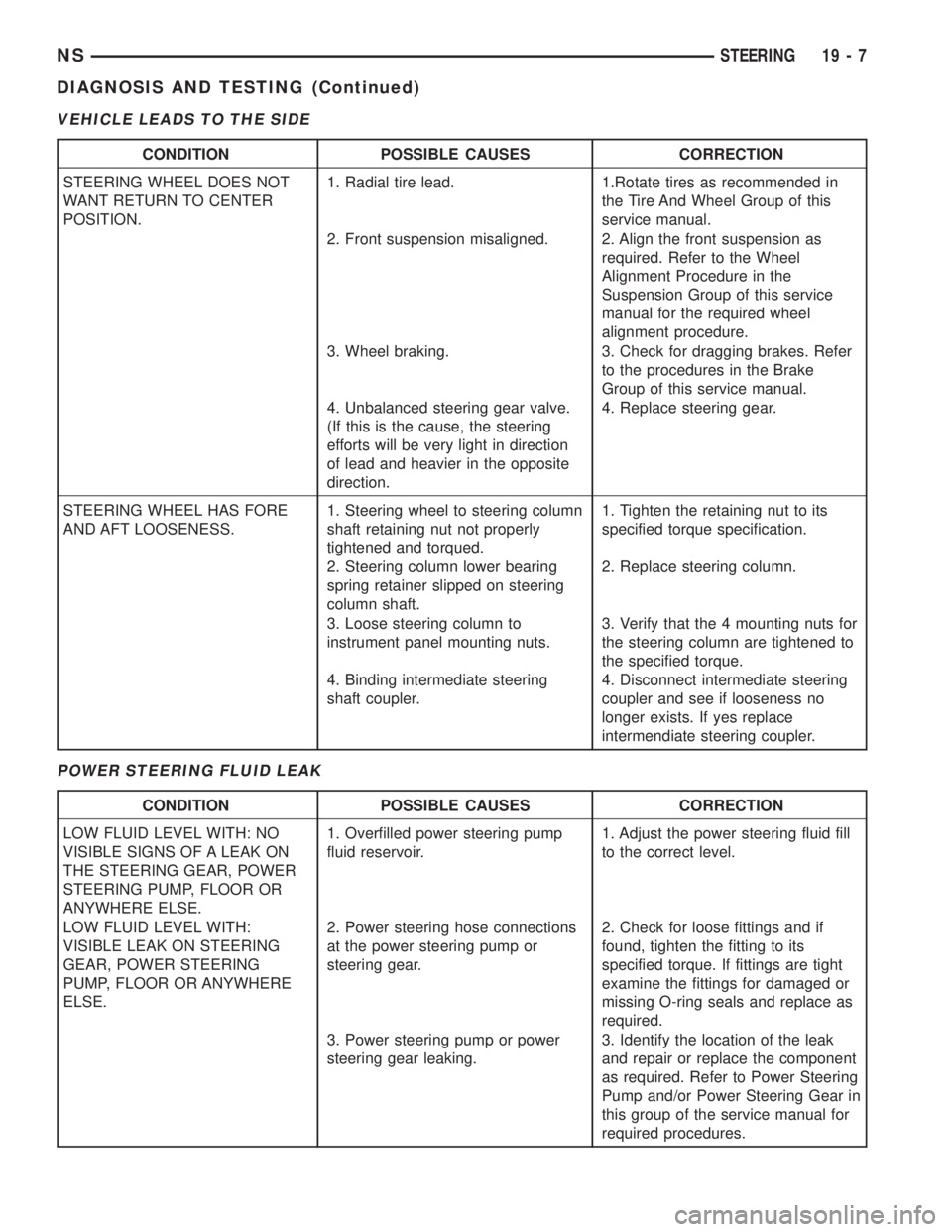
VEHICLE LEADS TO THE SIDE
POWER STEERING FLUID LEAK
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
STEERING WHEEL DOES NOT
WANT RETURN TO CENTER
POSITION.1. Radial tire lead. 1.Rotate tires as recommended in
the Tire And Wheel Group of this
service manual.
2. Front suspension misaligned. 2. Align the front suspension as
required. Refer to the Wheel
Alignment Procedure in the
Suspension Group of this service
manual for the required wheel
alignment procedure.
3. Wheel braking. 3. Check for dragging brakes. Refer
to the procedures in the Brake
Group of this service manual.
4. Unbalanced steering gear valve.
(If this is the cause, the steering
efforts will be very light in direction
of lead and heavier in the opposite
direction.4. Replace steering gear.
STEERING WHEEL HAS FORE
AND AFT LOOSENESS.1. Steering wheel to steering column
shaft retaining nut not properly
tightened and torqued.1. Tighten the retaining nut to its
specified torque specification.
2. Steering column lower bearing
spring retainer slipped on steering
column shaft.2. Replace steering column.
3. Loose steering column to
instrument panel mounting nuts.3. Verify that the 4 mounting nuts for
the steering column are tightened to
the specified torque.
4. Binding intermediate steering
shaft coupler.4. Disconnect intermediate steering
coupler and see if looseness no
longer exists. If yes replace
intermendiate steering coupler.
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
LOW FLUID LEVEL WITH: NO
VISIBLE SIGNS OF A LEAK ON
THE STEERING GEAR, POWER
STEERING PUMP, FLOOR OR
ANYWHERE ELSE.1. Overfilled power steering pump
fluid reservoir.1. Adjust the power steering fluid fill
to the correct level.
LOW FLUID LEVEL WITH:
VISIBLE LEAK ON STEERING
GEAR, POWER STEERING
PUMP, FLOOR OR ANYWHERE
ELSE.2. Power steering hose connections
at the power steering pump or
steering gear.2. Check for loose fittings and if
found, tighten the fitting to its
specified torque. If fittings are tight
examine the fittings for damaged or
missing O-ring seals and replace as
required.
3. Power steering pump or power
steering gear leaking.3. Identify the location of the leak
and repair or replace the component
as required. Refer to Power Steering
Pump and/or Power Steering Gear in
this group of the service manual for
required procedures.
NSSTEERING 19 - 7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1454 of 1938

(1) Remove cap from power steering fluid reser-
voir.
(2) Using a siphon pump, remove as much power
steering fluid as possible from the power steering
fluid reservoir.
(3) With the ignition key in the locked position
turn the steering wheel to the left until the steering
wheel is in the locked position.
(4) With the vehicle on the ground, disconnect the
steering column shaft coupler from the steering gear
intermediate coupler (Fig. 3).
(5) Raise vehicle on jack stands or centered on a
frame contact type hoist. See Hoisting in the Lubri-
cation and Maintenance section of this service man-
ual, for the required lifting procedure to be used for
this vehicle.
(6) Remove the front tires.
(7) Raise the heat sleeve (Fig. 4) on the power
steering return hose to expose the return hose to
steel tube connection. Remove the return hose from
the metal tube of the power steering fluid return line
(Fig. 4). Then allow the remaining power steering
fluid to drain from the system through the hose and
metal tube.
(8) Remove nut attaching outer tie rod end to
steering knuckle (Fig. 5).Nut is to be removed
from tie rod end using the following procedure,
hold tie rod end stud with a 11/32 socket while
loosening and removing nut with wrench.
(9) Remove both tie rod ends from steering knuck-
les, using Puller Special Tool MB-990635 or
MB-991113 (Fig. 6).
Fig. 3 Steering Column Shaft To Intermediate Shaft
Attachment
Fig. 4 Power Steering Fluid Return Hose
Connection
Fig. 5 Removing/Installing Tie Rod End Attaching
Nut
Fig. 6 Tie Rod End Removal From Steering Knuckle
19 - 28 STEERINGNS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1719 of 1938

TIRES AND WHEELS
CONTENTS
page page
TIRES.................................. 1WHEELS................................ 9
TIRES
INDEX
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
RADIAL-PLY TIRES....................... 2
REPLACEMENT TIRES.................... 3
SPARE TIRE (TEMPORARY)................ 2
TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES.............. 2
TIRE INFORMATION...................... 1
TIRE PRESSURE FOR HIGH-SPEED DRIVING . . 3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
LEAD CORRECTION CHART................ 4
PRESSURE GAUGES..................... 3
TIRE NOISE OR VIBRATION................ 4TIRE WEAR PATTERNS.................... 4
TREAD WEAR INDICATORS................ 3
SERVICE PROCEDURES
REPAIRING TIRE LEAKS................... 6
TIRE AND WHEEL MATCH MOUNTING........ 6
TIRE AND WHEEL ROTATION (NON-
DIRECTIONAL THREAD PATTERN).......... 6
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CLEANING TIRES........................ 7
SPECIFICATIONS
TIRE SPECIFICATIONS.................... 8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TIRE INFORMATION
Tires are designed and engineered for each specific
vehicle. They provide the best overall performance
for normal operation. The ride and handling charac-
teristics match the vehicle's requirements. With
proper care they will give excellent reliability, trac-
tion, skid resistance, and tread life.
Driving habits have more effect on tire life than
any other factor. Careful drivers will obtain, in most
cases, much greater mileage than severe use or care-
less drivers. A few of the driving habits which will
shorten the life of any tire are:
²Rapid acceleration
²Severe application of brakes
²High-speed driving
²Taking turns at excessive speeds
²Striking curbs and other obstacles
Radial ply tires are more prone to irregular tread
wear. It is important to follow the tire rotation inter-
val shown in the section on Tire Rotation. This will
help to achieve a greater tread-life potential.
TIRE IDENTIFICATION
Tire type, size, aspect ratio and speed rating are
encoded in the letters and numbers imprinted on the
side wall of the tire. Refer to the chart to decipher
the tire identification code (Fig. 1).
Performance tires will have a speed rating letter
after the aspect ratio number. The speed rating is not
always printed on the tire sidewall. The letterSindi-
cates that the tire is speed rated up to 112 mph.
²Qup to 100 mph
²Tup to 118 mph
²Uup to 124 mph
²Hup to 130 mph
²Vup to 149 mph
²Zmore than 149 mph (consult the tire manu-
facturer for the specific speed rating)
An All Season type tire will have eitherM+S,M
&SorM±S(indicating mud and snow traction)
imprinted on the side wall.
TIRE CHAINS
This vehicle was designed to allow the use of a
specified type of snow chain on the tires. Only com-
pact snow chains or other traction aidsmeeting SAE
type ªClass Sº specifications may be used.Any style
NSTIRES AND WHEELS 22 - 1
Page 1720 of 1938
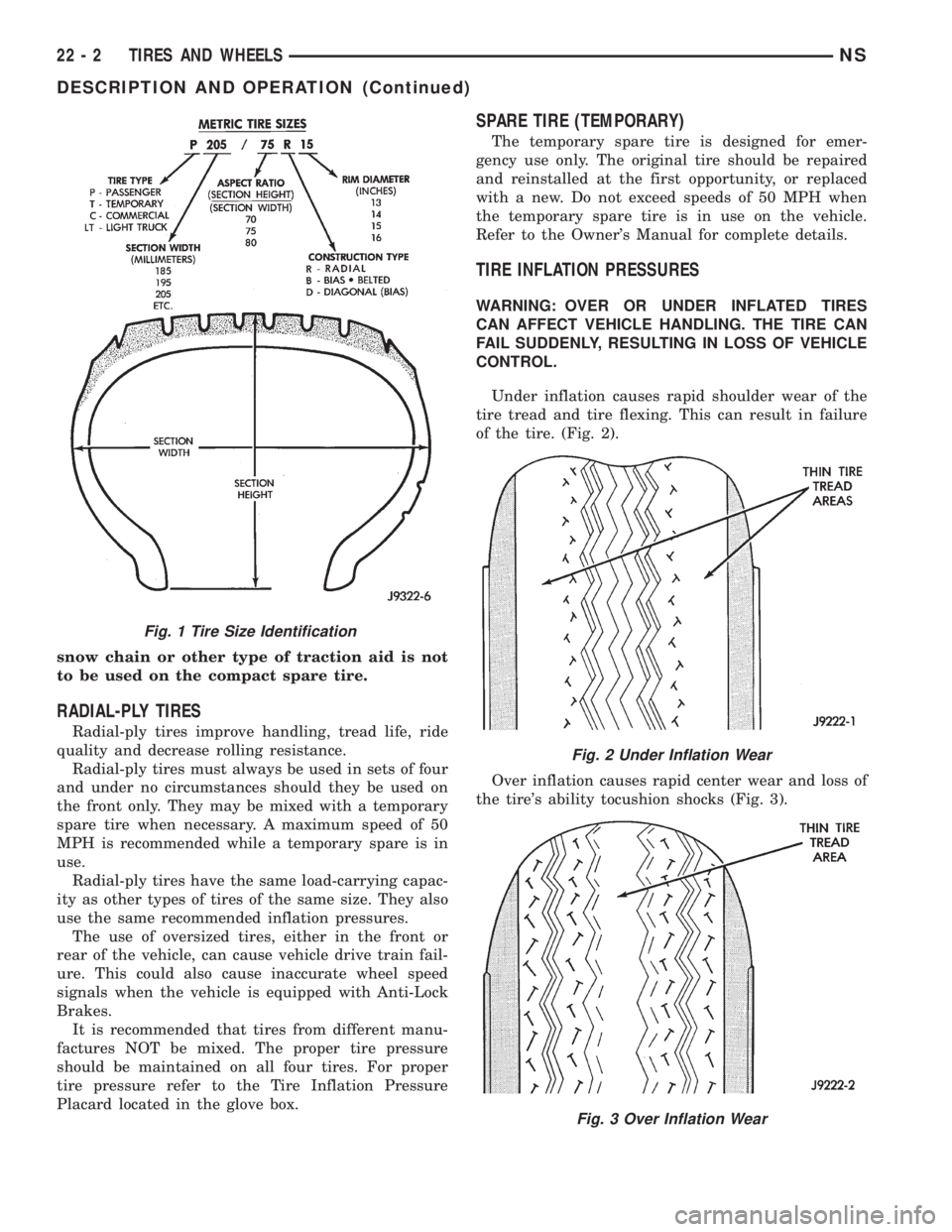
snow chain or other type of traction aid is not
to be used on the compact spare tire.
RADIAL-PLY TIRES
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life, ride
quality and decrease rolling resistance.
Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of four
and under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. They may be mixed with a temporary
spare tire when necessary. A maximum speed of 50
MPH is recommended while a temporary spare is in
use.
Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They also
use the same recommended inflation pressures.
The use of oversized tires, either in the front or
rear of the vehicle, can cause vehicle drive train fail-
ure. This could also cause inaccurate wheel speed
signals when the vehicle is equipped with Anti-Lock
Brakes.
It is recommended that tires from different manu-
factures NOT be mixed. The proper tire pressure
should be maintained on all four tires. For proper
tire pressure refer to the Tire Inflation Pressure
Placard located in the glove box.
SPARE TIRE (TEMPORARY)
The temporary spare tire is designed for emer-
gency use only. The original tire should be repaired
and reinstalled at the first opportunity, or replaced
with a new. Do not exceed speeds of 50 MPH when
the temporary spare tire is in use on the vehicle.
Refer to the Owner's Manual for complete details.
TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES
WARNING: OVER OR UNDER INFLATED TIRES
CAN AFFECT VEHICLE HANDLING. THE TIRE CAN
FAIL SUDDENLY, RESULTING IN LOSS OF VEHICLE
CONTROL.
Under inflation causes rapid shoulder wear of the
tire tread and tire flexing. This can result in failure
of the tire. (Fig. 2).
Over inflation causes rapid center wear and loss of
the tire's ability tocushion shocks (Fig. 3).
Fig. 1 Tire Size Identification
Fig. 2 Under Inflation Wear
Fig. 3 Over Inflation Wear
22 - 2 TIRES AND WHEELSNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1721 of 1938

Improper inflation can cause:
²Uneven wear patterns
²Reduced tread life
²Reduced fuel economy
²Unsatisfactory ride
²The vehicle to drift.
Proper tire air inflation pressure specifications can
be found on the Vehicle Tire Placard provided with
the vehicle. See owner's manual.
Tire pressures have been chosen to provide safe
operation, vehicle stability, and a smooth ride. Tire
pressure should be checked cold once per month.
Check tire pressure more frequently when the
weather temperature varies widely. Tire pressure will
decrease when the outdoor temperature drops.
Tire inflation pressures specified on the placard
are always cold inflation pressure. Cold inflation
pressure is obtained after the vehicle has not been
operated for at least 3 hours, or the vehicle is driven
less than one mile after being inoperative for 3
hours. Tire inflation pressures may increase from 2
to 6 pounds per square inch (psi) during operation.
Do not reduce this normal pressure build-up.
TIRE PRESSURE FOR HIGH-SPEED DRIVING
Chrysler Corporation advocates driving at safe
speeds within posted speed limits. Where speed lim-
its allow the vehicle to be driven at high speeds, cor-
rect tire inflation pressure is very important. For
speeds up to and including 75 mph (120 km/h), tires
must be inflated to the pressures shown on the tire
placard.
Vehicles loaded to the maximum capacity should
not be driven at speeds above 75 mph (120 km/h).
For emergency vehicles that are driven at speeds
over 90 mph (144 km/h), special high-speed tires
must be used. Consult tire manufacturer for correct
inflation pressure recommendations.
REPLACEMENT TIRES
The original equipment tires provide a proper bal-
ance of many characteristics such as:
²Ride
²Noise
²Handling
²Durability
²Tread life
²Traction
²Rolling resistance
²Speed capability
It is recommend that tires equivalent to the origi-
nal equipment tires be used when replacement is
needed.
Failure to use equivalent replacement tires may
adversely affect the safety and handling of the vehicle.
The use of oversize tires not listed in the specifica-
tion charts may cause interference with vehicle com-
ponents. Under extremes of suspension and steering
travel, interference with vehicle components may
cause tire damage.
WARNING: FAILURE TO EQUIP THE VEHICLE WITH
TIRES HAVING ADEQUATE SPEED CAPABILITY
CAN RESULT IN SUDDEN TIRE FAILURE.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
PRESSURE GAUGES
A quality air pressure gauge is recommended to
check tire pressure. After checking the air pressure,
replace valve cap finger tight.
TREAD WEAR INDICATORS
Tread wear indicators are molded into the bottom
of the tread grooves. When tread depth is 1.6 mm
(1/16 in.), the tread wear indicators will appear as a
13 mm (1/2 in.) band (Fig. 4).
Tire replacement is necessary when indicators
appear in two or more grooves or if localized balding
occurs.
Fig. 4 Tread Wear Indicators
NSTIRES AND WHEELS 22 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1722 of 1938

TIRE WEAR PATTERNS
Under inflation will cause wear on the shoulders of
tire. Over inflation will cause wear at the center of
tire.
Excessive camber causes the tire to run at an
angle to the road. One side of tread is then worn
more than the other (Fig. 5).
Excessive toe-in or toe-out causes wear on the
tread edges and a feathered effect across the tread
(Fig. 5).
TIRE NOISE OR VIBRATION
Radial-ply tires are sensitive to force impulses
caused by improper mounting, vibration, wheel
defects, or possibly tire imbalance.To find out if tires are causing the noise or vibra-
tion, drive the vehicle over a smooth road at varying
speeds. Note the noise level during acceleration and
deceleration. The engine, differential and exhaust
noises will change as speed varies, while the tire
noise will usually remain constant.
LEAD CORRECTION CHART
Use the following chart to correct a vehicle leading
or drifting problem.
Fig. 5 Tire Wear Patterns
22 - 4 TIRES AND WHEELSNS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1723 of 1938
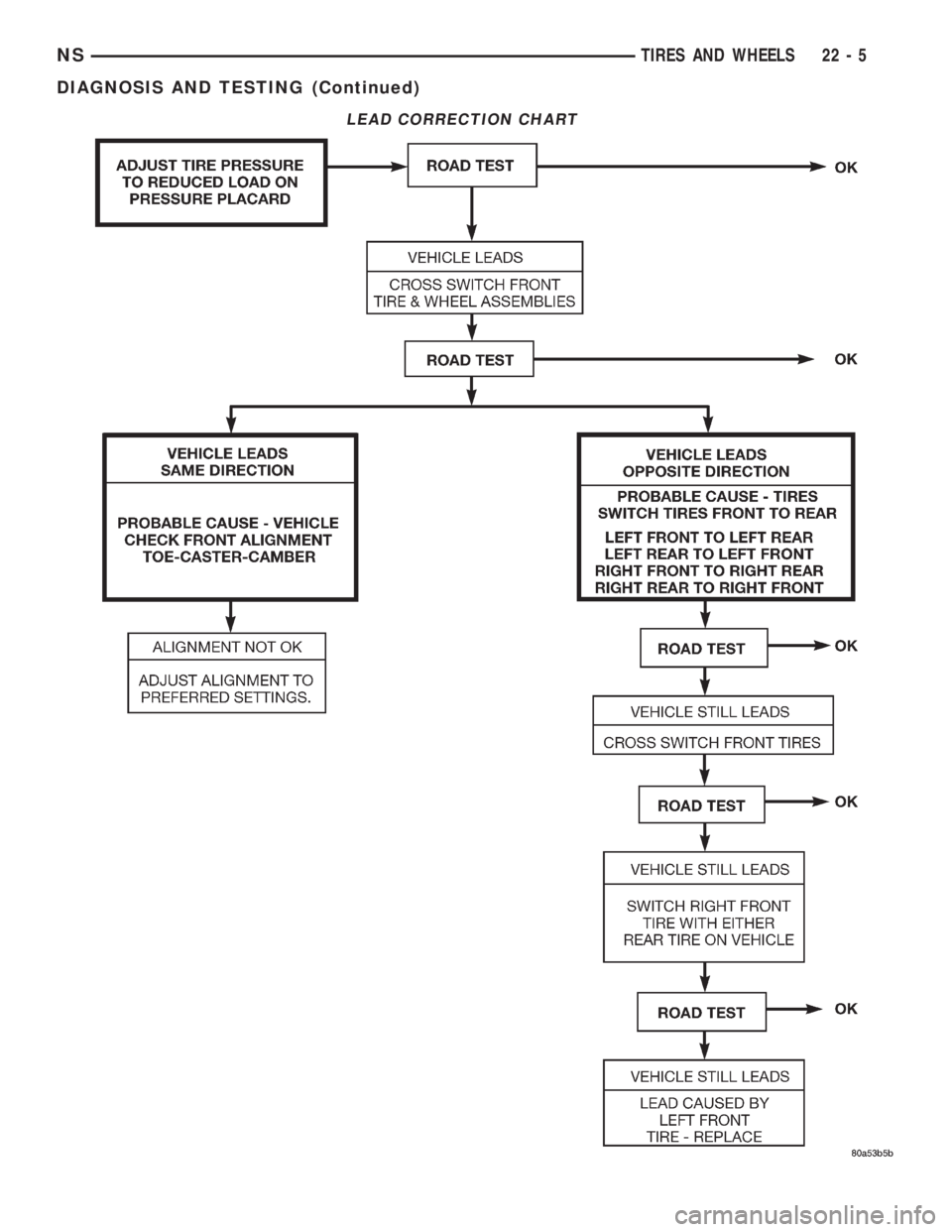
LEAD CORRECTION CHART
NSTIRES AND WHEELS 22 - 5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)