Page 17 of 30
17
EWS
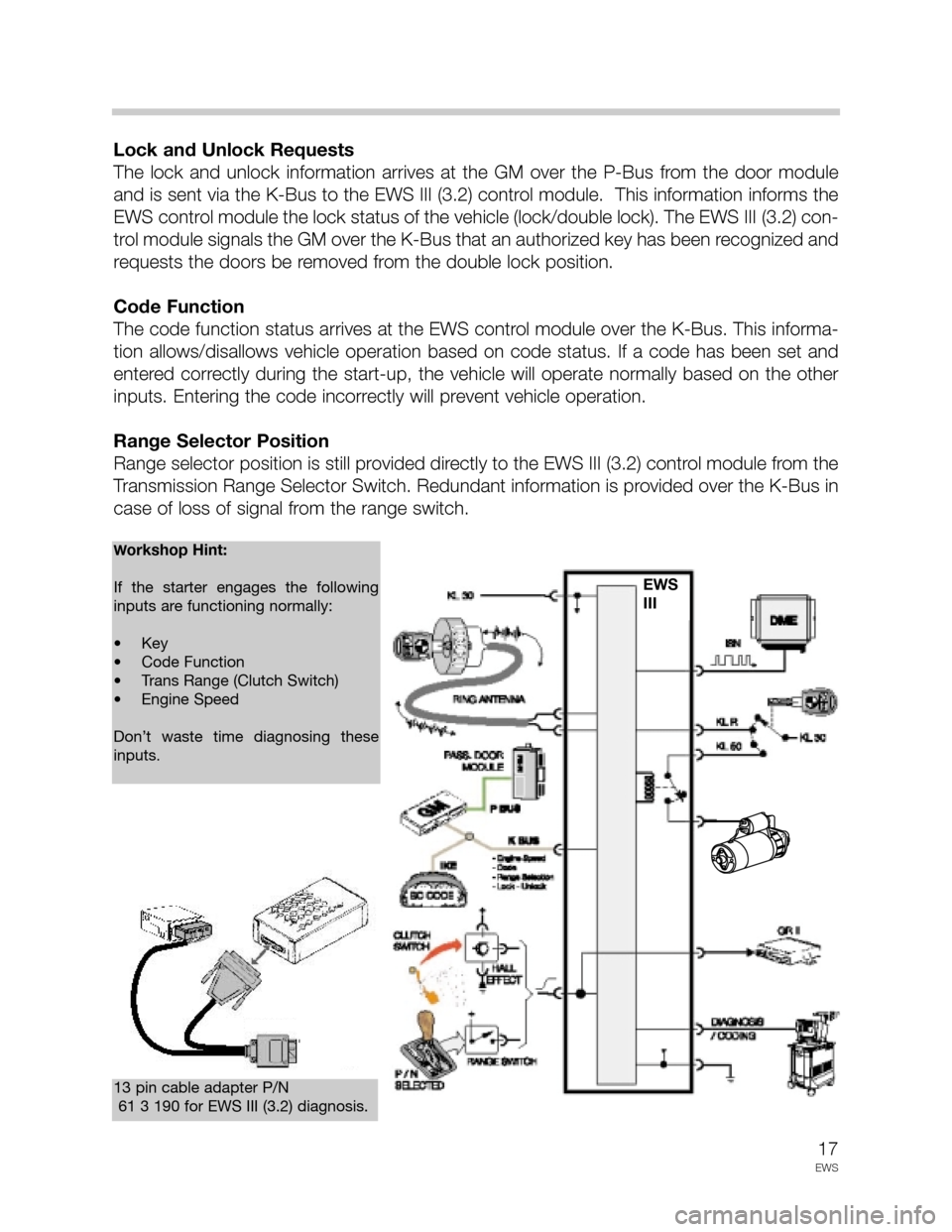
Lock and Unlock Requests
The lock and unlock information arrives at the GM over the P-Bus from the door module
and is sent via the K-Bus to the EWS III (3.2) control module. This information informs the
EWS control module the lock status of the vehicle (lock/double lock). The EWS III (3.2) con-
trol module signals the GM over the K-Bus that an authorized key has been recognized and
requests the doors be removed from the double lock position.
Code Function
The code function status arrives at the EWS control module over the K-Bus. This informa-
tion allows/disallows vehicle operation based on code status. If a code has been set and
entered correctly during the start-up, the vehicle will operate normally based on the other
inputs. Entering the code incorrectly will prevent vehicle operation.
Range Selector Position
Range selector position is still provided directly to the EWS III (3.2) control module from the
Transmission Range Selector Switch. Redundant information is provided over the K-Bus in
case of loss of signal from the range switch.
13 pin cable adapter P/N
61 3 190 for EWS III (3.2) diagnosis.
Workshop Hint:
If the starter engages the following
inputs are functioning normally:
• Key
• Code Function
• Trans Range (Clutch Switch)
• Engine Speed
Don’t waste time diagnosing these
inputs
.
EWS
III
Page 18 of 30

18
EWS
Clutch Switch
A Hall-Effect Switch is added to the clutch system to inform the EWS III (3.2) control mod-
ule of clutch status. Input from the switch replaces the signal from the Trans Range Selector
Switch on manual transmission equipped vehicles. High signal status indicates the clutch
is depressed and vehicle starting is allowed.
Principle of Operation
The starting sequence for the EWS III (3.2) is as follows:
• The key is inserted into the lock cylinder and switched “ON”. The EWS III control mod-
ule is powered through KL R and sends a 125kHz AM signal to the ring antenna. The
AM signal induces voltage in the key coil and powers up the transponder.
• Powered up, the key transponder sends the key identification code to the EWS III mod-
ule. The EWS III module verifies the key identification code and checks to see if the key
is enabled. If the key is correct and enabled, a password is sent to the transponder over
the 125kHz AM signal through the ring antenna.
• When the transponders accepts the password, it releases the changing code, which it
received from the EWS III module during the last start-up operation, to the EWS III mod-
ule via the ring antenna.
• The EWS III module compares the changing code received from the transponder with
the code stored in its memory and if they match the process is allowed to continue.
The EWS III module looks at the other inputs for correct status (e.g. Code function not
active, Transmission in P or N or clutch depressed, engine speed below specified RPM)
and energizes the the internal relay to begin starter operation.
• As the starter begins to operate, the EWS III module sends the ISN to the DME and if
verified as correct by the DME, drive away protection is cancelled and injection and igni-
tion is enabled. The EWS III module also sends a new changing code to the key
transponder through the ring antenna.
Replacement Procedures
Keys
Up to 6 additional keys may be ordered as replacement keys. The EWS III (3.2) module is
codeable for only 10 keys (4 delivered with vehicle and 6 replacement). The keys are
mechanically matched to the vehicle with the lock tumblers and electronically matched to
the EWS III (3.2) through unalterable coding.
Page 19 of 30

19
EWS
EWS III (3.2) Control Module
Replacement EWS III (3.2) Control Modules must be ordered VIN specific. The EWS III
modules contain the VIN and coding from the factory to recognize the key codes. Use of
EWS III modules from other vehicles will result in the keys not being recognized.
The EWS III (3.2) control module stores the ZCS coding and must be coded at time of
installation. The module must be aligned with the DME so that it stores the correct ISN.
There is no limit to the number of times the ISN may be changed in the EWS III module.
DME Control Module
DME Control Modules are “off the shelf” parts requiring programming during installation.
The ISN of the DME is not changeable and must be transferred to the EWS III (3.2) mod-
ule.
Key Activation
Keys that are lost or stolen may be deactivated or made to not operate the starter func-
tions. The SERVICE FUNCTIONS of the DISplus or MoDic for EWS III (3.2) contains a
“Bar/Release Code” function that activates and deactivates keys of the EWS III (3.2). Any
key may be “Barred” except the key in the ignition at the time of deactivation. The lost or
stolen key can be identified by the identification of the remaining keys.
There is no limit to the number of times a key can be activated/deactivated.
Notes
Page 20 of 30

20
EWS
EWS III (3.3)
EWS III (3.3) is installed in the 1998 E38 from 5/97 production, in the 1998 E39 from 9/97
production, in the E46beginning of production, in the E52and E53 beginning of pro-
duction.
Purpose of the System
The purpose of the EWS III (3.3) system is to add greater theft protection by providing a
higher level of sophistication than previous systems. The new “Rolling Code” provides an
additional theft deterrent through a changing of the ISN everytime the vehicle enters the
start sequence.
Components changed in the EWS III (3.3) system include:
• EWS III (3.3) Control Module.
• DME Control Module.
• Transmission Range Selection Input.
System Components
EWS III (3.3) Control Module
The EWS III (3.3) Control Module uses the same 13 pin connector as EWS III (3.2) but func-
tions differently. The EWS III (3.3) module has a “Rolling Code” ISN assigned to it during
manufacture. The “Rolling Code” is burned into
the module and cannot be overwritten by ZCS
Coding or DME alignment procedures.
The “Rolling Code” is a one way signal from the
EWS III (3.3) control module to the DME and is
similar in operation to the data exchange
between the EWS control module and the key
transponder.
The “Rolling Code” will be different each time the
start operation is begun. The “Codes” are taken
from the “Rolling Code Table” which is assigned
at the factory to the EWS III (3.3) control module
and the DME.
8510133
Workshop Hint:
While it is possible to initialize a key to another
vehicle to check for remote operation, use cau-
tion. All keys for Bothvehicles must be avail-
able. The initializing process, causes loss of
operation of keys previously initialized.
All keys must be initialized at the same time.
Page 21 of 30

21
EWS
DME Control Module
The DME Control Module has changed in that it is not the source of the ISN but now only
stores the “Rolling Code”. It compares the “Codes” to those sent to it by the EWS III (3.3)
control module. The “Rolling Code Table” assigned to the DME must match the table in the
EWS III (3.3) module. The “Rolling Code Table is “burned” into the DME during the pro-
gramming of the DME and cannot be change once “burned”.
Transmission Range Selection Input
With the introduction of the SKE type connectors on Transmission Control Modules the
direct input from the Transmission Range Selector Switch is eliminated. The input for range
selection is now received from the AGS Control Module.
On manual transmission vehicles clutch status is input directly into the DME.
Principle of Operation
The starting sequence of the EWS III (3.3) is as follows:
(Same as EWS III (3.2)
• The key is inserted into the lock cylinder and switched “ON”. The EWS III (3.3) control
module is powered through KL R and sends a 125kHz AM signal to the ring antenna.
The AM signal induces voltage in the key coil and powers up the transponder.
• Powered up, the key transponder sends the key identification code to the EWS III (3.3)
module. The EWS III (3.3) module verifies the key identification code and checks to see
if the key is enabled. If the key is correct and enabled, a password is sent to the
transponder over the 125kHz AM signal through the ring antenna.
• When the transponders accepts the password, it releases the changing code which it
received from the EWS III (3.3) module during the last start-up operation to the EWS III
(3.3) module via the ring antenna.
• The EWS III (3.3) module compares the changing code received from the transponder
with the code stored in its memory and if they match the process is allowed to contin-
ue. The EWS III (3.3) module looks at the other inputs for correct status (e.g. Code func-
tion not active, Transmission in P or N or clutch depressed, engine speed below spec-
ified RPM) and energizes the the internal relay to begin starter operation.
Page 22 of 30

22
EWS
New to EWS III (3.3)
• While energizing the internal starter relay, the EWS III (3.3) module calculates a stored
code from the “Rolling Code Table” and sends the calculated results to the DME.
• On receipt of the “Rolling Code” from the EWS III (3.3) the DME calculates it’s own
stored code and compares its results with the code it received from the EWS III (3.3).
If the “Codes” matchthe drive away protection is released and injection and igni-
tion are enabled and the engine starts.
If the “Codes” do NOTmatch, the DME “rolls forward” to the next code according
to the “Rolling Code Table” and makes the same calculations. The DME continues
this “forward roll” up to a maximum of 200 times or until a match is found. Failure
to find a match will result in the engine cranking but not starting.
• When the ignition is switched off and no engine RPM is present in both the DME and
the EWS III (3.3) control module each module will automatically “roll forward” to the next
predetermined code based on the “Rolling Code Table”. This new code is used for the
next starting sequence.
85101318510135
Workshop Hint:
If during diagnosis the key is switched on while the
DME or EWS modules are “Disconnected”, the align-
ment procedure will need to be carried out.
The“Alignment”procedure may be carried out an
umlimited number of times.
Page 23 of 30

23
EWS
Replacement Procedures
Keys
Up to 6 additional keys may be ordered as replacement keys. The EWS II control module
is codeable for only 10 keys (4 delivered with vehicle and 6 replacement).
EWS III (3.3) Control Module
Replacement EWS III (3.3) Control Modules are ordered VIN specific. The module is
received with the same “Rolling Code Table” as the original module. Once ZCS coded, the
DISplus software “resets” the current rolling code in the DME back to “Rolling Code” #1,
providing synchronization of both modules.
DME Control Modules
Replacement DME Control Modules are “off the shelf” and must be programmed for the
specific vehicle. After programming the DISplus software informs the EWS III (3.3) control
module that a new DME has been installed. The next time the ignition is switched on, the
EWS III (3.3) module will send the entire “Rolling Code Table” to the DME and reset it to
“Rolling Code” #1.
The DME will automatically burn the “Rolling Code Table” into its memory.
Once the table
has been burned into the DME memory it can NOT
be changed. For this reason once a
DME is “Married” to the vehicle it will not work in any other vehicle.
Under certain condition “Alignment” of the DME and EWS III (3.3) modules may still be nec-
essary. The alignment procedure only resets the code table to code #1 it does not change
the “Rolling Code Table”.
Key Activation
Keys that are lost or stolen may be deactivated or made to not operate the starter func-
tions. The SERVICE FUNCTIONS of the DISplus or MoDic for EWS III (3.3) contains a
“bar/release code” function that activates and deactivates keys of the EWS III (3.3). Any
key may be “Barred” except the key in the ignition at the time of deactivation. The lost or
stolen key can be identified by the identification of the remaining keys.
There is no limit to the number of times a key can be activated/deactivated.
Workshop Hint:
While checking key operation, don’t forget to
wait 10 seconds before inserting the next key.
You can not BARthe key in the ignition.Workshop Hint:
A dead key battery does not affect vehicle start-
ing.
Keys without replaceable batteries are not
charged if the ignition is in the KLO (Off) posi-
tion.
Page 24 of 30

24
EWS
EWS III D
EWS III D is installed on E36/7 beginning of production 99 Model Year. The system
does not have a K-Bus input.
Purpose of the System
The purpose of the EWS III D system is to provide the highest level of drive away protec-
tion available to vehicles without a K-Bus. The input side of the control module functions
the same as an EWS II (no bus inputs) system with the exception of an integrated EWS
module and transmitter/receiver module. The output side functions similar to an EWS III
(3.3) system with “Rolling codes”. The EWS III D control module is on the D-Bus for diag-
nostics.
Individual component inputs and system operation is the same as the mentioned previous
systems.
Replacement Procedures
Keys
Up to 6 additional keys may be ordered as replacement keys. The EWS III D control mod-
ule is codeable for only 10 keys (4 delivered with vehicle and 6 replacement).
EWS III D Control Module
Replacement EWS III D Control Modules are ordered VIN specific. The module is received
with the same “Rolling Code Table” as the original module. Once ZCS codes, the DISplus
software “resets” the current rolling code in the DME back to “Rolling Code” #1, providing
synchronization of both modules.
DME Control Modules
Replacement DME Control Modules are “off the shelf” and must be programmed for the
specific vehicle. After programming the DISplus software informs the EWS III D control
module that a new DME has been installed. The next time the ignition is switched on, the
EWS III D module will send the entire “Rolling Code Table” to the DME and reset it to
“Rolling Code” #1.
The DME will automatically burn the “Rolling Code Table” into its memory.
Once the table
has been burned into the DME memory it can NOT
be changed. For this reason once a
DME is “Married” to the vehicle it will not work in any other vehicle.