1995 MITSUBISHI 3000GT ignition coil
[x] Cancel search: ignition coilPage 481 of 738

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine i;ENGINE ELECTRICAL
- Ignition System16-35
OPERATIONl
Turn ignition switch to .“ON”position, and batteryvoltage will be applied to primary winding of
ignition coil.l
When crankshaft position sensor and camshaft
position sensor signal is input to engine control
module, engine control module makes ON-OFF
control of power transistors one by one.l When power transistor is turned on, current
flows from ignition coil (primary winding) to
ground through power transistor.l When power transistor A is turned from ON
to OFF, the spark plugs of No. 1 and No. 4
cylinders spark. Turning of power transistor B
from ON to OFF will produce sparking in spark
plugs of No. 2 and No. 5 cylinders. Furthermore,
when power transistor C is turned from ON toOFF, sparking is produced in spark plugs of
No. 3 and No. 6 cylinders.
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS1. Engine cranks, but does not start.
(1) Spark is insufficient or does not occur at
all (on spark plug).l Check ignition coil.
l Check camshaft position sensor and
crankshaft position sensorl Check power transistor.
l Check spark plugs.
l Check spark plug cable.
(2) Spark is good.
l Check ignition timing.
2. Engine idles roughly or stalls.
l Check spark plugs.
l Check ignition timing.
l Check ignition coil.
l Check spark plug cable.
3. Poor acceleration
l Check ignition timing.
l Check spark plug cable.
l Check ignition coil.
TSB Revision
Page 487 of 738

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE ELECTRICAL - lanition Svstem16-41
/
L
i
Analyzer
GroundL
01L1008
STANDARD WAVE-FORM
Observation ConditionsIGNITION PRIMARY VOLTAGE WAVE-FORM
CHECK
MEASUREMENT METHOD
(1)Remove the ignition coil connector and connect the special
tool (harness connector: MD998464) in between.
(2) When observing the No. 1 - No. 4 cylinder group, connectthe primary pickup of the analyzer probe to the ignition
coil side connector terminal No. 2 (black clip on the special
tool).
For the No. 2 - No. 5 cylinder group, connect to terminal
No. 1 (red clip), and for the No. 3
- No. 6 cylinder group,connect to terminal No. 4 (white clip).
(3) Ground the primary pickup ground terminal.
(4) Clamp the spark plug cable with the trigger pickup.
NOTE(1) Clamp the spark plug cable of cylinder No. 1, No.
2 or No. 3 which belongs to the same group of the
cylinder to which the primary pickup is connected.
(2) The wave-form of any cylinder in the same group
is displayed on the left side of the screen.
FUNCTION
PRIMARY
PATTERN HEIGHTHIGH (or LOW)
PAVERN SELECTOR
Engine revolutionsRASTER
Curb idle speed
(V)
100
Primary Primary*ignition ignition
voltage voltage
wave-form
owave-formkr
0
Zener
voltage
(Point C)
Dwell
section
b
Spark line (Point A)
/b-4
Wave damping reduction section (Point B)
/
Time
7EL0149
/ TSB Revision
Page 489 of 738

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE ELECTRICAL - Ignition System16-43
Wave-form Observation Points/
LPoint A: The height, length and slope of the spark line (refer to abnormal wave-form examples 1, 2, 3and 4) show the following trends.
Spark linePlug gapCondition of CompressionConcentra-Ignition timing High tension
electrodeforcetion of air mix-cable
tureLength Long
SmallNormalLowRichAdvanced
Leak
Short
LargeLarge wearHighLeanRetardedHigh
resistanceHeight High
LargeLarge wearHighLeanRetardedHigh
resistance
LowSmall
NormalLowRichAdvancedLeak
SlopeLargePlug is fouled-
Point B: Number of vibrations in reduction vibration section
(Refer to abnormal wave-form example 5)
Number of vibrationsCoil and condenser
I3 or higher/ Normal
Except aboveAbnormal
Point C: Height of Zener voltage
Height of Zener voltageProbable cause
HigherProblem in Zener diode
LowerAbnormal resistance in pri-
mary coil circuit
TSB Revision
Page 490 of 738

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE ELECTRICAL - Ignition System
EXAMPLES OF ABNORMAL WAVE-FORMS
Abnormal wave-form
Wave characteristics
Cause of problem
Example 1Spark line is high and short.
Spark plug gap is too large.
z01P0210
Example 2Spark line is low and long, and is
sloping. Also, the second half of
Spark plug gap is too small.the spark line is distorted. This
could be a result of misfiring.3
i
Example 3
zo1Po211
Spark line is low and long, and is
sloping. However, there is almostSpark plug gap is fouled.
no spark line distortion.
ZOlPO212
Example 4Spark line is high and short.Spark plug cable is nearly falling
off. (Causing a dual ignition)
ZOlPO213
Example 5No waves in wave damping set-tion.Rare short in ignition coil.
-l
zolPo214
TSB Revision
Page 491 of 738
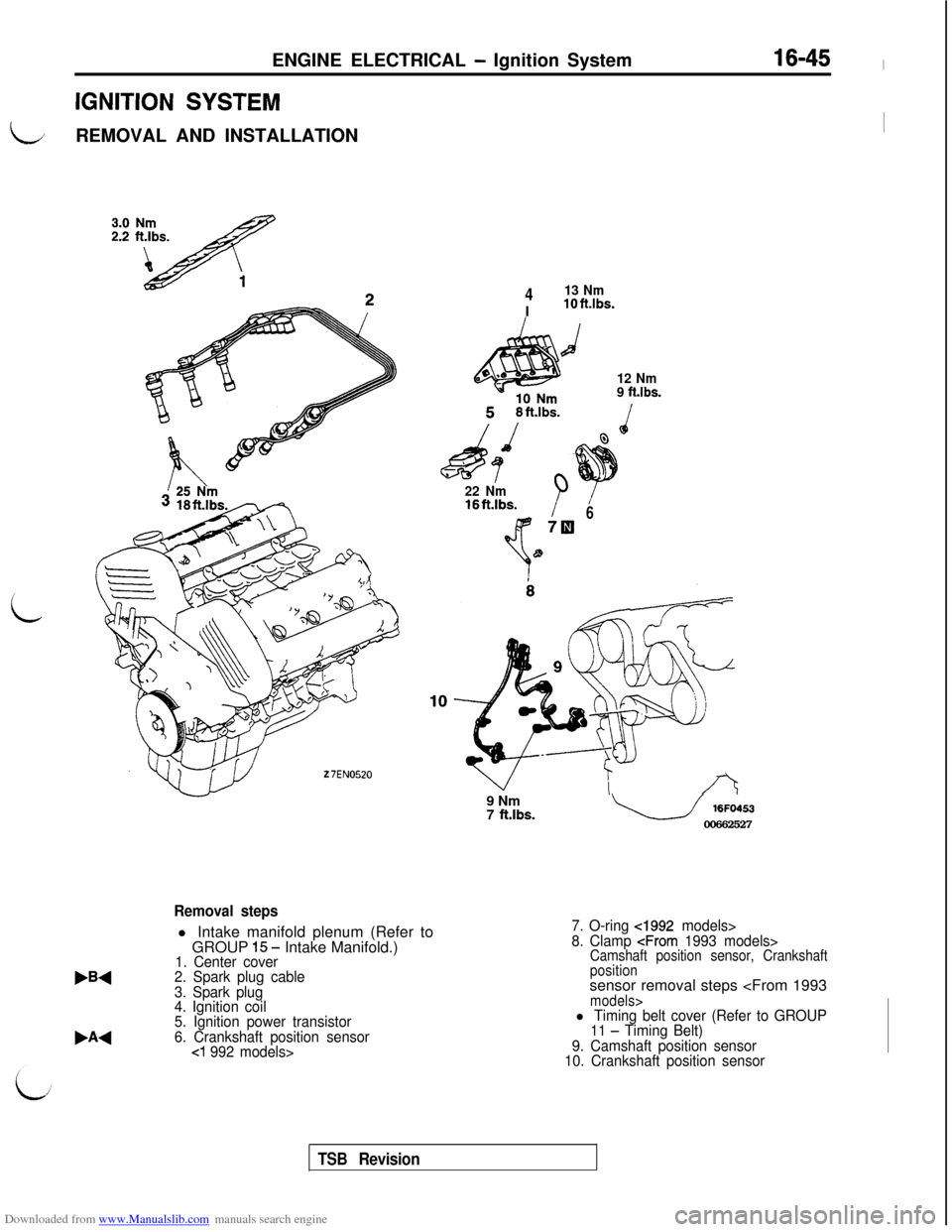
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE ELECTRICAL - Ignition System16-45 l
IGNITION SYSTEM
LREMOVAL AND INSTALLATIONI
i
27EN0520
413 NmIlOft.lbs.
d
12 Nm
9 ft.lbs.
22 Nm16ftAbs.B678
W1
,A4
Removal stepsl Intake manifold plenum (Refer to
GROUP
1.5 - Intake Manifold.)1. Center cover
2. Spark plug cable
3. Spark plug
4. Ignition coil
5. Ignition power transistor
6. Crankshaft position sensor
cl 992 models>9 Nm
7
ft.lbs.u 16FO453
00662527
7. O-ring cl992 models>
8. Clamp
positionsensor removal steps
11 - Timing Belt)
9. Camshaft position sensor
10. Crankshaft position sensor
TSB Revision
Page 494 of 738

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 16-48ENGINE ELECTRICAL - lanition Svstem
\/27EL0086
/DEL0087INSPECTION
SPARK PLUGCheck the plug gap and replace if the limit is exceeded.
Standard value:
1.0-l .l mm (.039-.043 in.)
Limit: 1.3 mm
(.051 in.)
Caution
1.Do not attempt to adjust the gap of the platinum plug.
2.Cleaning of the platinum plug may damage the plati-num tip. Therefore, if carbon deposits must be re-
moved, use a plug cleaner and complete cleaning with-
in 20 seconds for protection of the electrode. Do not
use wire brushes.
SPARK PLUG CABLE(1) Check cap and coating for cracks.
(2) Measure resistance.Limit: Max. 22
ksZ
IGNITION POWER TRANSISTOR
NOTE
An analog-type circuit tester should be used.No. l-No. 4 coil side
(1)Connect the negative (-) terminal of the 1.5 V power supply
to terminal (4) of the ignition power transistor; then check
whether there is continuity between terminal (13) and termi-nal (4) when terminal (3) and the positive
(+) terminal
are connected and disconnected.NOTE
Connect the (-) probe of the circuit tester to terminal (13).
Terminal 3 and (+) terminal
ConnectedTerminal 13 and terminal 4
Continuity
IUnconnectedINo continuitv
(2)Replace the ignition power transistor if there is a malfunc-
tion.No. ~-NO. 5 coil side
(1)Connect the negative (-) terminal of the 1.5 V power supply
to terminal (4) of the ignition power transistor; then check
whether there is continuity between terminal (12) and termi-nal (4) when terminal (2) and the positive
(+) terminal
are connected and disconnected.
NOTE
Connect the (-)
probe of the circuit tester to terminal (12).
[ TSB Revision
Page 495 of 738

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE ELECTRICAL b Ignition System16-49
27EL0089
Z7ELOOQO
1 Terminal 2 and (+) terminal/Terminal 12 and terminal 41
IConnectedIContinuitvI
IUnconnectedINo continuitvI
(2) Replace the ignition power transistor if there is a malfunc-
tion.No. ~-NO. 6 coil side
(1)Connect the negative (-) terminal of the 1.5 V power supply
to terminal (4) of the ignition power transistor; then check
whether there is continuity between terminal (11) and termi-nal (4) when terminal (1) and the positive
(+) terminal
are connected and disconnected.
NOTE
Connect the (-) probe of the circuit tester to terminal 11.
I Terminal 1 and (+) terminal/ Terminal 11 and terminal 41
-ConnectedIContinuityI
IUnconnectedINo continuityI
(2)Replace the ignition power transistor if there is a malfunc-
tion.
IGNITION COIL
Primary Coil Resistance
Measure the resistance between connector terminal (3) (pow-
er) and each coil terminal.Measuring point:
Coil A
(No.l-No.4 cylinder side coil) . . . . . . (2)-(3)Coil B (No.2-No.5 cylinder side coil) . . . . . .
(l)-(3)Coil C (No.3-No.6 cylinder side coil) . . . . . .
(4)-(3)Standard value: 0.67-0.81
Sz
TSB Revision
Secondary Coil Resistance
Measure the resistance between each coil high voltage termi-
nals.
Measuring point:Coil A (No. l-No. 4 cylinder side coil)
Coil B (No. ~-NO. 5 cylinder side coil)
Coil C (No. ~-NO. 6 cylinder side coil)
Standard value: 11.3-15.3
Wz
Page 514 of 738

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 54-18CHASSIS ELECTRICAL - Meters and Gauges
OPERATION
When the ignition key is at the “ON” position,the fuel gauge is activated.
l
When there is much fuel, the unit’s resistanceis small and the current flowing in the circuit
is great, so the gauge’s indicator indicates inthe “F” area.
l When there is little fuel, the unit’s resistance
is high and the current flowing in the circuit
is small, so the gauge’s indicator indicates inthe
“E” area.
lWhen the ignition key is at the “ON” position,
the engine coolant temperature gauge is acti-
vated.l
When the engine coolant temperature is high,
the unit’s resistance is low and there is a greatflow of current in the circuit, so the gauge’s
indicator indicates in the “H” area.
l
When the engine coolant temperature is low,
the unit’s resistance is high and there is a smallflow of current in the circuit, so the gauge’s
indicator indicates in the “C” area.
vehicle speed, and vehicle-speed signals areinput to systems (the MFI system, etc.) that
regulate according to the vehicle speed.
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS
1.The fuel gauge doesn’t function, or shows the
incorrect indication.
(1) Disconnect the connector of the fuel pumpand gauge unit assembly; the ‘F” side is
indicated when terminal (5) is then
grounded.l Check the fuel gauge.
2.The engine coolant temperature gauge doesn’t
function, or shows the incorrect indication.
(1)The “l-l” side is indicated when the connector
of the engine coolant temperature gauge
unit is disconnected and then grounded.l
Check the engine coolant temperature
gauge unit.
3. Systems dependent upon control according to
the vehicle speed do not function correctly.l Check the reed switch (mechanical
speedometer type)l Check the speed sensor (electrical
speedometer type)
coil pressure gauge>l
When the ignition key is at the “ON” position,
the oil pressure gauge is activated.
lWhen oil pressure is high, the internal contacts
of the gauge unit are kept closed for a longerperiod of time. This causes more current to
flow in the circuit, and the gauge pointer swings
to the high pressure side.
lWhen oil pressure is low, the internal contactsof the gauge unit open in a shorter period of
time. Therefore, there is less current flowing
in the circuit and the gauge pointer swings to
the low pressure side.
lWhen the ignition key is set to the “ON” position,the gauge indicator will be at
“0”.l
When the engine is started, the indicator will
move from
“0” to the minus (-) side, and then,as the boost level increases, it will move to
the plus
(+) side.
position, the voltage gauge operates and indi-
cates a battery voltage of approximately 12 V.l
When the engine is started, the voltage gauge
indicates a battery voltage of 12 to 16 V, indicat-ing that the battery is on charge.
4. The oil pressure gauge doesn’t function, or
shows the incorrect indication.
(1)The “H” side is indicated when the connectorof the oil pressure gauge unit is discon-
nected and then grounded.l Check the oil pressure gauge unit.
5.The meter illumination light does not illuminate.
(1) The tail lights illuminate.l Check the rheostat.
6. The voltage gauge doesn’t function, or shows
the incorrect indication.l Check the voltage gauge.
TSB Revision