1995 JEEP CHEROKEE coolant level
[x] Cancel search: coolant levelPage 368 of 2198

The gauge needle moves as the movable permanent
magnet aligns itself to the changing magnetic fields
created around it by the electromagnets.
COOLANT TEMPERATURE GAUGE
The coolant temperature gauge gives an indication
of engine coolant temperature. The coolant tempera-
ture sending unit is a thermistor that changes elec-
trical resistance with changes in engine coolant
temperature. High sending unit resistance causes
low coolant temperature readings. Low resistance
causes high coolant temperature readings. Sending
unit resistance values are shown in a chart in Spec-
ifications.
FUEL GAUGE
The fuel gauge gives an indication of the level of
fuel in the fuel tank. The fuel gauge sending unit has
a float attached to a swing-arm in the fuel tank. The
float moves up or down within the fuel tank as fuel
level changes. As the float moves, an electrical con-
tact on the swing-arm wipes across a resistor coil,
which changes sending unit resistance. High sending
unit resistance causes high fuel level readings. Low
resistance causes low fuel level readings. Sending
unit resistance values are shown in a chart in Spec-
ifications.
OIL PRESSURE GAUGE
The oil pressure gauge gives an indication of en-
gine oil pressure. The combination oil pressure send-
ing unit contains a flexible diaphragm. The
diaphragm moves in response to changes in engine
oil pressure. As the diaphragm moves, sending unit
resistance increases or decreases. High resistance on
the gauge side of the sending unit causes high oil
pressure readings. Low resistance causes low oil
pressure readings. Sending unit resistance values are
shown in a chart in Specifications.
SPEEDOMETER/ODOMETER
The speedometer/odometer give an indication of ve-
hicle speed and travel distance. The speedometer re-
ceives a vehicle speed pulse signal from the Vehicle
Speed Sensor (VSS). An electronic integrated circuit
contained within the speedometer reads and analyzes
the pulse signal. It then adjusts the ground path re-
sistance of one electromagnet in the gauge to control
needle movement. It also sends signals to an electric
stepper motor to control movement of the odometer
number rolls. Frequency values for the pulse signal
are shown in a chart in Specifications.
The VSS is mounted to an adapter near the trans-
fer case output shaft. The sensor is driven through
the adapter by a speedometer pinion gear. The
adapter and pinion vary with transmission, axle ratio
and tire size. Refer to Group 21 - Transmission and
Transfer Case for more information.
TACHOMETER
The tachometer gives an indication of engine speed
in Revolutions-Per-Minute (RPM). With the engine
running, the tachometer receives an engine speed
pulse signal from the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). An electronic integrated circuit contained
within the tachometer reads and analyzes the pulse
signal. It then adjusts the ground path resistance of
one electromagnet in the gauge to control needle
movement. Frequency values for the pulse signal are
shown in a chart in Specifications.
TRIP ODOMETER
The trip odometer is driven by the same electronic
integrated circuit as the speedometer/odometer. How-
ever, by depressing the trip odometer reset knob on
the face of the speedometer, the trip odometer can be
reset to zero. The trip odometer is serviced only as a
part of the speedometer/odometer gauge assembly.
VOLTMETER
The voltmeter is connected in parallel with the bat-
tery. With the ignition switch ON, the voltmeter in-
dicates battery or generator output voltage,
whichever is greater.
INDICATOR LAMPS
All indicator lamps, except the four-wheel drive in-
dicator, are located in the main cluster tell-tale area
above the steering column opening. Each of the
lamps is served by the main cluster printed circuit
and cluster connector. The four-wheel drive indicator
lamp is located in the gauge package cluster and is
served by the gauge package printed circuit and clus-
ter connector.
Up to eleven indicator lamps can be found in the
tell-tale area of the main cluster. These lamps are ar-
ranged in two rows, with six lamps in the upper row
and five lamps in the lower row.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM LAMP
The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) lamp is
switched to ground by the ABS module. The module
lights the lamp when the ignition switch is turned to
the START position as a bulb test. The lamp will
stay on for 3 to 5 seconds after vehicle start-up to in-
dicate a system self-test is in process. If the lamp re-
mains on after start-up, or comes on and stays on
while driving, it may indicate that the ABS module
has detected a system malfunction or that the system
has become inoperative. Refer to Group 5 - Brakes
for more information.
BRAKE WARNING LAMP
The brake warning lamp warns the driver that the
parking brake is applied or that the pressures in the
two halves of the split brake hydraulic system are
unequal. With the ignition switch turned ON, battery
JINSTRUMENT PANEL AND GAUGESÐYJ 8E - 25
Page 581 of 2198
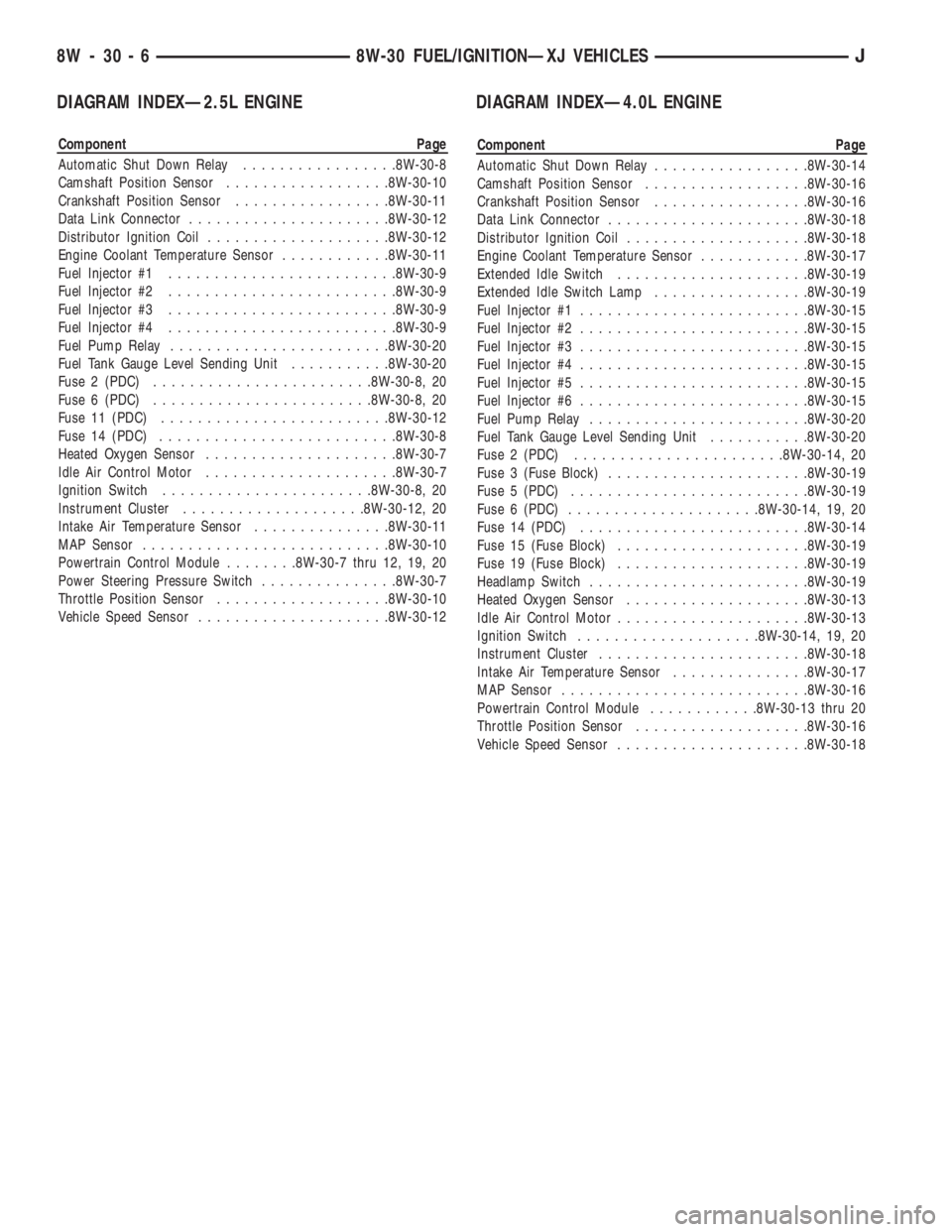
DIAGRAM INDEXÐ2.5L ENGINE
Component Page
Automatic Shut Down Relay.................8W-30-8
Camshaft Position Sensor..................8W-30-10
Crankshaft Position Sensor.................8W-30-11
Data Link Connector......................8W-30-12
Distributor Ignition Coil....................8W-30-12
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor............8W-30-11
Fuel Injector #1.........................8W-30-9
Fuel Injector #2.........................8W-30-9
Fuel Injector #3.........................8W-30-9
Fuel Injector #4.........................8W-30-9
Fuel Pump Relay........................8W-30-20
Fuel Tank Gauge Level Sending Unit...........8W-30-20
Fuse 2 (PDC)........................8W-30-8, 20
Fuse 6 (PDC)........................8W-30-8, 20
Fuse 11 (PDC).........................8W-30-12
Fuse 14 (PDC)..........................8W-30-8
Heated Oxygen Sensor.....................8W-30-7
Idle Air Control Motor.....................8W-30-7
Ignition Switch.......................8W-30-8, 20
Instrument Cluster....................8W-30-12, 20
Intake Air Temperature Sensor...............8W-30-11
MAP Sensor...........................8W-30-10
Powertrain Control Module........8W-30-7 thru 12, 19, 20
Power Steering Pressure Switch...............8W-30-7
Throttle Position Sensor...................8W-30-10
Vehicle Speed Sensor.....................8W-30-12
DIAGRAM INDEXÐ4.0L ENGINE
Component Page
Automatic Shut Down Relay.................8W-30-14
Camshaft Position Sensor..................8W-30-16
Crankshaft Position Sensor.................8W-30-16
Data Link Connector......................8W-30-18
Distributor Ignition Coil....................8W-30-18
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor............8W-30-17
Extended Idle Switch.....................8W-30-19
Extended Idle Switch Lamp.................8W-30-19
Fuel Injector #1.........................8W-30-15
Fuel Injector #2.........................8W-30-15
Fuel Injector #3.........................8W-30-15
Fuel Injector #4.........................8W-30-15
Fuel Injector #5.........................8W-30-15
Fuel Injector #6.........................8W-30-15
Fuel Pump Relay........................8W-30-20
Fuel Tank Gauge Level Sending Unit...........8W-30-20
Fuse 2 (PDC).......................8W-30-14, 20
Fuse 3 (Fuse Block)......................8W-30-19
Fuse 5 (PDC)..........................8W-30-19
Fuse 6 (PDC).....................8W-30-14, 19, 20
Fuse 14 (PDC).........................8W-30-14
Fuse 15 (Fuse Block).....................8W-30-19
Fuse 19 (Fuse Block).....................8W-30-19
Headlamp Switch........................8W-30-19
Heated Oxygen Sensor....................8W-30-13
Idle Air Control Motor.....................8W-30-13
Ignition Switch....................8W-30-14, 19, 20
Instrument Cluster.......................8W-30-18
Intake Air Temperature Sensor...............8W-30-17
MAP Sensor...........................8W-30-16
Powertrain Control Module............8W-30-13 thru 20
Throttle Position Sensor...................8W-30-16
Vehicle Speed Sensor.....................8W-30-18
8W - 30 - 6 8W-30 FUEL/IGNITIONÐXJ VEHICLESJ
Page 612 of 2198

INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
INDEX
page page
ABS Warning Lamp........................ 2
Brake Warning Lamp....................... 2
Charging System Indicator Lamp............... 3
Cluster Ground............................ 3
Diagram Index............................. 3
Engine Coolant Temperature Gauge............ 1
Engine Coolant Temperature Warning Lamp...... 1
Fuel Gauge.............................. 1
High-Beam Indicator Lamp................... 2
Instrument Cluster......................... 1Low Fuel Warning Lamp..................... 1
Low Washer Fluid Warning Lamp.............. 2
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)............... 2
Manual Transmission Up-Shift Lamp............ 2
Oil Pressure Gauge........................ 2
Oil Pressure Warning Lamp.................. 2
Seat Belt Indicator Warning Lamp.............. 2
Speedometer............................. 2
Tachometer.............................. 2
Turn Signal Indicator Lamps.................. 2
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
The instrument cluster contains the gauges and
warning lamps. All gauges have magnetic move-
ments.
When the ignition switch is in the START or RUN
position, circuit A21 feeds circuit F87 through fuse 17
in the fuse block. Circuit A1 from fuse 6 in the Power
Distribution Center (PDC) supplies voltage to circuit
A21. Circuit A1 is HOT at all times.
Circuit F87 connects to the cluster connector to
power the gauges and to the telltale connector to
power the warning lamps.
Circuit E2 from fuse 19 in the fuse block feeds the
illumination lamps. Circuit E2 originates at the head-
lamp switch and continues through fuse 19. The
headlamp switch powers circuit E2 when the parking
lamps or headlamp are ON.
Circuit Z2 provides ground for the indicator lamps
and illumination lamps.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE GAUGE
Circuit G20 connects the engine coolant tempera-
ture gauge to the engine coolant temperature sensor.
The sensor is a variable resistor and case grounded to
the engine. Circuit F87 connects to the instrument
cluster left connector and supplies voltage for the
gauge.
The gauge uses two coils. Current passing through
the coils creates a magnetic field. Position of the
gauge needle is controlled by the amount of current
passing through the coils to ground at the sensor.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE WARNING
LAMP
Circuit G20 connects the engine coolant tempera-
ture warning lamp to the engine coolant temperature
switch. When the switch closes, battery voltage from
circuit F87 flows through the lamp to ground through
the switch on circuit G20. The engine coolant tem-
perature switch is case grounded to the engine. Cir-cuit F87 connects to the instrument cluster connector
and supplies voltage for the lamp.
Circuit G20 also connects to the warning lamp to
ground when the ignition switch is in the START
position. When the ignition switch is in the START
position, the lamp illuminates for a bulb test.
FUEL GAUGE
The fuel level sensor is a variable resistor. Circuit
G4 connects the fuel level sensor to the fuel gauge in
the instrument cluster. Circuit F87 from fuse 17 in
the fuse block supplies voltage to the fuel gauge. The
fuel level sensor draws voltage from circuit F87
through the fuel gauge on circuit G4. Circuit G4
connects to circuit 57 in the fuel pump module har-
ness. Circuit 57 connects to the fuel level sensor.
Circuit 99 in the fuel pump module harness con-
nects to circuit Z1. Circuit Z1 provides the ground
path for the fuel level sensor. The grounding point for
circuit Z1 is the left side of the cowl panel.
As current flows through the coils in the fuel gauge,
it creates a magnetic field. One of the coils in the
gauge receives fixed current. The other coil is con-
nected to the level sensor. The magnetic field controls
the position of the fuel gauge pointer.
The fuel level sensor contains a variable resistor. As
the position of the float arm on the fuel level sensor
changes, the resistor changes the current flow
through second coil in the fuel gauge. A change in
current flow alters the magnetic field in the fuel
gauge, which changes the pointer position.
LOW FUEL WARNING LAMP
Circuit G4 connects the fuel level sensor to the fuel
gauge. The low fuel level module at the rear of the
gauge monitors resistance in circuit G4. The low fuel
level module powers an light emitting diode (LED)
when the resistance in circuit G4 reaches a calibrated
level. The LED illuminates the Low Fuel indicator.
Refer to Group 8E for additional information.
J8W-40 INSTRUMENT CLUSTERÐXJ VEHICLES 8W - 40 - 1
Page 860 of 2198

HELPFUL INFORMATION
²If the system loses ground for the Z11 circuits at
the right rear of the engine, the vehicle will not op-
erate. Check the connection at the ganged-ground cir-
cuit eyelet.
²Circuit F12 splices to supply battery voltage to the
vehicle speed control switch, back-up lamp switch,
A/C compressor clutch relay, windshield washer fluid
level sensor and radiator fan relay.
BRAKE SWITCH INPUT
Circuit K29 provides the brake switch input to the
PCM. Circuit K29 connects to cavity 29 of the PCM.
POWER (DEVICE) GROUND
Circuit Z12 connects to cavities 11 and 12 of the
PCM. The Z12 circuit provides ground for PCM inter-
nal drivers that operate high current devices like the
injectors and ignition coil.
Internal to the PCM, the power (device) ground cir-
cuit connects to the PCM sensor return circuit (from
circuit K4).
HELPFUL INFORMATION
²The grounding point for circuit Z12 is the right
rear of the engine.
²If the system loses ground for the Z12 circuits at
the rear of the engine, the vehicle will not operate.
Check the connection at the ganged-ground circuit
eyelet.
DIAGRAM INDEX
Component Page
Automatic Shut Down Relay.................8W-30-6
Camshaft Position Sensor...................8W-30-8
Crankshaft Position Sensor..................8W-30-9
Data Link Connector......................8W-30-11
Distributor Ignition Coil....................8W-30-11
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor.............8W-30-9
Fuel Injector #1.........................8W-30-7
Fuel Injector #2.........................8W-30-7
Fuel Injector #3.........................8W-30-7
Fuel Injector #4.........................8W-30-7
Fuel Injector #5.........................8W-30-7
Fuel Injector #6.........................8W-30-7
Fuel Pump Relay........................8W-30-12
Fuel Tank Gauge Level Sending Unit...........8W-30-12
Fuse 2 (PDC)...........................8W-30-6
Fuse 6 (PDC)...........................8W-30-6
Fuse 11 (PDC).......................8W-30-6, 11
Fuse 14 (PDC)..........................8W-30-6
Heated Oxygen Sensor....................8W-30-10
Idle Air Control Motor.....................8W-30-10
Ignition Switch.......................8W-30-6, 12
Instrument Cluster....................8W-30-11, 12
Intake Air Temperature Sensor................8W-30-9
MAP Sensor............................8W-30-8
Powertrain Control Module.............8W-30-6 thru 12
Throttle Position Sensor....................8W-30-8
Vehicle Speed Sensor.....................8W-30-11
J8W-30 FUEL/IGNITIONÐXJ-RHD 8W - 30 - 5
Page 1097 of 2198

CYLINDER COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE RADIATOR CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1 379
kPa (200 psi) maximum and 552 kPa (80 psi) recom-
mended.
Perform the test procedures on each cylinder ac-
cording to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
Refer to the Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leak-
age Test Diagnosis chart.
INSPECTION (ENGINE OIL LEAKS IN GENERAL)
Begin with a through visual inspection of the en-
gine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak. If
an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the fol-
lowing steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for ap-
proximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified, re-
pair per service manual instructions.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24km (15 miles), and
repeat step (3).
If the oil leak source is not positively identi-
fied at this time, proceed with the air leak detec-
tion test method as follows:
(1) Disconnect the breather cap to air cleaner hose
at the breather cap end. Cap or plug breather cap
nipple.
(2) Remove the PCV valve from the cylinder head
cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve grommet.
(3) Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and
regulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
(4) Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provide the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is de-
tected and identified, repair per service manual pro-
cedures.
(5) If the leakage occurs at the rear oil seal area,
refer to the section, Inspection for Rear Seal Area
Leak.
(6) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply
and remove the air hose and all plugs and caps. In-
stall the PCV valve and breather cap hose. Proceed
to step 7.
(7) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using
a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the en-
gine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The fol-
lowing steps should be followed to help pinpoint the
source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak:
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, distributor seal,
camshaft bore cup plugs oil galley pipe plugs, oil
9 - 6 ENGINESJ
Page 1111 of 2198

(a) Align the transmission torque converter hous-
ing with the engine.
(b) Loosely install the converter housing lower
bolts and install the next higher bolt and nut on
each side.
(c) Tighten all 4 bolts finger-tight.
(5) Install the engine support cushions (if re-
moved).
(6) Lower the engine and engine support cushions
onto the engine compartment brackets.
(7) Remove the engine lifting device.
(8) Raise the vehicle.
(9) If equipped with an automatic transmission:
(a) Install the converter-to-drive plate bolts. En-
sure the installation reference marks are aligned.
Tighten the bolts to 54 Nzm (40 ft. lbs.) torque.
(b) Install the converter-housing access cover.
(c) Install the exhaust pipe support.
(10) Install the remaining converter or flywheel
housing bolts.
(11) Install the starter motor and connect the ca-
ble. Tighten the bolts to 45 Nzm (33 ft. lbs.) torque.
(12) Tighten the engine support cushing through-
bolt nuts.
(13) Install the remaining flywheel and converter
housing bolts. Tighten the bolts to 38 Nzm (28 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(14) Connect the exhaust pipe to the manifold.
(15) Install the oil filter.
(16) Lower the vehicle.
(17) Connect the coolant hoses and tighten the
clamps.
(18) If equipped with power steering:
(a) Remove the protective caps
(b) Connect the hoses to the fittings at the steer-
ing gear. Tighten the nut to 52 Nzm (38 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(c) Fill the pump reservoir with fluid.
(19) Remove the pulley-to-water pump flange
alignment capscrew and install the fan and spacer or
Tempatrol fan assembly.
(20) Install the fan shroud and radiator and con-
denser (if equipped with air conditioning).
(21) Connect the radiator hoses.
(22) Connect the automatic transmission fluid
cooler pipes, if equipped.
(23) Connect the oxygen sensor wire connector.
(24) Connect the throttle valve rod and retainer.
Connect the throttle cable and install the rod. Install
the throttle valve rod spring.
(25) Connect the speed control cable, if equipped.
(26) Connect the fuel supply and return lines to
the throttle body.
(27) Connect all the vacuum hoses and wire con-
nectors.
(28) Connect the service valves to the A/C compres-
sor ports, if equipped with air conditioning.(29) Fill the power steering reservoir.
(30) Connect the battery cables.
(31) Install the hood.
(32) Install the air cleaner.
(33) Start the engine and inspect for leaks.
(34) Fill the cooling system.
(35) Stop the engine and check the fluid levels.
Add fluid, as required.
ENGINE ASSEMBLYÐYJ VEHICLES
REMOVAL
(1) Place a protective cloth over the windshield
frame. Raise the hood and rest it on the windshield
frame (Fig. 19).
(2) Disconnect the battery cable clamps and re-
move the battery.
WARNING: THE COOLANT IN A RECENTLY OPER-
ATED ENGINE IS HOT AND PRESSURIZED. USE
CARE TO PREVENT SCALDING BY HOT COOLANT.
CAREFULLY RELEASE THE PRESSURE BEFORE
REMOVING THE RADIATOR DRAIN COCK AND CAP.
(3) Remove the radiator drain cock and radiator
cap to drain the coolant. DO NOT waste usable cool-
ant. If the solution is clean, drain the coolant into a
clean container for reuse.
(4) Disconnect the wire connectors from the gener-
ator.
(5) Disconnect the ignition coil and distributor wire
connectors.
(6) Disconnect the oil pressure sender wire connec-
tor.
Fig. 19 Hood on Windshield Frame
9 - 20 2.5L ENGINEJ
Page 1113 of 2198

(14) Install the remaining flywheel housing bolts.
Tighten the bolts to 38 Nzm (28 ft. lbs.) torque.
(15) Install the starter motor and connect the ca-
ble. Tighten the bolts to 45 Nzm (33 ft. lbs.) torque.
(16) Install the oil filter.
(17) Lower the vehicle.
(18) Connect the coolant hoses and tighten the
clamps.
(19) If equipped with power steering:
(a) Remove the protective caps
(b) Connect the hoses to the fittings at the steer-
ing gear. Tighten the nut to 52 Nzm (38 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(c) Fill the pump reservoir with fluid.
(20) Remove the pulley-to-water pump flange
alignment capscrew and install the fan and spacer or
Tempatrol fan assembly.
(21) Tighten the serpentine drive belt according to
the specifications listed in Group 7, Cooling System.
(22) Install the fan shroud and radiator.
(23) Connect the radiator hoses.
(24) Connect the heater hoses.
(25) Connect the throttle valve rod and retainer.
(26) Connect the throttle cable and install the rod.
(27) Install the throttle valve rod spring.
(28) Connect the speed control cable, if equipped.
(29) Connect the oxygen sensor wire connector.
(30) Install the vacuum hose and check valve on
the brake booster.
(31) Connect the coolant temperature sensor wire
connector.
(32) Connect the idle speed actuator wire connec-
tor.
(33) Connect the fuel inlet and return hoses at the
fuel rail. Verify that the quick-connect fitting assem-
bly fits securely over the fuel lines by giving the fuel
lines a firm tug.
(34) Install the fuel line bracket to the intake man-
ifold.
(35) Connect all fuel injection wire connections.
(36) Install the engine ground strap.
(37) Connect the ignition coil wire connector.
(38) Remove the coolant temperature sending unit
to permit air to escape from the block. Fill the cool-
ing system with coolant. Install the coolant tempera-
ture sending unit when the system is filled.
(39) Install the battery and connect the battery ca-
bles.
(40) Install the air cleaner bonnet to the throttle
body.
(41) Install the air cleaner.
(42) Lower the hood and secure in place.
(43) Start the engine and inspect for leaks.
(44) Stop the engine and check the fluid levels.
Add fluid, as required.ENGINE CYLINDER HEAD COVER
A cured gasket is part of the engine cylinder head
cover.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Disconnect the Crankcase Ventilation (CCV)
vacuum hose from engine cylinder head cover (Fig.
1).
(3) Disconnect the fresh air inlet hose from the en-
gine cylinder head cover (Fig. 1).
(4) Remove the engine cylinder head cover mount-
ing bolts.
(5) Remove the engine cylinder head cover.
CLEANING
Remove any original sealer from the cover sealing
surface of the engine cylinder head and clean the
surface using a fabric cleaner.
Remove all residue from the sealing surface using
a clean, dry cloth.
INSPECTION
Inspect the engine cylinder head cover for cracks.
Replace the cover, if cracked.
The original dark grey gasket material should NOT
be removed. If sections of the gasket material are
missing or are compressed, replace the engine cylin-
der head cover. However, sections with minor damage
such as small cracks, cuts or chips may be repaired
with a hand held applicator. The new material must
be smoothed over to maintain gasket height. Allow
the gasket material to cure prior to engine cylinder
head cover installation.
INSTALLATION
(1) If a replacement cover is installed, transfer the
CCV valve grommet the oil filler cap from the origi-
nal cover to the replacement cover.
(2) Install engine cylinder head cover. Tighten the
mounting bolts to 10 Nzm (85 in. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 1 Engine Cylinder Head Cover
9 - 22 2.5L ENGINEJ
Page 1118 of 2198

CAUTION: Engine cylinder head bolts should be re-
used only once. Replace the head bolts if they were
used before or if they have a paint dab on the top
of the bolt.
(6) Coat the threads of bolt No.7, only, with Loctite
PST sealant or equivalent.
(7) Install all head bolts, except No.8 and No.10.
(8) Remove the dowels.
(9) Install No.8 and No.10 head bolts.
(10) Tighten the engine cylinder head bolts in se-
quence according to the following procedure (Fig. 6):
(a) Tighten all bolts in sequence (1 through 10)
to 30 Nzm (22 ft. lbs.) torque.
(b) Tighten all bolts in sequence (1 through 10)
to 61 Nzm (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
(c) Check all bolts to verify they are set to 61
Nzm (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
(d) Tighten bolts (in sequence):
²Bolts 1 through 6 to 149 Nzm (110 ft. lbs.) torque.
²Bolt 7 to 136 Nzm (100 ft. lbs.) torque.
²Bolts 8 through 10 to 149 Nzm (110 ft. lbs.) torque.
CAUTION: During the final tightening sequence,
bolt No.7 will be tightened to a lower torque than
the rest of the bolts. DO NOT overtighten bolt No.7.
(e) Check all bolts in sequence to verify the cor-
rect torque.
(f) If not already done, clean and mark each bolt
with a dab of paint after tightening. Should you en-
counter bolts which were painted in an earlier ser-
vice operation, replace them.
(11) Install the ignition coil and bracket assembly.
(12) Connect the temperature sending unit wire
connector.
(13) Install the spark plugs and tighten to 37 Nzm
(27 ft. lbs.) torque. Connect the ignition wires.
(14) Install the intake and exhaust manifolds (re-
fer to Group 11, Exhaust System and Intake Mani-
fold for the proper procedures).(15) Install the fuel lines and the vacuum advance
hose.
(16) If equipped, attach the power steering pump
and bracket.
(17) Install the push rods, rocker arms, pivots and
bridges in the order they were removed.
(18) Install the engine cylinder head cover.
(19) Attach the air conditioning compressor mount-
ing bracket to the engine cylinder head and block.
Tighten the bolts to 40 Nzm (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(20) Attach the air conditioning compressor to the
bracket. Tighten the bolts to 27 Nzm (20 ft. lbs.)
torque.
CAUTION: The serpentine drive belt must be routed
correctly. Incorrect routing can cause the water
pump to turn in the opposite direction causing the
engine to overheat.
(21) Install the serpentine drive belt and correctly
tension the belt (refer to Group 7, Cooling System for
the proper procedure).
(22) Install the air cleaner and ducting.
(23) Install the engine cylinder head cover.
(24) Connect the hoses to the thermostat housing
and fill the cooling system to the specified level (refer
to Group 7, Cooling Systems for the proper proce-
dure).
(25) The automatic transmission throttle linkage
and cable must be adjusted after completing the en-
gine cylinder head installation (refer to Group 21,
Transmissions for the proper procedures).
(26) Install the temperature sending unit and con-
nect the wire connector.
(27) Connect the fuel pipe and vacuum advance
hose.
(28) Connect negative cable to battery.
(29) Connect the upper radiator hose and heater
hose at the thermostat housing.
(30) Fill the cooling system. Check for leaks.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN DIRECT
LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT HANDS NEAR
THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR FAN. DO NOT WEAR
LOOSE CLOTHING.
(31) Operate the engine with the radiator cap off.
Inspect for leaks and continue operating the engine
until the thermostat opens. Add coolant, if required.
VALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS
This procedure is done with the engine cylinder
head removed from the block.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the engine cylinder head from the cyl-
inder block.
Fig. 6 Engine cylinder head Bolt Tightening
Sequence
J2.5L ENGINE 9 - 27