1996 CHEVROLET TAHOE tire pressure
[x] Cancel search: tire pressurePage 166 of 403

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Here’s how anti-lock works. Let’s say the road is wet.
You’re driving safely. Suddenly an animal jumps out
in
front of you.
You slam on the brakes. Here’s what happens
with ABS.
A computer senses that wheels are slowing down. If one
of the wheels is about to stop rolling, the computer will
separately work the brakes at each front wheel and at the
rear wheels. The anti-lock system can change the brake pressure faster
than any driver could. The computer
is programmed to
make the most
of available tire and road conditions.
You can steer around the obstacle while braking hard.
As you brake, your computer keeps receiving updates on
wheel speed and controls braking pressure accordingly.
4-7
Page 184 of 403

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Driving in Mud, Sand, Snow or Ice
When you drive in mud, snow or sand, your wheels
won’t.get good traction.
You can’t accelerate as
quickly, turning is more difficult, and
you’ll need
longer, braking distances.
It’s best to use a low gear when you’re
in mud -- the
deeper the mud, the lower the gear. In really deep mud,
the idea is to keep your vehicle moving
so you don’t
get stuck.
When you drive
on sand, you’ll sense a change in wheel
traction. But it
will depend upon how loosely packed the
sand is. On loosely packed sand (as
on beaches or sand
dunes) your tires will tend
to sink into the sand. This has
an effect on steering, accelerating and braking.
You may
want to reduce the air pressure in your tires slightly
when’driving on sand. This will improve traction. Hard
packed snow and ice offer the worst tire traction.
On these surfaces, it’s very easy to lose control.
On wet
ice, for example, the traction is
so poor that you will
have difficulty accelerating. And if you do get moving,
poor steering and difficult braking can cause
you to slide
out
of control.
I A CAUTION:
Driving on frozen lakes, ponds or rivers can be
dangerous. Underwater springs, currents under
the ice, or sudden thaws can weaken the ice. Your
vehicle could fall through the ice and you and
your passengers could drown. Drive your vehicle
on safe surfaces only.
Page 190 of 403

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Hydroplaning
Hydroplaning is dangerous. So much water can build up
under your tires that they can actually ride on the water.
’
This can happen if the road is wet enough and you’re
going fast enough. When your vehicle is hydroplaning,
it
has little or no contact with the road.
Hydroplaning doesn’t happen often.
But it can if your
tires haven’t much tread or if the pressure in one or
more is low. It can happen if a lot of water is standing on
the road. If
you can see reflections from trees, telephone
poles or other vehicles, and raindrops “dimple” the
water’s surface, there could be hydroplaning.
Hydroplaning usually happens at higher speeds. There
just isn’t a hard and fast rule about hydroplaning. The
best advice is to slow down when it is raining.
Driving Through Deep Standing Water
NOTICE:
If you drive too quickly through deep puddles or
standing water, water can come in through your
engine’s air intake and badly damage your
. engine. Never drive through water that is slightly
lower than the underbody of your vehicle. If you
- ..
through them very slowly. can’t avoid deep puddles or standing water, drive
~
z
Some Other Rainy Weather Tips
0
0 Besides slowing down, allow some extra following
distance. And be especially careful when
you pass
another vehicle. Allow yourself more clear room
ahead, and be prepared
to have your view restricted
by road spray.
Have good tires with proper tread depth.
(See
“Tires” in the Index.)
4-3 1
Page 193 of 403

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine The exit speed is usually posted.
Reduce your speed according to your speedometer, not
to.your sense of motion. After driving for any distance
at higher speeds, you may tend to think you are going
slower than you actually are.
Before Leaving on a Long Trip
Make sure you’re ready. Try to be well rested. If you
must start
,. when you’re not fresh -- such as after a day’s
work
-- don’t plan to make too many miles that first part
of the journey. Wear comfortable clothing and shoes you
can easily drive
in.
Is your vehicle ready for a long trip? If you keep it
serviced and maintained, it’s ready togo. If it needs
service, have it done before starting out.
Of course,
you’ll find experienced and able service experts in
GM
dealers all across North America. They’ll be ready and willing
to help if you need it. Here are some things
you can check before a trip:
0 Windshield Washer
Fluid: Is the reservoir full? Are
all windows clean inside and outside?
0 Wiper Blades: Are they in good shape?
0 Fuel, Engine Oil, Other Fluids: Have you checked
0 Lamps: Are they all working? Are the lenses clean?
Tires: They are vitally important to a safe,
all levels?
trouble-free trip.
Is the tread good enough for
long-distance driving? Are the tires all inflated
to the
recommended .pressure?
along your route? Should you delay your trip a short
time to avoid a major storm system?
0 Maps: Do you have up-to-date maps?
0 Weather Forecasts: What’s the weather outlook .
4-34
Page 200 of 403

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Run your engine only as long as you must. This saves
fuel. When
you run the engine, make it go a little faster
than just idle. That is, push the accelerator slightly. This
uses less fuel for the heat that you get and it keeps the
battery (or batteries) charged.
You will need a
well-charged battery (or batteries) to restart the vehicle,
and possibly for signaling later on with your headlamps.
Let the heater run for awhile.
If you have a diesel engine, you may have to run it at a
higher speed to get enough heat. Then, shut the engine
off and close the window almost all the way to preserve
the heat. Start the engine again and repeat this only
when you feel really uncomfortable from the cold. But
do it as little as possible. Preserve the fuel as long as
you
can. To help keep warm, you can get out of the vehicle
and
do some fairly vigorous exercises every half hour or
so until help comes.
Loading Your Vehicle
nun-
a-n SEE OWNER'S MANUAL FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
The Certification/Tire label.is found on the rear edge of
the driver's door.
The label shows the size of your original tires and the
inflation pressures needed to obtain the gross weight
capacity
of your vehicle. This is called the GVWR
(Gross Vehicle Weight Rating). The GVWR includes
the
weight of the vehicle, all occupants, fuel and cargo.
4-41
Page 296 of 403

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Tires
We don’t make tires. Your new vehicle comes with
high-quality tires made by a leading tire manufacturer.
If you ever have questions about your tire warranty and
where to obtain service, see your
GM Warranty booklet
for details.
A CAUTION:
Poorly maintained and improperly used tires
are dangerous.
0 Overloading your tires can cause
overheating as a result of too much friction.
You could have an air-out and a serious
accident. See “Loading Your Vehicle” in
the Index.
CAUTION: (Continued) CAUTION:
(Continued)
0
0
0
Underinflated tires pose the same danger as
overloaded tires. The resulting accident
could cause serious injury. Check all tires
frequently to maintain the recommended
pressure. Tire pressure should be checked
when your tires are cold.
Overinflated tires are more likely to be
cut, punctured or broken by
a sudden
impact
-- such as when you hit a pothole.
Keep tires at the recommended pressure.
Worn, old tires can cause accidents.
If your
tread is badly worn, or if your tires have
been damaged, replace them.
6-43
Page 297 of 403

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Inflation -- Tire Pressure
The CertificationRire label, which is on the rear edge of
the driver’s door, or on the incomplete vehicle document
in the cab, shows the correct inflation pressures for your
tires when they’re cold. “Cold” means your vehicle has
been sitting for at least three hours or driven no more
than
1 mile ( 1.6 km).
You can operate some vehicles at reduced inflation
pressures only when you’ll be carrying reduced loads.
On those vehicles, the minimum cold inflation pressures
for a typical reduced load are printed on the Improved
Ride Tire Pressure label located on the driver’s door.
Weigh the vehicle to find the load on each tire and see
the label
for the minimum cold inflation pressures for
that load.
NOTICE:
Don’t let anyone tell you that underinflation or
overinflation is
all right. It’s not. If your tires
don’t have enough air (underinflation), you can
get the following:
Too much flexing
Too much heat
Tire overloading
Bad wear
Bad handling
Bad fuel economy.
If your tires have too much air (overinflation),
you can get the following:
Unusual wear
Bad handling
Rough ride
Needless damage from road hazards.
6-44
Page 298 of 403
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine When to Check
Check your tires once a month or more. Also, check the
tire pressure of the spare tire.
How to Check
Use a good quality pocket-type gage to check tire
pressure.
You can’t tell.if your tires are properly inflated
simply by looking at them. Radial tires may look
properly inflated even when they’re underinflated.
Be sure to put the valve caps back on the valve
stems. They help prevent leaks by keeping out dirt
and moisture.
Tire Inspection and Rotation
Tires should be inspected every 6,000 to 8,000 miles
(10
000 to 13 000 km) for any signs of unusual wear.
If unusual wear is present, rotate your tires as soon as
possible and check wheel alignment. Also check for
damaged tires or wheels. See “When It’s Time for New
Tires” and “Wheel Replacement” later in this section for
more information.
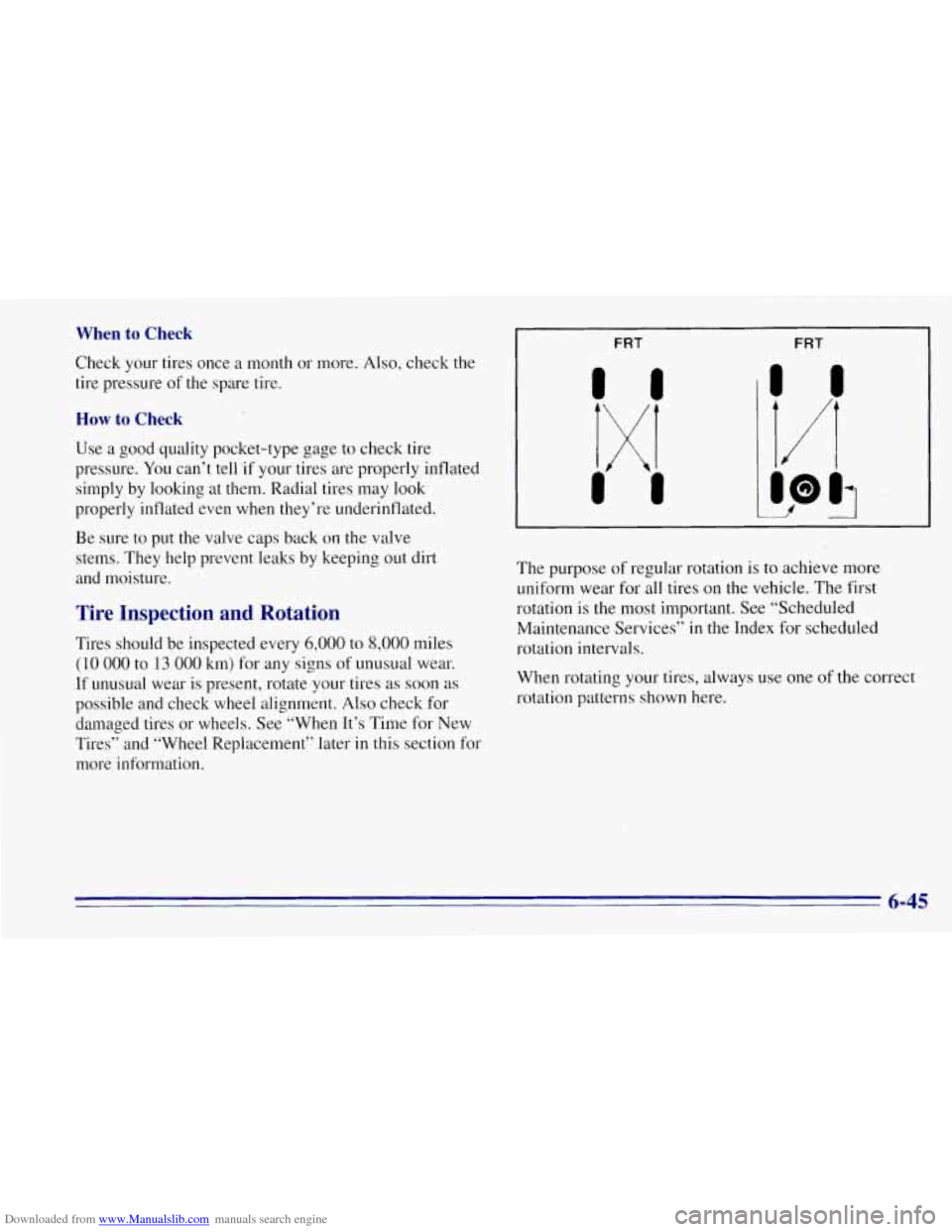
I FRT FRT
The purpose of regular rotation is to achieve more
uniform wear for all tires on the vehicle. The first
rotation
is the most important. See “Scheduled
Maintenance Services” in the Index for scheduled
rotation intervals.
When rotating your tires, always use one
of the correct
rotation patterns shown here.
6-45