1996 CHRYSLER VOYAGER engine coolant
[x] Cancel search: engine coolantPage 1379 of 1938

the intake manifold. Refer to Group 11, Exhaust Sys-
tem and Intake Manifold for information.
(21) Be sure that the vacuum hoses to the vacuum
pump are connected and not leaking. The pump is
located on the front of engine (internal) and is driven
from the crankshaft gear and chain (Fig. 20). Discon-
nect the hose and check for minimum vacuum from
the pump. Refer to Group 5, Brake System for spec-
ifications and procedures.(22) Be sure that the accessory drive belt is not
damaged or slipping.
(23) Verify there is a good connection at the engine
speed sensor. Refer to the Fuel Injection System in
this section for location of the engine speed sensor
location.
(24) Verify there is a good connection at the Mass
Air Flow Sensor, which is a part of the air intake
assembly.
AIR IN FUEL SYSTEM
Air will enter the fuel system whenever the fuel
supply lines, fuel filter/water separator, fuel filter
bowl, injection pump, high±pressure lines or injectors
are removed or disconnected. Air will also enter the
fuel system whenever the fuel tank has been run
empty.
Air trapped in the fuel system can result in hard
starting, a rough running engine, engine misfire, low
power, excessive smoke and fuel knock. After service
is performed, air must be bled from the system
before starting the engine.
Inspect the fuel system from the fuel tank to the
injectors for loose connections. Leaking fuel is an
indicator of loose connections or defective seals. Air
can also enter the fuel system between the fuel tank
and the injection pump. Inspect the fuel tank and
fuel lines for damage that might allow air into the
system.
For air bleeding, refer to Air Bleed Procedure in
the Service Procedures section of this group.
Fig. 18 Vehicle Speed SensorÐTypical
Fig. 19 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Location
Fig. 20 Vacuum Pump at Front of Engine
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1388 of 1938

(8) Disconnect the main engine wiring harness
from the glow plugs.
(9) Disconnect the four high±pressure fuel lines
from the fuel injection pump. Also disconnect fuel
lines at the fuel injectors. For procedures, refer to
High±Pressure Fuel Lines in this group. Place a rag
beneath the fittings to catch excess fuel.
(10) Remove plug from timing gear cover.
(11) The ªTop Dead Centerº (TDC) compression fir-
ing stroke must be determined as follows:
(a) Remove the valve cover, refer to Group 9,
Valve Cover Removal/Installation.
(b) Remove the right front tire and splash
shield. Using a socket attached to the end of crank-
shaft, rotate the engine (counterÐclockwise as
viewed from front).
(c) Rotate the engine until cylinder #4 rockers
are in between movement.
(d) Remove rocker arm assembly.
(e) Remove valve spring and keepers.CAU-
TION: When the piston is at TDC there is only
2 mm (.080 thousand) clearance between the
valve and piston.
(f) Let the valve set on top of piston. Install a
dial indicator to the top of the valve stem.
(g) Rotate engine back and forth to find the TDC
position with the indicator on the valve stem. Mark
the damper and timing cover for TDC.
NOTE: On later model 1997 engines, a hole in the
bottom of the clutch housing can be lined up with a
hole in the flywheel, allowing the engine to be held
at TDC with a special alignment tool, part # VM1035.(12) Remove injection pump drive gear nut (Fig.
41) and washer.CAUTION: Be very careful not to
drop the washer into the timing gear cover.
(13) A special 3±piece gear removal tool set
VM.1003 (Fig. 42) must be used to remove the injec-
tion pump drive gear from the pump shaft.
(a) Thread the adapter (Fig. 43) into the timing
cover.
(b) Thread the gear puller into the injection
pump drive gear (Fig. 43). This tool is also used to
hold the gear in synchronization during pump
removal.
(c) Remove the three injection pump±to±gear
cover mounting nuts (Fig. 44).CAUTION: This
step must be done to prevent breakage of the
Fig. 40 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
Fig. 41 Removing Pump Drive Gear Nut
Fig. 42 Pump Gear Tools
14 - 20 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1390 of 1938

(14) Gauge reading should be at 0.60 mm. If not,
the pump must be rotated for adjustment:
(a) Loosen the three injection pump mounting
nuts at the mounting flanges. These flanges are
equipped with slotted holes. The slotted holes are
used to rotate and position the injection pump for
fuel timing. Loosen the three nuts just enough to
rotate the pump.
(b) Rotate the pumpclockwise(as viewed from
front) until .60 mm is indicated on the dial indica-
tor gauge.
(c) Tighten the three pump mounting nuts to 30
N´m (22 ft. lbs.) torque.
(d) Recheck the dial indicator after tightening
the pump mounting nuts. Gauge should still be
reading 0.60 mm. Loosen pump mounting nuts and
readjust if necessary.
(15) Remove dial indicator and adapter tools.
(16) Install access plug and washer to rear of
injection pump.
(17) Install plug at timing gear cover.
(18) Remove dial indicator from valve stem.
(19) Install valve spring and keepers.
(20) Install rocker arm assembly and tighten nuts.
(21) Install and connect the four high±pressure
fuel lines to the fuel injection pump. Also connect
fuel lines at the fuel injectors. For procedures, refer
to High±Pressure Fuel Lines in this group.
(22) Install electrical connector at engine coolant
temperature sensor.
(23) Connect electrical connector at fuel shutdown
solenoid.(24) Connect the main engine wiring harness to
the glow plugs.
(25) Connect the fuel timing solenoid pigtail har-
ness to the engine wiring harness.
(26) Connect the overflow valve/banjo fitting (fuel
return line assembly). Replace copper gaskets before
installing.
(27) Connect the rubber fuel return and supply
hoses to metal lines at pump. Tighten hose clamps to
2 N´m (20 in. lbs.) torque.
(28) Install generator assembly.
(29) Install engine accessory drive belt. Refer to
Group 7, Cooling System for procedures.
(30) Install negative battery cable to battery.
(31) Start the engine and bring to normal operat-
ing temperature.
(32) Check for fuel leaks.
FUEL INJECTORS
Four fuel injectors are used on each engine. Of these
four, two different types are used. The fuel injector used
on cylinder number one is equipped with a fuel injector
sensor (Fig. 47). The other three fuel injectors are iden-
tical.
Do not place the fuel injector equipped with
the fuel injector sensor into any other location
except the cylinder number one position.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Thoroughly clean the area around the injector
with compressed air.
(3) Remove the fuel drain hoses (tubes) at each
injector (Fig. 48) being serviced. Each of these hoses
is slip±fit to the fitting on injector.
(4) Remove the high±pressure fuel line at injector
being removed. Refer to High±Pressure Fuel Lines in
this group for procedures.
(5) Remove the injector using special socket tool
number VM.1012A. When removing cylinder number
Fig. 46 Installing Dial Indicator and Special Adapter
Tools
Fig. 47 Fuel Injector SensorÐNumber±1 Cylinder
14 - 22 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1400 of 1938

FUEL INJECTION SYSTEMÐ2.0L ENGINE
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTIONÐ2.0L ENGINE............ 32
MODES OF OPERATIONÐ2.0L ENGINE..... 32
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
AIR CONDITIONING (A/C) RELAYÐPCM
OUTPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE................ 35
AIR CONDITIONING PRESSURE
TRANSDUCERÐPCM INPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE......................... 33
AIR CONDITIONING SWITCH SENSEÐ
PCM INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE.............. 33
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN (ASD) SENSEÐ
PCM INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE.............. 33
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAYÐ
PCM OUTPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE............ 35
BATTERY VOLTAGEÐPCM INPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE......................... 33
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐ
PCM INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE.............. 33
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐ
PCM INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE.............. 33
DATA LINK CONNECTORÐPCM OUTPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE......................... 35
ELECTRONIC EGR TRANSDUCERÐ
PCM OUTPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE............ 35
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORÐ
PCM INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE.............. 33
FUEL INJECTORSÐPCM OUTPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE......................... 35
FUEL PUMP RELAYÐPCM OUTPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE......................... 35
GENERATOR FIELDÐPCM OUTPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE......................... 35
HEATED OXYGEN SENSORÐPCM INPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE......................... 33
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTORÐPCM OUTPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE......................... 35
IGNITION COILÐPCM OUTPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE......................... 36KNOCK SENSORÐPCM INPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE......................... 34
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR (CHECK ENGINE)
LAMPÐPCM OUTPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE...... 36
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE
(MAP SENSOR)ÐPCM INPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE......................... 34
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULEÐ
2.0L ENGINE......................... 33
RADIATOR FAN CONTROL MODULEÐ
PCM OUTPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE............ 36
SPEED CONTROL SOLENOIDSÐ
PCM OUTPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE............ 36
SPEED CONTROLÐPCM INPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE......................... 34
STARTER RELAYÐPCM OUTPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE......................... 35
SYSTEM DIAGNOSISÐ2.0L ENGINE........ 33
TACHOMETERÐPCM OUTPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE......................... 36
THROTTLE BODYÐ2.0L ENGINE.......... 36
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR/ IDLE AIR
CONTROL MOTORÐPCM INPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE......................... 35
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ASD AND FUEL PUMP RELAYSÐ
2.0L ENGINE......................... 39
CAMSHAFT AND CRANKSHAFT
POSITION SENSOR................... 40
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR............................ 40
KNOCK SENSORÐ2.0L ENGINE........... 40
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE
(MAP) SENSORÐ2.0L ENGINE........... 39
THROTTLE BODY MINIMUM AIR FLOW..... 41
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR........... 40
VISUAL INSPECTIONÐSOHC............. 36
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE............................. 42
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTIONÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Introduction for 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L
engines under General Information in the Fuel Injec-
tion System section of group 14 for more information.
MODES OF OPERATIONÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Modes of Operation for 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L
engines under General Information in the Fuel Injec-
tion System section of group 14 for more information.
14 - 32 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
Page 1401 of 1938

DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
SYSTEM DIAGNOSISÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to System diagnosis for 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L
engines under Description and Operation in the Fuel
Injection System section of group 14 for more infor-
mation.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULEÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Powertrain Control Module for 2.4/3.0/
3.3/3.8L engines under Description and Operation in
the Fuel Injection System section of group 14 for
more information.
AIR CONDITIONING PRESSURE TRANSDUCERÐ
PCM INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Air Conditioning Pressure Transducer
for 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L engines under Description and
Operation in the Fuel Injection System section of
group 14 for more information.
AIR CONDITIONING SWITCH SENSEÐPCM
INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Air Conditioning Switch Sense for 2.4/
3.0/3.3/3.8L engines under Description and Operation
in the Fuel Injection System section of group 14 for
more information.
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN (ASD) SENSEÐPCM
INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Automatic Shutdown (ASD) Sense for
2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L engines under Description and Oper-
ation in the Fuel Injection System section of group 14
for more information.
BATTERY VOLTAGEÐPCM INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Battery Voltage for 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L
engines under Description and Operation in the Fuel
Injection System section of group 14 for more infor-
mation.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM INPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Camshaft Position Sensor for 2.4L
engine under Description and Operation in the Fuel
Injection System section of group 14 for more infor-
mation.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM
INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Crankshaft Position Sensor for 2.4L
engine under Description and Operation in the Fuel
Injection System section of group 14 for more infor-
mation.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORÐPCM
INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
The coolant temperature sensor threads into the
rear of the cylinder head, next to the camshaft posi-
tion sensor (Fig. 3). New sensors have sealant
applied to the threads.
Refer to the Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
for the 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L engines under Description and
Operation in the Fuel Injection System section of
group 14 for more information.
HEATED OXYGEN SENSORÐPCM INPUTÐ2.0L
ENGINE
Refer to the Heated Oxygen Sensor for 2.4/3.0/3.3/
3.8L engines under Description and Operation in the
Fuel Injection System section of group 14 for more
information.
Fig. 1 Camshaft Position SensorÐ2.0L Engine
Fig. 2 Crankshaft Posistion SensorÐ2.0L engine
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 33
Page 1402 of 1938
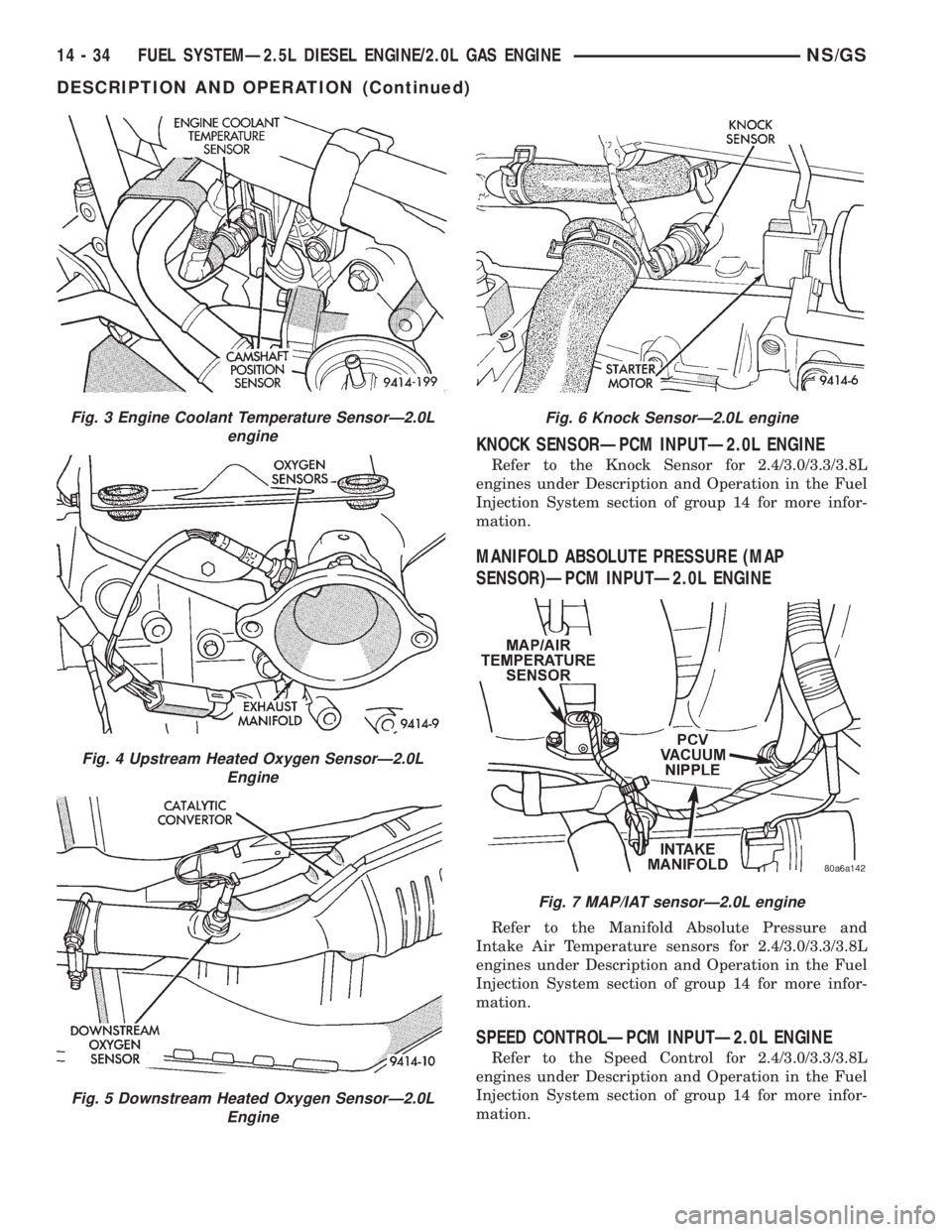
KNOCK SENSORÐPCM INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Knock Sensor for 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L
engines under Description and Operation in the Fuel
Injection System section of group 14 for more infor-
mation.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP
SENSOR)ÐPCM INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Manifold Absolute Pressure and
Intake Air Temperature sensors for 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L
engines under Description and Operation in the Fuel
Injection System section of group 14 for more infor-
mation.
SPEED CONTROLÐPCM INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Speed Control for 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L
engines under Description and Operation in the Fuel
Injection System section of group 14 for more infor-
mation.
Fig. 3 Engine Coolant Temperature SensorÐ2.0L
engine
Fig. 4 Upstream Heated Oxygen SensorÐ2.0L
Engine
Fig. 5 Downstream Heated Oxygen SensorÐ2.0L
Engine
Fig. 6 Knock SensorÐ2.0L engine
Fig. 7 MAP/IAT sensorÐ2.0L engine
14 - 34 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1405 of 1938
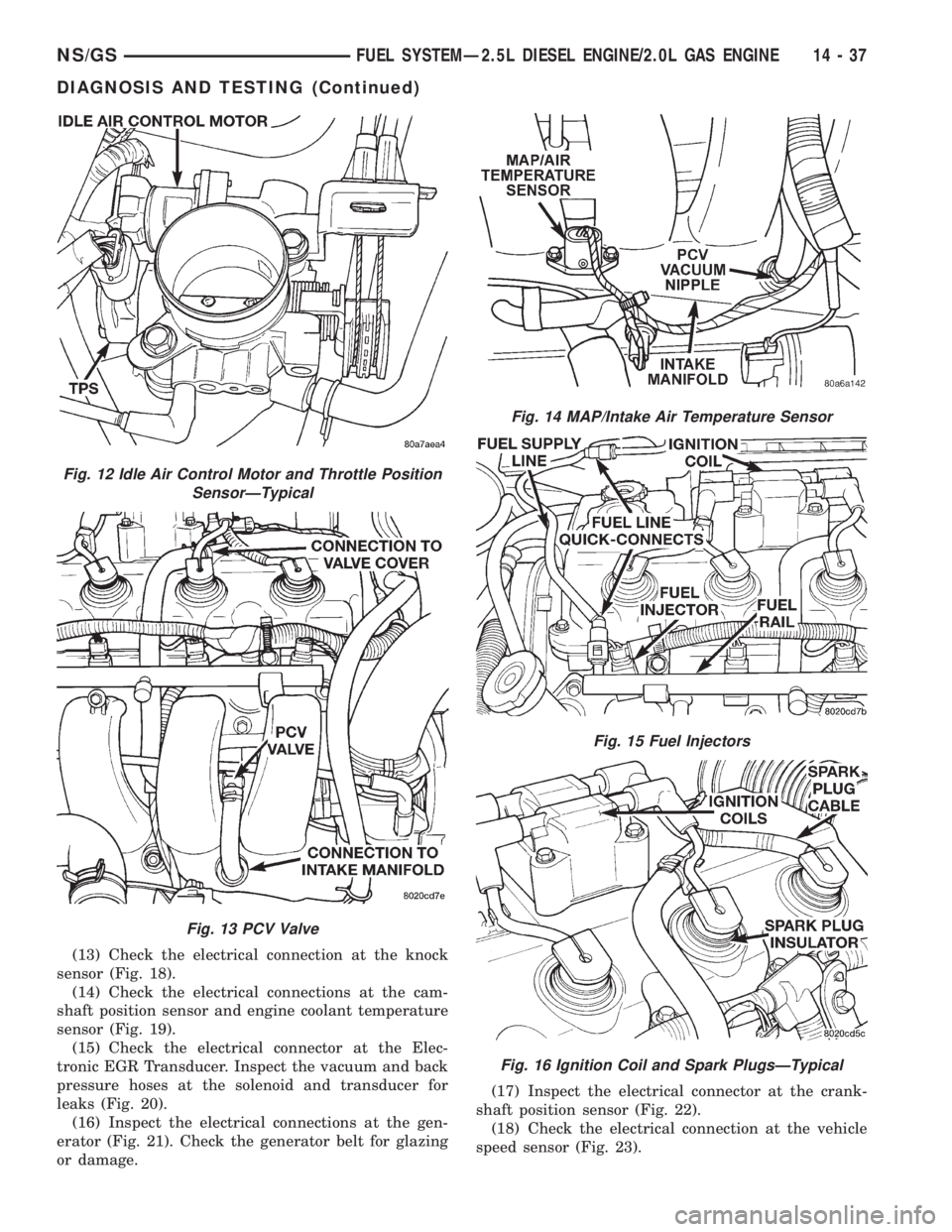
(13) Check the electrical connection at the knock
sensor (Fig. 18).
(14) Check the electrical connections at the cam-
shaft position sensor and engine coolant temperature
sensor (Fig. 19).
(15) Check the electrical connector at the Elec-
tronic EGR Transducer. Inspect the vacuum and back
pressure hoses at the solenoid and transducer for
leaks (Fig. 20).
(16) Inspect the electrical connections at the gen-
erator (Fig. 21). Check the generator belt for glazing
or damage.(17) Inspect the electrical connector at the crank-
shaft position sensor (Fig. 22).
(18) Check the electrical connection at the vehicle
speed sensor (Fig. 23).
Fig. 12 Idle Air Control Motor and Throttle Position
SensorÐTypical
Fig. 13 PCV Valve
Fig. 14 MAP/Intake Air Temperature Sensor
Fig. 15 Fuel Injectors
Fig. 16 Ignition Coil and Spark PlugsÐTypical
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 37
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1406 of 1938

(19) Check the electrical connection at the power
steering pressure switch on the power steering gear
housing (Fig. 24).
Fig. 17 Starter Motor and Ground Strap
Fig. 18 Knock Sensor
Fig. 19 Camshaft Position Sensor and Engine
Coolant Temperature Sensor
Fig. 20 Electronic EGR Transducer
Fig. 21 Generator
Fig. 22 Crankshaft Position Sensor
14 - 38 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)