1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER relay
[x] Cancel search: relayPage 1000 of 1938

Component/
GroundColor Location Fig.
Right Rear
Sliding Door
ContactBK RT B-Pillar 14
Right Rear
Sliding Door
Lock MotorBK At Motor N/S
Right Rear
SpeakerBK At Speaker 22
Right Rear Vent
MotorNAT At Motor 22
Right Rear
Wheel Speed
SensorGY Center Rear of
Floor Pan16
Right Repeater
LampGY At Lamp N/S
Right Speed
Control SwitchRight Side of
Steering Wheel
Pad11
Right Stop/Turn
Signal RelayBK LT Quarter
PanelN/S
Right Visor/
Vanity LampBK At Lamp 17
S02 BK Under Seat N/S
Seat Belt Switch BK RT B-Pillar N/S
Sentry Key
Immobilizer
ModuleBK Near Steering
Column at
Module11
Stop Lamp
SwitchGY Top of Brake
Pedal12
T05 BK LT Quarter
PanelN/S
T08 BK RT Quarter
PanelN/SComponent/
GroundColor Location Fig.
Throttle Position
SensorNAT On Throttle
Body5, 6, 7,
8, 9
Trailer Tow
ConnectorBK LT Quarter
PanelN/S
Transmission
Control ModuleBK RT Fender Side
Shield3
Transmission
Range SensorBK Top of
Transmission7. 9
Transmission
Control
SolenoidsBK Front of
Transmission7, 9
Turbine Speed
SensorGY Front of
Transmission7, 9
Turn Signal/
Hazard SwitchBK Part of
Multifunction
Switch11
Upstream
Heated Oxygen
SensorGY Rear of Engine 5, 6, 7,
8, 9
Vehicle Speed
Control ServoBK LT Rear of
Engine
Compartment5, 6, 7,
8, 9
Vehicle Speed
SensorBK Rear of
Transmission5, 6, 8
Windshield
Wiper SwitchBK Part of
Multifunction
Switch11
Wiper Module BK LT Side of
Engine2
8W - 90 - 36 8W - 90 CONNECTOR/GROUND LOCATIONSNS/GS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1026 of 1938
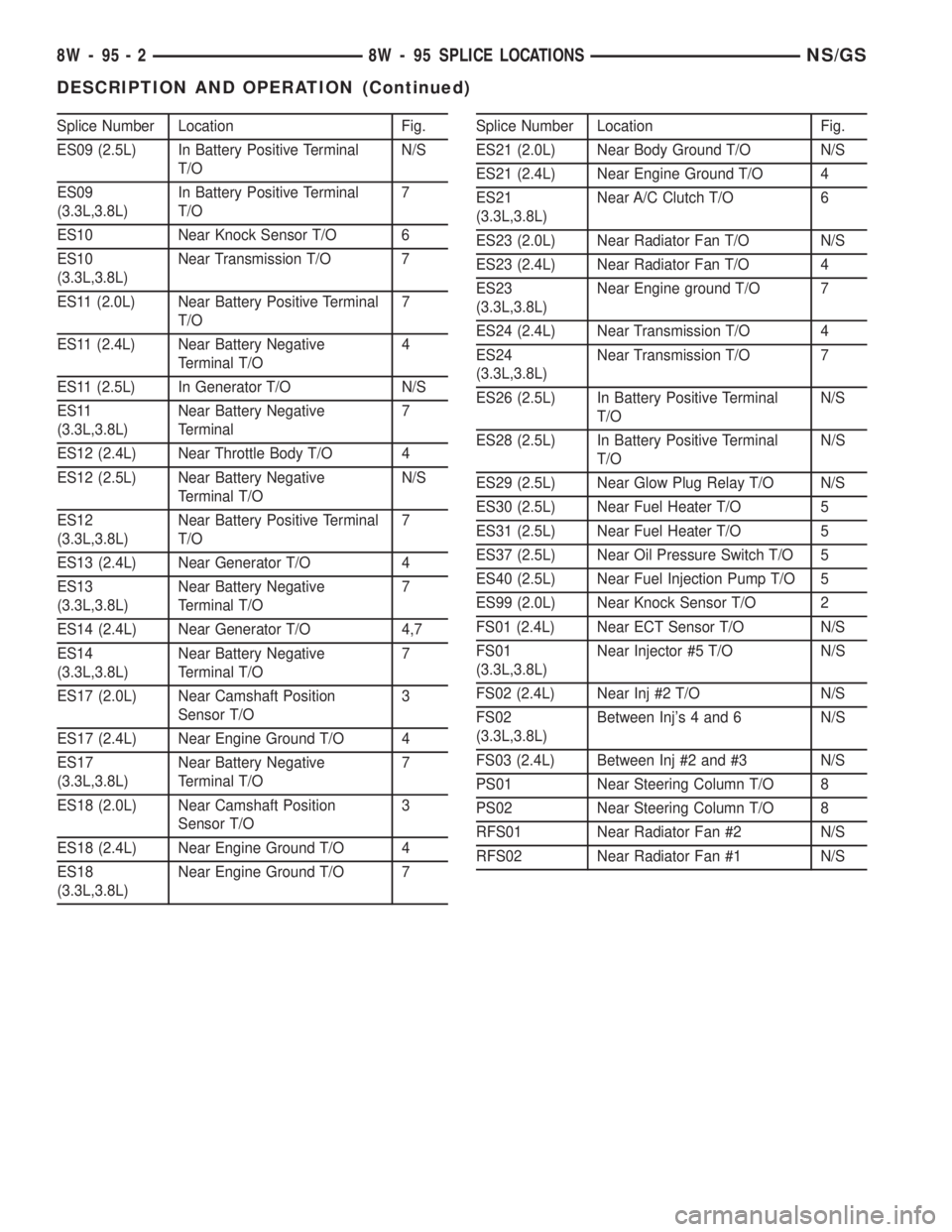
Splice Number Location Fig.
ES09 (2.5L) In Battery Positive Terminal
T/ON/S
ES09
(3.3L,3.8L)In Battery Positive Terminal
T/O7
ES10 Near Knock Sensor T/O 6
ES10
(3.3L,3.8L)Near Transmission T/O 7
ES11 (2.0L) Near Battery Positive Terminal
T/O7
ES11 (2.4L) Near Battery Negative
Terminal T/O4
ES11 (2.5L) In Generator T/O N/S
ES11
(3.3L,3.8L)Near Battery Negative
Terminal7
ES12 (2.4L) Near Throttle Body T/O 4
ES12 (2.5L) Near Battery Negative
Terminal T/ON/S
ES12
(3.3L,3.8L)Near Battery Positive Terminal
T/O7
ES13 (2.4L) Near Generator T/O 4
ES13
(3.3L,3.8L)Near Battery Negative
Terminal T/O7
ES14 (2.4L) Near Generator T/O 4,7
ES14
(3.3L,3.8L)Near Battery Negative
Terminal T/O7
ES17 (2.0L) Near Camshaft Position
Sensor T/O3
ES17 (2.4L) Near Engine Ground T/O 4
ES17
(3.3L,3.8L)Near Battery Negative
Terminal T/O7
ES18 (2.0L) Near Camshaft Position
Sensor T/O3
ES18 (2.4L) Near Engine Ground T/O 4
ES18
(3.3L,3.8L)Near Engine Ground T/O 7Splice Number Location Fig.
ES21 (2.0L) Near Body Ground T/O N/S
ES21 (2.4L) Near Engine Ground T/O 4
ES21
(3.3L,3.8L)Near A/C Clutch T/O 6
ES23 (2.0L) Near Radiator Fan T/O N/S
ES23 (2.4L) Near Radiator Fan T/O 4
ES23
(3.3L,3.8L)Near Engine ground T/O 7
ES24 (2.4L) Near Transmission T/O 4
ES24
(3.3L,3.8L)Near Transmission T/O 7
ES26 (2.5L) In Battery Positive Terminal
T/ON/S
ES28 (2.5L) In Battery Positive Terminal
T/ON/S
ES29 (2.5L) Near Glow Plug Relay T/O N/S
ES30 (2.5L) Near Fuel Heater T/O 5
ES31 (2.5L) Near Fuel Heater T/O 5
ES37 (2.5L) Near Oil Pressure Switch T/O 5
ES40 (2.5L) Near Fuel Injection Pump T/O 5
ES99 (2.0L) Near Knock Sensor T/O 2
FS01 (2.4L) Near ECT Sensor T/O N/S
FS01
(3.3L,3.8L)Near Injector #5 T/O N/S
FS02 (2.4L) Near Inj #2 T/O N/S
FS02
(3.3L,3.8L)Between Inj's 4 and 6 N/S
FS03 (2.4L) Between Inj #2 and #3 N/S
PS01 Near Steering Column T/O 8
PS02 Near Steering Column T/O 8
RFS01 Near Radiator Fan #2 N/S
RFS02 Near Radiator Fan #1 N/S
8W - 95 - 2 8W - 95 SPLICE LOCATIONSNS/GS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1221 of 1938

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ENGINE DIAGNOSISÐPERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT
CRANK OR CRANKS
SLOWLY1. Starting motor operating, but not cranking the
engine.1. Remove the starter motor. Check for broken
flywheel teeth or a broken starter motor spring.
2. Crankshaft rotation restricted. 2. Rotate the engine to check for rotational
resistance.
3. Starting circuit connections loose or corroded. 3. Clean and tighten connections.
4. Neutral safety or starter relay inoperative. 4. Check starter relay supply voltage and proper
operation of neutral safety switch (if equipped).
Replace defective parts.
5. Battery charge low. 5. Check Battery voltage. Replace battery if a
charge cannot be held.
6. No voltage to starter solenoid. 6. Check voltage to solenoid. If necessary, replace
the solenoid.
7. Solenoid or starter motor inoperative. 7. Replace starter motor.
ENGINE CRANKS, BUT
WILL NOT START, NO
SMOKE1. No fuel in supply tank. 1. Fill fuel supply.
2. Electrical fuel shutdown solenoid not operating. 2. Check for loose wires and verify that the fuel
shutdown solenoid is functioning. Check for fault
codes in the ECU.
3. Fuel injection system defective: Cranking speed
sensor. Loose connection between ECU and
harness. No power supply to the ECU. Loose
connection between injection pump and harness.3. Check for fault codes at ECU. Refer to Group 14,
Fuel System for repairs procedures.
4. Air intake or exhaust plugged. 4. Remove the obstruction.
5. Fuel filter plugged. 5. Drain fuel/water separator and replace fuel filter.
6. Excessive fuel inlet restriction. 6. Check for restriction. Correct cause.
7. Injection pump not getting fuel or fuel is aerated. 7. Check fuel flow/bleed fuel system.
8. One or more injectors worn or not operating
properly.8. Check/replace bad or improperly operating
injectors.
9. Camshaft out of time. 9. Check/correct timing chain sprocket alignment.
ENGINE HARD TO
START, OR WILL NOT
START, SMOKE FROM
EXHAUST1. Incorrect starting procedure. 1. The fuel shutoff solenoid control must be in the
run position. Ensure the proper procedure is being
used.
2. Cranking speed to slow. 2. Check the battery, starter motor and look for
loose or corroded wiring connections.
3. Cylinder head heater plugs defective. 3. Verify system is working. Verify connection
between heater plug relay and ECU. Repair/replace
inoperative parts.
4. Insufficient intake air 4. Inspect or replace air filter and check for
obstruction in air supply.
5. Air in fuel system or the fuel supply is
inadequate.5. Check the fuel flow through the filter and bleed
system. Locate and eliminate the air source.
6. Contaminated fuel. 6. Verify by operating the engine with clean fuel
from a temporary tank. Check for the presence of
gasoline. Drain and flush fuel supply tank. Replace
fuel/water separator filter.
7. Fuel screen plugged. 7. Check fuel screen.
8. One or more injectors worn or not operating
properly.8. Check/replace improperly operating injectors.
9. Injector pump out of time. 9. Check pump timing. Refer to Group 14, Fuel
System for procedure.
10. Engine compression low. 10. Check compression to identify the problem.
11. Fuel injection system defective. 11. Vacuum modulator defective causing EGR to
open in cold condition. Check for fault codes in the
ECU.
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 43
Page 1270 of 1938

(2) Tighten intake manifold fasteners in the fol-
lowing sequence (Fig. 16). Torque to 23 N´m (200 in.
lbs.). Repeat this procedure until all bolts are at
specified torque.
(3) Install intake manifold center support bracket
bolts (Y bracket):
²Fastener to block 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
²Fastener to intake 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.)
(4) Install fuel hose quick connector fitting to
chassis tubes.Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps and
Quick Connect Fittings in Group 14, Fuel Deliv-
ery.Push the fitting onto the chassis tube until it
clicks into place. Pull on the fitting to ensure com-
plete insertion.
(5) Reverse removal procedures 2 through 12 for
installation.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the ASD relay and fuel pump relay remain energized
for 7 minutes or until the test is stopped, or until
the ignition switch is turned to the Off position.
(6) With the ignition key in ON position, access
the DRB scan tool ASD Fuel System Test to pressur-
ize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
EXHAUST MANIFOLDÐ2.4L ENGINE
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and disconnect exhaust pipe from
the exhaust manifold at the flex-joint.
(2) Disconnect Oxygen Sensor lead wire at the rear
exhaust manifold (Fig. 17).
(3) Remove the bolts attaching the manifold to the
cylinder head. Remove manifold (Fig. 17).
(4) Inspect and clean manifold. Refer to Cleaning
and Inspection outlined in this section for proce-
dures.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install exhaust manifold with a new gasket
and tighten attaching nuts in the order shown in
(Fig. 17) to 20 N´m (175 in. lbs.).
(2) Attach exhaust pipe to exhaust manifold and
tighten bolt to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect heated oxygen sensor lead (Fig. 17).
INTAKE MANIFOLDÐ3.0L ENGINE
REMOVAL
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release proce-
dure(before attempting any repairs).Refer to
Group 14 Fuel System for procedure.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable. Drain cool-
ing system. See Cooling System, Group 7.
(3) Remove air inlet resonator to throttle body
hose.
(4) Remove throttle cable and transaxle kickdown
linkage (Fig. 18).
(5) Remove automatic idle speed (AIS) motor and
throttle position sensor (TPS) wiring connectors from
throttle body (Fig. 19).
(6) Remove vacuum hose harness from throttle
body.
(7) Remove PCV and Brake booster hoses from
Air Intake Plenum.
(8) Remove Ignition Coil from Intake Plenum
(Fig. 20).
(9) Remove wiring connectors from coolant temper-
ature sensor (Fig. 21).
(10) Remove vacuum connections from Air Intake
Plenum vacuum connector.
(11) Remove fuel hose from fuel rail (Fig. 21).
WARNING: WRAP SHOP TOWELS AROUND HOSES
TO CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
Fig. 17 Exhaust Manifold Attaching PointsÐ2.4L
Engine
Fig. 18 Throttle Cable Attachment
11 - 8 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLDNS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1273 of 1938

(10) Connect fuel line to fuel rail (Fig. 21). Torque
hose clamps to 1 N´m (10 in. lbs.).
(11) Connect vacuum harness to air intake ple-
num.
(12) Connect and coolant temperature sensor elec-
trical connector to sensor (Fig. 21).
(13) Connect PCV and brake booster supply hose
to intake plenum.
(14) Connect automatic idle speed (AIS) motor
and throttle position sensor (TPS) electrical connec-
tors (Fig. 19).
(15) Connect vacuum vapor harness to throttle
body (Fig. 19).
(16) Install throttle cable and transaxle kickdown
linkage (Fig. 18).
(17) Install air inlet resonator hose assembly to
throttle body.
(18) Install radiator to thermostat housing hose
and heater hose to heater pipe nipple.
(19) Fill cooling system. Refer to Filling the Cool-
ing System outlined in Group 7 Cooling System for
procedure.
(20) Connect negative battery cable.
(21) With the DRB Scan Tool use ASD Fuel Sys-
tem Test to pressurize system to check for leaks.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
The Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay will remain ener-
gized for 7 minutes or until the ignition switch is
turned to the OFF position, or Stop All Test is
selected.
EXHAUST MANIFOLDÐ3.0L ENGINE
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and disconnect exhaust pipe
from rear (cowl side) exhaust manifold at the flex-
joint.(2) Disconnect Oxygen Sensor lead wire at the
rear exhaust manifold (Fig. 28).
(3) Remove bolts attaching cross-over pipe to
manifold (Fig. 30).
(4) Remove rear heat shield (Fig. 29).
(5) Remove nuts attaching rear manifold to cylin-
der head and remove manifold.
(6) Lower vehicle and remove screws attaching
front heat shield to front manifold (Fig. 31).
(7) Remove bolts fastening crossover pipe to front
exhaust manifold and nuts fastening manifold to cyl-
inder head. Remove assemblies.
(8) Inspect and clean manifolds. Refer to Cleaning
and Inspection outlined in this section for proce-
dures.
INSTALLATION
Install the gaskets with the numbers 1-3-5
embossed on the top on the rear bank and those with
numbers 2-4-6 on the front (Radiator side) bank (Fig.
32).
(1) Install rear exhaust manifold and tighten
attaching nuts to 20 N´m (175 in. lbs.).
Fig. 27 Intake Plenum Tightening Sequence
Fig. 28 Disconnect Up Stream Heated Oxygen
Sensor Connection
Fig. 29 Rear Exhaust Manifold Heat Shield
NSEXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD 11 - 11
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1278 of 1938

CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
The Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay will remain ener-
gized for 7 minutes or until the ignition switch is
turned to the OFF position, or Stop All Test is
selected.
EXHAUST MANIFOLDSÐ3.3/3.8L ENGINE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove accessory drive belt. Refer to Accessory
Drive section located in Group 7 Cooling System for
procedure.
(3) Remove generator.
(4) Raise vehicle and disconnect exhaust pipe
from rear (cowl side) exhaust manifold at flex-joint.
(5) Disconnect down stream oxygen sensor connec-
tor.
(6) Lower exhaust system to gain access to rear
manifold.
(7) Separate EGR tube from rear manifold and
disconnect Heated Oxygen Sensor lead wire (Fig. 45).
(8) Remove heat shield from rear engine mount.
(9) Remove Generator/Power Steering Support
Strut (Fig. 45).
(10) Remove bolts attaching crossover pipe to
manifold (Fig. 45).
(11) Disconnect up stream oxygen sensor connec-
tor.
(12) Remove bolts attaching rear manifold to cyl-
inder head and remove manifold.
(13) Lower vehicle and remove screws attaching
front heat shield to front manifold (Fig. 46).
(14) Remove bolts fastening crossover pipe to
front exhaust manifold and nuts fastening manifold
to cylinder head. Remove assemblies (Fig. 47).
(15) Inspect and clean manifold. Refer to Cleaning
and Inspection outlined in this section for proce-
dures.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install rear exhaust manifold and tighten
attaching bolts to 23 N´m (200 in. lbs.).
(2) Install generator.
NOTE: Inspect crossover pipe fasteners for dam-
age from heat and corrosion. Replace if necessary.
(3) Using new gasket attach crossover pipe to
exhaust manifold and tighten bolts to 54 N´m (40 ft.
lbs.) and connect oxygen sensor lead (Fig. 45).
(4) Install EGR Tube and Generator/Power Steer-
ing Strut (Fig. 45).
(5) Using new gaskets install front exhaust mani-
fold and tighten attaching bolts to 23 N´m (200 in.
lbs.).(6) Attach exhaust crossover with a new gasket
and tighten fasteners to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 47).
(7) Connect up stream oxygen sensor connector.
(8) Install exhaust system.
Fig. 45 EGR Tube, Heated Oxygen Sensor and
Generator/Power Steering Strut
Fig. 46 Heat ShieldÐFront
Fig. 47 Crossover Pipe
11 - 16 EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLDNS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1299 of 1938

check valve, in the pump outlet, maintains pump
pressure during engine off conditions. The fuel pump
relay provides voltage to the fuel pump.
The fuel pump has a maximum deadheaded pres-
sure output of approximately 635 kPa (95 psi). The
regulator adjusts fuel system pressure to approxi-
mately 338 kPa (49 psi).
FUEL PUMP ELECTRICAL CONTROL
Voltage to operate the electric pump is supplied
through the fuel pump relay. For an electrical opera-
tional description of the fuel pump refer to fuel Pump
RelayÐPCM Output.
ELECTRICAL PUMP REPLACEMENT
The electric fuel pump is not serviceable. If the
fuel pump or electrical wiring harness needs replace-
ment, the complete fuel pump module must be
replaced. Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release
procedure before servicing the fuel pump.
FUEL LEVEL SENSOR
The level sensor is attached to the side of the fuel
pump module. The level sensor consists of a float, an
arm, and a variable resistor. As the fuel level
increases, the float and arm move up. This decreases
the sending unit resistance, causing the fuel gauge
on the instrument panel to read full.
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
The fuel system uses a nonadjustable pressure reg-
ulator that maintains fuel system pressure at
approximately 338 kPa (49 psi), 3.3l uses approxi-
mately 379 kPa (55 psi). The fuel pressure regulator
contains a diaphragm, calibrated spring and a fuel
return valve. The spring pushes down on the dia-
phragm and closes off the fuel return port. System
fuel pressure reflects the amount of fuel pressure
required to open the return port.
The pressure regulator is a mechanical device that
is NOT controlled by the PCM or engine vacuum.
FUEL INJECTORS
The fuel injectors are 12 ohm electrical solenoids
(Fig. 2). The injector contains a pintle that closes off
an orifice at the nozzle end. When electric current is
supplied to the injector, the armature and needle
move a short distance against a spring, allowing fuel
to flow out the orifice. Because the fuel is under high
pressure, a fine spray is developed in the shape of a
hollow cone. The spraying action atomizes the fuel,
adding it to the air entering the combustion chamber.
The injectors are positioned in the intake manifold.
Fuel injectors are not interchangeable between
engines.The injectors are positioned in the intake manifold
with the nozzle ends directly above the intake valve
port (Fig. 3).
FUEL TANK
The fuel tanks of all Chrysler Motors built vehicles
are equipped with fuel and vapor controls that allow
the vehicle to pass a full 360É rollover without fuel
leakage.
Front Wheel Drive fuel delivery systems contain a
fuel tank rollover valve. The valve is mounted on top
of the fuel tank. The valve functions as a tank pres-
sure control valve while the vehicle is upright, but
contains a check valve that prevents fuel from escap-
ing from the fuel tank when the vehicle is turned
over.
The fuel filler cap acts as a pressure/vacuum relief
valve. When air pressure inside the fuel tank gets too
high or too low, the fuel filler cap opens to relieve the
difference in pressure.
An evaporation control system restricts fuel evapo-
ration into the atmosphere and reduces unburned
Fig. 2 Fuel Injector
Fig. 3 Fuel Injector LocationÐTypical
NSFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1301 of 1938

(1) Remove cap from fuel pressure test port on fuel
rail.
(2) Connect Fuel Pressure Gauge C-4799B to test
port (Fig. 7).
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the ASD relay and fuel pump relay remain energized
for 7 minutes or until the test is stopped, or until
the ignition switch is turned to the Off position.
(3) Place the ignition key in the ON position.
Using the DRB scan tool, access ASD Fuel System
Test. The ASD Fuel System Test will activate the fuel
pump and pressurize the system.²If the gauge reading equals 338 kPa (49 psi)
3.3L uses approximately 379 kPa (55 psi) further
testing is not required. If pressure is not correct,
record the pressure.
²If pressure is above specifications, check for a
kinked or restricted fuel return tube (from filter to
pump module). If the fuel return tube is not pinched
or restricted, replace the fuel pressure regulator.
²If fuel pressure is below specifications, refer to
the diagnosis chart for Fuel Pressure Below Specifi-
cations.
(4)Replace Pressure test port cap when fin-
ished doing pressure test.
Fig. 6 Fuel Pressure Test PortÐ3.3/3.8LFig. 7 Checking Fuel Pressure at Fuel Rail
NSFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)