1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 1088 of 1938
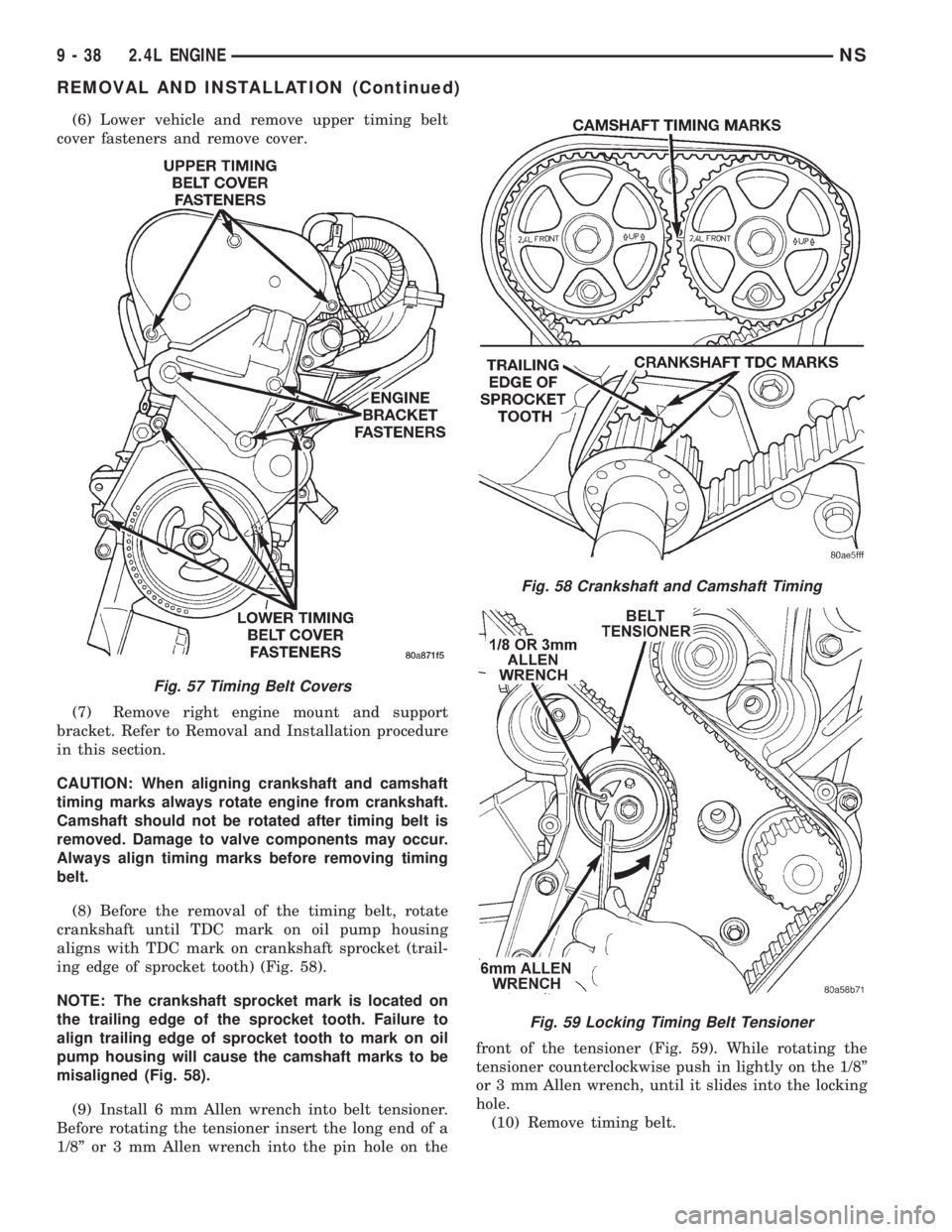
(6) Lower vehicle and remove upper timing belt
cover fasteners and remove cover.
(7) Remove right engine mount and support
bracket. Refer to Removal and Installation procedure
in this section.
CAUTION: When aligning crankshaft and camshaft
timing marks always rotate engine from crankshaft.
Camshaft should not be rotated after timing belt is
removed. Damage to valve components may occur.
Always align timing marks before removing timing
belt.
(8) Before the removal of the timing belt, rotate
crankshaft until TDC mark on oil pump housing
aligns with TDC mark on crankshaft sprocket (trail-
ing edge of sprocket tooth) (Fig. 58).
NOTE: The crankshaft sprocket mark is located on
the trailing edge of the sprocket tooth. Failure to
align trailing edge of sprocket tooth to mark on oil
pump housing will cause the camshaft marks to be
misaligned (Fig. 58).
(9) Install 6 mm Allen wrench into belt tensioner.
Before rotating the tensioner insert the long end of a
1/8º or 3 mm Allen wrench into the pin hole on thefront of the tensioner (Fig. 59). While rotating the
tensioner counterclockwise push in lightly on the 1/8º
or 3 mm Allen wrench, until it slides into the locking
hole.
(10) Remove timing belt.
Fig. 57 Timing Belt Covers
Fig. 58 Crankshaft and Camshaft Timing
Fig. 59 Locking Timing Belt Tensioner
9 - 38 2.4L ENGINENS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1111 of 1938

3.0L ENGINE
INDEX
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE COMPONENTS.................. 61
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER......... 61
ENGINE LUBRICATION................... 61
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE......... 62
SERVICE PROCEDURES
AUTO LASH ADJUSTER................... 62
CHECKING CRANKSHAFT END PLAY........ 65
FITTING CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS...... 63
FITTING MAIN BEARING.................. 63
VALVE SERVICE RECONDITION............ 66
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CAMSHAFT SEAL....................... 72
CAMSHAFT............................ 71
CRANKSHAFT.......................... 81
CYLINDER HEAD COVER................. 70
CYLINDER HEAD........................ 73
ENGINE ASSEMBLY...................... 69
ENGINE MOUNTS....................... 68
FRONT CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL............ 83OIL FILTER AND ADAPTOR................ 84
OILPAN ............................... 77
OIL PUMP............................. 84
PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD........... 78
REAR CRANKSHAFT SEAL................ 83
ROCKER ARMS......................... 72
TIMING BELT........................... 75
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFTS.............. 85
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
CYLINDER BORE........................ 87
CYLINDER HEAD........................ 86
OIL PUMP............................. 87
TIMING BELT........................... 86
ADJUSTMENTS
ENGINE MOUNTS....................... 88
SPECIFICATIONS
3.0L ENGINE........................... 89
TORQUE CHART 3.0L.................... 90
SPECIAL TOOLS
3.0L ENGINE........................... 91
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER
The engine identification number is located on the
rear of the cylinder block just below the cylinder
head (Fig. 1).
ENGINE LUBRICATION
System is a full flow filtration, pressure feed type.
The oil pump is mounted behind the timing belt
cover. The pump inner rotor is driven by the crank-
shaft. The engine oil pan contains a baffle plate to
control oil level fluctuation during engine operation.
ENGINE COMPONENTS
BLOCK:The cylinder block is a light weight
design created by reducing thickness in many parts
and a short 10 mm (3/8 in.) block skirt. High rigidity
is provided with ribs cast in the outer wall, a full
length water jacket, and a mono-block or beam type,
main bearing cap. This single unit four bearing cap
is designed to control vibration of the cylinder block
partition walls.
CRANKSHAFT:A six throw, five weight crank-
shaft is supported by four main bearings with num-
ber three being the thrust bearing. The six separate
connecting rod throws pins reduce torque fluctua-tions while a torsional vibration damper is used to
control torsion caused vibration of the crankshaft.
Rubber lipped seals are used at front and rear. The
Fig. 1 Engine Identification
NS3.0L ENGINE 9 - 61
Page 1112 of 1938

front seal is retained in the oil pump case and the
rear is retained in a block-mounted housing.
PISTONS:Are aluminum alloy with a steel strut,
short height, and thin wall so as to be autothermic
and light weight. The piston head with valve
recesses, in combination with the cylinder head,
forms a compact spherical head with clearance for
total valve lift with pistons at top dead center. The
piston skirt, top and second ring lands are finished to
a tapered roughness for oil retention and high resis-
tance to scuffing. Piston pins, pressed into place, join
the pistons to the connecting rods.
CYLINDER HEAD:The alloy cylinder heads fea-
ture cross-flow type intake and exhaust ports. Valve
guides and inserts are hardened cast iron. Valves of
heat resistance steel are arranged in a V with each
camshaft on center. To improve combustion speed the
chambers are a compact spherical design with a
squish area of approximately 30 percent of the piston
top area. The cylinder heads are common to either
cylinder bank by reversing the direction of installa-
tion.
CAMSHAFTS:Two overhead camshafts provide
valve actuation, one front (radiator side of cylinder
bank) and one rear. The front camshaft is provided
with a distributor drive and is longer. Both cam-
shafts are supported by four bearing journals, thrust
for the front camshaft is taken at journal two and
the rear at journal three. Front and rear camshaft
driving sprockets are interchangeable. The sprockets
and the engine water pump are driven by a single
notched timing belt.
ROCKER ARM SHAFTS:The shafts are retained
by the camshaft bearing journal caps. Four shafts are
used, one for each intake and exhaust rocker arm
assembly on each cylinder head. The hollow shafts
provide a duct for lubricating oil flow from the cylin-
der head to the valve mechanisms.
ROCKER ARMS:Are of light weight die-cast with
roller type follower operating against the cam shaft.
The valve actuating end of the rocker arms are
machined to retain hydraulic lash adjusters, elimi-
nating valve lash adjustment.
VALVES:Are made of heat resistant steel, valve
springs are especially designed to be short. The valve
spring wire cross-section is oval shaped and provides
the same spring tension as longer springs. Valve
spring retainers, locks and seals are conventional.
INTAKE MANIFOLD:The aluminum alloy mani-
fold is a cross type with long runners to improve
inertia. The runners, attaching below at the cylinder
head, also attach above and support an air plenum.
The air plenum chamber absorbs air pulsations cre-
ated during the suction phase of each cylinder.
EXHAUST MANIFOLDS:Both manifolds are a
log style made of ductile cast iron. Exhaust gasses,collected from the front cylinder bank, leave the front
manifold through an end outlet and are fed through
an upper crossover tube to the rear manifold. The
collected exhaust from both manifolds are combined,
and exit to the exhaust pipe through an articulated
joint.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
Check oil pressure using gauge at oil pressure
switch location. Oil pressure should be 41 kPa ( 6
psi.) at idle or 241 to 517 kPa (35 to 75 psi.) at 3000
RPM.
(1) Remove pressure sending unit and install oil
pressure gauge. (Fig. 2).
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, Do Not Run
engine at 3000 RPM.
(2) Warm engine at high idle until thermostat
opens.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
AUTO LASH ADJUSTER
The automatic lash adjusters are precision units
installed in machined openings in the valve actuating
ends of the rocker arms. Do not disassemble the auto
lash adjuster.
FUNCTION CHECK
Check auto adjusters for free play by inserting a
small wire through the air bleed hole in the rocker
arm andvery lightlypushing the auto adjuster ball
check down (Fig. 3). While lightly holding the check
ball down move the rocker up and down to check for
free play. If there is no play replace the adjuster.
Fig. 2 Checking Engine Oil Pressure
9 - 62 3.0L ENGINENS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1117 of 1938
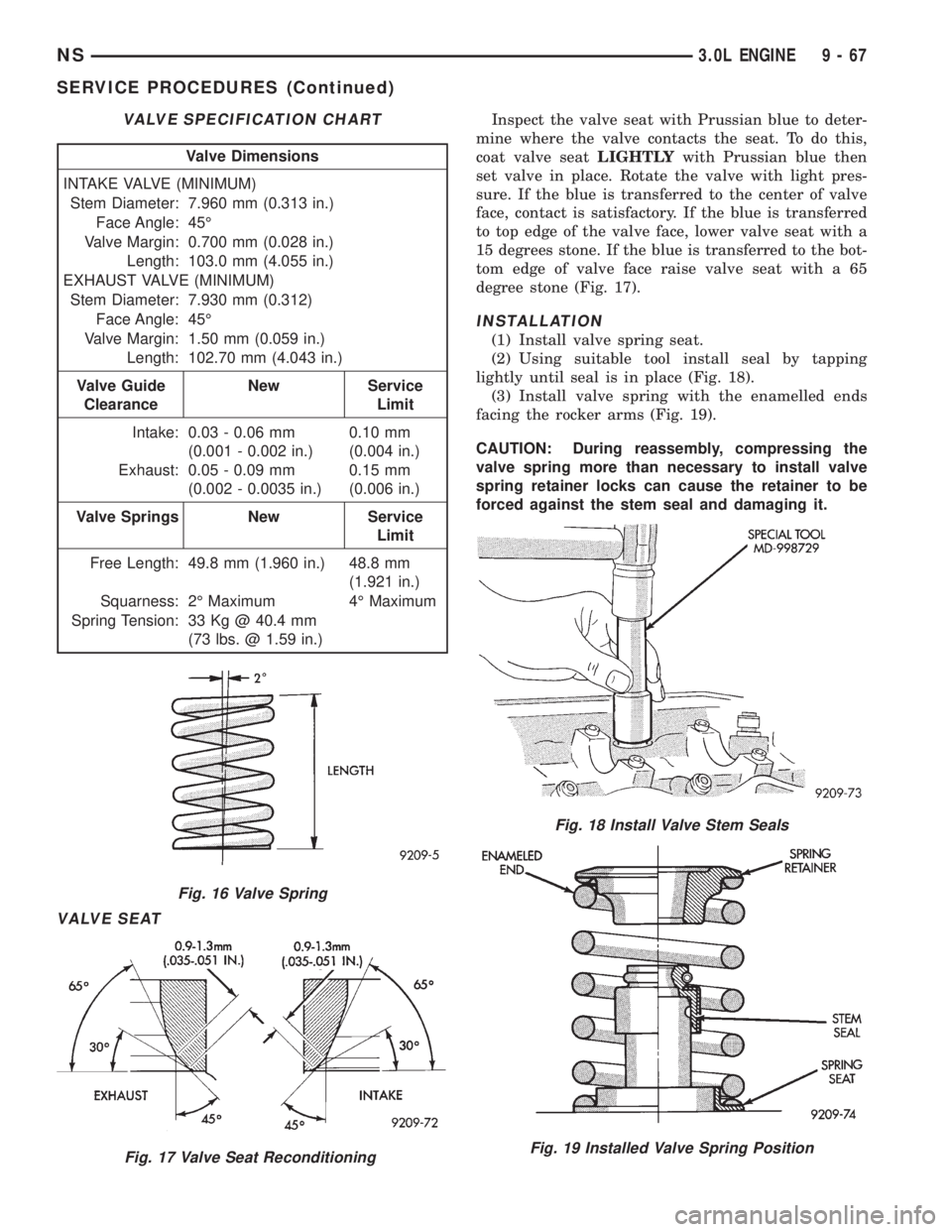
VALVE SEAT
Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue to deter-
mine where the valve contacts the seat. To do this,
coat valve seatLIGHTLYwith Prussian blue then
set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light pres-
sure. If the blue is transferred to the center of valve
face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is transferred
to top edge of the valve face, lower valve seat with a
15 degrees stone. If the blue is transferred to the bot-
tom edge of valve face raise valve seat with a 65
degree stone (Fig. 17).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install valve spring seat.
(2) Using suitable tool install seal by tapping
lightly until seal is in place (Fig. 18).
(3) Install valve spring with the enamelled ends
facing the rocker arms (Fig. 19).
CAUTION: During reassembly, compressing the
valve spring more than necessary to install valve
spring retainer locks can cause the retainer to be
forced against the stem seal and damaging it.
VALVE SPECIFICATION CHART
Valve Dimensions
INTAKE VALVE (MINIMUM)
Stem Diameter: 7.960 mm (0.313 in.)
Face Angle: 45É
Valve Margin: 0.700 mm (0.028 in.)
Length: 103.0 mm (4.055 in.)
EXHAUST VALVE (MINIMUM)
Stem Diameter: 7.930 mm (0.312)
Face Angle: 45É
Valve Margin: 1.50 mm (0.059 in.)
Length: 102.70 mm (4.043 in.)
Valve Guide
ClearanceNew Service
Limit
Intake: 0.03 - 0.06 mm
(0.001 - 0.002 in.)0.10 mm
(0.004 in.)
Exhaust: 0.05 - 0.09 mm
(0.002 - 0.0035 in.)0.15 mm
(0.006 in.)
Valve Springs New Service
Limit
Free Length: 49.8 mm (1.960 in.) 48.8 mm
(1.921 in.)
Squarness: 2É Maximum 4É Maximum
Spring Tension: 33 Kg @ 40.4 mm
(73 lbs. @ 1.59 in.)
Fig. 16 Valve Spring
Fig. 17 Valve Seat Reconditioning
Fig. 18 Install Valve Stem Seals
Fig. 19 Installed Valve Spring Position
NS3.0L ENGINE 9 - 67
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1123 of 1938
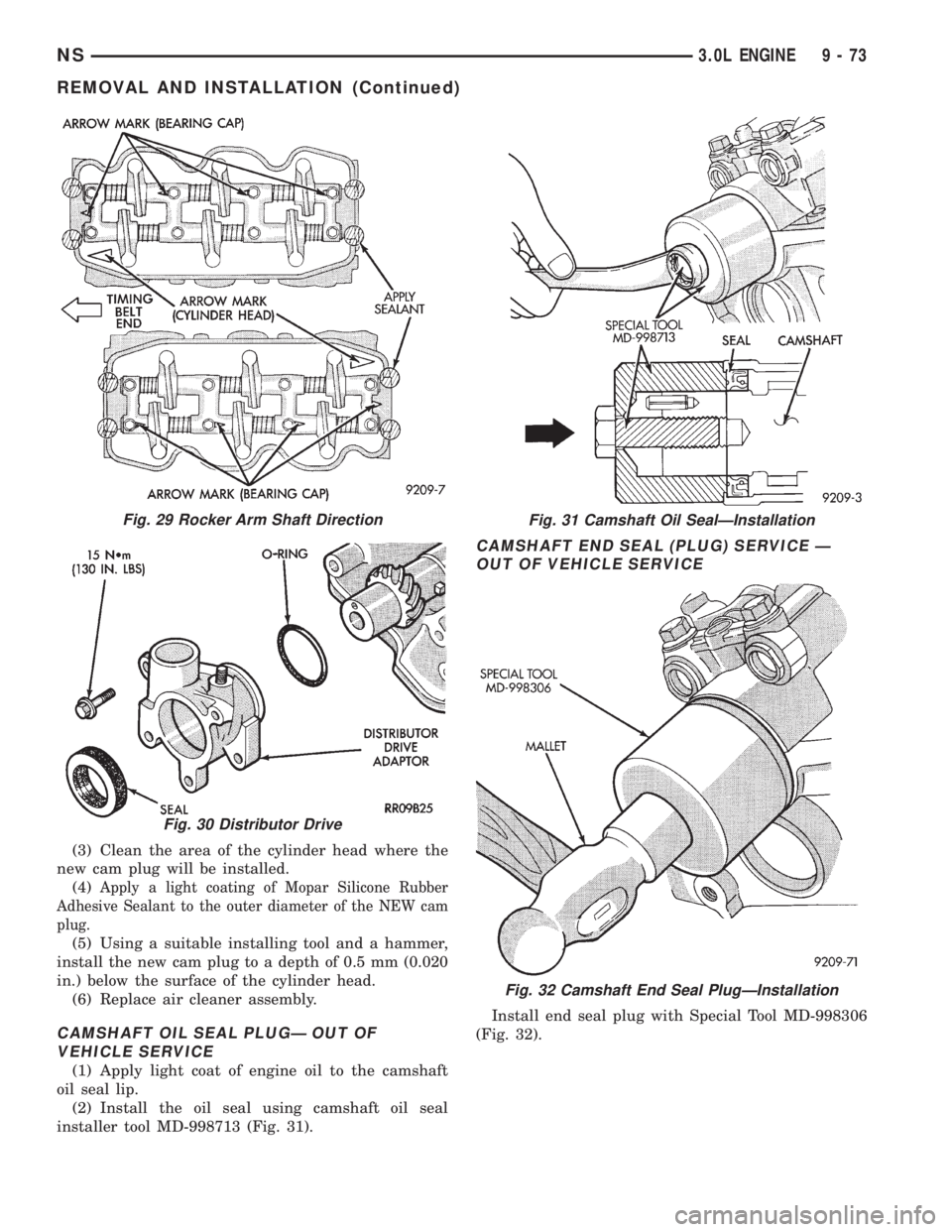
(3) Clean the area of the cylinder head where the
new cam plug will be installed.
(4)
Apply a light coating of Mopar Silicone Rubber
Adhesive Sealant to the outer diameter of the NEW cam
plug.
(5) Using a suitable installing tool and a hammer,
install the new cam plug to a depth of 0.5 mm (0.020
in.) below the surface of the cylinder head.
(6) Replace air cleaner assembly.
CAMSHAFT OIL SEAL PLUGÐ OUT OF
VEHICLE SERVICE
(1) Apply light coat of engine oil to the camshaft
oil seal lip.
(2) Install the oil seal using camshaft oil seal
installer tool MD-998713 (Fig. 31).
CAMSHAFT END SEAL (PLUG) SERVICE Ð
OUT OF VEHICLE SERVICE
Install end seal plug with Special Tool MD-998306
(Fig. 32).
Fig. 29 Rocker Arm Shaft Direction
Fig. 30 Distributor Drive
Fig. 31 Camshaft Oil SealÐInstallation
Fig. 32 Camshaft End Seal PlugÐInstallation
NS3.0L ENGINE 9 - 73
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1133 of 1938
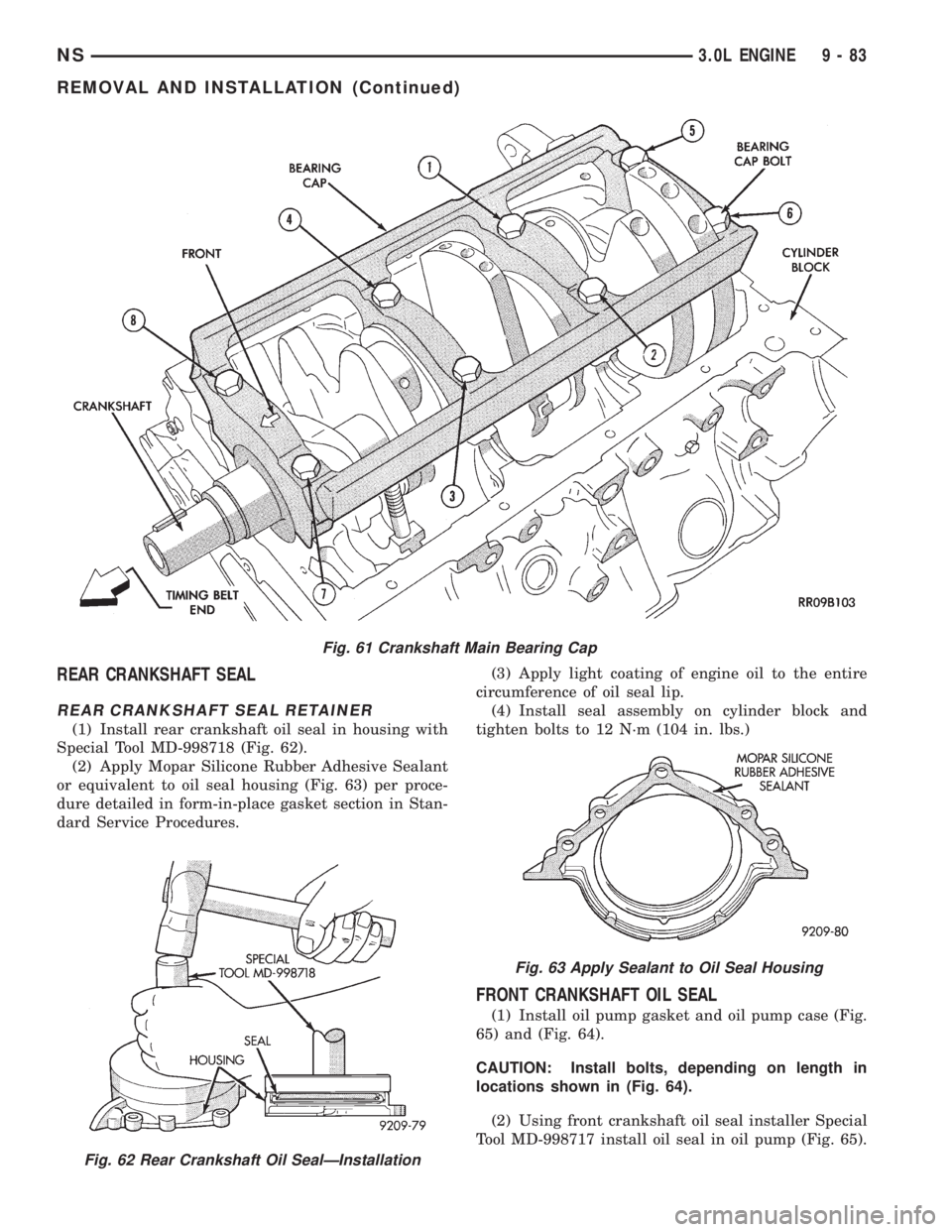
REAR CRANKSHAFT SEAL
REAR CRANKSHAFT SEAL RETAINER
(1) Install rear crankshaft oil seal in housing with
Special Tool MD-998718 (Fig. 62).
(2) Apply Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant
or equivalent to oil seal housing (Fig. 63) per proce-
dure detailed in form-in-place gasket section in Stan-
dard Service Procedures.(3) Apply light coating of engine oil to the entire
circumference of oil seal lip.
(4) Install seal assembly on cylinder block and
tighten bolts to 12 N´m (104 in. lbs.)
FRONT CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL
(1) Install oil pump gasket and oil pump case (Fig.
65) and (Fig. 64).
CAUTION: Install bolts, depending on length in
locations shown in (Fig. 64).
(2) Using front crankshaft oil seal installer Special
Tool MD-998717 install oil seal in oil pump (Fig. 65).
Fig. 62 Rear Crankshaft Oil SealÐInstallation
Fig. 61 Crankshaft Main Bearing Cap
Fig. 63 Apply Sealant to Oil Seal Housing
NS3.0L ENGINE 9 - 83
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1144 of 1938
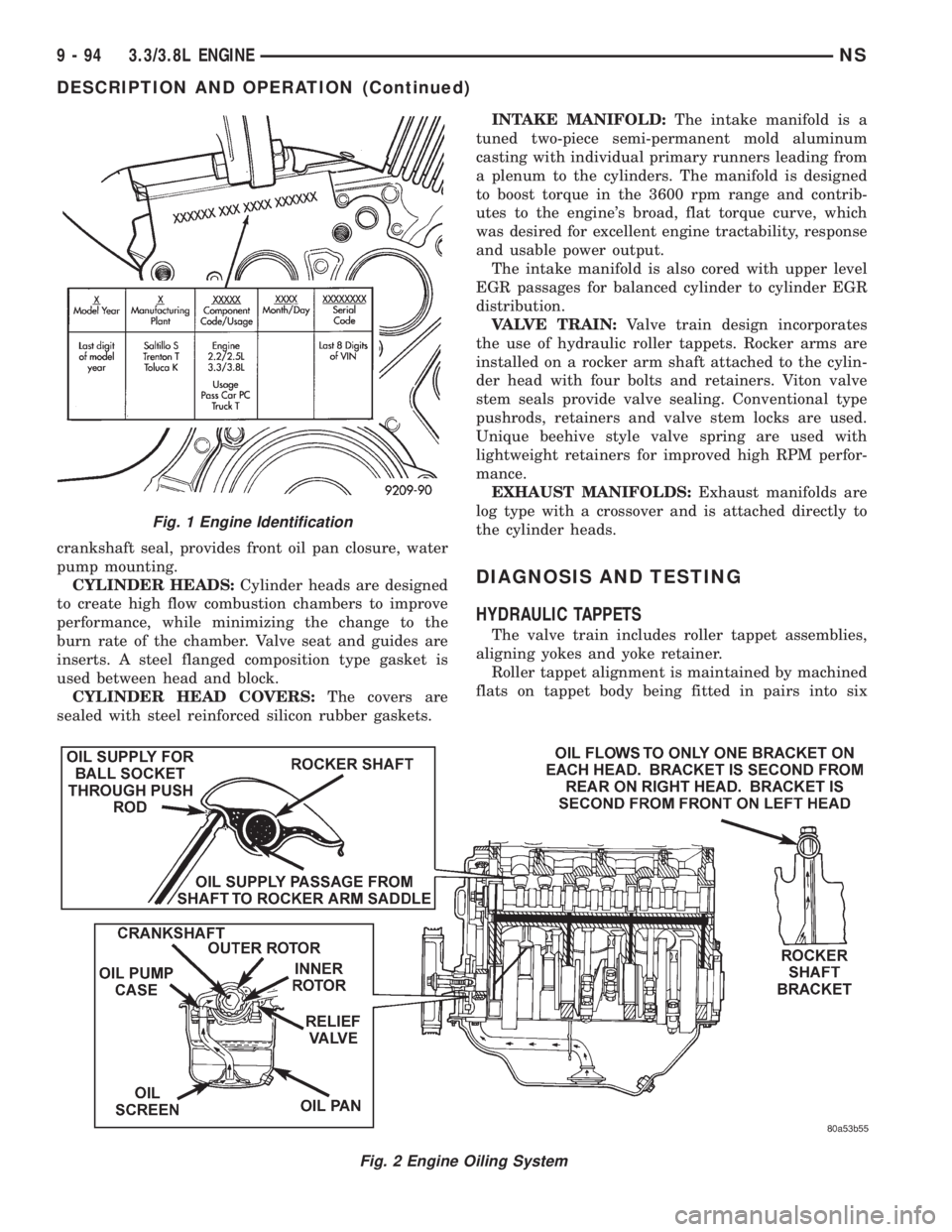
crankshaft seal, provides front oil pan closure, water
pump mounting.
CYLINDER HEADS:Cylinder heads are designed
to create high flow combustion chambers to improve
performance, while minimizing the change to the
burn rate of the chamber. Valve seat and guides are
inserts. A steel flanged composition type gasket is
used between head and block.
CYLINDER HEAD COVERS:The covers are
sealed with steel reinforced silicon rubber gaskets.INTAKE MANIFOLD:The intake manifold is a
tuned two-piece semi-permanent mold aluminum
casting with individual primary runners leading from
a plenum to the cylinders. The manifold is designed
to boost torque in the 3600 rpm range and contrib-
utes to the engine's broad, flat torque curve, which
was desired for excellent engine tractability, response
and usable power output.
The intake manifold is also cored with upper level
EGR passages for balanced cylinder to cylinder EGR
distribution.
VALVE TRAIN:Valve train design incorporates
the use of hydraulic roller tappets. Rocker arms are
installed on a rocker arm shaft attached to the cylin-
der head with four bolts and retainers. Viton valve
stem seals provide valve sealing. Conventional type
pushrods, retainers and valve stem locks are used.
Unique beehive style valve spring are used with
lightweight retainers for improved high RPM perfor-
mance.
EXHAUST MANIFOLDS:Exhaust manifolds are
log type with a crossover and is attached directly to
the cylinder heads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS
The valve train includes roller tappet assemblies,
aligning yokes and yoke retainer.
Roller tappet alignment is maintained by machined
flats on tappet body being fitted in pairs into six
Fig. 2 Engine Oiling System
Fig. 1 Engine Identification
9 - 94 3.3/3.8L ENGINENS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1146 of 1938

NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy tappets. If such is
the case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in the
tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
Valve tappet noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by exces-
sive leak-down around the unit plunger which will
necessitate replacing the tappet, or by the plunger
partially sticking in the tappet body cylinder. A heavy
click is caused either by a tappet check valve not
seating, or by foreign particles becoming wedged
between the plunger and the tappet body causing the
plunger to stick in the down position. This heavy
click will be accompanied by excessive clearance
between the valve stem and rocker arm as valve
closes. In either case, tappet assembly should be
removed for inspection and cleaning.
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
Check oil pressure using gauge at oil pressure
switch location. Oil pressure should be 34.47 kPa (5
psi.) at idle or 205 to 551 kPa (30 to 80 psi.) at 3000
RPM.
(1) Remove pressure sending unit and install oil
pressure gauge (Fig. 5).
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, do not run
engine at 3000 RPM.
(2) Warm engine at high idle until thermostat
opens.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
VALVE TIMING
(1) Remove front cylinder head cover and all 6
spark plugs.
(2) Rotate engine until the #2 piston is at TDC of
the compression stroke.
(3) Install a degree wheel on the crankshaft pulley.
(4) With proper adaptor, install a dial indicator
into #2 spark plug hole. Using the indicator find TDC
on the compression stroke.
(5) Position the degree wheel to zero.
(6) Remove dial indicator from spark plug hole.
(7) Place a 5.08 mm (0.200 in.) spacer between the
valve stem tip of #2 intake valve and rocker arm pad.
Allow tappet to bleed down to give a solid tappet
effect.
(8) Install a dial indicator so plunger contacts the
#2 intake valve spring retainer as nearly perpendic-
ular as possible. Zero the indicator.
(9) Rotate the engine clockwise until the intake
valve has lifted .254 mm (0.010 in.).
CAUTION: Do not turn crankshaft any further
clockwise as intake valve might bottom and result
in serious damage.
(10) Degree wheel should read 6 degrees BTDC to
6 degrees ATDC.
MEASURING TIMING CHAIN FOR STRETCH
(1) Place a scale next to timing chain so that any
movement of chain may be measured.
(2) Place a torque wrench and socket on camshaft
sprocket attaching bolt and apply torque in direction
of crankshaft rotation to take up slack; 41 N´m (30 ft.
lb.) with cylinder head installed or 20 N´m (15 ft. lb.)
with cylinder heads removed.With a torque
applied to the camshaft sprocket bolt, crank-
shaft should not be permitted to move. It may
be necessary to block crankshaft to prevent
rotation.
(3) Holding a scale even, with dimension reading
as shown (Fig. 6), along edge of chain links. Apply
torque in the reverse direction to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.)
with cylinder heads installed, or 20 N´m (15 ft. lbs.)
with cylinder heads removed. Check amount of chain
movement.
(4) Install a new timing chain, if its movement
exceeds 3.175 mm (1/8 inch).
(5) If chain is not satisfactory, refer to Timing
Chain Removal and Installation in this section.
Fig. 5 Checking Oil Pump Pressure
9 - 96 3.3/3.8L ENGINENS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)