1995 JEEP CHEROKEE seat
[x] Cancel search: seatPage 16 of 2198

ENGINE MAINTENANCE
INDEX
page page
Accessory Drive Belt....................... 21
Air Cleaner Element....................... 18
Air-Conditioner Compressor.................. 21
Battery................................. 20
Crankcase Ventilation System................ 19
Emission Control System................... 20
Engine Break-In.......................... 15
Engine Cooling System..................... 18
Engine Oil.............................. 15Engine Oil Change and Filter Replacement...... 16
Engine Oil Filter.......................... 17
Engine Supports.......................... 21
Exhaust System.......................... 21
Fuel Filter............................... 19
Fuel Usage StatementÐGas Engines.......... 19
Ignition Cables, Distributor Cap and Rotor....... 20
Rubber and Plastic Component Inspection....... 20
Spark Plugs............................. 20
ENGINE BREAK-IN
CAUTION: Wide open throttle operation in low
gears, before engine break-in period is complete,
can damage engine.
After first starting a new engine, allow it to idle for
15 seconds before shifting into a drive gear. Also:
²Drive the vehicle at varying speeds less than 88
km/h (55 mph) for the first 480 km (300 miles).
²Avoid fast acceleration and sudden stops.
²Do not drive at full-throttle for extended periods of
time.
²Do not drive at constant speeds.
²Do not idle the engine excessively.
A special break-in engine oil is not required. The
original engine oil installed is a high quality, energy
conserving lubricant. Special break-in oils are not
recommended. These oils could interfere with the
normal piston ring seating process.
New engines tend to consume more fuel and oil un-
til after the break-in period has ended.
ENGINE OIL
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE IR-
RITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER.
DO NOT WASH SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL
FUEL, THINNER, OR SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROB-
LEMS CAN RESULT.
DO NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE
OIL PROPERLY. CONTACT YOUR DEALER OR GOV-
ERNMENT AGENCY FOR LOCATION OF COLLEC-
TION CENTER IN YOUR AREA.
ENGINE OIL SPECIFICATION
CAUTION: Do not use non-detergent or straight
mineral oil when adding or changing crankcase lu-
bricant. Engine failure can result.
API SERVICE GRADE CERTIFIED
Use an engine oil that is API Service Grade Certi-
fied or an oil that conforms to the API Service Grade
SH or SH/CD. MOPAR provides engine oils that con-
form to all of these service grades.
SAE VISCOSITY
An SAE viscosity grade is used to specify the vis-
cosity grade of engine oil. SAE 30 specifies a single
viscosity engine oil. Engine oils also have multiple
viscosities. These are specified with a dual SAE vis-
cosity grade which indicates the cold-to-hot tempera-
ture viscosity range. Select an engine oil that is best
suited to your particular temperature range and vari-
ation (Fig.1).
ENERGY CONSERVING OIL
An Energy Conserving type oil is recommeded for
gasoline engines. They are designated as either EN-
ERGY CONSERVING or ENERGY CONSERVING
II.
Fig. 1 Temperature/Engine Oil Viscosity
JLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 15
Page 17 of 2198

CONTAINER IDENTIFICATION
Standard engine oil identification notations have
been adopted to aid in the proper selection of engine
oil. The identifying notations are located on the label
of engine oil plastic bottles and the top of engine oil
cans (Fig. 2).
ENGINE OIL ADDITIVES
In some instances, such as infrequent operation,
short trip driving, and during break-in after a major
overhaul, addition of special materials containing an-
ti-rust and anti-scuff additives are beneficial. A suit-
able product for this purpose is MOPAR Engine Oil
Supplement.
OIL LEVEL INDICATOR (DIPSTICK)
The engine oil level indicator (Dipstick) is located
at the right rear of both 2.5L engines and 4.0L en-
gines (Fig. 3).
CRANKCASE OIL LEVEL INSPECTION
CAUTION: Do not overfill crankcase with engine oil,
oil foaming and oil pressure loss can result.
Inspect engine oil level approximately every 800 ki-
lometers (500 miles). Unless the engine has exhibited
loss of oil pressure, run the engine for about five
minutes before checking oil level. Checking engine oil
level on a cold engine is not accurate.
To ensure proper lubrication of an engine, the en-
gine oil must be maintained at an acceptable level.
The acceptable levels are indicated between the ADD
and SAFE marks on the engine oil dipstick (Fig. 4
and 5).
(1) Position vehicle on level surface.
(2) With engine OFF, allow approximately ten min-
utes for oil to settle to bottom of crankcase, remove
engine oil dipstick.
(3) Wipe dipstick clean.
(4) Install dipstick and verify it is seated in the
tube.
(5) Remove dipstick, with handle held above the
tip, take oil level reading (Figs.4 and 5).
(6) Add oil only if level is below the ADD mark on
dipstick.
ENGINE OIL CHANGE AND FILTER REPLACEMENT
ENGINE OIL CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in Maintenance Schedules.
TO CHANGE ENGINE OIL
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.
(2) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands. Re-
fer to Hoisting and Jacking Recommendations in this
group.
Fig. 2 API Certification Mark
Fig. 3 Engine Oil Dipstick LocationÐTypical
Fig. 4 Engine Oil DipstickÐ2.5L Engine
0 - 16 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEJ
Page 24 of 2198

If the transmission is warm, lube oil could
drip out of the fill hole. This is acceptable but
the lube oil should not gush out of the fill hole.
(2) If not acceptable, raise the lube oil level to the
bottom edge of the transmission fill hole.
Add lube oil in small amounts to raise the
level.
(3) Install the fill-hole plug in the transmission.
Tighten the plug with 37 Nzm (27 ft. lbs.) torque.
LUBE OIL CHANGE
When it becomes necessary to change manual
transmission lube oil, use the following procedure.
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the fill-hole plug from the transmis-
sion.
(3) Place a container to collect the lube oil under
the transmission drain-hole plug.
(4) Remove the drain-hole plug and drain the lube
oil from the transmission into the container.
Care should be exercised when disposing
used lube oil after it has been drained from a
transmission.
(5) Install the drain-hole plug in the transmission.
Tighten the plug with 37 Nzm (27 ft. lbs.) torque.
(6) Fill the transmission until the lube oil begins to
drip out of the fill hole.
(7) Install the fill-hole plug in the transmission.
Tighten the plug with 37 Nzm (27 ft. lbs.) torque.
(8) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
The automatic transmission fluid should be
changed and bands adjusted at the intervals de-
scribed in the Maintenance Schedules section of this
Group. The automatic transmission should be in-
spected for fluid leaks and proper fluid level whenother under hood service is performed. Refer to
Group 21, Transmission for proper service proce-
dures.
CAUTION: To minimize fluid contamination, verify
that dipstick is seated in the fill tube after fluid level
reading is taken.
TO INSPECT THE TRANSMISSION FLUID
LEVEL
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE DRIVE BELT, PULLEYS OR FAN
BLADE. DO NOT STAND IN A DIRECT LINE WITH
THE FAN BLADE.
(1) Be sure transmission fluid is at normal operat-
ing temperature. Normal operating temperature is
reached after approximately 15 miles (25km) of oper-
ation.
(2) Position the vehicle on a level surface. This is
important for an accurate fluid level check.
(3) While sitting in driver seat, apply brakes and
place gear selector in each position, then move the
selector to:
²XJ vehicles-P (Park).
²YJ vehicles-N (Neutral).
(4) Apply parking brake.
(5) Raise hood and wipe off dipstick handle to pre-
vent dirt from entering fill tube. Then remove trans-
mission fluid level indicator (dipstick) and wipe clean
with a wiping cloth.
(6) Install dipstick and verify it is seated in fill
hole or tube.
(7) Remove dipstick, with handle above tip, take
fluid level reading. If the vehicle has been driven for
at least 15 minutes before inspecting fluid level,
transmission can be considered hot and reading
should be in the OK area. If vehicle has run for less
than 15 minutes and more than 60 seconds transmis-
sion can be considered warm and reading should be
above MIN mark. Add fluid only if level is below
MIN mark on dipstick when transmission is warm
(Fig. 4).
CAUTION: Do not overfill automatic transmission,
leakage or damage can result.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION FLUID
SPECIFICATION
When it becomes necessary to add fluid or when
the ATF is replaced, use:
²MOPAR Dexron IIE/Mercon ATFonlyfor AW-4
automatic transmissions (XJ vehicles).
²MOPAR ATF PLUS type 7176 (YJ vehicles).
Fig. 3 Manual Transmission Fill- & Drain-Hole
PlugsÐTypical
JLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 23
Page 30 of 2198

hose unless the caliper must also be removed
for maintenance.Support the caliper with a
hanger to prevent brake fluid hose damage.
(2) Remove the dust cap, the cotter pin, the nut re-
tainer, the adjustment nut, and the thrust washer
from the spindle (Fig. 3). Discard the cotter pin.
(3) Remove the wheel outer bearing from the hub.
(4) Remove the wheel hub/disc brake rotor from
the spindle.
(5) Remove the seal and the inner wheel bearing
from the hub cavity.
(6) After removal, inspect both front wheel bearing
races for indications of pitting, brinelling and exces-
sive heat.
(7) Wipe the spindle clean and apply a small
amount of chassis/wheel bearing lubricant (NLGI
GC-LB lubricant) to prevent rust. Wipe the wheel
hub cavity clean.
CAUTION: Do not over-fill the wheel hub cavity with
lubricant. Excessive lubricant can cause overheat-
ing and bearing damage. Also, excessive lubricant
can be forced out of the wheel hub cavity and con-
taminate the brake rotor/pads.
(8) Partially fill the wheel hub cavity with chassis/
wheel bearing lubricant (NLGI GC-LB lubricant).
(9) Pack the wheel bearings with chassis/wheel
bearing lubricant (NLGI GC-LB lubricant). Ensure
that sufficient lubricant is forced between the bear-
ing rollers.
(10) Install the wheel inner bearing in the wheel
hub and install a replacement seal.
(11) Clean the disc brake rotor contact surfaces, if
necessary.
(12) Install the wheel hub/disc brake rotor on the
spindle.
(13) Install the wheel outer bearing, the thrust
washer, and the spindle nut.(14) Tighten the spindle nut with 28 Nzm (21 ft.
lbs.) torque while rotating the disc brake rotor to
seat the bearings.
(15) Loosen the spindle nut 1/2 turn. While rotat-
ing the disc brake rotor, tighten the spindle nut with
2Nzm (19 in. lbs.) torque.
(16) Install the nut retainer and a replacement cot-
ter pin.
(17) Clean the dust cap and apply wheel bearing
lubricant to the inside surface.Do not fill the dust
cap with lubricant.
(18) Install the dust cap.
(19) Install the disc brake caliper.
POWER STEERING SYSTEM
The power steering fluid level should be inspected
when other under hood service is performed. For
proper service procedures, refer to Group 19, Steer-
ing.
Inspect the power steering system (Fig. 4, and 5)
for the sources of fluid leaks, steering gear housing
cracks and ensure that the steering gear is securely
attached to the vehicle frame rail. Inspect the steer-
ing damper for leaks and loose connections.
FLUID SPECIFICATION
Use MOPAR Power Steering Fluid, or an equiva-
lent product.
POWER STEERING FLUID INSPECTION
WARNING: ENGINE MUST NOT BE RUNNING WHEN
INSPECTING POWER STEERING FLUID LEVEL,
PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
Fig. 3 2WD Front Wheel BearingsÐXJ Vehicles
Fig. 4 Power Steering SystemÐXJ Vehicles
JLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 29
Page 33 of 2198
(2) Note any indication of drum/rotor overheating,
wheel dragging or the vehicle pulling to one side
when the brakes are applied.
(3) Evaluate any performance complaints received
from the owner/operator.
(4) Repair the brake system as necessary. Refer to
Group, 5 Brakes for additional information and ser-
vice procedures.
TIRES
RECOMMENDED MAINTENANCE
The general condition of the tires and the inflation
pressures should be inspected at the same time the
engine oil is changed and the oil filter is replaced.
In addition, the tires/wheels should be rotated at
the intervals described in the Maintenance Schedules
section of this group.
INSPECTION
Inspect the tires for excessive wear, damage, etc.
Test the tires for the recommended inflation pres-sure. Refer to the tire inflation pressure decal located
on the inside of the glove box door, and also to Group
22, Tires And Wheels.
ROTATION
Refer to Group 22, Tires And Wheels for the recom-
mended method of tire/wheel rotation for a Jeep ve-
hicle.
BODY COMPONENTS
LUBRICATION REQUIREMENTS
All Jeep operating mechanisms and linkages
should be lubricated when necessary. The door
weatherstrip seals should be lubricated to prolong
their life as well as to improve door sealing.
LUBRICANT SPECIFICATIONS
All applicable exterior and interior vehicle operat-
ing mechanisms should be:
²Inspected
²Cleaned
²Pivot/sliding contact areas on the mechanisms
should then be lubricated.
Multi-purpose NLGI GC-LB MOPAR Multi-Mileage
Lubricant or an equivalent, should be used to lubri-
cate the mechanisms. The door weatherstrip seals
should be lubricated with silicone lubricant spray.
Refer to the Body Lubricant Specifications chart be-
low for additional lubricant applications.
LUBRICATION
All pivoting and sliding contact areas, should be lu-
bricated periodically to ensure quiet, easy operation
and to protect against wear and corrosion. Areas in-
clude:
²Seat tracks.
²Door hinges/latches/strikers.
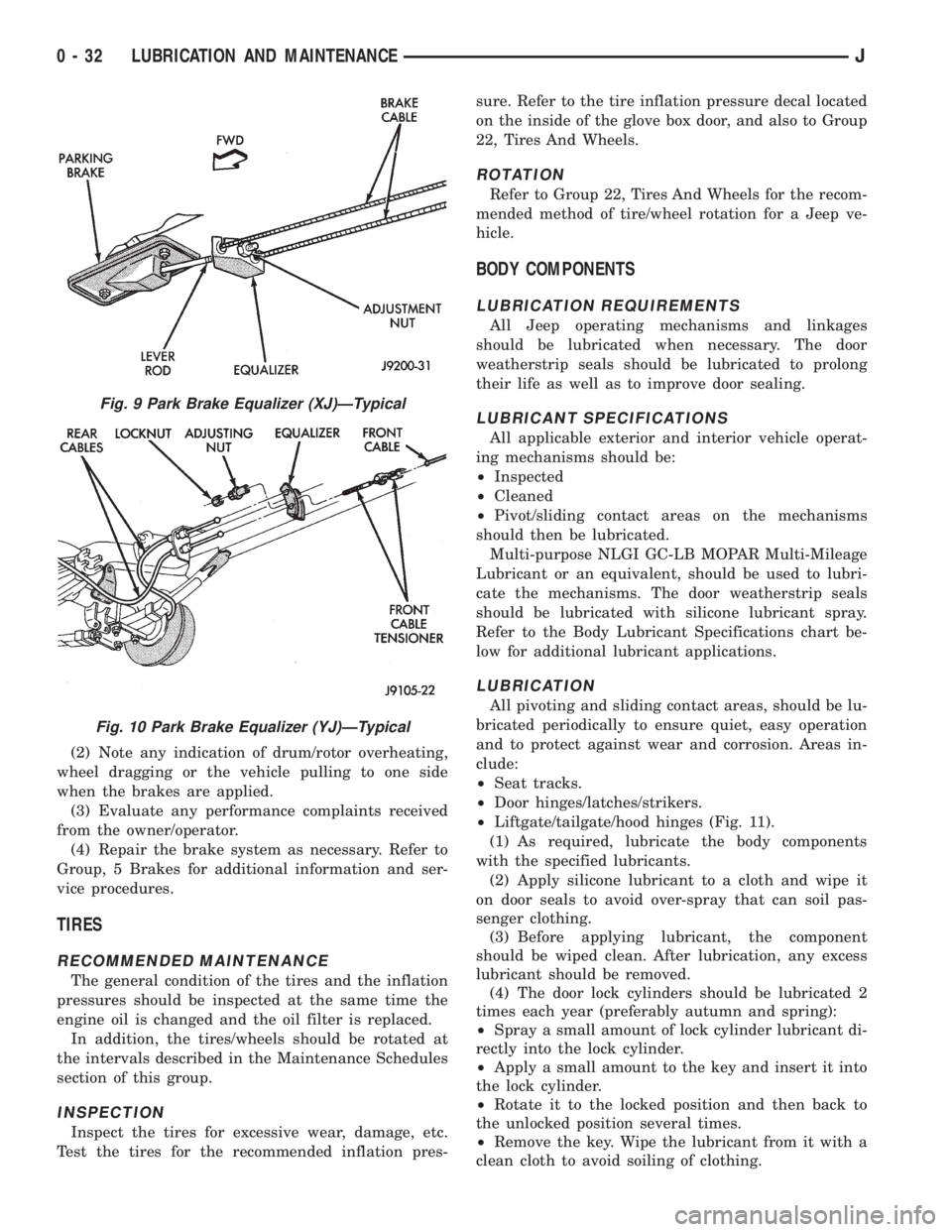
²Liftgate/tailgate/hood hinges (Fig. 11).
(1) As required, lubricate the body components
with the specified lubricants.
(2) Apply silicone lubricant to a cloth and wipe it
on door seals to avoid over-spray that can soil pas-
senger clothing.
(3) Before applying lubricant, the component
should be wiped clean. After lubrication, any excess
lubricant should be removed.
(4) The door lock cylinders should be lubricated 2
times each year (preferably autumn and spring):
²Spray a small amount of lock cylinder lubricant di-
rectly into the lock cylinder.
²Apply a small amount to the key and insert it into
the lock cylinder.
²Rotate it to the locked position and then back to
the unlocked position several times.
²Remove the key. Wipe the lubricant from it with a
clean cloth to avoid soiling of clothing.
Fig. 9 Park Brake Equalizer (XJ)ÐTypical
Fig. 10 Park Brake Equalizer (YJ)ÐTypical
0 - 32 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCEJ
Page 37 of 2198

the opposite wheel. Wheels are attached to a hub/
bearings which bolts to the knuckles. The hub/bear-
ing is not serviceable and is replaced as a unit.
Steering knuckles pivot on replaceable ball studs at-
tached to the axle tube yokes.
The upper and lower suspension arms are different
lengths, with bushings at both ends. They bolt the
axle assembly to the body. The lower arms uses
shims at the body mount to allow for adjustment of
caster and drive shaft pinion angle. The suspension
arm travel is limited through the use of jounce
bumpers in compression and shocks absorbers in re-
bound.
Suspension components which use rubber bushings
should be tightened at vehicle ride height. This will
prevent premature failure of the bushing and main-
tain ride comfort. Bushings must never be lubricated.
The coil springs control ride quality and maintain
proper ride height. The coil springs mount up in the
fender shield which is part of the unitized body
bracket. A rubber isolator is located between the top
of the spring and the frame. The bottom of the spring
seats on a axle pad and is retained with a clip.
The shock absorbers dampen jounce and rebound of
the vehicle over various road conditions. The top of
the shock absorbers are bolted to the body. The bot-
tom of the shocks are bolted to the axle spring
bracket.
The stabilizer bar is used to minimize vehicle body
roll during turns. The spring steel bar helps to con-
trol the vehicle body in relationship to the suspen-
sion. The bar extends across the front underside of
the chassis and connects to the body rails. Links are
connected from the bar to the axle brackets. Stabi-
lizer bar mounts are isolated by rubber bushings.
The track bar is used to minimize front axle side-
to-side movement. The bar is attached to a frame rail
bracket with a ball stud and isolated with a bushing
at the axle bracket.
TUBE AXLE (2WD VEHICLES)
The front axle used on two-wheel drive vehicles is
a one-piece, tubular axle (Fig. 2). The tubular axle
mounts in the same bracketry as the four-wheel
drive axle.
The steering knuckles and hub bearing assemblies
are the same as used on the Model 30 drive axle.
YJ VEHICLES
The Wrangler (YJ) front suspension is leaf spring
design comprised of (Fig. 3);
²Drive axle
²Track bar
²Stabilizer bar
²Leaf springs
²Dual-action shock absorbers
²Jounce bumpers (used to limit the travel of the
suspension)The front suspension has semi-elliptic multi-leaf
springs mounted to the axle assembly. The rearward
end of the springs are mounted to the frame rail
hangers. The forward end of the springs are attached
to the frame with shackles. The springs and shackles
use rubber bushings to isolate road noise. The shack-
les allow the springs to change their length as the
vehicle moves over various road conditions. The
Fig. 2 Front AxleÐ2WD Vehicles
Fig. 3 YJ Front Suspension
2 - 2 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 49 of 2198

INSTALLATION
(1) Position the lower retainer and grommet on the
upper stud. Insert the shock absorber through the
shock tower hole.
(2) Install the lower bolts and nuts. Tighten nuts
to 23 Nzm (17 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install the upper grommet and retainer on the
stud in the engine compartment. Install the nut and
tighten to 10 Nzm (8 ft. lbs.) torque.
COIL SPRING
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle. Position a hy-
draulic jack under the axle to support it.
(2) Remove the wheel if necessary.
(3) Mark and disconnect the front propeller shaft
from the axle.
(4) Disconnect the lower suspension arms from the
axle (Fig. 6).
(5) Disconnect the stabilizer bar link and shock ab-
sorber from the axle.
(6) Disconnect the track bar from the frame rail
bracket.(7) Disconnect the drag link from the pitman arm.
(8) Lower the axle until the spring is free from the
upper mount. Remove the coil spring clip (Fig. 6) and
remove the spring.
(9) Pull jounce bumper out of mount.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install jounce bumper into mount.
(2) Position the coil spring on the axle pad. Install
the spring clip and bolt (Fig. 6). Tighten bolt to 21
Nzm (16 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Raise the axle into position until the spring
seats in the upper mount.
(4) Connect the stabilizer bar links and shock ab-
sorbers to the axle bracket. Connect the track bar to
the frame rail bracket.
(5) Install the lower suspension arms to the axle.
DO NOT TIGHTEN AT THIS TIME.
(6) Install the front propeller shaft to the axle.
(7) Remove the supports and lower the vehicle.
(8) Tighten lower suspension arms nuts to 115 Nzm
(85 ft. lbs.) torque.
2 - 14 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 66 of 2198
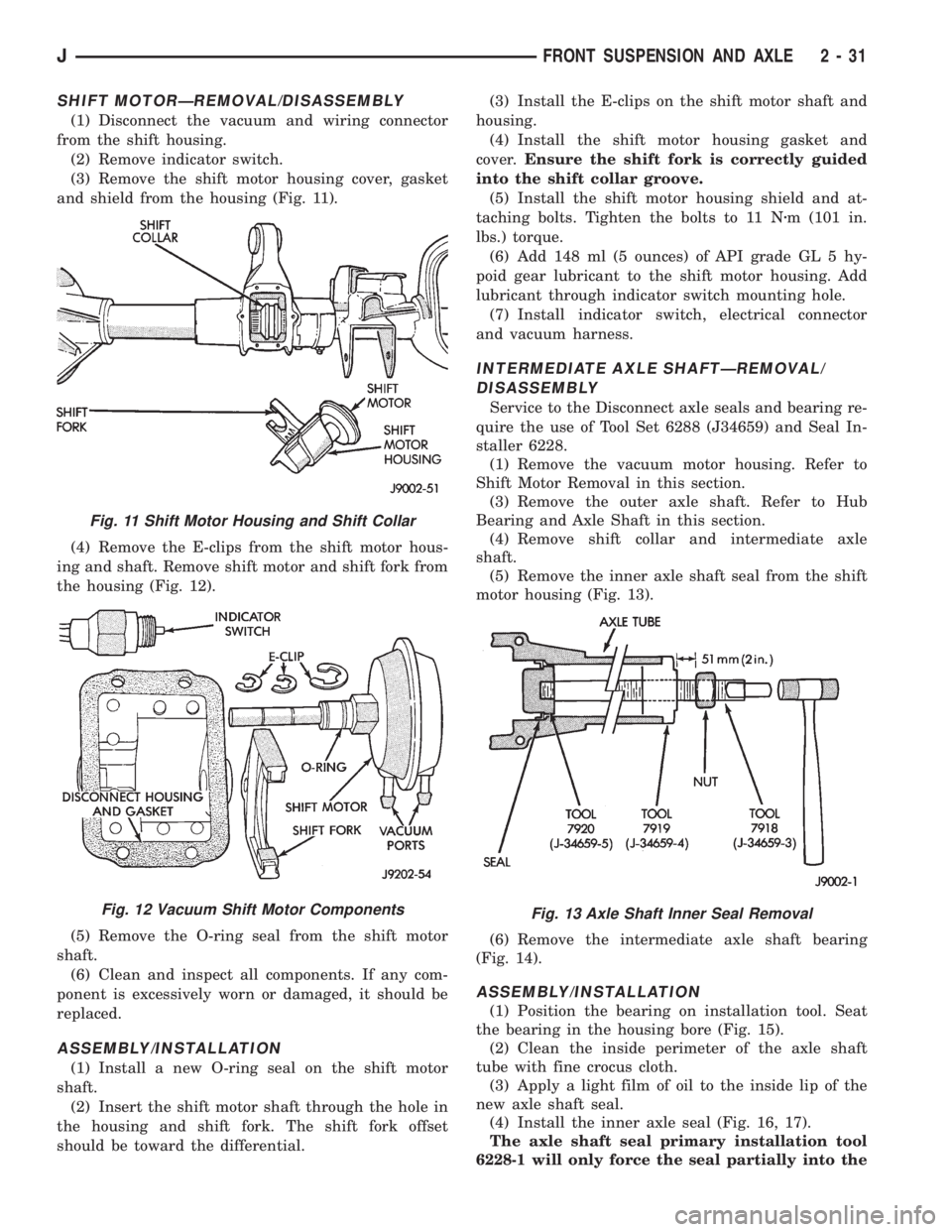
SHIFT MOTORÐREMOVAL/DISASSEMBLY
(1) Disconnect the vacuum and wiring connector
from the shift housing.
(2) Remove indicator switch.
(3) Remove the shift motor housing cover, gasket
and shield from the housing (Fig. 11).
(4) Remove the E-clips from the shift motor hous-
ing and shaft. Remove shift motor and shift fork from
the housing (Fig. 12).
(5) Remove the O-ring seal from the shift motor
shaft.
(6) Clean and inspect all components. If any com-
ponent is excessively worn or damaged, it should be
replaced.
ASSEMBLY/INSTALLATION
(1) Install a new O-ring seal on the shift motor
shaft.
(2) Insert the shift motor shaft through the hole in
the housing and shift fork. The shift fork offset
should be toward the differential.(3) Install the E-clips on the shift motor shaft and
housing.
(4) Install the shift motor housing gasket and
cover.Ensure the shift fork is correctly guided
into the shift collar groove.
(5) Install the shift motor housing shield and at-
taching bolts. Tighten the bolts to 11 Nzm (101 in.
lbs.) torque.
(6) Add 148 ml (5 ounces) of API grade GL 5 hy-
poid gear lubricant to the shift motor housing. Add
lubricant through indicator switch mounting hole.
(7) Install indicator switch, electrical connector
and vacuum harness.
INTERMEDIATE AXLE SHAFTÐREMOVAL/
DISASSEMBLY
Service to the Disconnect axle seals and bearing re-
quire the use of Tool Set 6288 (J34659) and Seal In-
staller 6228.
(1) Remove the vacuum motor housing. Refer to
Shift Motor Removal in this section.
(3) Remove the outer axle shaft. Refer to Hub
Bearing and Axle Shaft in this section.
(4) Remove shift collar and intermediate axle
shaft.
(5) Remove the inner axle shaft seal from the shift
motor housing (Fig. 13).
(6) Remove the intermediate axle shaft bearing
(Fig. 14).
ASSEMBLY/INSTALLATION
(1) Position the bearing on installation tool. Seat
the bearing in the housing bore (Fig. 15).
(2) Clean the inside perimeter of the axle shaft
tube with fine crocus cloth.
(3) Apply a light film of oil to the inside lip of the
new axle shaft seal.
(4) Install the inner axle seal (Fig. 16, 17).
The axle shaft seal primary installation tool
6228-1 will only force the seal partially into the
Fig. 11 Shift Motor Housing and Shift Collar
Fig. 12 Vacuum Shift Motor ComponentsFig. 13 Axle Shaft Inner Seal Removal
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 31