1994 JAGUAR XJ6 automatic transmission
[x] Cancel search: automatic transmissionPage 56 of 521

Cooling System (AJl6) m
4.1.1 COOLING SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
4.1.1.1 Major Components
o Main engine crossflow radiator, incorporating a concentric tube cooler for the power steering fluid mounted in
the right
-hand radiator side tank. Vehicles with automatic transmission have a transmission fluid cooler
mounted in the left
-hand radiator side tank; for 4,O liter supercharged engines a six-plate cooler is fitted; other
vehicles have
a tube-type cooler. Adouble-action temperature switch, for controlling the radiator cooling fans,
is mounted in the left
-hand radiator side tank.
0 Two electrically operated radiator cooling fans, mounted behind the main radiator.
0 Coolant circulating pump, belt driven from the engine crankshaft.
0 Coolant header tank with pressure relief cap and coolant level probe.
o Engine thermostat.
4.1.1.2
0 Heater matrix.
o Electrically operated coolant circulating pump, mounted on the left-hand side of the engine bulkhead.
o Solenoid operated valve, located adjacent to the coolant circulating pump.
Components for Climate Control System
4.1.1.3 Components for Supercharged Engine
0 0 Supercharger crossflow radiator, mounted in front of the main radiator. The supercharger radiator is reverse- circuited, i.e. the coolant inlet is at the bottom of the radiator.
0 Electrically operated coolant circulating pump, located at the left-hand side of the main radiator.
4.1.1.4 Operation
The configuration of the cooling system for normally aspirated and supercharged (4,O liter) engines is shown in Sub- section 4.1.2.
The cooling system is pressurized, which allows the system to operate at a higher temperature without overheating.
The header tank is fitted with a pressure relief cap to protect the system against overpressure.
Under cold start conditions, coolant is forced by the engine driven water pump through the cylinder block and cylinder
head to the thermostat housing. The thermostat is closed to give rapid engine warm up, hence the coolant is returned
directly to the water pump inlet. When normal engine operating temperature is reached, the thermostat opens and
coolant is diverted through the radiator before returning to the water pump inlet. In vehicles fitted with
a supercharger,
coolant is circulated through the supercharger radiator and intercooler by the supercharger water pump. The super- charger cooling circuit uses the same coolant header tank as the main engine cooling system.
The radiator cooling fans operate in series and parallel under the control of the double
-action radiator mounted tem- perature switch. The fans are also controlled by the climate control system on vehicles fitted with air conditioning.
Under hot operating conditions, the fans may continue to operate after the engine has been switched off. The fans
stop automatically when the coolant temperature has been reduced sufficiently.
The system also provides the coolant supply for the climate control system, which is described in Section
14.
X300 VSM 1 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 66 of 521

Cooling System (V12
4.2.1 COOLING SYSTEM DESCRIPTION I
4.2.1.1 Major Components
o Engine crossflow radiator, incorporating a concentric tube cooler for the power steering fluid mounted in the
left
-hand radiator side tank. Vehicles with automatic transmission have a six-plate transmission fluid cooler
mounted in the right
-hand radiator side tank. A double-action temperature switch, for controlling the electric
radiator cooling fans, is mounted in the left
-hand radiator side tank.
0 Engine driven, viscous-coupled, radiator cooling fan
0 Two electrically operated radiator cooling fans, mounted in front of the radiator.
o Coolant circulating pump, belt driven from the engine crankshaft.
0 Coolant header tank with pressure relief cap and coolant level probe.
0 Two engine thermostats, one in each cylinder bank.
4.2.1.2
0 Heater matrix.
0 Electrically operated coolant circulating pump, mounted on the left-hand side of the engine bulkhead.
o Solenoid operated valve, located adjacent to the coolant circulating pump.
Components for Climate Control System
1
4.2.1.3 Operation
The configuration of the cooling system is shown in Sub-section 4.2.2.
The cooling system is pressurized, which allows the system to operate at a higher temperature without overheating.
The header tank is fitted with a pressure relief cap to protect the system against overpressure.
Under cold start conditions, coolant is forced by the engine driven water pump through each cylinder block and cylin
- der head to the thermostat housings. The thermostats are closed to give rapid engine warm up, hence the coolant is
returned via the engine cross pipe to the water pump inlet. When normal engine operating temperature is reached,
the thermostats open and coolant is diverted through the radiator before returning to the water pump inlet.
If the engine driven fan is unable to provide sufficient cooling, the electrically operated fans operate in series and paral
-
lel underthe control of the radiator mounted temperature switch. Under hot operating conditions, the electric fans may
continue to operate after the engine has been switched off. The fans stop automatically when the coolant temperature
has been reduced sufficiently.
The system also provides the coolant supply for the climate control system, which is described in Section 14.
I
I X300 VSM 1 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 116 of 521

Manual Transmission & clutch (AJ16)
I Molykote FB 180 grease
Brake (clutch) fluid
- minimum
DOT 4
Dexron IID Transmission oil
Loctite
573
Tivoli Kay Adhesives No. 5696
Withdrawal arm pivots / Gearshift lever ball
Clutch hydraulic system
Front cover securing bolts
Exhaust sealer also used
in
ZF automatic
transmissions
Application
Material removal to clean up clutch face
IU SERVICE DATA
Specification
Up to lmm maximum
X300 VSM iii Issue 1 August 1994
Page 136 of 521
Automatic Transmission (AJ16)
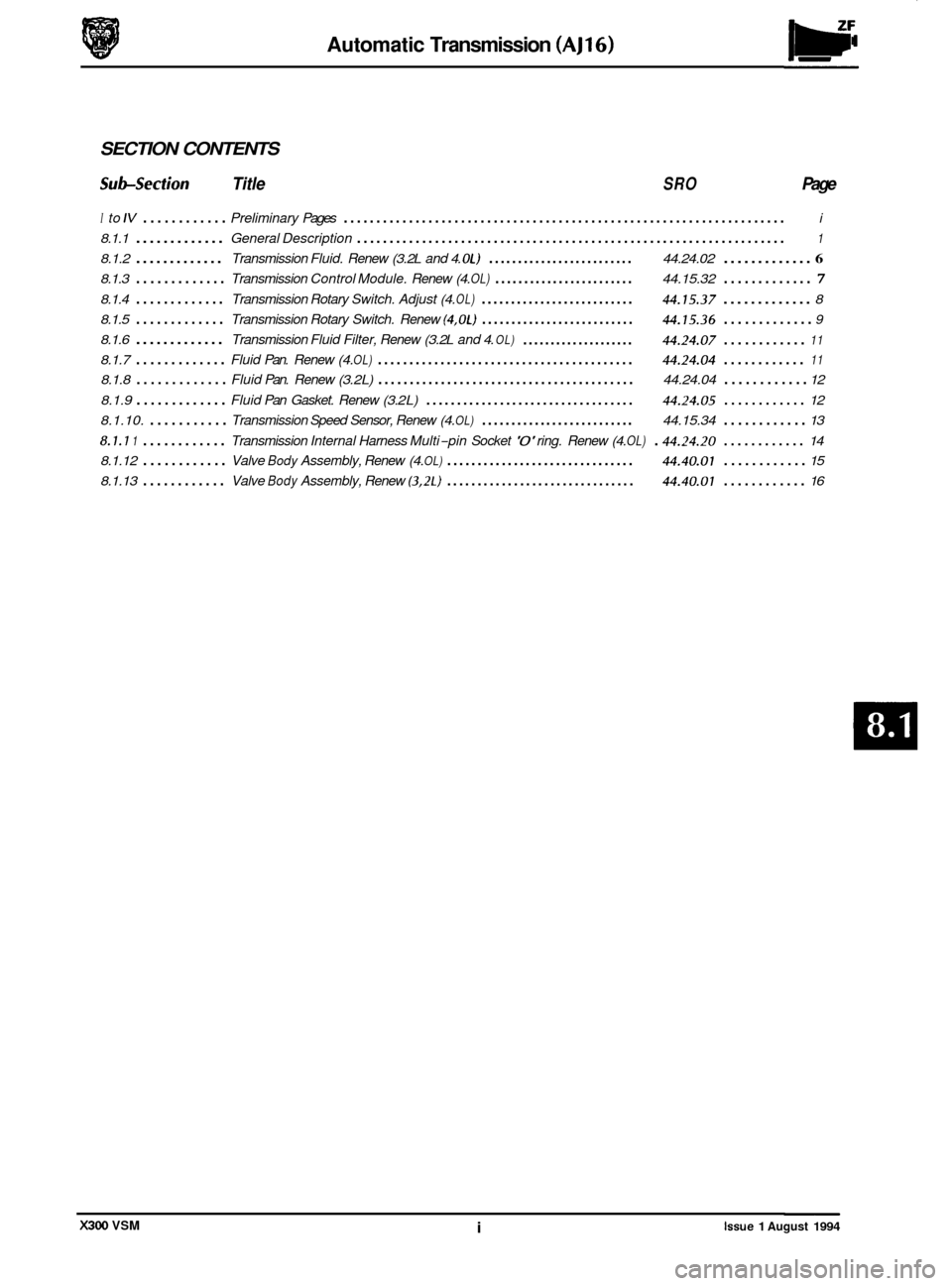
SECTION CONTENTS
Subsection Title SRO Page
I to IV ............ Preliminary Pages .................................................................... i
8.1.1 ............. General Description .................................................................. 1
8.1.2 ............. Transmission Fluid. Renew (3. 2L and 4. OL) ......................... 44.24.02 ............. 6
8.1.3 ............. Transmission Control Module. Renew (4. OL) ........................ 44.15.32 ............. 7
8.1.4 ............. Transmission Rotary Switch. Adjust (4. OL) .......................... 44.15.37 ............. 8
8.1.5
............. Transmission Rotary Switch. Renew (4.0L) .......................... 44.15.36 ............. 9
8.1.6 ............. Transmission Fluid Filter, Renew (3. 2L and 4. OL)
8.1.7 ............. Fluid Pan. Renew (4. OL) ......................................... 44.24.04 ............
8.1.8 ............. Fluid Pan. Renew (3. 2L) ......................................... 44.24.04 ............ 12
8.1.9
............. Fluid Pan Gasket. Renew (3. 2L) .................................. 44.24.05 ............ 12
8.1.10.
........... Transmission Speed Sensor, Renew (4. OL) .......................... 44.15.34 ............ 13
8.1.1 1 ............ Transmission Internal Harness Multi-pin Socket '0' ring. Renew (4. OL) . 4424.20 ............ 14
Valve Body Assembly, Renew (4. OL) ............................... 44.40.01 ............ 15
.................... 44.24.07 ............ 11
11
8.1.12 ............
8.1.13 ............ Valve Body Assembly, Renew (3.2L) ............................... 44.40.01 ............ 16
X300 VSM i Issue 1 August 1994
Page 138 of 521

Automatic Transmission (AJ16)
8.1.1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
’ This section provides information relating to the automatic transmissionsfitted to the 3,2 liter engine (ZF 4 HP 22 trans- mission) and the 4,O liter normally aspirated engine (ZF 4 HP 24 E transmission). The general arrangement of the two
units is shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2. The two automatic transmission units differ in the type of control unit employed:
the purely hydraulic control used in the ZF 4 HP 22 unit shifts gears automatically at predetermined points, while the
electronic-hydrauliccontrol oftheZF 4 HP 24 E unit providesforoptimized shift point sand shift quality based on engine
and transmission data received by the Transmission Control Module (TCM).
P \R J44-607
1. Torque converter 8. Shift lever positions:
2. Throttle cable
‘P - Park
3. 4
-speed gear train ‘R‘ - Reverse
4. Output flange ‘N’ - Neutral
5. Transmission control unit
6. Oil outlet (drain plug) 9. Dipstick/ oil filler tube
7. Shift cable attachment 10. Oil cooler connection
‘D‘
- Drive - Fully automatic
control
Fig. 1 ZF 4 HP 22 Transmission
X300 VSM 1 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 139 of 521

I 1 I
8-
/ /
7, 6
'4 '5
J4L- 688
1. Torque converter 6. Rotary switch positions:
2. &speed gear train 'P - Park
3. Output flange 'R' - Reverse
4. Transmission control unit 'N' - Neutral
5. Oil outlet (drain plug) 'D' - Drive
(Fully automatic control)
7. Dipstick/ oil filler tube
8. Oil cooler connection
Fig.
2 ZF 4 HP 24 E Transmission
X300 VSM Issue 1 August 1994 2
Page 140 of 521

Automatic Transmission (AJ16)
Both types of automatic transmission comprise a hydrodynamic torque converter driving an epicyclic gear train which
provides four forward ratios and reverse. Gearshift selection is made by a hydraulic (or electronichydraulic) trans- mission control unit. Six gearshift positions are provided:
Position
'P' (Park) -the driven wheels are mechanically locked at the transmission.
Position
'R' (Reverse) - reverse gear selected.
Position
'N' (Neutral) - engine disconnected from drive-line and wheels.
Position 'D' (Drive)
- all four speed ranges are selected automatically with lock-up available in top gear only.
Position
'3' - automatic selection of the lowest three speed ranges only.
Position '2'
- automatic selection of the lowest two speed ranges only; the transmission is prevented from shift- ing up to the third and top speed ranges.
Immediate selection of a lower ratio is also available, within mapped limits, by 'kick
-down' (pressing the accelerator
pedal down beyond the normal full throttle position) for example when overtaking.
A brake pedal/gearshift interlock is incorporated in the shift lever mechanism. Theshift lever may only be movedfrom
the 'P' (Park) position if the ignition key switch is in position 'll', and the foot brake is applied. The ignition key cannot
be removed from the ignition switch unless the shift lever is in the 'P' (Park) position. Once the ignition key has been
removed, the shift lever is locked in the Park position. The gearshift interlock may be over-ridden manually in the event
of an electrical failure or when it is required to move the vehicle manually for access, ie for removal of the propeller
shaft.
8.1.1.1
Gearshift selection causes the appropriate gear to be selected through a cable operated shift lever on the side of the
Gear Selection (ZF 4HP 22)
transmission unit. When a gea; is selected, the shift points are determined by accelerator pedal position through a
throttle cable connection and by pressures equivalent to road speed derived from a centrifugal governor on the output
shaft.
Gearshift speed and quality are controlled by the hydraulic control unit located in the lower part of the transmission
housing. The control unit contains selector valve, control pistons and pressure valves.
The hydraulic control unit can be overridden by 'kickdown'. This is actuated by the final travel of the accelerator pedal
and causes the next lower gear to be selected.
8.1.1.2
Gearshift selection causes the appropriate gear to be selected through a cable operated shift lever on the side of the
transmission unit; the shift lever also operates a rotary switch attached to the side of the transmission unit. When a
gear is selected, the rotary switch provides an output or combination of outputs to the TCM, which continuously moni
- tors the gear selected in addition to output shaft speed and transmission oil temperature. Information from the Engine
Control Module (ECM) representing engine speed, load and throttle position is also fed to the TCM to enable the most
suitable gear to be selected.
Gear selection and gearshift speeds are controlled by the manually operated selector valve, a solenoid operated pres
- sure regulator and three solenoid valves. On receipt of signalsfrom the TCM, the three solenoid valves MVI, MV2 and
MV3, in various combinations with the safety valve, determine the appropriate gear range. The TCM, on receipt of
information of engine state and road speed, determines the shift speed.
The Performance Mode switch, located on the shift lever surround, provides two alternative shift speed patterns:
1. 'Normal (Economy) Mode' - designed for everyday use.
2. 'Sport Mode'
- gear shift takes place at higher road speeds to enhance performance.
The 'kick
-down' switch, located beneath the accelerator pedal, is actuated by the final travel of the pedal and signals
to the TCM that the next lower gear is to be selected.
Gear Selection (ZF 4 HP 24 E)
X300 VSM 3 Issue 1 August 1994
Page 141 of 521

Automatic Transmission (AJ16)
8.1.1.3 Shift Speeds
3,2 Liter
Up to 'kickdown point' D4 - D3 D3 - D2
D2 - D1 -
km/h 102 - 114 67 - 78
36 - 50 -
- mile / h 64-71 42 - 48 22 - 31
'Kick-down' available D4 - D3 D3 - D2 D2 - D1
mile I h 86-99 61 -67 30 - 37 -
kmlh 139 - 160 98- 108 48 - 60 -
available speed) -
km/h 108- 123 - -
- - Manual inhibit (maximum D4 - D3 D3 - D2
- - mile 1 h NOT INHIBITED 67 -76
TCC
- Torque converter clutch
Issue 1 August 1994 4 X300 VSM