1994 JEEP CHEROKEE power steering
[x] Cancel search: power steeringPage 108 of 1784

SPEED CONTROLÐPCM INPUT
The speed control system provides three separate
inputs to the powertrain control module (PCM); On/
Off, Set and Resume. The On/Off input informs the
PCM that the speed control system has been acti-
vated. The Set input informs the PCM that a fixed
vehicle speed has been selected. The Resume input
indicates to the PCM that the previous fixed speed is
requested.
The speed control operating range is from 50 km/h
to 142 km/h (35 to 85 mph). Inputs that effect speed
control operation are:
²Park/neutral switch
²Vehicle speed sensor
²Throttle position sensor
Refer to Group 8H for further speed control infor-
mation.
SENSOR RETURNÐPCM INPUT
Sensor Return provides a low noise ground refer-
ence for all system sensors.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS)ÐPCM INPUT
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is mounted on
the throttle body (Figs. 14 or 15). The TPS is a vari-
able resistor that provides the powertrain control
module (PCM) with an input signal (voltage) that
represents throttle blade position. The sensor is con-
nected to the throttle blade shaft. As the position of
the throttle blade changes, the resistance of the TPS
changes.
The PCM supplies approximately 5 volts to the
TPS. The TPS output voltage (input signal to the
PCM) represents the throttle blade position. The
PCM receives an input signal voltage from the TPS.
This will vary in an approximate range of from 1
volt at minimum throttle opening (idle), to 4 volts at
wide open throttle. Along with inputs from other sen-
sors, the PCM uses the TPS input to determine cur-rent engine operating conditions. In response to
engine operating conditions, the PCM will adjust fuel
injector pulse width and ignition timing.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The vehicle speed sensor (Fig. 16) is located in the
extension housing of the transmission (2 wheel drive)
or on the transfer case extension housing (4 wheel
drive). The sensor input is used by the powertrain
control module (PCM) to determine vehicle speed and
distance traveled.
The speed sensor generates 8 pulses per sensor rev-
olution. These signals, in conjunction with a closed
throttle signal from the throttle position sensor, indi-
cate a closed throttle deceleration to the PCM. When
the vehicle is stopped at idle, a closed throttle signal
is received by the PCM (but a speed sensor signal is
not received).
Under deceleration conditions, the PCM adjusts the
idle air control (IAC) motor to maintain a desired
MAP value. Under idle conditions, the PCM adjusts
the IAC motor to maintain a desired engine speed.
Fig. 13 Power Steering Pump Pressure SwitchÐXJ
Models
Fig. 14 Throttle Position SensorÐ2.5L Engine
Fig. 15 Throttle Position SensorÐ4.0L Engine
JFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 23
Page 139 of 1784

MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTION (MFI)ÐCOMPONENT REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
INDEX
page page
Accelerator Pedal and Throttle Cable......... 54
Air Cleaner Housing...................... 54
Air Conditioning (A/C) Clutch Relay........... 54
Air Filter............................... 54
Automatic Shut Down (ASD) Relay........... 54
Brake Switch............................ 54
Camshaft Position Sensor.................. 54
Crankshaft Position Sensor................. 55
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor.......... 55
Fuel Filter.............................. 55
Fuel Injector............................ 55
Fuel Pump Module....................... 56
Fuel Pump Relay........................ 56
Fuel Rail Assembly....................... 56
Fuel System Pressure Release Procedure...... 56
Fuel Tank Pressure Relief/Rollover Valve...... 56
Fuel Tanks............................. 56Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps.......... 56
Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor................. 56
Ignition Coil............................. 57
Intake Air Temperature Sensor.............. 54
Intake Manifold.......................... 57
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor..... 57
Oxygen (O2S) Sensor..................... 57
Park Neutral Switch....................... 58
Power Steering Pressure SwitchÐ2.5L
Engine Only........................... 58
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)............ 58
Quick-Connect Fittings..................... 59
Throttle Body............................ 59
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS).............. 59
Torque Converter Clutch Relay.............. 60
Vehicle Speed Sensor..................... 60
ACCELERATOR PEDAL AND THROTTLE CABLE
Refer to the Accelerator Pedal and Throttle Cable
section of this group for removal/installation proce-
dures.
AIR CONDITIONING (A/C) CLUTCH RELAY
The A/C clutch relay is located in the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC) (Figs. 1 or 2). For location of
this relay within the PDC, refer to label on PDC
cover.
AIR CLEANER HOUSING
Refer to Group 25, Emission Control System.
AIR FILTER
Refer to Group 25, Emission Control System.
AUTOMATIC SHUT DOWN (ASD) RELAY
The ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution
Center (Figs. 1 or 2) (PDC). For location of this relay
within the PDC, refer to label on PDC cover.
BRAKE SWITCH
Refer to Group 5, Brakes for removal/installation
procedures.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
For removal/installation procedures, refer to Group
8D, Ignition System. See Camshaft Position Sensor.
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The intake manifold air temperature sensor is in-
stalled into the intake manifold plenum (Figs. 3 or
4).
Fig. 1 PDCÐYJ Models
Fig. 2 PDCÐXJ Models
14 - 54 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 143 of 1784

(3) Lower the vehicle.
PARK NEUTRAL SWITCH
Refer to Group 21, Transmissions for park neutral
switch service.
POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCHÐ2.5L
ENGINE ONLY
The power steering pressure switch is installed in
the power steering high pressure hose (Figs. 11 or
12).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the electrical connector from the
power steering pressure switch.
(2) Place a small container or shop towel beneath
the switch to collect any excess fluid.
(3) Remove the switch.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the power steering switch.
(2) Connect the electrical connector to the switch.(3) Check power steering fluid and add as neces-
sary.
(4) Start the engine and again check power steer-
ing fluid. Add fluid if necessary.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
On XJ models, the PCM is located in the engine
compartment next to the air cleaner (Fig. 13). On YJ
models, the PCM is located in the engine compart-
ment behind the windshield washer fluid reservoir
(Fig. 14).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable at the
battery.
(2) YJ Models Only: Remove the windshield
washer fluid tank.
(3) Loosen the 60-Way connector mounting bolt
(Figs. 13 or 14).
(4) Remove the electrical connector by pulling
straight back.
(5) Remove the three PCM mounting bolts.
(6) Remove PCM.
Fig. 11 Power Steering Pressure SwitchÐYJ Models
Fig. 12 Power Steering Pressure SwitchÐXJ Models
Fig. 13 PCM LocationÐXJ Models
Fig. 14 PCM LocationÐYJ Models
14 - 58 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 154 of 1784

SERVICE BRAKE DIAGNOSIS
INDEX
page page
Component Inspection...................... 8
Diagnosing Parking Brake Problems.......... 10
Diagnosing Service Brake Problems........... 8
Diagnosis Procedures...................... 7
General Information........................ 7Master Cylinder/Power Booster Test.......... 11
Power Booster Check Valve Test............ 11
Power Booster Vacuum Test................ 12
Preliminary Brake Check.................... 7
Road Testing............................ 7
GENERAL INFORMATION
The diagnosis information in this section covers
service brake components which include:
²disc brake calipers
²disc brakeshoes
²drum brake wheel cylinders
²drum brakeshoes and brake drums
²drum brake support plates
²parking brake mechanism
²master cylinder/combination valve
²vacuum power brake booster
²brake pedal and brakelight switch
²brake warning light
DIAGNOSIS PROCEDURES
Service brake diagnosis involves determining if a
problem is related to a mechanical, hydraulic or vac-
uum operated component. A preliminary brake
check, followed by road testing and component in-
spection are needed to determine a problem cause.
Road testing will either verify proper brake opera-
tion or confirm the existence of a problem. Compo-
nent inspection will, in most cases, identify the
actual part responsible for a problem.
The first diagnosis step is the preliminary brake
check. This involves inspecting fluid level, parking
brake action, wheel and tire condition, checking for
obvious leaks or component damage and testing
brake pedal response. A road test will confirm or
deny the existence of a problem. The final diagnosis
procedure involves road test analysis and a visual in-
spection of brake components.
PRELIMINARY BRAKE CHECK
(1) If amber antilock light is illuminated, refer to
Antilock Brake System Diagnosis. However, if red
warning light is illuminated, or if neither warning
light is illuminated, continue with diagnosis.
(2) Check condition of tires and wheels. Damaged
wheels and worn, damaged, or underinflated tires
can cause pull, shudder, tramp and a condition simi-
lar to grab.
(3) If complaint was based on noise when braking,
check suspension components. Jounce front and rearof vehicle and listen for noise that might be caused
by loose, worn, or damaged suspension or steering
components.
(4) Inspect brake fluid level:
(a) If vehicle has one-piece master cylinder, fluid
level should be to 6 mm (1/4 in.) of reservoir rim. If
vehicle two-piece, removable reservoir, correct level
is to top of indicator rings in reservoir.
(b) On models with ABS brakes, preferred level
is to MAX mark on reservoir. Acceptable level is
between MAX and MIN marks.
(c) Remember that fluid level in the front and
rear reservoir compartments will decrease in pro-
portion to normal lining wear. However, if fluid
level is abnormally low, look for leaks at calipers,
wheel cylinders, brakelines and master cylinder.
(5) Inspect brake fluid condition:
(a) Fluid should be reasonably clear and free of
foreign material.Note that brake fluid tends to
darken over time. This is normal and should
not be mistaken for contamination. If fluid is
clear of foreign material, it is OK.
(b) If fluid is highly discolored, or appears to con-
tain foreign material, drain out a sample with a
clean suction gun. Pour sample in a glass container
and note condition.
(c) If fluid separates into layers, obviously con-
tains oil, or a substance other than brake fluid,
system seals and cups will have to be replaced and
hydraulic system flushed.
(6) Check parking brake operation. Verify free
movement and full release of cables and foot pedal or
hand lever. Also note if vehicle was being operated
with parking brake partially applied.
(7) Check brake pedal operation. Verify that pedal
does not bind and has adequate free play. If pedal
lacks free play, check pedal and power booster for be-
ing loose or for bind condition. Do not road test until
condition is corrected.
(8) If components inspected look OK, road test the
vehicle.
ROAD TESTING
(1) If amber warning light is illuminated, problem
is with antilock system component. Refer to Antilock
Brake System Diagnosis.
JBRAKES 5 - 7
Page 188 of 1784

4). The engine intake manifold serves as the vacuum
source for booster operation.
The booster is mounted on the engine compartment
side of the dash panel. The master cylinder is
mounted on attaching studs at the front of the
booster. The master cylinder central valves are di-
rectly actuated by the booster push rod.
The pedal travel sensor is mounted in the forward
face of the booster shell. The sensor plunger is actu-
ated by the booster diaphragm plate.
PEDAL TRAVEL SENSOR
The pedal travel sensor signals brake pedal posi-
tion to the antilock ECU. The sensor signal is based
on changes in electrical resistance. The resistance
changes occur in steps that are generated by changes
in brake pedal position. A resistance signal gener-
ated by changing brake pedal position, will cause the
ECU to run the antilock pump when necessary.
The sensor is a plunger-type, electrical switch
mounted in the forward housing of the power brake
booster (Fig. 5). The sensor plunger is actuated by
movement of the booster diaphragm plate.
The tip on the sensor plunger is color coded. The
tip must be matched to the color dot on the face of
the brake booster front shell (Fig. 5).
WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
A sensor is used at each wheel. The sensors convert
wheel speed into an electrical signal. This signal is trans-
mitted to the antilock electronic control unit (ECU).
A gear-type tone ring serves as the trigger mecha-
nism for each sensor. The tone rings are mounted at
the outboard ends of the front and rear axle shafts.
Different sensors are used at the front and rear
wheels (Fig. 6). The front/rear sensors have the same
electrical values but are not interchangeable.
ELECTRONIC CONTROL UNIT (ECU)
A separate electronic control unit (ECU) monitors,
operates and controls the antilock system (Fig. 7).
The ECU contains dual microprocessors. The logic
block in each microprocessor receives identical sensor
signals. These signals are processed and compared si-
multaneously (Fig. 8).
The ECU is located under the instrument panel. It
is located at the right side of the steering column.
The power up voltage source for the ECU is through
the ignition switch in the On and Run positions.
The antilock ECU is separate from the other vehi-
cle electronic control units. It contains a self check
program that illuminates the amber warning light
when a system fault is detected. Faults are stored in
a diagnostic program memory and are accessible
with the DRB II scan tool.
ABS faults remain in memory until cleared, or until af-
ter the vehicle is started approximately 50 times. Stored
faults arenoterased if the battery is disconnected.
ACCELERATION SWITCH
An acceleration switch (Fig. 9), provides an addi-
tional vehicle deceleration reference during 4-wheel
drive operation. The switch is monitored by the anti-
lock ECU at all times.
The switch reference signal is utilized by the ECU
when all wheels are decelerating at the same speed.
Equal wheel speeds occur during braking in undiffer-
entiated 4-wheel ranges.
Fig. 5 Pedal Travel Sensor Location
Fig. 6 Wheel Speed Sensors
JBRAKES 5 - 41
Page 190 of 1784

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM OPERATION
INDEX
page page
ABS Operation in Antilock Braking Mode....... 43
ABS Operation in Normal Braking Mode....... 43
Acceleration Switch Operation............... 45
ECY Operation.......................... 46HCU Pump and Pedal Travel Sensor Operation . 44
HCU Solenoid Valve Operation.............. 43
System Power-Up and Initialization........... 43
Wheel Speed Sensor Operation............. 45
SYSTEM POWER-UP AND INITIALIZATION
The antilock system is in standby mode with the
ignition switch in Off or Accessory position. The an-
tilock electrical components are not operational.
Turning the ignition switch to On or Run position
allows battery voltage to flow through the switch to
the ECU ignition terminal.
The ABS system is activated when battery voltage
is supplied to the ECU. The ECU performs a system
initialization procedure at this point. Initialization
consists of a static and dynamic self check of system
electrical components.
The static check occurs immediately after the igni-
tion switch is turned to the On position. The dynamic
check occurs when vehicle road speed reaches ap-
proximately 10 kph (6 mph). During the dynamic
check, the ECU briefly cycles the pump to verify op-
eration. The HCU solenoids are checked continu-
ously.
If an ABS component exhibits a fault during ini-
tialization, the ECU illuminates the amber warning
light and registers a fault code in the microprocessor
memory.
ABS OPERATION IN NORMAL BRAKING MODE
The ECU monitors wheel speed sensor inputs con-
tinuously while the vehicle is in motion. However,
the ECU will not activate any ABS components as
long as sensor inputs and the acceleration switch in-
dicate normal braking.
During normal braking, the master cylinder, power
booster and wheel brake units all function as they
would in a vehicle without ABS. The HCU compo-
nents are not activated.
ABS OPERATION IN ANTILOCK BRAKING MODE
The purpose of the antilock system is to prevent
wheel lockup during periods of high wheel slip. Pre-
venting lockup helps maintain vehicle braking action
and steering control.
The antilock ECU activates the system whenever
sensor signals indicate periods of high wheel slip.
High wheel slip can be described as the point where
wheel rotation begins approaching zero (or lockup)
during braking. Periods of high wheel slip occur
when brake stops involve high pedal pressure and
rate of vehicle deceleration.The antilock system retards lockup during high
slip conditions by modulating fluid apply pressure to
the wheel brake units.
Brake fluid apply pressure is modulated according
to wheel speed, degree of slip and rate of decelera-
tion. A sensor at each wheel converts wheel speed
into electrical signals. These signals are transmitted
to the ECU for processing and determination of
wheel slip and deceleration rate.
The Jeep ABS system has three fluid pressure con-
trol channels. The front brakes are controlled sepa-
rately and the rear brakes in tandem (Fig. 10). A
speed sensor input signal indicating high slip condi-
tions activates the ECU antilock program.
Two solenoid valves are used in each antilock con-
trol channel (Fig. 11). The valves are all located
within the HCU valve body and work in pairs to ei-
ther increase, hold, or decrease apply pressure as
needed in the individual control channels.
The solenoid valves are not static during antilock
braking. They are cycled continuously to modulate
pressure. Solenoid cycle time in antilock mode can be
measured in milliseconds.
HCU SOLENOID VALVE OPERATION
Normal Braking
During normal braking, the HCU solenoid valves
and pump are not activated. The master cylinder and
power booster operate the same as a vehicle without
an ABS brake system.
Antilock Pressure Modulation
Solenoid valve pressure modulation occurs in three
stages which are: pressure increase, pressure hold,
and pressure decrease. The valves are all contained
in the valve body portion of the HCU.
Pressure Decrease
The outlet valve is opened and the inlet valve is
closed during the pressure decrease cycle (Fig. 11).
A pressure decrease cycle is initiated when speed
sensor signals indicate high wheel slip at one or
more wheels. At this point, the ECU opens the outlet
valve. Opening the outlet valve also opens the hy-
draulic return circuit to the master cylinder reser-
JANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM OPERATION 5 - 43
Page 243 of 1784

DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOL-
ANT CAN OCCUR.
(1) Drain sufficient coolant from the radiator to de-
crease the level below the water pump heater hose
inlet.
(2) Remove the heater hose.
(3) Inspect the inlet for metal casting flash or
other restrictions.
Remove the pump from engine before remov-
ing restriction to prevent contamination of the
coolant with debris. Refer to Water Pump Re-
moval.
WATER PUMPSÐREMOVAL/INSTALLATION
REMOVALÐALL MODELS
The water pump on all models can be removed
without discharging the air conditioning system (if
equipped).
CAUTION: All engines have a reverse (counter-
clockwise) rotating water pump. The letter R is
stamped into the back of the water pump impeller
(Fig. 1) to identify. Engines from previous model
years, depending upon application, may be
equipped with a forward (clockwise) rotating water
pump. Installation of the wrong water pump will
cause engine over heating.The water pump impeller is pressed on the rear of
the pump shaft and bearing assembly. The water
pump is serviced only as a complete assembly.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE BLOCK DRAIN
PLUG(S) OR LOOSEN RADIATOR DRAINCOCK
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE.
SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If the solution
is clean, drain coolant into a clean container for re-
use.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Drain the cooling system. Refer to Draining
Cooling System in this group.
(3)XJ models with 4.0L engine equipped with
A/C or heavy duty cooling system:
Loosen (but do not remove at this time) the four
water pump pulley-to-water pump hub mounting
bolts (Fig. 3).
XJ models with 4.0L engine without A/C or
heavy duty cooling system; or any 2.5L engines;
or any YJ models:
Loosen (but do not remove at this time) the four
fan hub-to-water pump pulley mounting nuts (Fig.
4).
The engine accessory drive belt must be removed
prior to removing the fan (if installed at pump) or
fan pulley.
(4) Remove engine drive belt as follows:
(a) Loosen two rear power steering pump mount-
ing bolts A (Fig. 5).
(b) Loosen upper pump pivot bolt B and lower
lock nut C (Figs. 6 or 7).
(c) Loosen pump adjusting bolt D (Fig. 5) until
belt can be removed.
(d) Remove belt.
(5) Check condition of all pulleys.
(6) The power steering pump must be removed
from its cast mounting bracket to gain access to bolt
Fig. 2 Impeller TestÐTypical
Fig. 3 Water Pump Pulley Bolts
7 - 10 COOLING SYSTEMJ
Page 244 of 1784
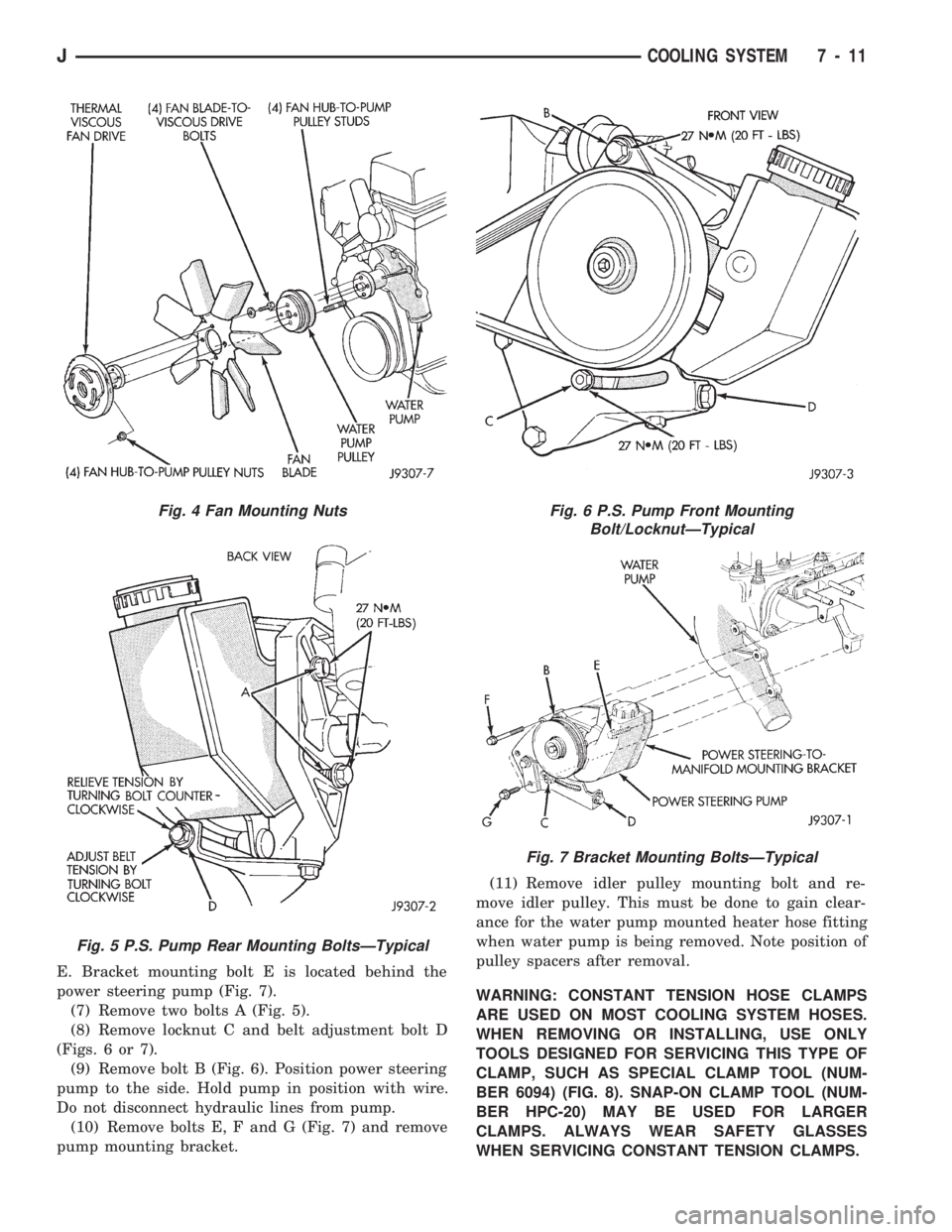
E. Bracket mounting bolt E is located behind the
power steering pump (Fig. 7).
(7) Remove two bolts A (Fig. 5).
(8) Remove locknut C and belt adjustment bolt D
(Figs. 6 or 7).
(9) Remove bolt B (Fig. 6). Position power steering
pump to the side. Hold pump in position with wire.
Do not disconnect hydraulic lines from pump.
(10) Remove bolts E, F and G (Fig. 7) and remove
pump mounting bracket.(11) Remove idler pulley mounting bolt and re-
move idler pulley. This must be done to gain clear-
ance for the water pump mounted heater hose fitting
when water pump is being removed. Note position of
pulley spacers after removal.
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUM-
BER 6094) (FIG. 8). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUM-
BER HPC-20) MAY BE USED FOR LARGER
CLAMPS. ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES
WHEN SERVICING CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
Fig. 4 Fan Mounting Nuts
Fig. 5 P.S. Pump Rear Mounting BoltsÐTypical
Fig. 6 P.S. Pump Front Mounting
Bolt/LocknutÐTypical
Fig. 7 Bracket Mounting BoltsÐTypical
JCOOLING SYSTEM 7 - 11