1995 JEEP YJ stop start
[x] Cancel search: stop startPage 261 of 2158

group. Fill radiator to top and install radiator cap.
Add sufficient coolant to reserve/overflow tank to
raise level to FULL mark.
(3) With heater control unit in the HEAT position,
operate engine with radiator cap in place.
(4) After engine has reached normal operating
temperature, shut engine off and allow it to cool.
(5) Add coolant to reserve/overflow tank as neces-
sary.Only add coolant when the engine is cold.
Coolant level in a warm engine will be higher
due to thermal expansion.
COOLING SYSTEM CLEANING/REVERSE FLUSHING
CAUTION: The cooling system normally operates at
97-to-124 kPa (14-to-18 psi) pressure. Exceeding
this pressure may damage the radiator or hoses.
CLEANING
Drain cooling system and refill with water. Run en-
gine with radiator cap installed until upper radiator
hose is hot. Stop engine and drain water from sys-
tem. If water is dirty, fill system with water, run en-
gine and drain system. Repeat until water drains
clean.
REVERSE FLUSHING
Reverse flushing of the cooling system is the forc-
ing of water through the cooling system. This is done
using air pressure in the opposite direction of normal
coolant flow. It is usually only necessary with very
dirty systems with evidence of partial plugging.
REVERSE FLUSHING RADIATOR
Disconnect the radiator hoses from the radiator fit-
tings. Attach a section of radiator hose to the radia-
tor bottom outlet fitting and insert the flushing gun.
Connect a water supply hose and air supply hose to
the flushing gun.
CAUTION: The cooling system normally operates at
97-to-124 kPa (14-to-18 psi) pressure. Exceeding
this pressure may damage the radiator or hoses.
Allow the radiator to fill with water. When radiator
is filled, apply air in short blasts allowing radiator to
refill between blasts. Continue this reverse flushing
until clean water flows out through rear of radiator
cooling tube passages. For more information, refer to
operating instructions supplied with flushing equip-
ment. Have radiator cleaned more extensively by a
radiator repair shop.
REVERSE FLUSHING ENGINE
Drain the cooling system. Remove the thermostat
housing and thermostat. Install the thermostat hous-
ing. Disconnect the radiator upper hose from the ra-
diator and attach the flushing gun to the hose.Disconnect the radiator lower hose from the water
pump. Attach a lead away hose to the water pump
inlet fitting.
CAUTION: On XJ models, be sure that the heater
control valve is closed (heat off). This is done to
prevent coolant flow with scale and other deposits
from entering the heater core.
Connect the water supply hose and air supply hose
to the flushing gun. Allow the engine to fill with wa-
ter. When the engine is filled, apply air in short
blasts, allowing the system to fill between air blasts.
Continue until clean water flows through the lead
away hose. For more information, refer to operating
instructions supplied with flushing equipment.
Remove the lead away hose, flushing gun, water
supply hose and air supply hose. Remove the thermo-
stat housing and install thermostat. Install the ther-
mostat housing with a replacement gasket. Refer to
Thermostat Replacement. Connect the radiator
hoses. Refill the cooling system with the correct an-
tifreeze/water mixture.
CHEMICAL CLEANING
In some instances, use a radiator cleaner (Mopar
Radiator Kleen or equivalent) before flushing. This
will soften scale and other deposits and aid the flush-
ing operation.
CAUTION: Be sure instructions on the container are
followed.
TESTING COOLING SYSTEM FOR LEAKS
ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT METHOD
All Jeep models have a leak detection additive
added to the cooling system before they leave the fac-
tory. The additive is highly visible under ultraviolet
light (black light). If the factory original coolant has
been drained, pour one ounce of additive into the
cooling system. The additive is available through the
part's department. Place the heater control unit in
HEAT position. Start and operate the engine until
the radiator upper hose is warm to the touch. Aim
the commercially available black light tool at the
components to be checked. If leaks are present, the
black light will cause the additive to glow a bright
green color.
The black light can be used along with a pressure
tester to determine if any external leaks exist (Fig.
20).
PRESSURE TESTER METHOD
The engine should be at the normal operating tem-
perature. Recheck the system cold if the cause of
coolant loss is not located during warm engine exam-
ination.
7 - 22 COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURESJ
Page 263 of 2158

CAUTION: Do not operate the engine with a spark
plug shorted for more than a minute. The catalytic
converter may be damaged.
Isolate the compression leak by shorting each
spark plug to the cylinder block. The gauge pointer
should stop or decrease vibration when spark plug
for leaking cylinder is shorted. This happens because
of the absence of combustion pressure.
COMBUSTION LEAKAGE TEST (WITHOUT
PRESSURE TESTER)
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If the solution
is clean, drain the coolant into a clean container for
reuse.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
Drain sufficient coolant to allow for thermostat re-
moval. Refer to Thermostat Replacement. Disconnect
the water pump drive belt.
Disconnect the upper radiator hose from the ther-
mostat housing. Remove the housing and thermostat.
Install the thermostat housing.
Add coolant to the radiator to bring the level to
within 6.3 mm (1/4 in) of the top of the thermostat
housing.
CAUTION: Avoid overheating. Do not operate the
engine for an excessive period of time. Open the
draincock immediately after the test to eliminate
boil over of coolant.
Start the engine and accelerate rapidly three times
(to approximately 3000 rpm) while observing the
coolant. If internal engine combustion gases are leak-
ing into the cooling system, bubbles will appear in
the coolant. If bubbles do not appear, there is no in-
ternal combustion gas leakage.
COOLANT RESERVE/OVERFLOW SYSTEM
The system works along with the radiator pressure
cap. This is done by using thermal expansion and
contraction of the coolant to keep the coolant free of
trapped air. It provides:
²A volume for coolant expansion and contraction.
²A convenient and safe method for checking/adjust-
ing coolant level at atmospheric pressure. This is
done without removing the radiator pressure cap.
²Some reserve coolant to the radiator to cover mi-
nor leaks and evaporation or boiling losses.
As the engine cools, a vacuum is formed in the
cooling system of both the radiator and engine. Cool-ant will then be drawn from the coolant tank and re-
turned to a proper level in the radiator.
The coolant reserve/overflow system consists of a
radiator mounted pressurized cap, a plastic reserve/
overflow tank (Figs. 22, 23 or 24), a tube (hose) con-
necting the radiator and tank, and an overflow tube
on the side of the tank.
Fig. 22 Reserve/Overflow TankÐYJ Models
Fig. 23 Reserve/Overflow TankÐXJ ModelsÐExcept
Right Hand Drive
7 - 24 COOLING SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURESJ
Page 336 of 2158

For diagnostics, refer to the appropriate Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures service manual for operation
of the DRB scan tool.
SPARK PLUGS
For spark plug removal, cleaning, gap adjustment
and installation, refer to the Component Removal/In-
stallation section of this group.
Faulty carbon and/or gas fouled plugs generally
cause hard starting, but they will clean up at higher
engine speeds. Faulty plugs can be identified in a
number of ways: poor fuel economy, power loss, de-
crease in engine speed, hard starting and, in general,
poor engine performance.
Remove the spark plugs and examine them for
burned electrodes and fouled, cracked or broken por-
celain insulators. For identification, keep plugs ar-
ranged in the order in which they were removed from
the engine. An isolated plug displaying an abnormal
condition indicates that a problem exists in the cor-
responding cylinder. Replace spark plugs at the inter-
vals recommended in the maintenance chart in
Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance.
Spark plugs that have low mileage may be cleaned
and reused if not otherwise defective. Refer to the
following Spark Plug Condition section of this group.
CONDITION
NORMAL OPERATING
The few deposits present on the spark plug will
probably be light tan or slightly gray in color. This is
evident with most grades of commercial gasoline
(Fig. 19). There will not be evidence of electrode
burning. Gap growth will not average more than ap-
proximately 0.025 mm (.001 in) per 1600 km (1000
miles) of operation. Spark plugs that have normal
wear can usually be cleaned, have the electrodes
filed, have the gap set and then be installed.Some fuel refiners in several areas of the United
States have introduced a manganese additive (MMT)
for unleaded fuel. During combustion, fuel with MMT
causes the entire tip of the spark plug to be coated
with a rust colored deposit. This rust color can be
misdiagnosed as being caused by coolant in the com-
bustion chamber. Spark plug performance is not af-
fected by MMT deposits.
COLD FOULING/CARBON FOULING
Cold fouling is sometimes referred to as carbon
fouling. The deposits that cause cold fouling are ba-
sically carbon (Fig. 19). A dry, black deposit on one or
two plugs in a set may be caused by sticking valves
or defective spark plug cables. Cold (carbon) fouling
of the entire set of spark plugs may be caused by a
clogged air cleaner element or repeated short operat-
ing times (short trips).
WET FOULING OR GAS FOULING
A spark plug coated with excessive wet fuel or oil is
wet fouled. In older engines, worn piston rings, leak-
ing valve guide seals or excessive cylinder wear can
cause wet fouling. In new or recently overhauled en-
gines, wet fouling may occur before break-in (normal
oil control) is achieved. This condition can usually be
resolved by cleaning and reinstalling the fouled
plugs.
OIL OR ASH ENCRUSTED
If one or more spark plugs are oil or oil ash en-
crusted (Fig. 20), evaluate engine condition for the
cause of oil entry into that particular combustion
chamber.
ELECTRODE GAP BRIDGING
Electrode gap bridging may be traced to loose de-
posits in the combustion chamber. These deposits ac-
cumulate on the spark plugs during continuous stop-
and-go driving. When the engine is suddenly
Fig. 18 PCM LocationÐXJ ModelsFig. 19 Normal Operation and Cold (Carbon) Fouling
8D - 12 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 353 of 2158

IGNITION SWITCHÐYJ MODELS
GENERAL INFORMATION
This section will cover the electrical portion
of the ignition switch. To service the mechani-
cal ignition key switch, refer to Group 19,
Steering.
Refer to Group 8W, Wiring for ignition switch wir-
ing circuits.
The ignition switch is mounted under the instru-
ment panel on the lower section of the steering col-
umn. The headlamp dimmer switch is mounted
beside the ignition switch (Fig. 11). Both of these
switches (ignition and dimmer) share the same
mounting screws.
The switch is connected to the ignition key lock as-
sembly by a remote actuator rod. This remote actua-
tor rod fits into an access hole on the bottom of the
ignition switch (Fig. 12).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable at the
battery.
(2) Remove the windshield wiper intermittent con-
trol module and its bracket (if equipped).
(3) Place the ignition key lock in ACCESSORY po-
sition.
(4) Remove the two headlamp dimmer switch at-
taching nuts. Lift the switch from steering column
while disengaging actuator rod.
Before removing dimmer switch, tape the two
remote control actuator rods (ignition switchand dimmer) to the steering column. This will
prevent accidental disengagement from the up-
per part of the steering column.
(5) Remove the ignition switch-to-steering column
attaching screws.
(6) Disengage the ignition switch from the remote
actuator rod by lifting straight up. Remove switch
from steering column.
(7) Remove wiring from switch as follows:
Two electrical connectors are used to connect all
wiring to the ignition switch. One of the connectors is
installed (interlocked) over the top of the other con-
nector. Remove wiring from switch by disconnecting
the (black) harness connector first and then the other
connector. Remove the switch from the vehicle.
SWITCH TESTING
To test the ignition switch circuity and continuity,
proceed as follows. Place the slide bar (on the igni-
tion switch) (Fig. 12) into the detent position to be
tested. An ohmmeter or continuity light may be used
to check switch continuity. Refer to the Ignition
Switch Continuity Tests chart for continuity tests.
Refer to (Fig. 13) for the lettered/numbered terminal
positions.All wiring must be disconnected from
the ignition switch before performing any con-
tinuity testing.
There are five positions on the ignition switch. The
switch positions (in order) are: ACCESSORY, OFF-
LOCK, OFF, ON AND START (Figs. 14 or 15). Each
position has a detent stop (except START), which isFig. 11 Ignition Switch/Headlamp Dimmer SwitchÐ
Typical
Fig. 12 Ignition Switch/Remote Actuator RodÐ
Typical
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 29
Page 360 of 2158

HEADLAMP HIGH BEAM INDICATOR LAMP
The high beam indicator lamp is controlled by the
headlamp dimmer (multi-function) switch. One side
of the indicator bulb is grounded at all times. The
other side of the bulb receives battery feed through
the contacts of the dimmer switch when the multi-
function switch stalk is actuated to turn the head-
lamp high beams on. Refer to Group 8L - Lamps for
more information.
LOW FUEL WARNING LAMP
A Light-Emitting Diode (LED) on the face of the
fuel gauge will light when the fuel level falls below
approximately 4 gallons. A low fuel warning module
attached to the rear of the fuel gauge controls when
the LED will light. When the module senses 66.5
ohms or more resistance from the fuel level sending
unit for 10 continuous seconds, the LED will light.
When the module senses 63.5 ohms or less resistance
from the fuel level sending unit for 20 continuous
seconds, the LED is turned off.
LOW OIL PRESSURE WARNING LAMP
The low oil pressure warning lamp lights with the
ignition switch in the ON position and the engine not
running. The lamp should be off when the engine is
running. Battery voltage is supplied to one side of
the indicator bulb when the ignition switch is turned
ON. The warning lamp side of the combination oil
pressure sending unit is connected to the other side
of the bulb. When normal engine oil pressure is ap-
plied to the sending unit, resistance on the warning
lamp side is high and the lamp goes off. When engine
oil pressure is too low, resistance on the warning
lamp side of the sending unit is low, which causes
the bulb to light.
LOW WASHER FLUID WARNING LAMP
The low washer fluid warning lamp indicates when
the fluid level in the washer reservoir is too low. The
washer fluid level sensor uses a float in the reservoir
to monitor fluid level. The action of the float opens or
closes the switch within the sensor that provides ig-
nition-switched battery voltage to the lamp bulb. Re-
fer to Group 8K - Wiper and Washer Systems for
more information.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP
The CHECK ENGINE or Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) lights each time the ignition switch is
turned ON, and stays on for 3 seconds as a bulb test.
If the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) receives an
incorrect signal or no signal from certain fuel oremission system related circuits or components, the
lamp is turned on. This will indicate that the PCM
has recorded a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) in
electronic memory for a circuit or component mal-
function. Refer to Group 14 - Fuel System for more
information.
SEAT BELT REMINDER LAMP
The seat belt reminder lamp lights for 4 to 8 sec-
onds after the ignition switch is turned to the ON po-
sition. A timer in the chime/buzzer module controls
ignition-switched battery feed to the lamp. Refer to
Group 8U - Chime/Buzzer Warning Systems for more
information.
TURN SIGNAL INDICATOR LAMPS
The left and right turn signal indicator lamps are
controlled by the turn signal and hazard warning
(multi-function) switches. One side of the bulb for
each lamp is grounded at all times. The other side of
the bulb receives battery feed through the contacts of
the multi-function switch when the turn signal lever
(multi-function switch stalk) or hazard warning but-
ton are actuated. Refer to Group 8J - Turn Signal
and Hazard Warning Systems for more information.
UPSHIFT INDICATOR LAMP
Vehicles equipped with manual transmissions have
an optional upshift indicator lamp. Ground feed for
the lamp is switched by the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM). The lamp lights to indicate when the
driver should shift to the next highest gear for best
fuel economy. The PCM will turn the lamp off after 3
to 5 seconds if the upshift is not performed. The lamp
will remain off until the vehicle stops accelerating
and is brought back to the range of lamp operation,
or until the transmission is shifted into another gear.
The indicator lamp is normally on when the igni-
tion switch is turned ON and is turned off when the
engine is started. The lamp will be turned on during
vehicle operation according to engine speed and load.
CLUSTER ILLUMINATION LAMPS
All cluster illumination lamps receive battery feed
from the instrument lamps fuse in the fuseblock
module through the panel dimmer rheostat of the
headlamp switch. When the park or headlamps are
on, the cluster illumination lamps light. Illumination
brightness can be adjusted by rotating the headlamp
switch knob (clockwise to dim, counterclockwise to
brighten).
8E - 4 INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESÐXJJ
Page 382 of 2158

voltage is supplied to one side of the indicator bulb. A
ground path for the bulb is provided by 3 switches.
The bulb will light when:
²the brake warning switch is closed (indicating un-
equal brake system hydraulic pressures possibly due
to brake fluid leakage)
²the ignition switch is in the START position (bulb
test)
²the parking brake switch is closed (parking brake
is applied).
Refer to Group 5 - Brakes for more information.
FOUR-WHEEL DRIVE INDICATOR LAMP
This lamp lights when the transfer case is engaged
in the 4H or 4L position. Voltage is supplied to one
side of the indicator bulb. A switch on the front axle
disconnect housing is connected to the other side of
the indicator bulb. When the switch is closed, a path
to ground is provided and the indicator bulb lights.
HEADLAMP HIGH BEAM INDICATOR LAMP
The high beam indicator lamp is controlled by the
headlamp dimmer switch. One side of the indicator
bulb is grounded at all times. The other side of the
bulb receives battery feed through the contacts of the
dimmer switch when the turn signal switch lever is
actuated to turn the headlamp high beams on. Refer
to Group 8L - Lamps for more information.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP
The CHECK ENGINE or Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) lights each time the ignition switch is
turned ON, and stays on for 3 seconds as a bulb test.
If the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) receives an
incorrect signal or no signal from certain fuel or
emission system related circuits or components, the
lamp is turned on. This will indicate that the PCM
has recorded a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) in
electronic memory for a circuit or component mal-
function. Refer to Group 14 - Fuel System for more
information.
SEAT BELT REMINDER LAMP
The seat belt reminder lamp lights for 4 to 8 sec-
onds after the ignition switch is turned to the ON po-sition. A timer in the chime/buzzer module controls
ignition-switched battery feed to the lamp. Refer to
Group 8U - Chime/Buzzer Warning Systems for more
information.
TURN SIGNAL INDICATOR LAMPS
The left and right turn signal indicator lamps are
controlled by the turn signal and hazard warning
switches. One side of the bulb for each lamp is
grounded at all times. The other side of the bulb re-
ceives battery feed through the contacts of the turn
signal switch, when the turn signal lever or hazard
warning button are actuated. Refer to Group 8J -
Turn Signal and Hazard Warning Systems for more
information.
UPSHIFT INDICATOR LAMP
Vehicles equipped with manual transmissions have
an optional upshift indicator lamp. Ground feed for
the lamp is switched by the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM). The lamp lights to indicate when the
driver should shift to the next highest gear for best
fuel economy. The PCM will turn the lamp off after 3
to 5 seconds if the upshift is not performed. The lamp
will remain off until the vehicle stops accelerating
and is brought back to the range of lamp operation,
or until the transmission is shifted into another gear.
The indicator lamp is normally on when the igni-
tion switch is turned ON and is turned off when the
engine is started. The lamp will be turned on during
vehicle operation according to engine speed and load.
CLUSTER ILLUMINATION LAMPS
All cluster illumination lamps receive battery feed
from the instrument lamps fuse in the fuseblock
module through the panel dimmer switch. When the
park or headlamps are on, the cluster illumination
lamps light. Illumination brightness can be adjusted
by rotating the panel dimmer thumb-wheel, which is
next to the headlamp switch.
8E - 26 INSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESÐYJJ
Page 422 of 2158
SPEED CONTROL SWITCH
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AN AIR-
BAG, REFER TO GROUP 8M - RESTRAINT SYS-
TEMS BEFORE ATTEMPTING STEERING WHEEL
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE
TO TAKE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT
IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POS-
SIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable. Remove
speed control switch from steering wheel.
(2) Check speed control switch continuity as shown
in chart (Fig. 2). If OK, reinstall switch. If not OK,
replace switch.
STOP LAMP SWITCH
(1) Unplug the connector at the stop lamp switch.
With the brake pedal released, check switch for con-
tinuity at the switch side of connector (Fig. 3) as fol-
lows:
(a) There should be continuity between the black
and white/pink wires.
(b) There should be continuity between the yel-
low/red and dark blue/red wires.
(c) There should be no continuity between pink
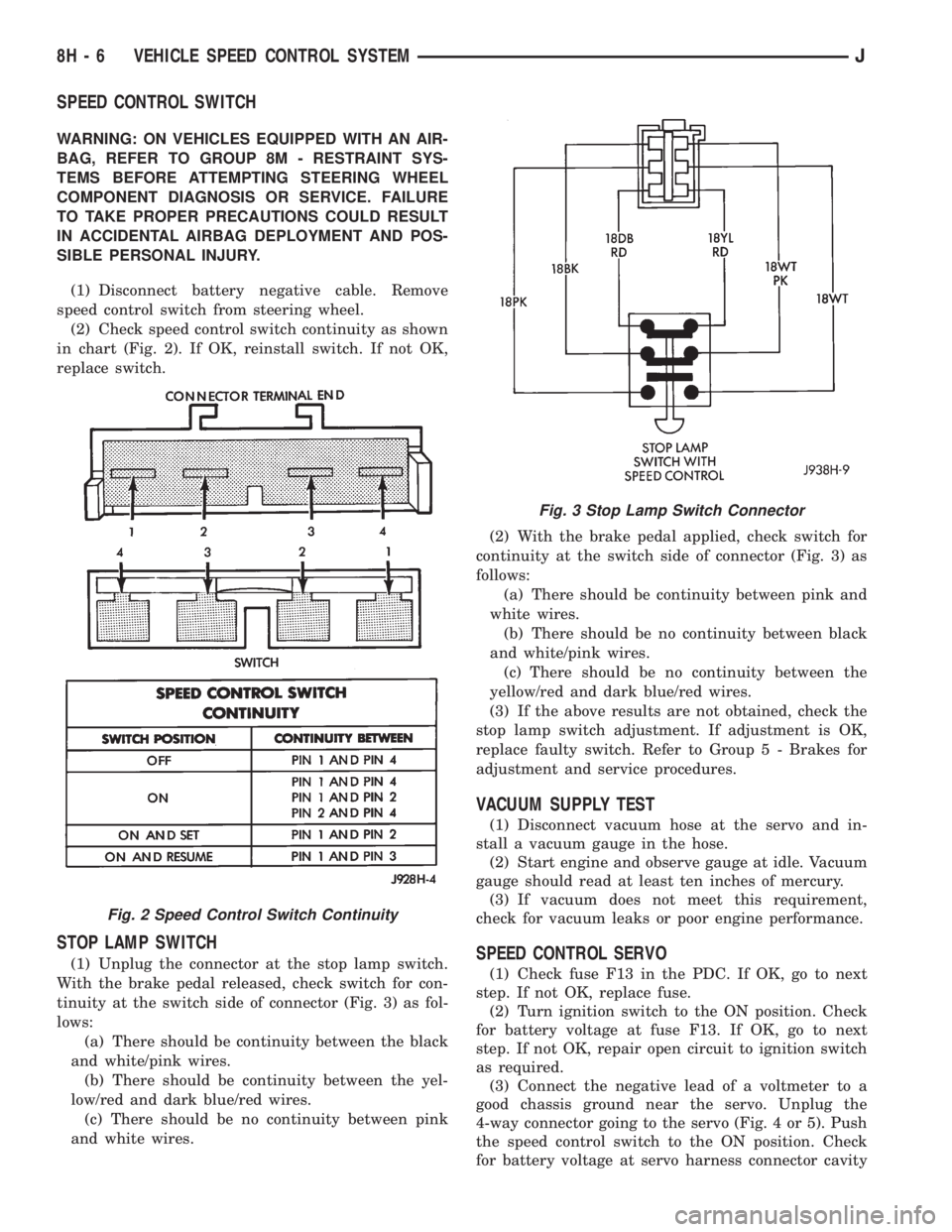
and white wires.(2) With the brake pedal applied, check switch for
continuity at the switch side of connector (Fig. 3) as
follows:
(a) There should be continuity between pink and
white wires.
(b) There should be no continuity between black
and white/pink wires.
(c) There should be no continuity between the
yellow/red and dark blue/red wires.
(3) If the above results are not obtained, check the
stop lamp switch adjustment. If adjustment is OK,
replace faulty switch. Refer to Group 5 - Brakes for
adjustment and service procedures.
VACUUM SUPPLY TEST
(1) Disconnect vacuum hose at the servo and in-
stall a vacuum gauge in the hose.
(2) Start engine and observe gauge at idle. Vacuum
gauge should read at least ten inches of mercury.
(3) If vacuum does not meet this requirement,
check for vacuum leaks or poor engine performance.
SPEED CONTROL SERVO
(1) Check fuse F13 in the PDC. If OK, go to next
step. If not OK, replace fuse.
(2) Turn ignition switch to the ON position. Check
for battery voltage at fuse F13. If OK, go to next
step. If not OK, repair open circuit to ignition switch
as required.
(3) Connect the negative lead of a voltmeter to a
good chassis ground near the servo. Unplug the
4-way connector going to the servo (Fig. 4 or 5). Push
the speed control switch to the ON position. Check
for battery voltage at servo harness connector cavity
Fig. 2 Speed Control Switch Continuity
Fig. 3 Stop Lamp Switch Connector
8H - 6 VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEMJ
Page 557 of 2158

POWER DISTRIBUTION
GENERAL INFORMATION
This section covers the Power Distribution Center
(PDC) and all circuits involved with it. For additional
information on system operation, refer to the appro-
priate section of the wiring diagrams.
DIAGRAM INDEX
Component Page
A/C Compressor Clutch Relay..............8W-11-3, 11
ABS Control Module.....................8W-11-6, 7
ABS Power Relay......................8W-11-3, 6
ABS Pump Motor Relay..................8W-11-3, 7
Automatic Shut Down Relay................8W-11-3, 9
Chime/Buzzer Module..................8W-11-10, 14
Circuit Breaker Cavity 16 (Fuse Block)..........8W-11-13
Combination Flasher......................8W-11-17
Daytime Running Lamp Module.............8W-11-5, 10
Diode D101............................8W-11-6
Engine Starter Motor Relay................8W-11-3, 4
Fuel Pump Relay.......................8W-11-3, 8
Fuse 1 (PDC)..........................8W-11-13
Fuse 3 (PDC)..........................8W-11-12
Fuse 4 (Fuse Block)......................8W-11-14
Fuse 4 (PDC)..........................8W-11-15
Fuse 5 (PDC)..........................8W-11-14
Fuse 6 (PDC)....................8W-11-4, 7, 10, 15
Fuse 7 (Fuse Block).......................8W-11-7
Fuse 7 (PDC)...........................8W-11-4
Fuse 8 (PDC)...........................8W-11-7
Fuse 9 (Fuse Block)......................8W-11-12
Fuse 9 (PDC)..........................8W-11-13
Fuse 10 (PDC)........................8W-11-6, 8
Fuse 11 (Fuse Block).....................8W-11-13
Fuse 11 (PDC).........................8W-11-10
Fuse 12 (PDC).........................8W-11-15Component Page
Fuse 13 (PDC)..........................8W-11-4
Fuse 14 (PDC)..........................8W-11-8
Fuse 15 (Fuse Block).....................8W-11-14
Fuse 15 (PDC)..........................8W-11-8
Fuse 16 (PDC).........................8W-11-12
Fuse 17 (Fuse Block).....................8W-11-10
Headlamp Delay Module.................8W-11-10, 14
Headlamp Switch........................8W-11-14
Headlamp Dimmer Switch..................8W-11-14
Horn Rear Window Relay..................8W-11-17
Horn Relay............................8W-11-17
Ignition Switch...................8W-11-4, 7, 10, 15
In-Line Circuit Breaker (Stop Lamp Relay)........8W-11-13
LCD Illumination Relay....................8W-11-17
Overhead Console.....................8W-11-10, 14
Powertrain Control Module..........8W-11-4, 5, 8, 9, 11
Power Distribution Center...................8W-11-2
Power Door Lock Relay...................8W-11-16
Power Door Unlock Relay..................8W-11-16
Radiator Fan Control Relay................8W-11-3, 11
Remote Keyless Entry Module.............8W-11-10, 12
Relay Center...........................8W-11-16
Telltale Connector (I.P. Cluster)..........8W-11-6, 10, 12
Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Relay...........8W-11-15
Transmission Control Module...............8W-11-5, 8
J8W-11 POWER DISTRIBUTIONÐXJ VEHICLES 8W - 11 - 1