1995 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 214 of 873

Tdi
9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION OPERATION EDC
Under start up conditions, signals from the crank
speed and water temperature sensors are relayed to
the ECM to control starting fuel quantity and injection
timing. Once the engine has started the ECM initiates
a 'closed loop' monitoring system for fuel quantity,
injector timing and EGR relative to the appropriate
engine operating conditions.
As driver demand increases, signals from the throttle
position sensor are received by the ECM together with
crank speed and position pulses. The ECM signals
the injection pump to adjust fuel quantity and timing
relative to driver demand.
As engine coolant, fuel and air temperature changes
the ECM will correct fuel delivery and injection timing
for more efficient and accurate running. The ECM will
also make corrections for atmospheric pressure on
injection timing and EGR.
Electronic Control Unit (ECM)
The EDC system is controlled by the ECM located in
the drivers footwell on the 'A' post beneath the fascia.
The unit consists of a microprocessor with integrated
circuits and components and is connected to the main
harness by a 55 pin plug.
Inputs to the ECM from engine sensors control start of
injection, injected fuel quantity, fuel cut-off and EGR.
The ECM will also make corrections for engine
coolant, fuel and air temperature and atmospheric
pressure.Injection pump
The injection pump incorporates actuator controlled
injected fuel quantity and solenoid operated timing
which operate in response to ECM signals against
driver demand, engine speed, temperature and boost
pressure.
A fuel cut-off facility and fuel temperature sensor is
incorporated in the pump.
Injection timing sensor
An inductive sensor in No 4 injector body monitors
needle movement. This forms part of a 'closed loop'
system to control start of injection.
The system measures timing, relating the needle
movement signal to crank position (determined by
flywheel pulses from the engine speed sensor).
Air flow sensor
The Air Flow Sensor is mounted on a bracket
attached to the wheel arch valance, and connected by
hose to the air cleaner and turbo charger inlet.
The unit consists of a flap valve airflow sensor which
measures the fresh air flow into the engine. The
sensor informs the ECM and, provided that the other
conditions are met, will implement EGR.
Engine speed sensor
The engine speed sensor is an active inductive sensor
mounted on the flywheel housing. Pulses from the
sensor activated by radial slots in the flywheel give
engine speed and position information to the ECM.
Page 228 of 873

Tdi
11
REPAIR FUEL INJECTION PUMP AND TIMING
Service repair no - 19.30.07
NOTE: The following text refers to a Tdi
vehicle with a manual gearbox without
electronic diesel control. Where reference
is made to the timing tool substitute the following
information for automatic and EDC variants.
If manual gearbox:Timing tool LRT-12-044 fits into
the base of the flywheel housing
If manual gearbox with EDC:Timing tool
LRT-12-085 must be used and also fits into the base
of the flywheel housing.
If automatic gearbox:Timing tool LRT-12-044 fits
into the larger bolt hole of coverplate on engine
backplate, sited near to the rear of sump. Pin locates
in ring gear.
Remove
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Remove injection pipes, pump to injector.
3.Remove oil filler cap from rocker cover.
4.Viewing valve mechanism through filler aperture,
turn crankshaft clockwise until No. 1 cylinder is
just before TDC.
5.Refit oil filler cap.
6.Remove blanking plug from flywheel housing.
7.Fit timing tool LRT-12-044 to flywheel housing,
do not engage centre pin.
8.Continue rotating crankshaft clockwise until
centre pin engages with timing slot in flywheel.
9.Remove injection pump access plate, complete
with gasket, from front cover plate.
10.Fit pin from LRT-12-045 to injection pump gear.
11.Remove drive gear to pump hub fixing bolts and
plate.
Page 230 of 873

Tdi
13
REPAIR Refit
21.Remove blanks from pump.
22.Remove special tool pin from pump.
23.Clean mating faces of pump and front cover.
24.Fit pump to cover with a new gasket and secure
with nuts. Tighten to
25 Nm.
25.Attach pump to bracket and finger tighten nuts
and bolts
26.First tighten bolts securing bracket to block and
then bolts securing pump to bracket.
27.Connect spill return, main fuel pipes. Tighten to
25 Nm.
28.Connect boost signal pipe and secure with banjo
bolts. Tighten to
10 Nm.
29.Connect stop control solenoid lead.
30.Connect throttle cable and where applicable
hand throttle cable.
31.Remove special tool LRT-12-045.
32.Fit gear lock plate.
33.Fit pin from special tool LRT-12-045.
34.Secure gear with bolts.
35.Remove special tool pin.
36.Turn crankshaft two complete revolutions, check
timing pin from LRT-12-045 can be fully and
easily inserted into the pump. At the same time
check flywheel timing pin LST-12-044 can also
be inserted in the flywheel slot.
37.If, with the flywheel timing pin located, the timing
pin cannot be inserted cleanly into the injection
pump, carry out the following:
(a) Ensure flywheel timing pin is disengaged
from slot in flywheel.
(b) Turn the crankshaft the small amount
necessary to enable the timing pin to be
inserted into the pump.
(c) Loosen the three pump gear retaining
bolts.
(d) Turn the crankshaft to T.D.C..
(e) Check that the timing pin is an easy fit in
the pump and that the flywheel timing pin
locates.
(f) Tighten the pump gear retaining bolts to
the correct torque.
(g) Remove the timing pin from the pump and
the timing tool from the flywheel housing.
38.Using antisieze compound, fit the blanking plug
to flywheel housing. Tighten to
12 Nm.
39.Fit access plate with gasket to front cover plate.
Tighten to
25 Nm.
40.Refit injector pipes. Tighten to29 Nm.
Page 246 of 873

MFI
3
FAULT DIAGNOSIS FUEL PRESSURE CHECK
In order to check the fuel pressure it is necessary to
first depressurise the fuel system as follows:
WARNING: Under normal operating
conditions the multiport fuel injection
system is pressurised by a high pressure
fuel pump, operating at up to 2.3 to 2.5 bar. When
engine is stationary pressure is maintained within
system. To prevent pressurised fuel escaping and
to avoid personal injury it is necessary to
depressurise multiport fuel injection system
before any service operations are carried out.
If vehicle has not been run there will be a small
amount of residual pressure in fuel line. The
depressurising procedure must still be carried out
before disconnecting any component within the
fuel system.
The spilling of fuel is unavoidable during this
operation. Ensure that all necessary precautions
are taken to prevent fire and explosion.
A Pressure gauge 18G1500
B Fuel tank and pump
C Fuel filter
D Fuel injectors x 8
E Regulator1.Remove fuel pump relay module.
See Repair,
Multiport Fuel Injection Relay
2.Start and run engine.
3.When sufficient fuel has been used to cause fuel
line pressure to drop, injectors will become
inoperative, resulting in engine stall. Switch off
ignition.
4.Disconnect battery negative lead. .
NOTE: Fuel at low pressure will remain in
system. To remove low pressure fuel,
place absorbent cloth around fuel pipe at
the filter during disconnection.
5.Connect the pressure gauge on the outlet from
the filter, located on the chassis under the right
rear wheel arch.
6.Reconnect the battery and turn the ignition to
position II while observing the pressure gauge.
Results
Expected reading 2,39-2,672 kgf/cm
2
Pressure drop-max 0.7 kgf/cm2in one minute.
If pressure is low check that filter is not blocked
and pump is operating satisfactorily. Then
recheck pressure. If pressure is still low renew
regulator.
See Repair, Fuel Pressure
Regulator
Page 247 of 873

MFI
1
REPAIR AIR CLEANER ASSEMBLY
Service repair no - 19.10.01
Remove
3.9 V8 vehicle illustrated
1.Release 2 clips securing air cleaner to air flow
sensor.
2. 3.9 V8 only:Release clip and disconnect hose
from air cleaner.
4.0 V8 only:Release clip and disconnect
multiplug from intake air temperature sensor.
See FUEL SYSTEM SFI, Repair, Intake Air
Temperature Sensor
3.From below wheel arch, release 2 rubber
mountings securing bottom of air cleaner to
body.
4.Slide air cleaner backwards and release from
mounting bracket.
5.Remove air cleaner assembly.
Do not carry out
further dismantling if component is removed
for access only.
6.Release 4 clips securing top of air cleaner and
remove.
7.Withdraw air cleaner element and discard.
8. 4.0 V8 only:Remove intake air temperature
sensor from cover.
9.Remove rubber mountings.
Refit
10.Fit rubber mountings to new body.
11. 4.0 V8 only:Fit intake air temperature sensor to
new cover. Tighten to
8Nm.
12.Fit new air cleaner element and secure in
position.
13.Reverse removal procedure.
NOTE: Pull rubber mountings from below
to secure unit to wheel arch.AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
Service repair no - 19.10.08
Remove
1.Release four clips retaining air cleaner cover.
2.Release two clips to air flow meter.
3.Remove air cleaner cover, retain air flow meter
'O'ring.
4.Remove element.
Refit
5.Fit new element.
6.Fit O ring.
7.Position air cleaner cover, secure two clips to air
flow meter.
8.Secure four air cleaner cover clips.
Page 254 of 873
19FUEL SYSTEM
8
REPAIR 10.Remove fuel rail and injectors.
11.Remove injector retaining clips, ease injectors
from rail. Remove and discard 'O' rings from
injectors.
12.Remove fuel pressure regulator if required.
Refit
13.FitNEW'O' rings, to injectors. Lightly coat 'O'
rings with silicon grease 300. Insert injectors into
fuel rail, multi-plug connections facing outwards.
14.Refit retaining clips.
CAUTION: Care must be taken when
refitting the fuel rail and injectors to intake
manifold to prevent damage to 'O' rings.
15.Fit aNEW'O' ring to pressure regulator lightly
coat 'O' ring with silicon grease 300 and secure
regulator to the fuel rail.
16.Fit fuel rail and heater pipe assemblies to intake
manifold. Secure rail and pipes in position with
five bolts.
17.Reverse removal procedure. 2 to 7.
18.Pressurise fuel system and check for fuel leaks
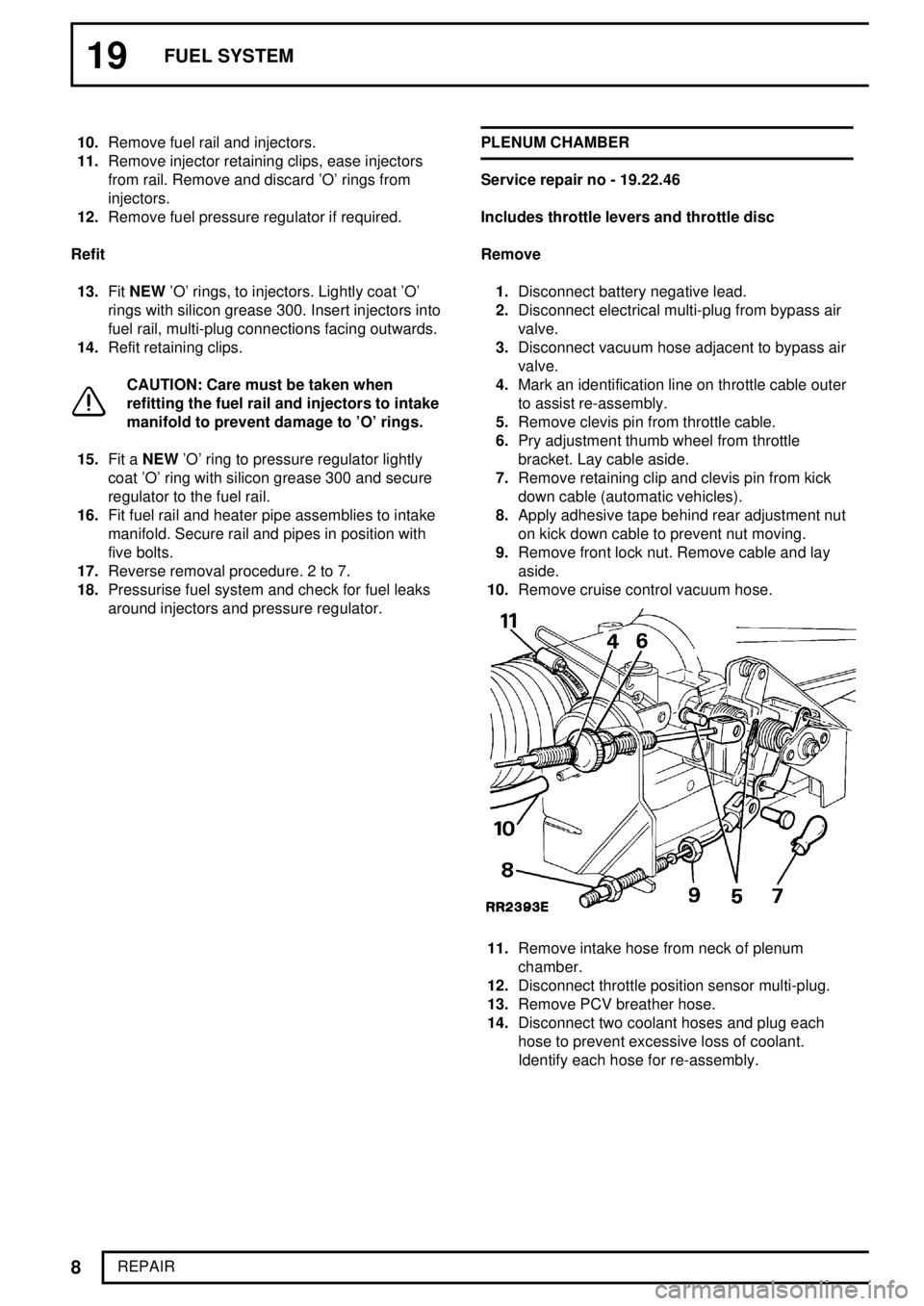
around injectors and pressure regulator.PLENUM CHAMBER
Service repair no - 19.22.46
Includes throttle levers and throttle disc
Remove
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Disconnect electrical multi-plug from bypass air
valve.
3.Disconnect vacuum hose adjacent to bypass air
valve.
4.Mark an identification line on throttle cable outer
to assist re-assembly.
5.Remove clevis pin from throttle cable.
6.Pry adjustment thumb wheel from throttle
bracket. Lay cable aside.
7.Remove retaining clip and clevis pin from kick
down cable (automatic vehicles).
8.Apply adhesive tape behind rear adjustment nut
on kick down cable to prevent nut moving.
9.Remove front lock nut. Remove cable and lay
aside.
10.Remove cruise control vacuum hose.
11.Remove intake hose from neck of plenum
chamber.
12.Disconnect throttle position sensor multi-plug.
13.Remove PCV breather hose.
14.Disconnect two coolant hoses and plug each
hose to prevent excessive loss of coolant.
Identify each hose for re-assembly.
Page 263 of 873
MFI
17
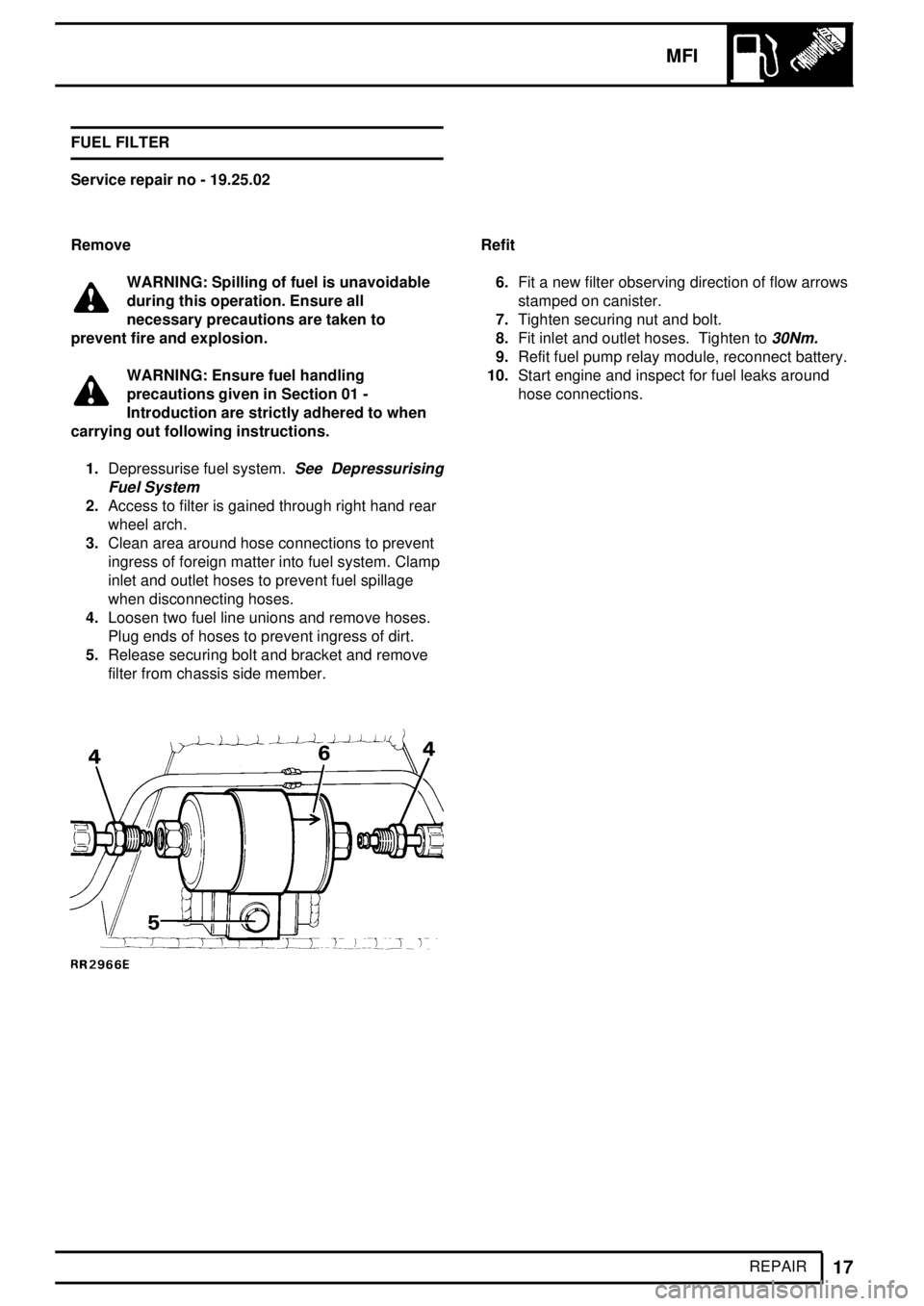
REPAIR FUEL FILTER
Service repair no - 19.25.02
Remove
WARNING: Spilling of fuel is unavoidable
during this operation. Ensure all
necessary precautions are taken to
prevent fire and explosion.
WARNING: Ensure fuel handling
precautions given in Section 01 -
Introduction are strictly adhered to when
carrying out following instructions.
1.Depressurise fuel system.
See Depressurising
Fuel System
2.Access to filter is gained through right hand rear
wheel arch.
3.Clean area around hose connections to prevent
ingress of foreign matter into fuel system. Clamp
inlet and outlet hoses to prevent fuel spillage
when disconnecting hoses.
4.Loosen two fuel line unions and remove hoses.
Plug ends of hoses to prevent ingress of dirt.
5.Release securing bolt and bracket and remove
filter from chassis side member.
Refit
6.Fit a new filter observing direction of flow arrows
stamped on canister.
7.Tighten securing nut and bolt.
8.Fit inlet and outlet hoses. Tighten to
30Nm.
9.Refit fuel pump relay module, reconnect battery.
10.Start engine and inspect for fuel leaks around
hose connections.
Page 272 of 873

SFI
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
Description
The engine management system (EMS) maintains
optimum engine performance over the entire
operating range. The correct amount of fuel is
metered into each cylinder inlet tract and the ignition
timing is adjusted at each spark plug.
The system is controlled by the ENGINE CONTROL
MODULE (ECM) which receives data from sensors
located on and around the engine. From this
information it provides the correct fuel requirements
and ignition timing at all engine loads and speeds.
The fuel injection system uses a hot wire Mass Air
Flow Sensor to calculate the amount of air flowing into
the engine.
The ignition system does not use a distributor. It is a
direct ignition system (DIS), using four double ended
coils. The circuit to each coil is completed by
switching inside the ECM.
The on board diagnostic system detects any faults
which may occur within the EMS. Fault diagnosis
includes failure of all EMS sensors and actuators,
emissions related items, fuel supply and exhaust
systems.
The system incorporates certain default strategies to
enable the vehicle to be driven in case of sensor
failure. This may mean that a fault is not detected by
the driver. The fault is indicated by illumination of the
malfunction indicator light (MIL) on North American
specification vehicles.
A further feature of the system is 'robust
immobilisation'.Crankshaft position sensor (CKP Sensor)
The crankshaft position sensor is the most important
sensor on the engine. It is located in the left hand side
of the flywheel housing and uses a different thickness
of spacer for manual and automatic gearboxes. The
signal it produces informs the ECM:
- the engine is turning
- how fast the engine is turning
- which stage the engine is at in the cycle.
As there is no default strategy, failure of the
crankshaft sensor will result in the engine failing to
start. The fault is indicated by illumination of the
malfunction indicator light (MIL) on North American
specification vehicles.
Camshaft position sensor (CMP Sensor)
The camshaft position sensor is located in the engine
front cover. It produces one pulse every two
revolutions. The signal is used in two areas, injector
timing corrections for fully sequential fuelling and
active knock control.
If the camshaft sensor fails, default operation is to
continue normal ignition timing. The fuel injectors will
be actuated sequentially, timing the injection with
respect to top dead centre. Injection will either be
correct or one revolution out of synchronisation. The
fault is not easily detected by the driver. The fault is
indicated by illumination of the malfunction indicator
light (MIL) on North American specification vehicles.
Mass air flow sensor (MAF Sensor)
The 'hot wire' type mass air flow sensor is mounted
rigidly to the air filter and connected by flexible hose to
the plenum chamber inlet. The sensing element of the
MAF Sensor is a hot wire anenometer consisting of
two wires, a sensing wire which is heated and a
compensating wire which is not heated. Air flows
across the wires cooling the heated one, changing its
resistance. The ECM measures this change in
resistance and calculates the amount of air flowing
into the engine.
As there is no default strategy, failure will result in the
engine starting, and dying when it reaches 550
rev/min, when the ECM detects no MAF Sensor
signal. The fault is indicated by illumination of the
malfunction indicator light (MIL) on North American
specification vehicles.