1994 HONDA INTEGRA Wheel
[x] Cancel search: WheelPage 340 of 1413
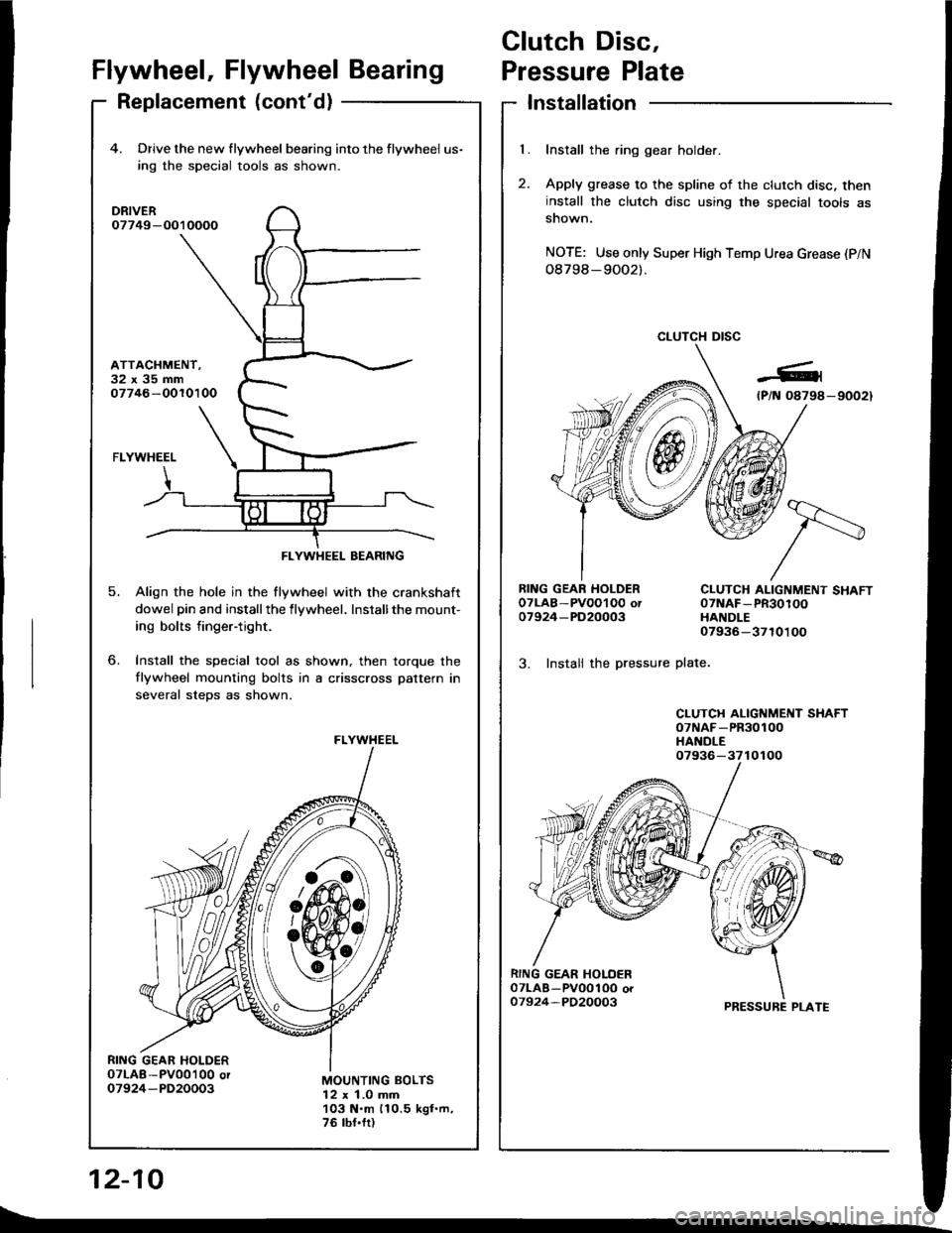
Clutch Disc,
l.
t
Flywheel, Flywheel BearingPressure Plate
Replacement (cont'd)Installation
Install the ring gear holder.
Apply grease to the spline of the clutch disc, theninstall the clutch disc using the special tools assnown.
NOTE: Use only Super High Temp Urea Grease (P/N
08798-9OO2).
CLUTCH DISC
RING GEAR HOLDEROTLAB-PVOOI O0 ot07924-PD20003
3. Instali the pressure
CLUTCH ALIGNMENT SHAFT07NAF-PR30100HANDLE07936-3710100
plate.
CLUTCH ALIGNMENT SHAFToTNAF-PR30100HANDLE
PRESSURE PLATE
12-10
4. Drive the new flywheel bearing into the flywheel us-
ing rhe special tools as shown.
DRIVER07749-O010000
ATTACHMENT.32x35mm07746-OOlO100
o.
5.
FLYWHEEL
Align the hole in the flywheel with the crankshaft
dowel pin and installthe flywheel. Installthe mount-
ing bolts finger-tight.
Install the special tool as shown, then torque the
flywheel mounting bolts in a crisscross pattern in
several steDs as shown.
MOUNTING BOLTS12 x 1.0 mm103 N.m 110.5 kgf.m,76 tbf.fr)
FLYWHEEL BEARING
FLYWHEEL
07936-3710100
t\_
Page 391 of 1413

'19.Install the slave cylinder, then install the clutch pipe
bracket.
NOTE: Use only Super High Temp Urea Grease
(P/N 08798 - 9002).
CLUTCH PIPE6x1.0mm9.8 N.m {1.0 kgf.m, 7 lbf ft)
8 x 1.25 mm22 N-m 12.2 kgl.tr't,16 rbf.ftl
20.
21.
tPlN 08798 - 90021
VSS CONNECTOR
Connect the vehicle speed sensor (VSS) conneclor
and the starter motor cables.
Install the wire harness clamPs.
6x1.0mm9.8 N.m (1.0 kgt m,7 lbf ftl
WIREHARNESSCLAMPS
8 x 1.25 mm8.8 N.m 10.9 kgf.m,6.s tbf.ft)
STARTERMOTORCABLES
22, lnstall the lower radiator hose clamp on the trans-
mission hang€r B.
23. Connect the transmission ground wire and the
back-up light switch connector.
16 tbf.fttBACK.UP LIGI{TSWITCH CONNECTOR
GROUND WIRE HANGER B
Install the air cleaner housing assembly and the air24.
intake duct.
AIR CLEANERHOUSINGASSEMALY
6x1.0mm9.8 N.m 11.0 kgt'm,7 lbtftl
AIR INTAKE DUCT
Refill the transmission with oil (see page 13-3).
Connect the positive (+) cable first, then connect the
negative ( - ) cable to the battery.
Check the clutch operation.
Shift the transmission. and check for smooth opera-
tron.
29. Check the front wheel alignment (see section 18).
9\
\<
27.
28.
13-49
Page 395 of 1413

The Automatic Transmission is a combination of a 3-e,ement torque convefter and triple-shaft electfonically controlled
automatic transmission which provides 4 speeds forward and 1 speed reverse. The entire unit is positioned in line with
the engine.
Torque Converter, Gears and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump, turbine and stator assembly in a single unit, The torque converter is connected
to the engine crankshaft so they turn together as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the torque converter
is a ring gear which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being staned. The entire torque converter assem-
bly serves as a flywheel while transmitting power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has three parallel shafts, the mainshaft. countershaft and sub-shaft. The mainshatt is in line with the
engine crankshaft.
The mainshaft includes the clutches for 1 st, and 2ndl4th, and gears for 3rd. 2nd, 4th, reverse and l st (3rd gear is in-
tegral with the mainshaft, while reverse gear is integral with the 4th gear).
The countershaft includes the 3rd clutch and gears Ior 3rd, 2nd,4th, reverse, lst and parking. Reverse and 4th gears
can be locked to the countershaft at its center, providing 4th gear or reverse, depending on which way the selector is moved.
The sub-shaft includes the lst-hold clutch and gears for 1st and 4th
The gears on the mainshait are in constant mesh with those on the countershaft and sub-shaft. When certain combina-
tions of gears in the transmission are engaged by the clutches, power is transmitted from the mainshaft to the counter-
shaft via the sub-shatt to provide @, E, tr. tr and @ position.
Electronic Control
The electronic control system consists of the Transmission Control Module {TCM), sensors, and 4 solenoid valves. Shift-
ing and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions.
The TCM is located below the dashboard, behind the left side kick panel on the driver's side.
Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main valve body, secondary valve body, regulator valve body. servo body, and lock-up valve
body throuqh the respective separator plates.
They are bolted on the torque converter housing.
The main valve body contains the manual valve, 1-2 shift valve, 2-3 shift valve, Clutch Pressure Cont.ol (CPC) valve,
4th exhaust valve, relief valve, and oil pump gears.
The secondary valve body contains the 4-3 kick-down valve,3-2 kick-down valve,2-3 orifice cont.ol valve, 3-4 shitt
valve, orifice control valve. modulator valve, and servo control valve
The regulator valve body contains the pressure regulator valve. lock-up control valve, torque converter check valve, and
cooler check valve.
The servo bodv contains the servo valve which is integrated with the reverse shift fork, throttle valve B, and accumulators.
The lock-ug valve bodv contains the lock-up shift valve and lock-up timing B valve. and is bolted on the secondary valve
body.
Fluid from the regulator passes through the manual valve to the various control valves.
Shitt Control Mochanism
Input to the TCM i.om various sensors located throughout the car determines which shift control solenoid valve should
be activated.
Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes
a line to one of the clutches. engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear.
Lock-up Mechanism
In @ position. in 2nd, 3rd and 4th, and E position in 3rd, pressurized tluid can be drained from the back of the tor-
que converter through an oil passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held against the torque converter cover. As this
takes Dlace, the mainshaft rotates at the same speed as the engine crankshatt. Together with hydraulic control, the TCM
optimizes the timing ol the lock-up mechanism.
The lock-up valves control the range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B, and throttle valve B
When lock-up control solenoid valves A and B activate, modulator pressure changes. Lock-up control solenoid valves
A and B are mounted on the torque converter housing, and are controlled by the TCM.
(cont'd)
14-3
Page 396 of 1413
![HONDA INTEGRA 1994 4.G Workshop Manual Description
(contd)
Gear Selection
The selector lever has seven posirions; E PARK, E REVERSE, N NEUTRAL, @ 1st through 4th positions. E 1st
through 3rd positions, Ql2nd gear and [] 1st gear.
Starting HONDA INTEGRA 1994 4.G Workshop Manual Description
(contd)
Gear Selection
The selector lever has seven posirions; E PARK, E REVERSE, N NEUTRAL, @ 1st through 4th positions. E 1st
through 3rd positions, Ql2nd gear and [] 1st gear.
Starting](/manual-img/13/6067/w960_6067-395.png)
Description
(cont'd)
Gear Selection
The selector lever has seven posirions; E PARK, E REVERSE, N NEUTRAL, @ 1st through 4th positions. E 1st
through 3rd positions, Ql2nd gear and [] 1st gear.
Starting is possible only in @ and I Oosition through use ot a slide-type, neutral-safety switch.
Automatic Tlansaxle {A/T) Gear Position Indicatol
A/T gear pos;tion indicator in the instrumenl panel shows what gear has been selected without having look down at
the console.
Position Description
l3?]] PARK Front wheels locked; parking pawl engaged with parking gear on countershatt. All clutches
reteaseo,
[R] REVERSE Reverse; reverse selector engaged with countershalt reverse gear and 4th clutch locked.
N NEUTRAL All clurches released.
D+l DRIVE General driving; starts off in 'lst, shifts automatically to 2nd, 3rd, then 4th, depending on vehicle
('lst through 4th) speed and throttle position. Do'vnshifts through 3rd, 2nd and 1st on deceleration to stop.
The lock-up mechanism comes into operation in 2nd, 3rd and 4th when the transmission in lDtposrtron.
Dgi DRIVE For rapid acceleration at highway speeds and general driving; starts off in 1st. shifts automatical-(1st through 3rd) ly to 2nd then 3rd, depending on vehicle speed and throttle position. Downshifts through lower
gears on deceleration to stop. The lock-up mechanism comes into operation in 3rd.
El SECOND Driving in 2nd geari stays in 2nd gear, does not shift up and down.
For engine braking or better traction starting off on loose or slippery surfece.
L]l FIRST Driving in 1st gear; stays in lst gear, does not shilt up.
For engine braking.
14-4
Page 398 of 1413

Description
Clutches
The four speed automatic transmission uses hydraulically actuated clutches to engage or disengage the transmission gears.
When clutch pressure is introduced into the clutch drum, the clutch piston is applied. This presses the iriction discs and
steel plates together, locking them so they don't slip. Power is then transmitted through the engaged clutch pack tojts hub-mounted gear.
Likewise, when clutch pressure is bled from the clutch pack. the piston releases the friction discs and steel plates, and
they are {ree to slide past each other while disengaged. This allows the gear to spin independently on its shaft, transmit-
ting no power.
1st ClutchThe l st clutch engages/disengages 1st gear, and is located at the end of the mainshaft, just behind the right side cover.
The 1st clutch is supplied clutch pressure by its oil feed pipe within the mainshaft.
1st-hold clutchThe 1st-hold clutch engages/disengages 1st-hold or I Fosition, and is located at the center ol the sub-shaft. The 1st-
hold clutch is supplied clulch pressure by its oil feed pipe within the sub-shait.
2nd ClutchThe 2nd clutch engages/disengages 2nd gear, and is located at the center of the mainshaft. The 2nd clutch is joined
back-to-back to the 4th clutch. The 2nd clutch is supplied clutch pressure through the mainshaft by a circuit connected
to the regulator valve body.
3rd Clutch
The 3rd clutch engages/disengages 3rd gea.. and is located at the end oJ the countershaft, opposite the right side cover.
The 3rd clutch is supplied clutch pressure by its oil feed pipe within the countershaft,
4th clurch
The 4th clutch engages/disengages 4th gear. as well as reverse gear, and is located at the center of the mainshaft.
The 4th clutch is joined back-to-back to the 2nd clutch. The 4th clutch is supplied clutch pressure by its oil feed pipe
within the mainshalt.
One-way Clutch
The one-way clutch is posjtioned between the parking gear and 1st gear. with the parking gear splined to the counter-
shaft. The 1st gear provides the outer race, and the parking gear provides the inner race surface. The one-way clutch
locks up when power is transmitted from the mainshaft 1st gear to the countershaft lst ggel _The 1st clutch and gears remain engaged in the 1st. 2nd. 3rd, and 4th gear ranges in the @, E or E position.
However, the one-way clutch disengages when the 2nd. 3rd, or 4th clutches/gears are applied in the E, lD.l o, Eoosttton.
This is because the increased rotational speed of the gears on the countershaft over-ride the locking "speed range" of
the one-way clutch. Thereafter, the one-way clutch free-wheels with the lst clutch still engaged.
COUNTERSHAFT 1ST GEAR
FREE
:>
LOCKS
aF
NOTE:View trom right side cover side.
14-6
Page 403 of 1413

L!_j Position Deceleration
The power tlow when decelerating is as follows;
1. Rolling resistance lrom the road surface goes through the tront wheels to the final drive gear, then to the sub-shaft
1st gear via the 4th gear, and lst-hold clutch which is applied during deceleration.
2. The one-way clutch becomes free at this time because torque reverses.
3. The counterforce conveyed to the countershaft 4th gear turns the sub-shaft 4th gear via the mainshaft 4th gear.
At this time, since hydraulic pressure is also applied to the 1st clutch, counterfo.ce is also transmitted to the main-
shaft. As a result, engine braking can be obtained with lst gea.-
CLUTCH
SUB-SHAFT4TH GEARSUB-SHAFT 1ST GEARTOROUE CONVENTER
FINAL DRIVE
SUB'STIAFT
lST CLUTCH
MAINSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT
REVEFSE SELECTOR HUB
REVERSE SELECTOR
(cont'dl
4TI1 GEAB
14-11
Page 478 of 1413

Symptom-to-Component Chart
Hydraulic System
SYMPTOMCheck these items on the
PROBABLE CAUSE ListCheck these items
on the NOTES List
Engine runs, but car does not move in any gear.1, 6, 7, 16K,L,R,S
Car moves in @ and @, but not in @, @ or Iposataon.a, 29, 44. 4ac,M,o
Car moves in E, @, [, @, uut not in E position.9,30,49C, L
car moves in p:1, [o-il, [2-], [!, uut not in E position.1, 11, 22, 34, 38, 39, 40c,L,o
Car moves in N position.1, 8, 9, 10, 11,46,47C,D
Excessive idle vibration.5, 1'1B,K,L
Slips in all gears.6, 7, 16C,L
No engine braking in E position.12C,D,L
Slips in 1st gear.8, 29, 44, 4Ac,N,o
Slips in 2nd gear.9, 20, 23, 30, 49C, L
Slips in 3rd gear.10, 21 , 23, 31 , 49C,L
Slips in 4th gear.11, 23, 32, 44C,L,N
Slips in reverse gear.11,32,34,44C,N
Flares on 1-2 upshilt.3, 15, 23E,L,V
Flareson2 3 upshilt.3, 15, 23, 24, 49E,L,V
Flares on 3-4 upshift.3, 15, 23, 25, 49E,L,N,V
No upshift; transmission stays in 1st gear.14,19,G, L
No downshift to lst gear.12. 19G, L
Late upshift.14
Erratic shitting.2, 14,26
Harsh shift (up and down shiftingl.2, 4, 15, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27,
47A,E, H, I, L,V
Harsh shitt {1-2).2, 9. 15, 23C,D,E,V
Harshshilt (2-3).2, 10, 15, 23, 24C,D,E,H,L,V
Harsh shift (3-4).2,| 1, 15, 23, 25C, D, E, I,L,V
Harsh kick'down shifts.2, 15, 23, 26, 27. 2AE,L,O,V
Harsh kick-down shift 12 1)48o
Harsh downshift at closed throttle.2, 15, 23FT
Harsh shift when manually shifting to E] position.33L
Axle{s} slips out of transmission on turns.43,50
Axlels) stuck in transmission.43L,O
Ratcheting noise when shifting inro E position.6,7,38,39,40K,L,O
Loud popping noise when taking ott in E position.3a,39,40L,O
Ratcheting noise when shifting from E to E position or from Eto N I oosition.38,33,40,45L,O
Noise from transmission in all selector lever positions.6, 11K,L,O
Noise trom transmission only when wheels are rolling.39, 42L,O
Gear whine, rpm related (pitch changes with shitts).a, 13, 41K,L,O
Gear whine, speed rel6ted (pitch changes with speed).38, 42L,O
Transmission will not shift into 4th gear in @ position1,21,24.32L
Lock-up clutch does not lock-up smoothly.17, 36, 37L
Lock-up clutch does not operate properlV.2.3. 14, 15. 18, 35, 36, 37E,L,V
Transmission has multitude of problems shitting.
At disassembly, large particles oI metal are found on magnet.43L,O
14-86
Page 480 of 1413

Symptom-to-Component Ghart
Hydraulic System (cont'd)
The following symptoms can be caused
by improper repair or assemblv
Check these items on the
PROBABLE CAUSE DUE TO
IMPROPER REPAIR List
Items on the
NOTES List
Car creeps in E position.R1, R2
Car does not move in @ or @ position.R4
Transmission locks up in @ position.R3, Rl2
Excessive drag in transmission.R6K.R
Excessive vibration, rom related.R7
Noise with wheels moving onlyR5
Main seal pops out.R8
Various shifting problems.R9, R1O
Harsh upshifts.R11
PROBABLE CAUSE DUE TO IMPROPER REPAIR
R1lmproper clutch cleatance.
R2.lmDroDer qear clearance.
Parking brake lever installed upside down.
One-way (spragl clutch installed upside down,
Reverse selector hub installed upside down.
Oil oumo bindind
Torque converter not fully seated in oil pump.
Main seal improperly installed.
Springs improperly installed,
Valves improperly installed.
Ball check valves not installed.
Shitt fork bolt not installed.
R3.
R4.
R5.
R6.
R7.
R8.
R9.
R10.
R11
R12.
14-88