1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER tow
[x] Cancel search: towPage 1181 of 1938

SPLASH LUBRICATION
Oil returning to the pan from pressurized compo-
nents supplies lubrication to the valve stems. Cylin-
der bores and wrist pins are splash lubricated from
directed slots on the connecting rod thrust collars.
ENGINE COMPONENTS
CYLINDER BLOCK AND BEDPLATE ASSEM-
B LY:A partial open deck is used for cooling and
weight reduction with water pump molded into the
block. Nominal wall thickness is 4 mm. The bedplate
incorporates main bearing caps. Rear seal retainer is
integral with the block.
CRANKSHAFT:A nodular cast iron crankshaft is
used. The engine has 5 main bearings, with number
3 flanged to control thrust. The 52 mm diameter
main and 48 mm diameter crank pin journals (all)
have undercut fillet radiuses that are deep rolled for
added strength. To optimize bearing loading 8 coun-
terweights are used. Hydrodynamic seals provide end
sealing, where the crankshaft exits the block.
Anaerobic gasket material is used for parting line
sealing. A sintered iron timing belt sprocket is
mounted on the crankshaft nose. This sprocket trans-
mits crankshaft movement, via timing belt to the
camshaft sprocket providing timed valve actuation.
PISTONS:The SOHC EngineDOES NOThave
provision for a free wheeling valve train. Non free
wheeling valve train means, in the event of a broken
timing belt Pistons will contact the Valves. All
engines use pressed-in piston pins to attach forged
powdered metal connecting rods. The connecting rods
are a cracked cap design and are not repairable. Hexhead cap screw are used to provide alignment and
durability in the assembly. Pistons And Connecting
rods are serviced as an assembly.
PISTON RINGS:The piston rings include a
molybdenum faced top ring for reliable compression
sealing and a taper faced intermediate ring for addi-
tional cylinder pressure control. Oil Control Ring
Package consist of 2 steel rails and a expander
spacer.
CYLINDER HEADÐSOHC:It features a Single
Over Head Camshaft, four-valves per cylinder cross
flow design. The valves are arranged in two inline
banks, with the two intake per cylinder facing
toward the radiator. The exhaust valves facing
toward the dash panel. Rocker arm shafts mount
directly to the cylinder head. It incorporates powder
metal valve guides and seats. The hollow rocker arm
shafts supplies oil to the hydraulic lash adjusters,
camshaft and valve mechanisms.
CAMSHAFTÐSOHC:The nodular iron camshaft
has five bearing journals and 3 cam lobes per cylin-
der. Provision for cam position sensor on the cam at
the rear of cylinder head which also acts as thrust
plate. A hydrodynamic oil seal is used for oil control
at the front of the camshaft.
VALVESÐSOHC:Four valves per cylinder are
actuated by roller rocker arms/hydraulic lash adjust-
ers assemblies which pivot on rocker arm shafts. All
valves have 6 mm diameter chrome plated valve
stems. The valve train has 33 mm (1.299 inch) diam-
eter intake valves and 28 mm (1.10 inch) diameter
exhaust valves. Viton rubber valve stem seals are
integral with spring seats. Valve springs, spring
retainers, and locks are conventional design.
INTAKE MANIFOLD:The intake manifold is a
molded plastic composition, attached to the cylinder
head with ten fasteners. This long branch design
enhances low and mid-range torque.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD:The exhaust manifold is
made of nodular cast iron for strength and high tem-
peratures. Exhaust gasses exit through a machined,
articulated joint connection to the exhaust pipe.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure switch and install gauge
assembly C-3292 with adaptor.
(2) Run engine until thermostat opens.
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, Do Not per-
form the 3000 RPM test in the next step.
(3) Oil Pressure:Curb Idle25 kPa (4 psi) mini-
mum3000 RPM170-550 kPa (25-80 psi).
Fig. 2 Engine Lubrication SystemÐ SOHC
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1187 of 1938

NOTE: Inspect the rocker arm for scoring, wear on
the roller or damage to the rocker arm (Fig. 16)
Replace if necessary. Check the location where the
rocker arms mount to the shafts for wear or dam-
age. Replace if damaged or worn. The rocker arm
shaft is hollow and is used as a lubrication oil duct.
Check oil holes for clogging with small wire, clean
as required. Lubricate the rocker arms and spacers.
Install onto shafts in their original position (Fig. 15).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Set crankshaft to 3 notches before TDC
before installing rocker arm shafts. Refer to Timing
Belt System and Camshaft Seal Service of this sec-
tion for procedure.
(1) Install rocker arm/hydraulic lash adjuster
assembly making sure that adjusters are at leastpartially full of oil. This is indicated by little or no
plunger travel when the lash adjuster is depressed. If
there is excessive plunger travel. Place the rocker
arm assembly into clean engine oil and pump the
plunger until the lash adjuster travel is taken up. If
travel is not reduced, replace the assembly. Hydraulic
lash adjuster and rocker arm are serviced as an
assembly.
(2) Install rocker arm and shaft assemblies with
NOTCH in the rocker arm shafts pointing up and
toward the timing belt side of the engine (Fig. 17).
Install the retainers in their original positions on the
exhaust and intake shafts (Fig. 15).
CAUTION: When installing the intake rocker arm
shaft assembly be sure that the plastic spacers do
not interfere with the spark plug tubes. If the spac-
ers do interfere rotate until they are at the proper
angle. To avoid damaging the spark plug tubes, do
not attempt rotating the spacers by forcing down
the shaft assembly.
(3) Tighten bolts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.) in
sequence shown in (Fig. 18).
Fig. 15 Rocker Arm Shaft Assemblies
Fig. 16 Rocker Arm Assemblies
Fig. 17 Rocker Arm Shaft Notches
Fig. 18 Rocker Arm Shaft Tightening Sequence
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 9
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1197 of 1938

(4) Using Tool 6771 to remove front crankshaft oil
seal (Fig. 55). Do not damage the seal contact area
on the crankshaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install new seal by using Tool 6780±1 (Fig. 56).(2) Place seal into opening with seal spring
towards the inside of engine. Install seal until flush
with cover.
(3) Install crankshaft sprocket (Fig. 57). Using
Special Tool 6792.
NOTE: Make sure the word ªfrontº on the sprocket
is facing you.
(4) Install timing belt and covers. Refer to Timing
Belt System in this section for installation.
(5) Install crankshaft damper (Fig. 58). Use thrust
bearing/washer and 12M-1.75 x 150 mm bolt from
Fig. 47 Crankshaft Sprocket Timing
Fig. 48 Camshaft Timing Mark
Fig. 49 Adjusting Crankshaft Sprocket for Timing
Belt Installation
Fig. 50 Crankshaft and Camshaft Timing
Fig. 51 Crankshaft DamperÐInstallation
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 19
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1199 of 1938
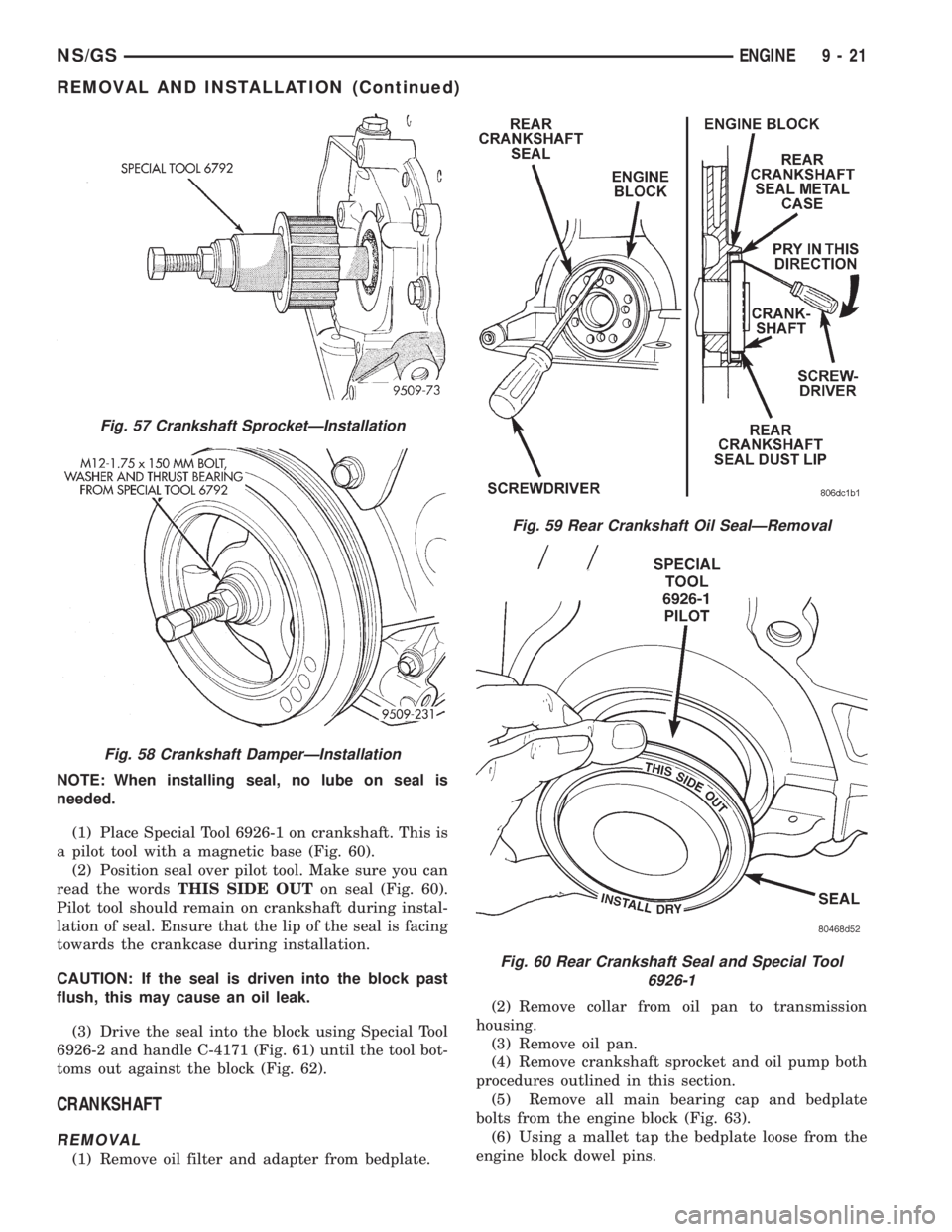
NOTE: When installing seal, no lube on seal is
needed.
(1) Place Special Tool 6926-1 on crankshaft. This is
a pilot tool with a magnetic base (Fig. 60).
(2) Position seal over pilot tool. Make sure you can
read the wordsTHIS SIDE OUTon seal (Fig. 60).
Pilot tool should remain on crankshaft during instal-
lation of seal. Ensure that the lip of the seal is facing
towards the crankcase during installation.
CAUTION: If the seal is driven into the block past
flush, this may cause an oil leak.
(3) Drive the seal into the block using Special Tool
6926-2 and handle C-4171 (Fig. 61) until the tool bot-
toms out against the block (Fig. 62).
CRANKSHAFT
REMOVAL
(1) Remove oil filter and adapter from bedplate.(2) Remove collar from oil pan to transmission
housing.
(3) Remove oil pan.
(4) Remove crankshaft sprocket and oil pump both
procedures outlined in this section.
(5) Remove all main bearing cap and bedplate
bolts from the engine block (Fig. 63).
(6) Using a mallet tap the bedplate loose from the
engine block dowel pins.
Fig. 57 Crankshaft SprocketÐInstallation
Fig. 58 Crankshaft DamperÐInstallation
Fig. 59 Rear Crankshaft Oil SealÐRemoval
Fig. 60 Rear Crankshaft Seal and Special Tool
6926-1
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 21
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1203 of 1938

filter on until gasket contacts base. Tighten to 21
N´m (15 ft. lbs.).
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove Timing Belt. Refer to Timing Belt Sys-
tem, in this section.
(3) Remove Oil Pan. Refer to Oil Pan Removal in
this section.
(4) Remove Crankshaft Sprocket using Special Tool
6793 and insert C-4685-C2 (Fig. 70).
(5) Remove oil pick-up tube.
(6) Remove oil pump (Fig. 71) and front crankshaft
seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Make sure all surfaces are clean and free of oil
and dirt.(2) Apply MopartGasket Maker to oil pump as
shown in (Fig. 72). Install o±ring into oil pump body
discharge passage.
(3) Prime oil pump before installation.
(4) Align oil pump rotor flats with flats on crank-
shaft as you install the oil pump to the block.
NOTE: Front crankshaft seal MUST be out of pump
to align, or damage may result.
(5) Torque all oil pump attaching bolts to 28 N´m
(250 in. lbs.)
(6) Install new front crankshaft seal using Special
Tool 6780 (Fig. 73).
(7) Install crankshaft sprocket, using Special Tool
6792 (Fig. 74).
(8) Install oil pump pick-up tube and oil pan.
(9) Install Timing Belt. Refer to procedure outlined
in this section.
(10) Connect negative cable to battery.
PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD
REMOVAL
(1) Remove top ridge of cylinder bores with a reli-
able ridge reamer before removing pistons from cyl-
inder block.Be sure to keep tops of pistons
covered during this operation. Mark piston with
matching cylinder number (Fig. 75).
(2) Remove oil pan. Scribe the cylinder number on
the side of the rod and cap (Fig. 76) for identification.
(3) Pistons will have a stamping in the approxi-
mate location shown in (Fig. 75). These stamps will
be either a directional arrow or a weight identifica-
tion for the assembly. L is for light and H is for
heavy. These assemblies should all be the same
weight class. Service piston assemblies are marked
with a S and can be used with either L or H produc-
tion assemblies. The weight designation stamps
should face toward the timing belt side of the engine.
(4) Pistons and connecting rods must be removed
from top of cylinder block. Rotate crankshaft so that
each connecting rod is centered in cylinder bore.
(5) Remove connecting rod cap boltsDo not use
old bolts if reinstalling connecting rod.Push
each piston and rod assembly out of cylinder bore.
NOTE: Be careful not to nick crankshaft journals.
(6) After removal, install bearing cap on the mat-
ing rod.
(7) Piston and Rods are serviced as an assembly.
PISTON RINGÐREMOVAL
(1) ID mark on face of upper and intermediate pis-
ton rings must point toward piston crown.
Fig. 69 Engine Oil Filter
Fig. 70 Crankshaft SprocketÐRemoval
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 25
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1206 of 1938

on the thrust direction. Staggering ring gap is impor-
tant for oil control.
PISTON AND ROD ÐINSTALLATION
(1) Before installing pistons and connecting rod
assemblies into the bore, be sure that compression
ring gaps are staggered so that neither is in line with
oil ring rail gap.
(2) Before installing the ring compressor, make
sure the oil ring expander ends are butted and the
rail gaps located as shown in (Fig. 80).
(3) Immerse the piston head and rings in clean
engine oil, slide the ring compressor, over the piston
(Fig. 81).Be sure position of rings does not
change during this operation.
(4) The weight stamp designation L or H will be in
the front half of the piston should face toward the
front of the engine for SOHC engine. The arrow
should face toward the front of the engine for DOHC
engine (Fig. 75).
(5) Rotate crankshaft so that the connecting rod
journal is on the center of the cylinder bore. Insertrod and piston assembly into cylinder bore and guide
rod over the crankshaft journal.
(6) Tap the piston down in cylinder bore, using a
hammer handle. At the same time, guide connecting
rod into position on connecting rod journal.
(7) Install rod caps. InstallNewbolts and tighten
to 27 N´m (20 ft.lb.) Plus 1/4 turn.
VIBRATION DAMPER
NOTE: If a gap is found in the crankshaft damper,
in the area where the Poly-V Generator belt rides
this is normal and is acceptable (Fig. 82).
REMOVAL
(1) Remove accessory drive belts. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling System for procedure outlined in that sec-
tion.
(2) Remove crankshaft damper bolt. Remove
damper using the large side of Special Tool 1026 and
insert 6827±A (Fig. 83).
Fig. 80 Piston Ring End Gap Position
Fig. 81 Installing Piston
Fig. 82 Weld Gap
Fig. 83 Crankshaft DamperÐRemoval
9 - 28 ENGINENS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1228 of 1938

VALVE STAND DOWN
Valve stand down is to maintain the adequate com-
pression ratio.
(1) Invert cylinder head.
(2) Fit each valve to its respective valve guide.
(3) Using a straight edge and feeler gauge (Fig. 9),
check valve head stand down: Inlet valve head stand
down .80 to 1.2 mm (.031 to .047 in.) and exhaust
valve stand down .79 to 1.19 mm (.031 to .047 in).
(4) If valve head stand down is not in accordance
with above, discard original valves, check stand down
with new valves and recut valve seat inserts to
obtain correct stand down.
VALVE GUIDE HEIGHT
(1) Valve Guides height requirement.
(2) Measurement A (Fig. 10): 13.50 - 14.00 mm.
VALVE STEM-TO-GUIDE CLEARANCE
MEASUREMENT
(1) Measure and record internal diameter of valve
guides. Valve guide internal diameter is 8.0 to 8.015
mm (.3149 to .3155 in.).
(2) Measure valve stems and record diameters.
Intake valve stem diameter 7.94 to 7.96 mm (.3125 to
.3133 in). Exhaust valve stem diameter 7.92 to 7.94
mm (.3118 to .31215 in).(3) Subtract diameter of valve stem from internal
diameter of its respective valve guide to obtain valve
stem clearance in valve guide. Clearance of inlet
valve stem in valve guide is .040 to .075 mm (.0015
to .0029 in). Clearance of exhaust valve stem in valve
guide is .060 to .095 mm (.0023 to .0037 in).
(4) If valve stem clearance in valve guide exceeds
tolerances, new valve guides must be installed.
FITTING PISTON RING
(1) Wipe cylinder bore clean. Insert ring and push
down with piston to ensure it is square in bore. The
ring gap measurement must be made with the ring
positioning at least 12 mm (0.50 in.) from bottom of
cylinder bore (Fig. 11). Check gap with feeler gauge.
Top compression ring gap .25 to .50mm (.0098 to
.0196 in.). Second compression ring gap .25 to .35mm
(.0098 to .0137 in.). Oil control ring gap .25 to .58mm
(.0098 to .0228 in.).
(2) If ring gaps exceed dimension given, new rings
or cylinder liners must be fitted. Keep piston rings in
piston sets.
(3) Check piston ring to groove clearance (Fig. 12).
Top compression ring gap .08 to .130mm (.0031 to
.0051 in.). Second compression ring gap .070 to
.102mm (.0027 to .0040 in.). Oil control ring gap .040
to .072mm (.0015 to .0028 in.).
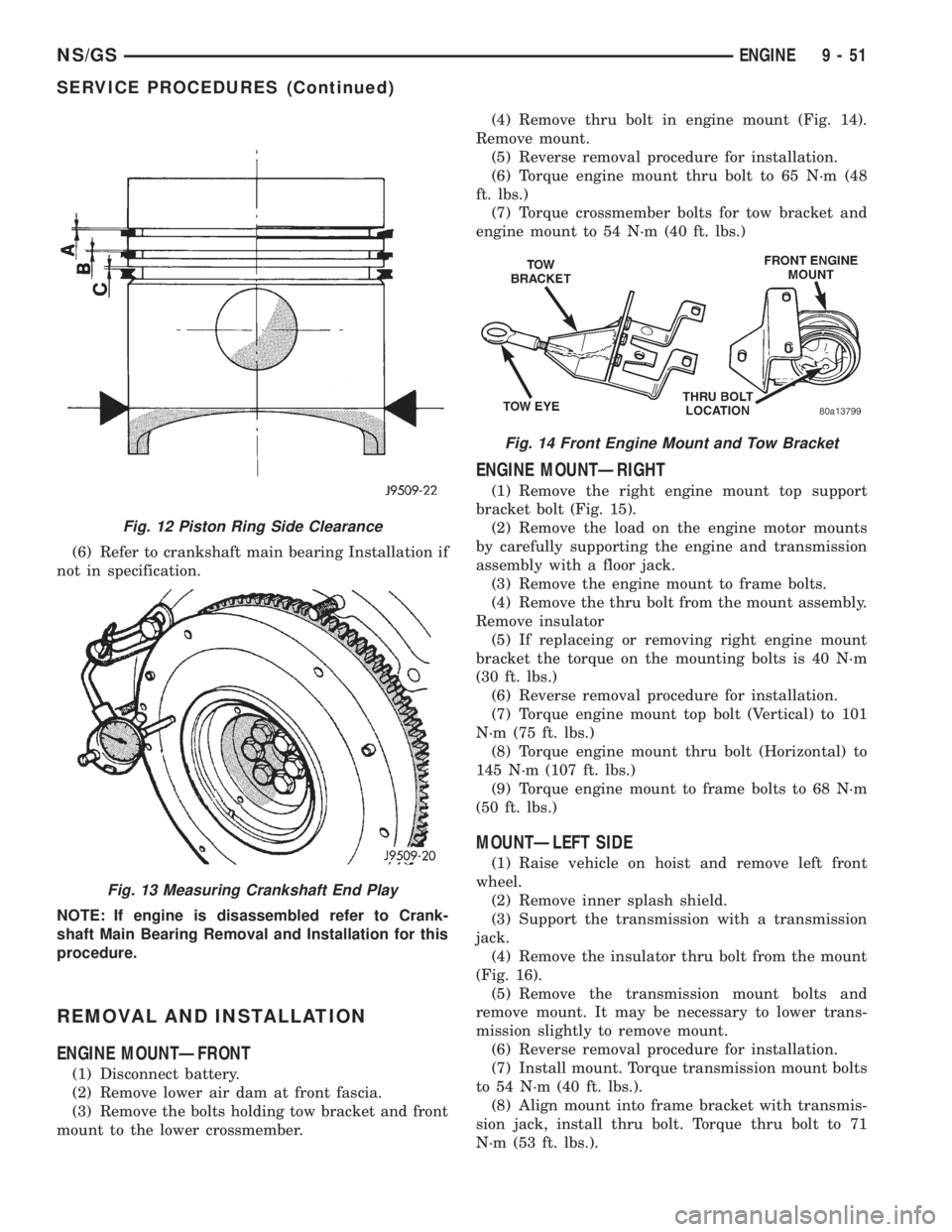
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
(1) Attach dial indicator to engine block (Fig. 13).
(2) Move crankshaft toward front of engine and
zero indicator.
(3) Move crankshaft toward the rear of engine and
record measurement.
(4) Subtract specified crankshaft end float from
figure obtained. Crankshaft end float 0.08 to
0.21mm.
(5) Select thrust washer which will give correct
end float.
Fig. 9 Checking Valve Stand Down
Fig. 10 Valve Guide Height
Fig. 11 Ring Gap Measurement
9 - 50 ENGINENS/GS
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1229 of 1938
(6) Refer to crankshaft main bearing Installation if
not in specification.
NOTE: If engine is disassembled refer to Crank-
shaft Main Bearing Removal and Installation for this
procedure.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
ENGINE MOUNTÐFRONT
(1) Disconnect battery.
(2) Remove lower air dam at front fascia.
(3) Remove the bolts holding tow bracket and front
mount to the lower crossmember.(4) Remove thru bolt in engine mount (Fig. 14).
Remove mount.
(5) Reverse removal procedure for installation.
(6) Torque engine mount thru bolt to 65 N´m (48
ft. lbs.)
(7) Torque crossmember bolts for tow bracket and
engine mount to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
ENGINE MOUNTÐRIGHT
(1) Remove the right engine mount top support
bracket bolt (Fig. 15).
(2) Remove the load on the engine motor mounts
by carefully supporting the engine and transmission
assembly with a floor jack.
(3) Remove the engine mount to frame bolts.
(4) Remove the thru bolt from the mount assembly.
Remove insulator
(5) If replaceing or removing right engine mount
bracket the torque on the mounting bolts is 40 N´m
(30 ft. lbs.)
(6) Reverse removal procedure for installation.
(7) Torque engine mount top bolt (Vertical) to 101
N´m (75 ft. lbs.)
(8) Torque engine mount thru bolt (Horizontal) to
145 N´m (107 ft. lbs.)
(9) Torque engine mount to frame bolts to 68 N´m
(50 ft. lbs.)
MOUNTÐLEFT SIDE
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist and remove left front
wheel.
(2) Remove inner splash shield.
(3) Support the transmission with a transmission
jack.
(4) Remove the insulator thru bolt from the mount
(Fig. 16).
(5) Remove the transmission mount bolts and
remove mount. It may be necessary to lower trans-
mission slightly to remove mount.
(6) Reverse removal procedure for installation.
(7) Install mount. Torque transmission mount bolts
to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(8) Align mount into frame bracket with transmis-
sion jack, install thru bolt. Torque thru bolt to 71
N´m (53 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 12 Piston Ring Side Clearance
Fig. 13 Measuring Crankshaft End Play
Fig. 14 Front Engine Mount and Tow Bracket
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 51
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)