1995 LAND ROVER DISCOVERY coolant temperature
[x] Cancel search: coolant temperaturePage 237 of 873

MFI
1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION DESCRIPTION
Hot Wire Multiport Fuel Injection
The 'Hot Wire' Multiport fuel injection system derives
its name from the mass air flow sensor which uses
one cold wire and one electrically heated wire to
measure the volume of air entering the engine.
The function of the system is to supply the exact
amount of fuel directly into the intake manifold
according to the prevailing engine operating
conditions.
To monitor these conditions, various sensors are fitted
to the engine to measure engine parameters. Data
from the sensors is received by the Engine control
module (ECM), the ECM will then determine the exact
amount of fuel required at any condition.
The ECM having received data from the sensors
produces pulses, the length of which will determine
the simultaneous open time of each bank of injectors
in turn, which will govern the amount of fuel injected.
Engine control module - ECM
The Multiport fuel injection system is controlled by the
14 CUX Engine Control Module comprising of a
microprocessor with integrated circuits and
components mounted on printed circuit boards. The
ECM is connected to the main harness by a 40 pin
plug.
Injectors
The eight fuel injectors are fitted between the
pressurized fuel rail and inlet manifold. Each injector
comprises a solenoid operated needle valve with a
movable plunger rigidly attached to the nozzle valve.
When the solenoid is energized the plunger is
attracted off its seat and allows pressurized fuel into
the intake manifold.Engine coolant temperature sensor
The engine coolant temperature sensor is located in
the front of the thermostat housing. The sensor
provides engine coolant information to the ECM. The
ECM increases the injector opening time when cold to
provide improved driveability, and reduces the
opening time as the engine reaches normal operating
temperature.
Engine fuel temperature sensor
The engine fuel temperature sensor is located in the
rail on the RH side of the ram housing. The sensor
sends fuel temperature data to the ECM, the ECM on
receiving the data will adjust the injector open time
accordingly to produce good hot starting in high
ambient temperatures.
Idle air control valve
The idle air control valve is screwed into a housing
attached to the rear of the plenum chamber, between
the plenum chamber and bulkhead. The idle air
control valve has two windings which enable the
motor to be energised in both directions thus opening
or closing the air valve as required by the ECM.
The idle air control valve will open and allow extra air
into the plenum chamber to maintain engine idle
speed when the engine is under increased (Electrical
and Mechanical) loads.
The idle air control valve will control engine idle speed
when the vehicle is stationary.
Heated oxygen sensors (0
2sensors) - Catalyst
vehicles
The two heated oxygen sensors are located forward
of the catalysts mounted in the exhaust downpipes.
The sensors monitor the oxygen content of the
exhaust gases and provide feedback information of
the air/fuel ratio to the ECM. Each sensor is heated by
an electrical element to improve its response time
when the ignition is switched on.
Page 239 of 873

MFI
3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Tune select resistor -
To suit individual market requirements a tune select
resistor is connected across pins 5 and 27 of the
ECM.
It is located adjacent to the ECM, and strapped to the
MFI cable assembly. The value of the resistor is
dependent on the market application:
Red wire, 180 ohms, Australia, Rest of world.
Green wire, 470 Ohms, UK and Europe - non catalyst.
Yellow wire 910 Ohms, Saudi non catalyst.
White wire, 3K9 Ohms, European catalyst
Condenser fans
It should be noted that under high coolant
temperatures, when the engine is switched off, the
condenser fans will be activated and will run for
approximately ten minutes.Vehicle speed sensor
The vehicle speed sensor is located on the side of the
Transfer box adjacent to the parking brake. The
sensor provides road speed data to the ECM. The
ECM in turn detects vehicle movement from the road
speed input and ensures that idle air control mode is
disengaged. Should the vehicle speed sensor fail in
service the ECM idle air control would become erratic.
The sensor also provides road speed data to the
electric speedometer and cruise control ECU.
Inertia fuel shutoff switch
The inertia fuel shutoff switch is a mechanically
operated switch, located on the bulkhead adjacent to
the washer reservoir under bonnet [hood].
The switch is normally closed and is in line with the
fuel pump. In the event of a sudden impact the switch
opens, and disconnects the electrical feed to the fuel
pump. The switch is reset by pressing down the
button.
WARNING: Check the integrity of the fuel
system before the inertia switch is reset.
Relay modules
The two multiport fuel injection relays are located in
the RH footwell area behind the 'A' post panel. The
main relay module is energized via the ECM when the
ignition is switched on and supplies current to the
multiport fuel injection system. The fuel pump relay
module is energized by the ECM which in turn
operates the fuel pump to pressurize the fuel system.
Page 240 of 873

19FUEL SYSTEM
4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ENGINE MOUNTED COMPONENTS
1. By-pass air valve (stepper motor).
2. Fuel pressure regulator.
3. Air flow meter.
4. Throttle potentiometer.
5. Fuel temperature sensor.
6. Coolant temperature sensor.
7. Fuel injector.
Page 252 of 873

19FUEL SYSTEM
6
REPAIR ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Service repair no - 19.22.18
Remove
1.Position drain tray to collect coolant spillage.
2.Disconnect multiplug from coolant sensor.
3.Remove sensor from thermostat housing.
4.Remove and discard copper washer.
Refit
5.Fit a new copper washer.
6.Fit sensor and tigten securely.
7.Top-up cooling system.
8.Run engine, check for water leaks around
sensor.DEPRESSURISING FUEL SYSTEM
WARNING: Under normal operating
conditions the Multiport fuel injection
system is pressurised by a high pressure
fuel pump, operating at up to 2.3 to 2.5 bar When
engine is stationary pressure is maintained within
system. To prevent pressurised fuel escaping and
to avoid personal injury it is necessary to
depressurise multiport fuel injection system
before any service operations are carried out.
If vehicle has not been run there will be a small
amount of residual pressure in fuel line. The
depressurising procedure must still be carried out
before disconnecting any component within the
fuel system.
The spilling of fuel is unavoidable during this
operation. Ensure that all necessary precautions
are taken to prevent fire and explosion.
1.Remove fuel pump relay module.
See
Multiport Fuel Injection Relays
2.Start and run engine.
3.When sufficient fuel has been used to cause fuel
line pressure to drop, injectors will become
inoperative, resulting in engine stall. Switch off
ignition.
4.Disconnect battery negative lead.
NOTE: Fuel at low pressure will remain in
system. To remove low pressure fuel,
place absorbent cloth around fuel feed
hose at fuel rail.
5.Disconnect either:
a) Nut and olive at fuel rail
OR
b) Hose at inlet end of fuel filter.
Refit
6.Refit fuel feed hose.
7.Refit fuel pump relay module, reconnect battery.
8.Crank engine (engine will fire in approximately 6
to 8 seconds).
Page 260 of 873
19FUEL SYSTEM
14
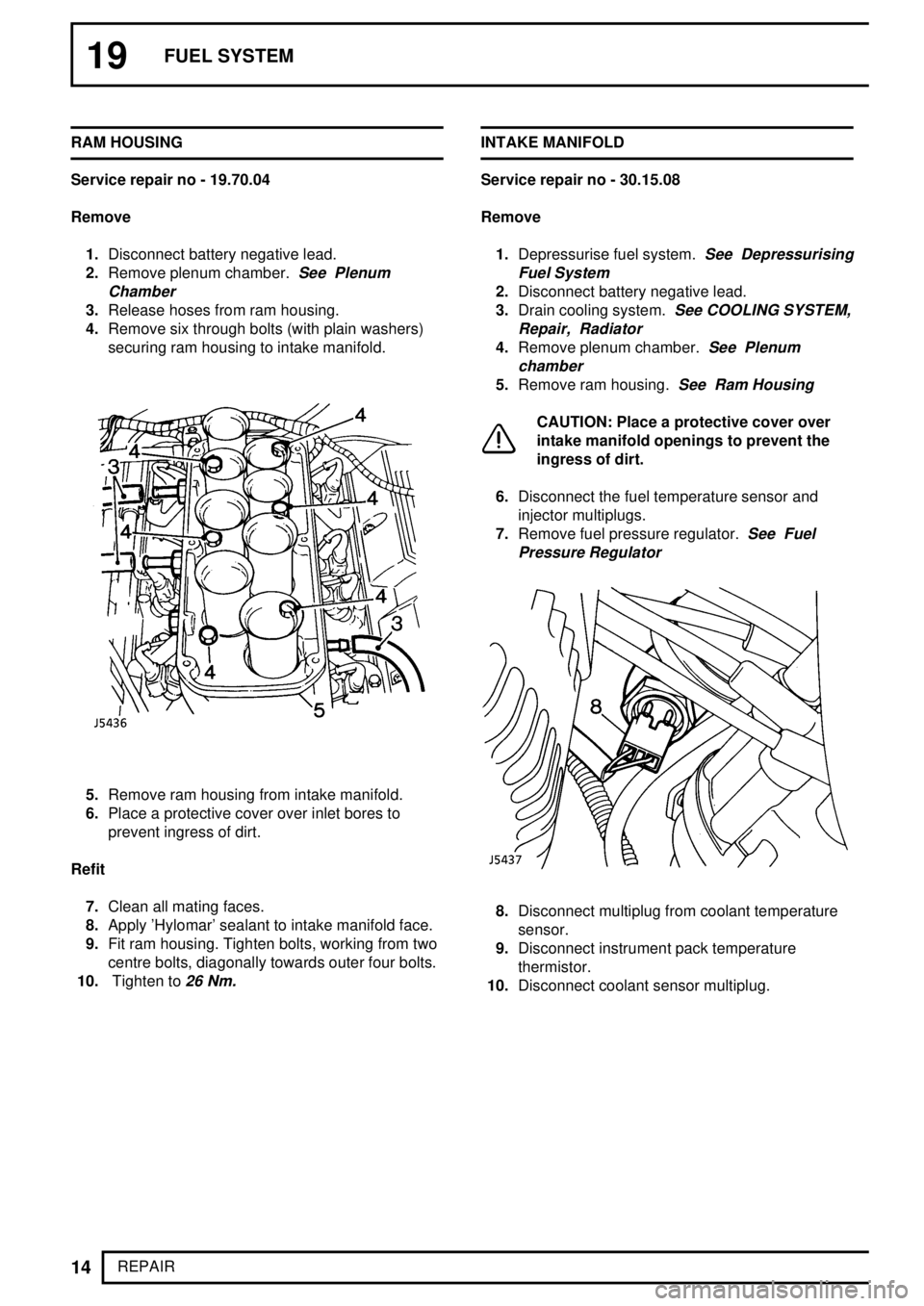
REPAIR RAM HOUSING
Service repair no - 19.70.04
Remove
1.Disconnect battery negative lead.
2.Remove plenum chamber.
See Plenum
Chamber
3.Release hoses from ram housing.
4.Remove six through bolts (with plain washers)
securing ram housing to intake manifold.
5.Remove ram housing from intake manifold.
6.Place a protective cover over inlet bores to
prevent ingress of dirt.
Refit
7.Clean all mating faces.
8.Apply 'Hylomar' sealant to intake manifold face.
9.Fit ram housing. Tighten bolts, working from two
centre bolts, diagonally towards outer four bolts.
10.Tighten to
26 Nm.
INTAKE MANIFOLD
Service repair no - 30.15.08
Remove
1.Depressurise fuel system.
See Depressurising
Fuel System
2.Disconnect battery negative lead.
3.Drain cooling system.
See COOLING SYSTEM,
Repair, Radiator
4.Remove plenum chamber.See Plenum
chamber
5.Remove ram housing.See Ram Housing
CAUTION: Place a protective cover over
intake manifold openings to prevent the
ingress of dirt.
6.Disconnect the fuel temperature sensor and
injector multiplugs.
7.Remove fuel pressure regulator.
See Fuel
Pressure Regulator
8.Disconnect multiplug from coolant temperature
sensor.
9.Disconnect instrument pack temperature
thermistor.
10.Disconnect coolant sensor multiplug.
Page 273 of 873

19FUEL SYSTEM
2
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION REV: 09/95 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM COMPONENT
LOCATION - PRE ADVANCED EVAPS
1. Engine control module
2. Ignition coils
3. Fuel pressure regulator
4. Mass air flow sensor
5. Relay module
- Main relay
- Fuel pump relay
6. Engine coolant temperature sensor
7. Camshaft position sensor
8. Throttle position sensor
Page 275 of 873

19FUEL SYSTEM
4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION Throttle position sensor (TP Sensor)
The throttle position sensor is mounted on the plenum
chamber and connected directly to the throttle shaft.
The sensor is a variable resistor, the signal from
which (0 - 5V) informs the ECM of the actual position
of the throttle disc. As there is no default strategy,
failure of the sensor will result in poor idle and lack of
throttle response. If failure occurs in the closed
position the engine will only reach 1750 rev/min when
the ECM will initiate overrun fuel cut off. The fault is
indicated by illumination of the malfunction indicator
light (MIL) on North American specification vehicles.
Engine coolant temperature sensor (ECT Sensor)
This sensor consists of a temperature dependant
resistive metal strip. The resistance of the strip varies
considerably with coolant temperature, i.e. from 28K
ohms at - 30°C to 90 ohms at 130°C, and 300 Ohms
at 85°C. The ECT Sensor signal is vital to engine
running, as the correct fuelling is dependant upon
engine temperature i.e. richer mixture at low
temperatures. If the sensor is disconnected or failure
occurs a default value will be supplied to the system.
The initial default value selected will be based on the
value of the air intake temperature. This will increase
to a nominal warmed up value over an individual time,
programmed for each default value. The fault may not
be evident to the driver, there may be a hot restart
problem. The fault is indicated by illumination of the
malfunction indicator light (MIL) on North American
specification vehicles.Intake air temperature sensor (IAT Sensor)
This is another resistive sensor, located in the body of
the air cleaner. The resistance varies with changes in
air temperature. The signal from the IAT Sensor is
used to retard the ignition timing if the air temperature
rises above 55°C. If the sensor is disconnected or
failure occurs a default value will be supplied to the
system. The default value selected will represent
normal operating conditions. The fault may not be
evident to the driver, there may be slight power loss in
high ambient temperatures. The fault is indicated by
illumination of the malfunction indicator light (MIL) on
North American specification vehicles.
Page 279 of 873

19FUEL SYSTEM
8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ADD: 09/95 ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM COMPONENT
LOCATION - ADVANCED EVAPS
1.Engine control module (ECM)
2.Ignition coils
3.Fuel pressure regulator
4.Mass air flow (MAF) sensor
5.Relay module
- Main relay
- Fuel pump relay
6.Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
7.Camshaft position (CMP) sensor
8.Throttle position (TP) sensor