1995 JEEP YJ ECU
[x] Cancel search: ECUPage 238 of 2158

(3) Install clutch master cylinder push rod on
pedal. Secure rod with washer(s) and new cotter pin.
(4) Connect clutch pedal position switch wires.
(5) Install instrument panel lower trim cover, if re-
moved.
FLYWHEEL SERVICE
Inspect the flywheel whenever the clutch disc,
cover and housing are removed for service. Check
condition of the flywheel face, hub, ring gear teeth,
and flywheel bolts.
Minor scratches, burrs, or glazing on the flywheel
face can be reduced with 180 grit emery cloth. How-
ever, the flywheel should be replaced if the disc con-
tact surface is severely scored, heat checked, cracked,
or obviously worn.
Flywheel machining is not recommended. The fly-
wheel surface is manufactured with a unique contour
that would be negated by machining. However,
cleanup of minor flywheel scoring can be performed
by hand with 180 grit emery, or with surface grind-
ing equipment. Replace the flywheel if scoring is
deeper than 0.0762 mm (0.003 in.).
Heavy stock removal by grinding isnot recom-
mended.Excessive stock removal can result in fly-
wheel cracking or warpage after installation. It can
also weaken the flywheel and interfere with proper
clutch release.
Check flywheel runout if misalignment is sus-
pected. Runout should not exceed 0.08 mm (0.003
in.). Measure runout at the outer edge of the fly-
wheel face with a dial indicator. Mount the dial indi-
cator on a stud installed in place of one of the
flywheel attaching bolts.
Clean the crankshaft flange before mounting the
flywheel. Dirt and grease on the flange surface may
cock the flywheel causing excessive runout.
Check condition of the flywheel hub and attaching
bolts. Replace the flywheel if the hub exhibits cracks
in the area of the attaching bolt holes.
Install new attaching bolts whenever the flywheelis replaced and use Mopar Lock N' Seal, or Loctite
242 on the replacement bolt threads.
Recommended flywheel bolt torques are:
²142 Nzm (105 ft. lbs.) for 6-cylinder flywheels
²68 Nzm (50 ft. lbs.) plus an additional turn of 60É
for 4-cylinder flywheels
Inspect the teeth on the starter ring gear.If the
teeth are worn or damaged, the flywheel should
be replaced as an assembly. This is the recom-
mended and preferred method of repair.
In cases where a new flywheel is not readily avail-
able, a replacement ring gear can be installed. How-
ever, the following precautions must be observed to
avoid damaging the flywheel and replacement gear.
(a) Mark position of the old gear for alignment
reference on the flywheel. Use a scriber for this
purpose.
(b) Wear protective goggles or approved safety
glasses. Also wear heat resistent gloves when han-
dling a heated ring gear.
(c) Remove the old gear by cutting most of the
way through it (at one point) with an abrasive cut-
off wheel. Then complete removal with a cold chisel
or punch.
(d) The ring gear is a shrink fit on the flywheel.
This means the gear must be expanded by heating
in order to install it.The method of heating and
expanding the gear is extremely important.
Every surface of the gear must be heated at the
same time to produce uniform expansion. An oven
or similar enclosed heating device must be used.
Temperature required for uniform expansion is ap-
proximately 375É F.
CAUTION: Do not use an oxy/acetylene torch to re-
move the old gear, or to heat and expand a new
gear. The high temperature of the torch flame can
cause localized heating that will damage the fly-
wheel. In addition, using the torch to heat a replace-
ment gear will cause uneven heating and
expansion. The torch flame can also anneal the
gear teeth resulting in rapid wear and damage after
installation.
(e) The heated gear must be installed evenly to
avoid misalignment or distortion. A shop press and
suitable press plates should be used to install the
gear if at all possible.
(f) Be sure to wear eye and hand protection.
Heat resistent gloves and safety goggles are needed
for personal safety. Also use metal tongs, vise grips,
or similar tools to position the gear as necessary
for installation.
(g) Allow the flywheel and ring gear to cool down
before installation. Set the assembly on a work-
bench and let it cool in normal shop air.
Fig. 16 Clutch Pedal Mounting (XJ)
6 - 16 CLUTCH SERVICEJ
Page 273 of 2158

VISCOUS FAN DRIVE
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Also refer to the previous section on Cooling Sys-
tem Fans.
The thermal viscous fan drive (Fig. 38 or 39) is a
silicone-fluid-filled coupling used to connect the fan
blades to either the engine or the water pump shaft.
The coupling allows the fan to be driven in a normal
manner. This is done at low engine speeds while lim-
iting the top speed of the fan to a predetermined
maximum level at higher engine speeds.
A thermostatic bimetallic spring coil is located on
the front face of the viscous fan drive unit (a typical
viscous unit is shown in figure 40). This spring coil
reacts to the temperature of the radiator discharge
air. It engages the viscous fan drive for higher fan
speed if the air temperature from the radiator rises
above a certain point. Until additional engine cooling
is necessary, the fan will remain at a reduced rpm re-
gardless of engine speed.
Only when sufficient heat is present, will the vis-
cous fan drive engage. This is when the air flowing
through the radiator core causes a reaction to the bi-
metallic coil. It then increases fan speed to provide
the necessary additional engine cooling.
Once the engine has cooled, the radiator discharge
temperature will drop. The bimetallic coil again re-
acts and the fan speed is reduced to the previous dis-
engaged speed.
CAUTION: Engines equipped with serpentine drive
belts have reverse rotating fans and viscous fan
drives. They are marked with the word REVERSE to
designate their usage. Installation of the wrong fan
or viscous fan drive can result in engine overheat-
ing.CAUTION: If the viscous fan drive is replaced be-
cause of mechanical damage, the cooling fan
blades should also be inspected. Inspect for fatigue
cracks, loose blades, or loose rivets that could
have resulted from excessive vibration. Replace fan
blade assembly if any of these conditions are
found. Also inspect water pump bearing and shaft
assembly for any related damage due to a viscous
fan drive malfunction.
NOISE
It is normal for fan noise to be louder (roar-
ing) when:
²The underhood temperature is above the engage-
ment point for the viscous drive coupling. This may
occur when ambient (outside air temperature) is very
high.
²Engine loads and temperatures are high such as
when towing a trailer.
²Cool silicone fluid within the fan drive unit is be-
ing redistributed back to its normal disengaged
(warm) position. This can occur during the first 15
seconds to one minute after engine start-up on a cold
engine.
LEAKS
Viscous fan drive operation is not affected by small
oil stains near the drive bearing. If leakage appears
excessive, replace the fan drive unit.
TESTING
If the fan assembly free-wheels without drag (the
fan blades will revolve more than five turns when
spun by hand), replace the fan drive. This spin test
must be performed when the engine is cool.
For the following test, the cooling system must be
in good condition. It also will ensure against exces-
sively high coolant temperature.
WARNING: BE SURE THAT THERE IS ADEQUATE
FAN BLADE CLEARANCE BEFORE DRILLING.
(1) Drill a 3.18-mm (1/8-in) diameter hole in the
top center of the fan shroud.
(2) Obtain a dial thermometer with an 8 inch stem
(or equivalent). It should have a range of -18É-to-
105ÉC (0É-to-220É F). Insert thermometer through the
hole in the shroud. Be sure that there is adequate
clearance from the fan blades.
(3) Connect a tachometer and an engine ignition
timing light (timing light is to be used as a strobe
light).
(4) Block the air flow through the radiator. Secure
a sheet of plastic in front of the radiator (or air con-
ditioner condenser). Use tape at the top to secure the
plastic and be sure that the air flow is blocked.
Fig. 40 Typical Viscous Fan Drive
7 - 34 COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURESJ
Page 283 of 2158

ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
GENERAL INFORMATION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
An optional engine block heater is available for all
models. The heater is equipped with a power cord.
The cord is attached to an engine compartment com-
ponent with tie-straps. The heater warms the engine
providing easier engine starting and faster warm-up
in low temperatures. The heater is mounted in a core
hole of the engine cylinder block (in place of a freeze
plug) with the heating element immersed in engine
coolant. Connect the power cord to a grounded 110-
120 volt AC electrical outlet with a grounded, three-
wire extension cord.
WARNING: DO NOT OPERATE ENGINE UNLESS
BLOCK HEATER CORD HAS BEEN DISCONNECTED
FROM POWER SOURCE AND SECURED IN PLACE.
BLOCK HEATER SPECIFICATIONS
²2.5L 4-Cylinder Engine: 115 Volts 400 Watts
²4.0L 6-Cylinder Engine: 120 Volts 600 Watts
REMOVAL
Refer to correct illustration (Figures 11, 12 or 13)
when servicing block heater.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND PRES-
SURIZED. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
(1) Drain coolant from radiator and engine cylinder
block.(2) Unplug power cord from block heater.
(3) Loosen screw in center of block heater (Figs. 11,
12 or 13).
(4) Remove block heater from cylinder block.
INSTALLATION
(1) Thoroughly clean the engine core hole and the
block heater seat.
(2) Insert block heater assembly into core hole
with element loop pointingUp.
(3) Seat block heater flush against block face.
Tighten mounting screw to 3.6 Nzm (32 in. lbs.)
torque.
(4) Fill cooling system with coolant. Pressurize sys-
tem and inspect for leaks.
(5) Plug power cord into block heater. Route cord
away from moving parts, linkages and exhaust sys-
tem components. Secure cord in place with tie-straps.
Fig. 13 Heater and CordÐYJ Models
Fig. 11 Heater and CordÐXJ with 2.5L 4-Cylinder
Engine
Fig. 12 Heater and CordÐXJ with 4.0L 6-Cylinder
Engine
7 - 44 ENGINE BLOCK HEATERJ
Page 295 of 2158

IGNITION-OFF DRAW
GENERAL INFORMATION
Ignition-Off Draw (IOD) refers to power being
drained from the battery with the ignition switch
turned OFF. A normal vehicle electrical system will
draw from 5 to 20 milliamps (0.005 - 0.020 amps).
This is with the ignition switch in the OFF position,
and all non-ignition controlled circuits in proper
working order. The 20 milliamps are needed to sup-
ply PCM memory, digital clock memory, and electron-
ically-tuned radio memory.
A vehicle that has not been operated for approxi-
mately 20 days, may discharge the battery to an in-
adequate level. When a vehicle will not be used for
20 days or more (stored), remove the IOD fuse in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). This will reduce
battery discharging.
Excessive battery drain can be caused by:
²electrical items left on
²faulty or improperly adjusted switches
²internally shorted generator
²intermittent shorts in the wiring.
If the IOD is over 20 milliamps, the problem must
be found and corrected before replacing a battery. In
most cases, the battery can be charged and returned
to service.
DIAGNOSIS
Testing for high-amperage IOD must be per-
formed first to prevent damage to most milli-
amp meters.
(1) Verify that all electrical accessories are off.
Turn off all lamps, remove ignition key, and close all
doors. If the vehicle is equipped with illuminated en-
try or electronically-tuned radio, allow the systems to
automatically shut off (time out). This may take up
to 3 minutes.
(2) Determine that the underhood lamp is operat-
ing properly, then disconnect or remove bulb.
(3) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(4) Connect a typical 12-volt test lamp (low-watt-
age bulb) between the negative cable clamp and the
battery negative terminal. Make sure that the doors
remain closed so that illuminated entry is not acti-
vated.The test lamp may light brightly for up to 3 min-
utes, or may not light at all, depending upon the ve-
hicle's electrical equipment. The term brightly, as
used throughout the following tests, implies the
brightness of the test lamp will be the same as if it
were connected across the battery.
The test lamp must be securely clamped to the neg-
ative cable clamp and battery negative terminal. If
the test lamp becomes disconnected during any part
of the IOD test, the electronic timer function will be
activated and all tests must be repeated.
(5) After 3 minutes the test lamp should turn off
or be dimly lit, depending upon the vehicle's electri-
cal equipment. If the test lamp remains brightly lit,
do not disconnect it. Remove each fuse or circuit
breaker (refer to Group 8W - Wiring Diagrams) until
test lamp is either off or dimly lit. This will isolate
each circuit and identify the source of the high-am-
perage draw.
If the test lamp is still brightly lit after disconnect-
ing each fuse and circuit breaker, disconnect the wir-
ing harness from the generator. If test lamp now
turns off or is dimly lit, see Charging System in this
group to diagnose faulty generator. Do not disconnect
the test lamp.
After high-amperage IOD has been corrected, low-
amperage IOD may be checked. It is now safe to in-
stall a milliamp meter to check for low- amperage
IOD.
(6) With test lamp still connected securely, clamp a
milliamp meter between battery negative terminal
and negative cable clamp.
Do not open any doors or turn on any electri-
cal accessories with the test lamp disconnected
or the milliamp meter may be damaged.
(7) Disconnect test lamp. Observe milliamp meter.
The current draw should not exceed 0.020 amp. If
draw exceeds 20 milliamps, isolate each circuit by re-
moving circuit breakers and fuses. The milliamp
meter reading will drop when the source of the draw
is disconnected. Repair this circuit as necessary,
whether a wiring short, incorrect switch adjustment
or a component failure is found.
8A - 10 BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICSJ
Page 343 of 2158

CAUTION: On some models, two bolts are used to
secure the sensor to the transmission. These bolts
are specially machined to correctly space the unit
to the flywheel. Do not attempt to install any other
bolts.
(3) Connect the electrical connector to the sensor.
(4) Install clip on sensor wire harness.
(5) Install clip over fuel rail mounting stud. Install
clip mounting nut.
INSTALLATIONÐYJ MODELS WITH 4.0L
6-CYLINDER ENGINE AND AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
(1) Install the sensor into the access hole on the
transmission.
(2) Install sensor mounting bolt (Fig. 6).
(3) Tighten sensor mounting bolt to 6-to-8 Nzm (50-
to-70 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Connect the electrical connector to sensor.
(5) Install the clip to sensor wire harness.
(6) Install clip over fuel rail mounting stud. Install
clip mounting nut.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
For an operational description, diagnosis and re-
moval/installation procedures, refer to Group 14,
Fuel System.
DISTRIBUTOR
GENERAL INFORMATION
All distributors contain an internal oil seal that
prevents oil from entering the distributor housing.
The seal is not serviceable.
Factory replacement distributors are equipped with
a plastic alignment pin already installed. The pin is
located in an access hole on the bottom of the distrib-
utor housing (Fig. 7). It is used to temporarily lock
the rotor to the cylinder number 1 position during in-
stallation. The pin must be removed after installing
the distributor.
The camshaft position sensor is located in the dis-
tributor on all engines (Fig. 8). For removal/installa-
tion procedures, refer to Camshaft Position Sensor.
Distributor removal is not necessary for sensor re-
moval.
Refer to figure 8 for an exploded view of the dis-
tributor.
A fork with a slot is supplied on the bottom of the
distributor housing where the housing base seats
against the engine block (Fig. 8). The centerline of
the slot aligns with the distributor holddown bolt
hole in the engine block. Because of the fork, the dis-
tributor cannot be rotated. Distributor rotation is not
necessary as all ignition timing requirements are
handled by the powertrain control module (PCM).The position of the distributor determines fuel syn-
chronization only. It does not determine ignition tim-
ing.
Do not attempt to modify this fork to attain
ignition timing.
Fig. 7 Plastic Alignment Pin
Fig. 8 DistributorÐ2.5L Or 4.0L EnginesÐTypical
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 19
Page 348 of 2158
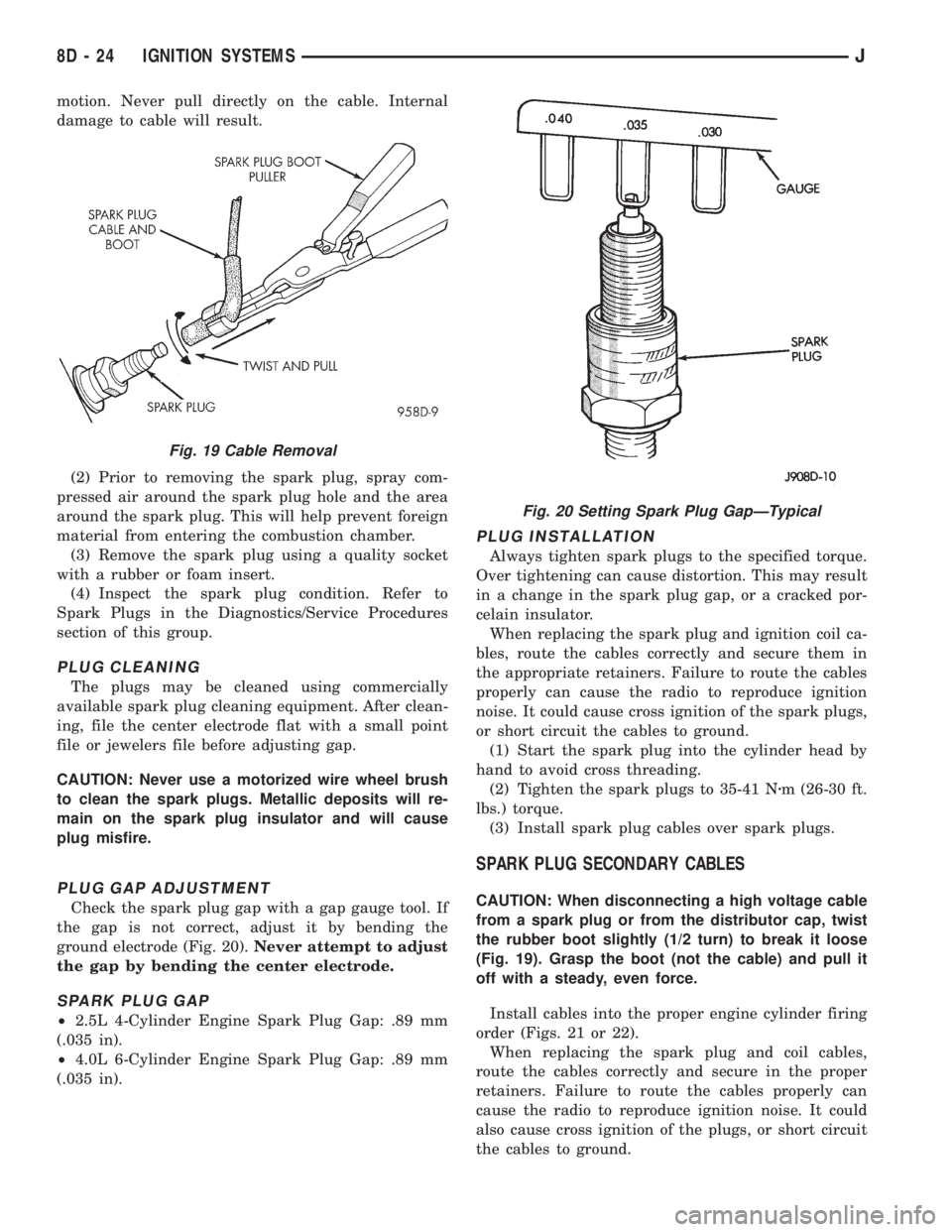
motion. Never pull directly on the cable. Internal
damage to cable will result.
(2) Prior to removing the spark plug, spray com-
pressed air around the spark plug hole and the area
around the spark plug. This will help prevent foreign
material from entering the combustion chamber.
(3) Remove the spark plug using a quality socket
with a rubber or foam insert.
(4) Inspect the spark plug condition. Refer to
Spark Plugs in the Diagnostics/Service Procedures
section of this group.
PLUG CLEANING
The plugs may be cleaned using commercially
available spark plug cleaning equipment. After clean-
ing, file the center electrode flat with a small point
file or jewelers file before adjusting gap.
CAUTION: Never use a motorized wire wheel brush
to clean the spark plugs. Metallic deposits will re-
main on the spark plug insulator and will cause
plug misfire.
PLUG GAP ADJUSTMENT
Check the spark plug gap with a gap gauge tool. If
the gap is not correct, adjust it by bending the
ground electrode (Fig. 20).Never attempt to adjust
the gap by bending the center electrode.
SPARK PLUG GAP
²2.5L 4-Cylinder Engine Spark Plug Gap: .89 mm
(.035 in).
²4.0L 6-Cylinder Engine Spark Plug Gap: .89 mm
(.035 in).
PLUG INSTALLATION
Always tighten spark plugs to the specified torque.
Over tightening can cause distortion. This may result
in a change in the spark plug gap, or a cracked por-
celain insulator.
When replacing the spark plug and ignition coil ca-
bles, route the cables correctly and secure them in
the appropriate retainers. Failure to route the cables
properly can cause the radio to reproduce ignition
noise. It could cause cross ignition of the spark plugs,
or short circuit the cables to ground.
(1) Start the spark plug into the cylinder head by
hand to avoid cross threading.
(2) Tighten the spark plugs to 35-41 Nzm (26-30 ft.
lbs.) torque.
(3) Install spark plug cables over spark plugs.
SPARK PLUG SECONDARY CABLES
CAUTION: When disconnecting a high voltage cable
from a spark plug or from the distributor cap, twist
the rubber boot slightly (1/2 turn) to break it loose
(Fig. 19). Grasp the boot (not the cable) and pull it
off with a steady, even force.
Install cables into the proper engine cylinder firing
order (Figs. 21 or 22).
When replacing the spark plug and coil cables,
route the cables correctly and secure in the proper
retainers. Failure to route the cables properly can
cause the radio to reproduce ignition noise. It could
also cause cross ignition of the plugs, or short circuit
the cables to ground.
Fig. 19 Cable Removal
Fig. 20 Setting Spark Plug GapÐTypical
8D - 24 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 355 of 2158
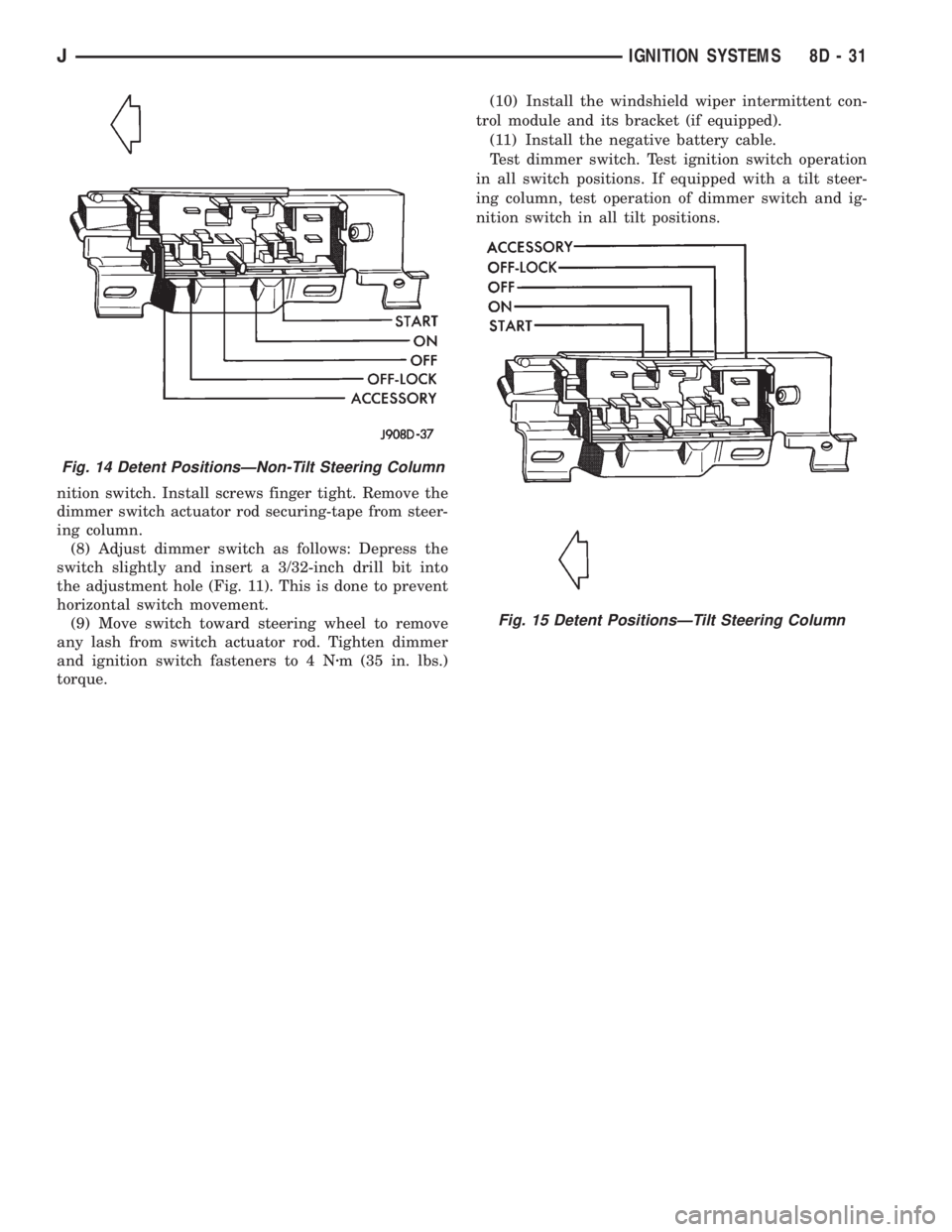
nition switch. Install screws finger tight. Remove the
dimmer switch actuator rod securing-tape from steer-
ing column.
(8) Adjust dimmer switch as follows: Depress the
switch slightly and insert a 3/32-inch drill bit into
the adjustment hole (Fig. 11). This is done to prevent
horizontal switch movement.
(9) Move switch toward steering wheel to remove
any lash from switch actuator rod. Tighten dimmer
and ignition switch fasteners to 4 Nzm (35 in. lbs.)
torque.(10) Install the windshield wiper intermittent con-
trol module and its bracket (if equipped).
(11) Install the negative battery cable.
Test dimmer switch. Test ignition switch operation
in all switch positions. If equipped with a tilt steer-
ing column, test operation of dimmer switch and ig-
nition switch in all tilt positions.
Fig. 14 Detent PositionsÐNon-Tilt Steering Column
Fig. 15 Detent PositionsÐTilt Steering Column
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 31
Page 376 of 2158

(3) Reach under the instrument panel and depress
the switch shaft release/retainer button (Fig. 14).
Pull the switch control knob and shaft outward.
(4) Remove the headlamp switch retaining nut
from the front of the instrument panel (Fig. 15).(5) Disconnect the wire harness connector from the
switch.
(6) Remove the headlamp switch from the instru-
ment panel.
(7) Reverse removal procedures to install.
INSTRUMENT PANEL REMOVE/INSTALL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove the following (Fig. 16):
²parking brake release handle
²lower heat/AC duct below steering column
²ash receiver
²lower instrument panel
²cluster bezel
²cluster assembly
²radio
²climate control panel
²instrument panel switches
²headlamp switch
²antenna connector
²blower motor resistors
²ground lead
²unplug glove box lamp
²defroster cowl outlet panel
Remove driver's side heat/AC outlet to gain
access to driver's side defroster cowl outlet
panel retaining clip to aid in removal (Fig. 17).
²instrument panel attaching bolts
²steering column attaching bolts
²instrument panel assembly.
The instrument panel wiring harness is at-
tached to the back of the instrument panel as-
sembly and must be installed correctly.
(3) To install instrument panel, position instru-
ment panel assembly on side mounting bolts (Fig.
18).
(4) Route wiring harnesses and secure instrument
panel assembly mounting points.
(5) Connect tube to lap cooler.
(6) Reverse removal procedures to complete instal-
lation.
Fig. 13 Printed Circuit And Cluster Connector
Fig. 14 Headlamp Switch Knob And Shaft Remove/
Install
Fig. 15 Headlamp Switch Remove/Install
8E - 20 INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESÐXJJ