1995 JEEP YJ ABS
[x] Cancel search: ABSPage 158 of 2158

pedal. The proper course of action is to bleed the sys-
tem, or replace thin drums and suspect quality brake
lines and hoses.
HARD PEDAL OR HIGH PEDAL EFFORT
A hard pedal or high pedal effort may be due to lin-
ing that is water soaked, contaminated, glazed, or
badly worn. The power booster or check valve could
also be faulty. Test the booster and valve as described
in this section.
BRAKE DRAG
Brake drag occurs when the lining is in constant
contact with the rotor or drum. Drag can occur at one
wheel, all wheels, fronts only, or rears only. It is a
product of incomplete brakeshoe release. Drag can be
minor or severe enough to overheat the linings, ro-
tors and drums. A drag condition also worsens as
temperature of the brake parts increases.
Brake drag also has a direct effect on fuel economy.
If undetected, minor brake drag can be misdiagnosed
as an engine or transmission/torque converter prob-
lem.
Minor drag will usually cause slight surface char-
ring of the lining. It can also generate hard spots in
rotors and drums from the overheat/cool down pro-
cess. In most cases, the rotors, drums, wheels and
tires are quite warm to the touch after the vehicle is
stopped.
Severe drag can char the brake lining all the way
through. It can also distort and score rotors and
drums to the point of replacement. The wheels, tires
and brake components will be extremely hot. In se-
vere cases, the lining may generate smoke as it chars
from overheating.
An additional cause of drag involves the use of in-
correct length caliper mounting bolts. Bolts that are
too long can cause a partial apply condition. The cor-
rect caliper bolts have a shank length of 67 mm
(2.637 in.), plus or minus 0.6 mm (0.0236 in.). Refer
to the Disc Brake service section for more detail on
caliper bolt dimensions and identification.
Some common causes of brake drag are:
²loose or damaged wheel bearing
²seized or sticking caliper or wheel cylinder piston
²caliper binding on bolts or slide surfaces
²wrong length caliper mounting bolts (too long)
²loose caliper mounting bracket
²distorted rotor, brake drum, or shoes
²brakeshoes binding on worn/damaged support
plates
²severely rusted/corroded components
²misassembled components.
If brake drag occurs at all wheels, the problem may
be related to a blocked master cylinder compensatorport or faulty power booster (binds-does not release).
The condition will worsen as brake temperature in-
creases.
The brakelight switch can also be a cause of drag.
An improperly mounted or adjusted brakelight
switch can prevent full brake pedal return. The re-
sult will be the same as if the master cylinder com-
pensator ports are blocked. The brakes would be
partially applied causing drag.
BRAKE FADE
Brake fade is a product of overheating caused by
brake drag. However, overheating and subsequent
fade can also be caused by riding the brake pedal,
making repeated high deceleration stops in a short
time span, or constant braking on steep roads. Refer
to the Brake Drag information in this section for
causes.
PEDAL PULSATION (NON-ABS BRAKES ONLY)
Pedal pulsation is caused by parts that are loose,
or beyond tolerance limits. This type of pulsation is
constant and will occur every time the brakes are ap-
plied.
Disc brake rotors with excessive lateral runout or
thickness variation, or out of round brake drums are
the primary causes of pulsation.
On vehicles with ABS brakes, remember that pedal
pulsation is normal during antilock mode brake
stops. If pulsation occurs during light to moderate
brake stops, a standard brake part is either loose, or
worn beyond tolerance.
BRAKE PULL
A front pull condition could be the result of:
²contaminated lining in one caliper
²seized caliper piston
²binding caliper
²wrong caliper mounting bolts (too long)
²loose caliper
²loose or corroded mounting bolts
²improper brakeshoes
²damaged rotor
²incorrect wheel bearing adjustment (at one wheel)
A worn, damaged wheel bearing or suspension com-
ponent are further causes of pull. A damaged front
tire (bruised, ply separation) can also cause pull.
Wrong caliper bolts (too long) will cause a partial ap-
ply condition and pull if only one caliper is involved.
A common and frequently misdiagnosed pull condi-
tion is where direction of pull changes after a few
stops. The cause is a combination of brake drag fol-
lowed by fade at the dragging brake unit.
As the dragging brake overheats, efficiency is so re-
duced that fade occurs. If the opposite brake unit is
still functioning normally, its braking effect is magni-
5 - 6 SERVICE BRAKE DIAGNOSISJ
Page 162 of 2158

BRAKE FLUIDÐBRAKE BLEEDINGÐBRAKELINES AND HOSES
INDEX
page page
Brake Bleeding (With ABS Brakes)............ 11
Brake Bleeding (With Standard Brakes)......... 11
Brake Bleeding Recommendations............ 10
Brake Fluid Contamination.................. 10Brake Fluid Level......................... 10
Brakeline Charts.......................... 12
Brakelines and Hoses...................... 12
Recommended Brake Fluid.................. 10
RECOMMENDED BRAKE FLUID
Recommended brake fluid for Jeep vehicles is Mo-
par brake fluid, or an equivalent fluid meeting SAE
J1703 and DOT 3 standards. The recommendation
applies to models with standard or ABS brakes.
Use new brake fluid to top off the master cyl-
inder or refill the system. Never use reclaimed
fluid, fluid not meeting the SAE/DOT standards
or fluid from an unsealed container. Do not use
fluid from any container that has been left
open for any length of time. Fluid in open con-
tainers can absorb moisture.
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL
Always clean the master cylinder reservoir and
cover or cap before adding fluid. This avoids having
dirt from the cap or reservoir exterior fall into the
fluid.
If the vehicle has a one piece master cylinder, cor-
rect fluid level is to within 6 mm (1/4 in.) of the res-
ervoir rim (Fig. 1).
If the vehicle has a plastic reservoir with a single
cap, preferred fluid level is to the FULL mark (Fig.
2).
CAUTION: Do not allow brake fluid to contact
painted surfaces. Fluid spills must be cleaned up
immediately as brake fluid can loosen and lift paint.
BRAKE FLUID CONTAMINATION
Oil in the fluid will cause brake system rubber
seals to soften and swell. The seals may also become
porous and begin to deteriorate.If fluid contamination is suspected, drain off a sam-
ple from the master cylinder. A suction gun or similar
device can be used for this purpose.
Empty the drained fluid into a glass container.
Contaminants in the fluid will cause the fluid to sep-
arate into distinct layers. If contamination has oc-
curred, the system rubber seals, hoses and cups must
be replaced and the system thoroughly flushed with
clean brake fluid.
BRAKE BLEEDING RECOMMENDATIONS
²Use Mopar DOT 3 brake fluid, or an equivalent
meeting SAE/DOT standards J1703-F and DOT 3, to
fill and bleed the system.
²Bleeding can be performed manually, or with vac-
uum or pressure equipment. Vacuum and pressure
bleeding equipment are both available. Both types
are effective but should be used only as described in
the manufacturers instructions.
²Do not allow the master cylinder to run out of
fluid when bleeding the brakes. An empty cylinder
will allow additional air to be drawn into the system.
Check fluid level frequently during bleed operations.
²Do not pump the brake pedal at any time while
bleeding. Air in system will be compressed into small
Fig. 1 Correct Fluid Level (4-Cylinder Models)
Fig. 2 Correct Fluid Level (All Except 4-Cylinder
Models)
5 - 10 BRAKE FLUIDÐBRAKE BLEEDINGÐBRAKELINES AND HOSESJ
Page 163 of 2158

bubbles that are distributed throughout the hydrau-
lic system. This will make extra bleeding operations
necessary.
²Bleed only one wheel brake unit at a time and use
a bleed hose to bleed each wheel brake unit (Fig. 3).
²Attach one end of bleed hose to the bleed screw
and insert the opposite hose end in a glass container
partially filled with brake fluid (Fig. 3). A glass con-
tainer makes it easier to see air bubbles as they exit
the bleed hose. Be sure the end of the bleed hose is
immersed in fluid; this prevents air from being
drawn back into cylinder and brakeline.
BRAKE BLEEDING (WITH STANDARD BRAKES)
(1) If master cylinder has been overhauled or a
new cylinder will be installed, bleed cylinder on
bench before installation. This shortens time needed
to bleed system and ensures proper cylinder opera-
tion.
(2) Wipe master cylinder reservoir and cap clean
with shop towels. Then fill cylinder reservoir with
Mopar brake fluid.
(3) Open all caliper and wheel cylinder bleed
screws. Close bleed screws after fluid begins flowing
from each bleed screw.
(4) Top off master cylinder reservoir again.
(5) Bleed master cylinder and combination valve at
brakeline fittings. Have helper operate brake pedal
while bleeding cylinder and valve.
(6) Bleed wheel brakes in recommended sequence
which is: right rear; left rear; right front; left front.
Bleed procedure is as follows:
(a) Open caliper or wheel cylinder bleed fitting
1/2 to 3/4 turn.
(b) Have helper depress and hold brake pedal to
floorpan.
(c) Tighten bleed fitting and have helper release
brake pedal. Continue bleeding operation until
fluid entering bleed container is clear and free of
bubbles.
(d) Repeat bleeding operation at remaining
wheel brake units.
(7) Top off master cylinder fluid level and verify
proper brake operation before moving vehicle.
BRAKE BLEEDING (WITH ABS BRAKES)
ABS system bleeding requires conventional bleed-
ing methods plus use of the DRB scan tool. The pro-
cedure involves performing a conventional bleed,
followed by use of the scan tool to cycle and bleed the
HCU pump and solenoids. A second conventional
bleed procedure is then required remove any air re-
maining in the system.
(1) If a new master cylinder is to be installed,
bleed cylinder on bench before installing it in vehicle.
Refer to procedure in section covering master cylin-
der service.(2) Wipe master cylinder reservoir and cap clean
before removing cap. This avoids having dirt fall into
fluid. Then fill reservoir with Mopar brake fluid.
(3) Perform conventional brake bleed as described
in steps (4) and (5).
(4) Bleed master cylinder and combination valve at
brakeline fittings. Have helper depress and release
brake pedal while bleeding cylinder and valve.
(5) Bleed wheel brakes in recommended sequence
which is: right rear; left rear; right front; left front.
Bleed procedure is as follows:
(a) Attach bleed hose to caliper bleed screw. Im-
merse end of hose in glass container partially filled
with brake fluid. Be sure hose end is submerged in
fluid (Fig. 3).
(b) Have helper depress and hold brake pedal to
floorpan.
(c) Open bleed screw 1/2 turn. Close bleed screw
when brake pedal contacts floorpan.Do not pump
brake pedal at any time while bleeding. This
compresses air into small bubbles which are
distributed throughout system. Additional
bleeding operations will then be necessary to
remove all trapped air from the system.
(d) Repeat bleeding operation at each wheel
brake unit fluid entering glass container is free of
air bubbles. Check reservoir fluid level frequently
and add fluid if necessary.
(6) Perform HCU bleed procedure with DRB scan
tool as follows:
(a) Connect scan tool to ABS diagnostic connec-
tor. Connector is under carpet at front of console,
just under instrument panel center bezel.
(b) Select CHASSIS SYSTEM, followed by
TEVES ABS BRAKES, then BLEED BRAKES.
When scan tool displays TEST COMPLETE, dis-
Fig. 3 Typical Bleed Hose And Fluid Container
JBRAKE FLUIDÐBRAKE BLEEDINGÐBRAKELINES AND HOSES 5 - 11
Page 164 of 2158

connect scan tool and proceed to next step.
(7)Repeatconventional bleed procedure described
in steps (4) and (5).
(8) Top off master cylinder fluid level and verify
proper brake operation before moving vehicle.
BRAKELINES AND HOSES
Metal brakelines and rubber brake hoses should be
inspected periodically and replaced if damaged.
Rubber brake hoses should be replaced if cut,
cracked, swollen, or leaking. Rubber hoses must be
replaced as they are not repairable.
Steel brakelines should be inspected any time the
vehicle is in for normal maintenance. This is impor-
tant on high mileage vehicles. It is especially impor-
tant when the vehicle is operated on roads that are
salted during winter months.
Heavily rusted/corroded brake rotors, drums,
support plates, and brakelines should be
cleaned and carefully inspected. Heavy rust
buildup can hide severe damage to a compo-
nent. Severely rusted parts should be replaced
if condition is suspect.
BRAKELINE CHARTS
Brakeline routing and connections are displayed in
Figures 4 through 10. Routing for both right hand drive
(RHD) and left hand drive (LHD) models is provided.
Fig. 4 Brakeline Routing (YJ With ABS)
Fig. 5 Front Brake Hose And Sensor Wire Routing
(RHD XJ With ABS)
5 - 12 BRAKE FLUIDÐBRAKE BLEEDINGÐBRAKELINES AND HOSESJ
Page 165 of 2158
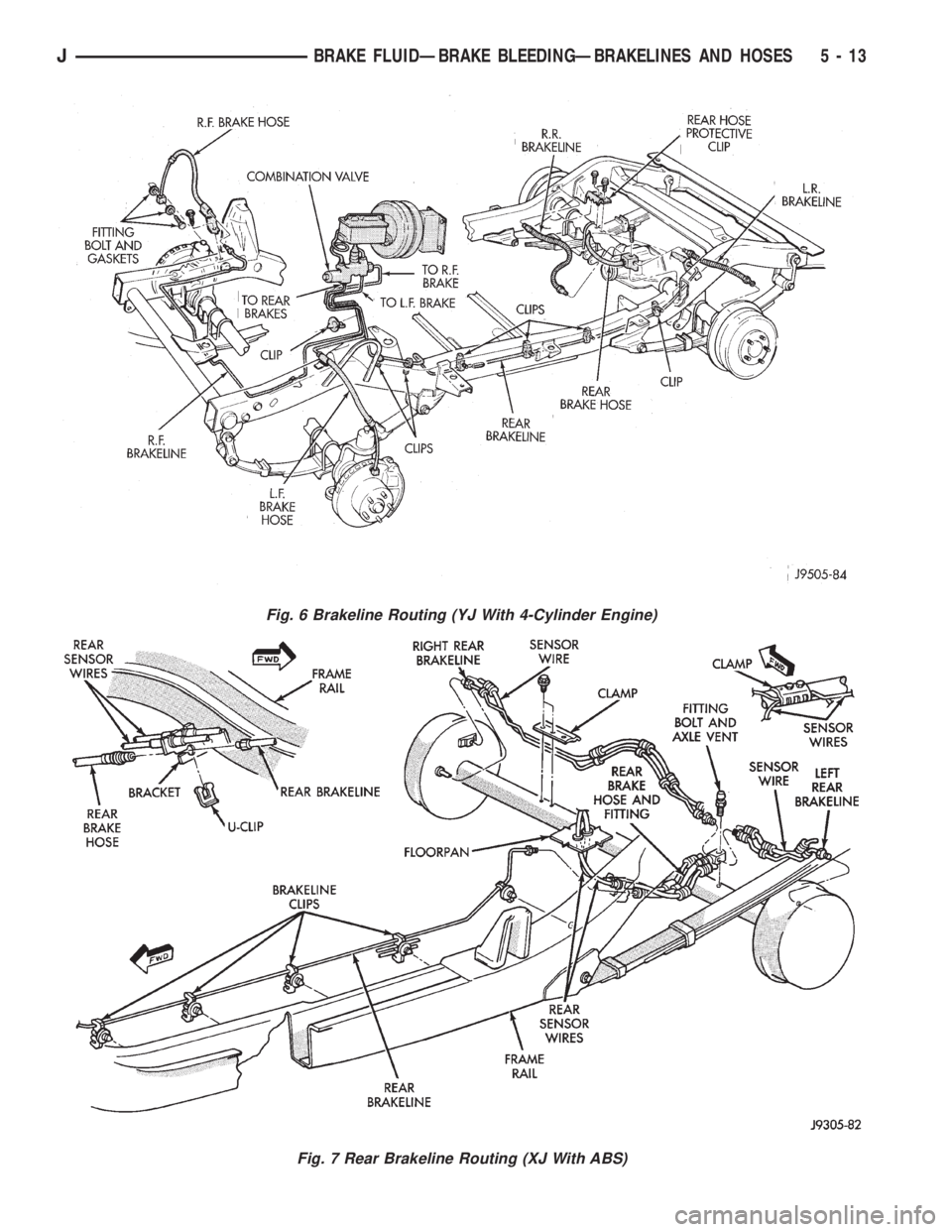
Fig. 6 Brakeline Routing (YJ With 4-Cylinder Engine)
Fig. 7 Rear Brakeline Routing (XJ With ABS)
JBRAKE FLUIDÐBRAKE BLEEDINGÐBRAKELINES AND HOSES 5 - 13
Page 166 of 2158
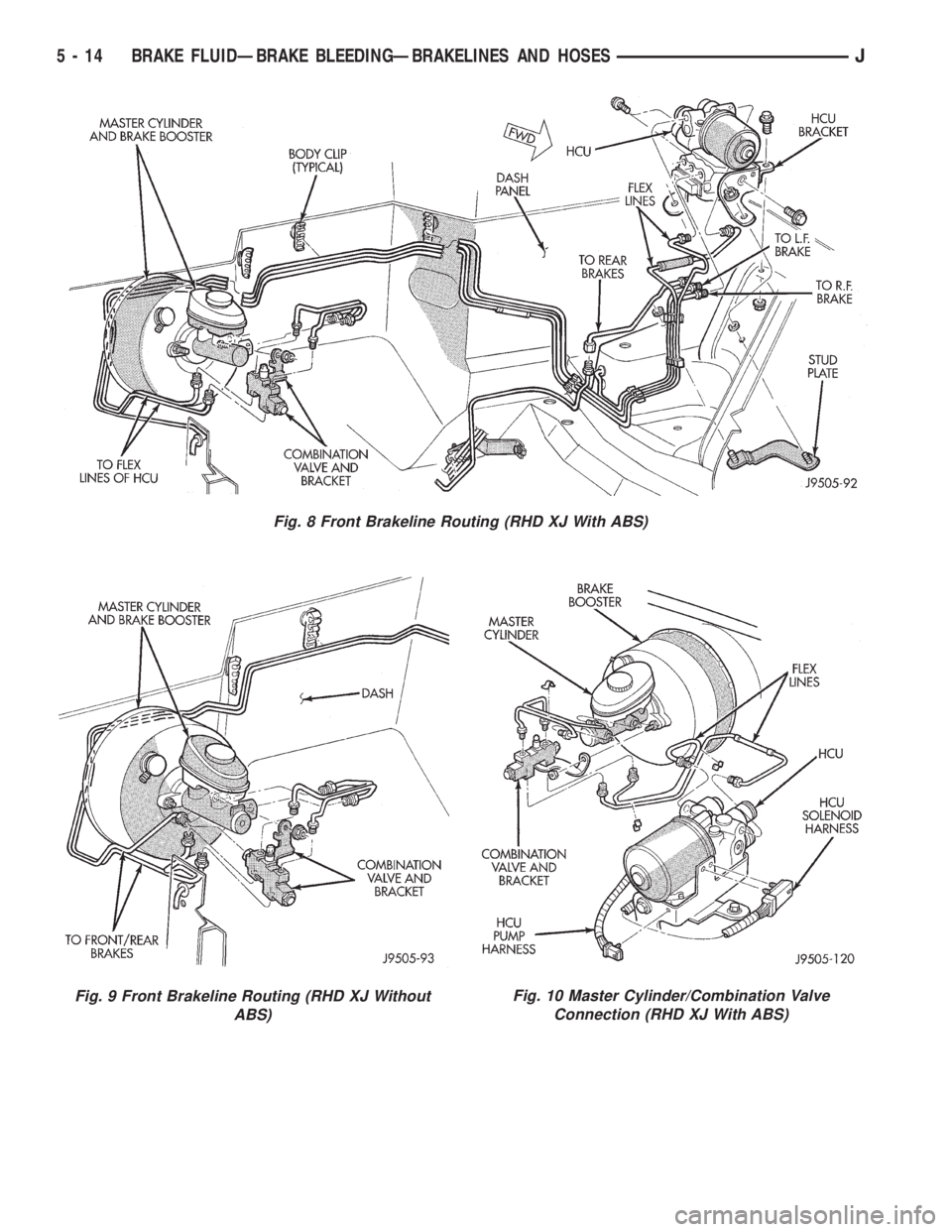
Fig. 9 Front Brakeline Routing (RHD XJ Without
ABS)Fig. 10 Master Cylinder/Combination Valve
Connection (RHD XJ With ABS)
Fig. 8 Front Brakeline Routing (RHD XJ With ABS)
5 - 14 BRAKE FLUIDÐBRAKE BLEEDINGÐBRAKELINES AND HOSESJ
Page 167 of 2158

MASTER CYLINDERÐCOMBINATION VALVE
INDEX
page page
Combination Valve Replacement (Non-ABS)..... 16
General Service Information................. 15
Master Cylinder and Combination Valve Installation
(With ABS)............................. 20
Master Cylinder and Combination Valve Removal
(With ABS)............................. 17Master Cylinder Bench Bleeding.............. 21
Master Cylinder Installation (Non-ABS)......... 16
Master Cylinder Overhaul (4-Cylinder Models).... 16
Master Cylinder Removal (Non-ABS)........... 15
Reservoir Replacement (2-Piece Master Cylinder) . 19
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION
Master Cylinder
Two different master cylinders are used. A one-piece
cast aluminum cylinder is used on 4-cylinder YJ models
(Fig. 1). All other models have a two-piece master cylin-
der with removable nylon reservoir (Fig. 2).
The two master cylinders are serviced differently.
The reservoir and grommets are the only replaceable
parts on the two-piece master cylinder. The one-piece
master cylinder can be overhauled when necessary.
Combination Valve
A combination valve is used in all models. The
valve contains a pressure differential valve and
switch and a rear brake proportioning valve. The
valve is not repairable. It must be replaced if diagno-
sis indicates this is necessary.
The pressure differential switch is connected to the
brake warning light. The switch is actuated by move-
ment of the switch valve. The switch monitors fluid
pressure in the separate front/rear brake hydraulic cir-
cuits.
A decrease or loss of fluid pressure in either hydraulic
circuit will cause the switch valve to shuttle to the low
pressure side. Movement of the valve pushes the switch
plunger upward. This action closes the switch internal
contacts completing the electrical circuit to the red
warning light. The switch valve will remain in an actu-
ated position until repairs are made.
The rear proportioning valve is used to balance front-
rear brake action. The valve allows normal fluid flow
during moderate effort brake stops. The valve only con-
trols (meters) fluid flow during high effort brake stops.
MASTER CYLINDER REMOVAL (NON-ABS)
(1) Remove air cleaner hose, cover and housing.
Fig. 1 Master Cylinder And Combination Valve
(4-Cyl. YJ Models)
Fig. 2 Master Cylinder And Combination Valve (All
Except 4-Cyl. YJ Models)
JMASTER CYLINDERÐCOMBINATION VALVE 5 - 15
Page 168 of 2158

(2) Disconnect brake lines at master cylinder and
combination valve.
(3) Remove nuts attaching master cylinder to
booster studs.
(4) Remove master cylinder.
(5) Remove cylinder cover and drain fluid.
(6) If two-piece master cylinder reservoir requires
service, refer to reservoir replacement procedure in
this section.
MASTER CYLINDER INSTALLATION (NON-ABS)
(1) Bleed master cylinder on bench before installa-
tion. Refer to procedure in this section.
(2) If new two-piece master cylinder is being in-
stalled, remove plastic protective sleeve from primary
piston shank. Also check condition of seal at rear of
cylinder body. Reposition seal if dislodged. Replace
seal if cut, or torn.
(3) Clean cylinder mounting surface of brake booster.
Use shop towel wetted with brake cleaner for this pur-
pose. Dirt, grease, or similar materials will prevent
proper cylinder seating and could result in vacuum leak.
(4) Slide master cylinder onto brake booster studs.
(5) Install nuts attaching master cylinder to booster
studs. Tighten nuts to 25 Nzm (220 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Connect brakelines to master cylinder and com-
bination valve (Figs. 1 and 2).
(7) Fill and bleed brake system.
COMBINATION VALVE REPLACEMENT (NON-ABS)
The combination valve is not a repairable compo-
nent. The valve is serviced as an assembly whenever
diagnosis indicates replacement is necessary.
(1) Remove air cleaner cover and hose for access to
valve, if necessary.
(2) Disconnect differential pressure switch wire at
combination valve. Do not pull switch wire to discon-
nect. Unsnap connecter lock tabs to remove.
(3) Disconnect brakelines at combination valve and
remove valve.
(4) Connect brakelines to replacement valve. Start
line fittings by hand to avoid cross threading.
Tighten fittings snug but not to required torque at
this time.
(5) Connect wire to pressure differential switch.
(6) Bleed brakes.
(7) Tighten brakeline fittings to 18-24 Nzm
(160-210 in. lbs.) torque after bleeding.
MASTER CYLINDER OVERHAUL (4-CYLINDER
MODELS)
CYLINDER DISASSEMBLY
(1) Examine cylinder cover seal. Discard seal if
torn or distorted.
(2) Clamp cylinder in vise (Fig. 3).(3) Remove piston retaining snap ring. Press and
hold primary piston inward with wood dowel or sim-
ilar tool. Then remove snap ring (Fig. 4).
(4) Remove and discard primary piston (Fig. 5).
Piston is serviced only as assembly.
(5) Remove secondary piston (Fig. 6). Apply air
pressure through rear outlet port to ease piston out
of bore. Cover small ports at bottom of rear reservoir
with towel to prevent air leakage.
(6) Discard secondary piston. Do not disassemble
piston as components are only serviced as assembly.
MASTER CYLINDER CLEANING AND
INSPECTION
Clean the cylinder with Mopar brake cleaning sol-
vent or clean brake fluid. Remove cleaning residue
with compressed air.
Inspect the cylinder bore. A light discoloration of
Fig. 3 Mounting Cylinder In Vise
Fig. 4 Removing/Installing Piston Snap Ring
5 - 16 MASTER CYLINDERÐCOMBINATION VALVEJ