1994 CHEVROLET BLAZER steering wheel
[x] Cancel search: steering wheelPage 68 of 348

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Theft
Vehicle theft is big business, especially in some cities. Although your
vehicle has a number of theft deterrent features, we know that nothing we
put on
it can make it impossible to steal. However, there are ways you can
help.
Key in the Ignition
If you walk away from your vehicle with the keys inside, it’s an easy target
for joy riders or professional thieves
- so don’t do it.
When you park your vehicle and open the driver’s door, you’ll hear a tone
reminding you to remove your key from the ignition and take
it with you.
Always
do this. Your steering wheel will be locked, and so will your
ignition. If you have an automatic transmission, taking your key out
also
locks your transmission. And remember to lock the doors.
Parking at Night
Park in a lighted spot, close all windows and lock your vehicle. Remember
to keep your valuables out of sight. Put them
in a storage area, or take them
with you.
Parking Lots
If you park in a lot where someone will be watching your vehicle, it’s best
to lock
it up and take your keys. But what if you have to leave your ignition
key? What
if you have to leave something valuable in your vehicle?
0 Put your valuables in a storage area, like your glove box.
Lock the glove box.
Lock all the doors except the driver’s.
Then take the door key with you.
2-14
Page 69 of 348

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine New Vehicle “Break-In ’’
L
NOTICE:
Your modern vehicle doesn’t need an elaborate “break-in.” But
it will perform better in the long run if you follow these
guidelines:
0 Keep your speed at 55 mph (88 km/h) or less for the first 500
miles (SO4 km).
0 Don’t drive at any one speed - fast or slow - for the first
500 miles (804 km). Don’t make full-throttle starts.
Avoid making hard stops for the first 200 miles (322 km) or
so. During this time your new brake linings aren’t yet broken
in. Hard stops with new linings can mean premature wear and
earlier replacement. Follow this “breaking-in” guideline
every time you get new brake linings.
Ignition Switch
tion key lets you turn
1. OFF
2. RUN
3. START
4. ACC
5. LOCK
ACC (Accessory): ACC lets you use things like the radio and the
windshield wipers when the engine is off.
To get into ACC, push in the key
and turn
it toward you. Your steering wheel will remain locked, just as it
was before you inserted the key.
2- 15
Page 70 of 348

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine NOTICE:
Prolonged operation of accessories in the ACC position could
drain your battery and prevent you from starting your vehicle.
LOCK: This position locks your ignition, steering wheel and transmission.
It’s a theft deterrent feature. You will only be able to remove your key when
the ignition is turned to LOCK.
OFF: This position lets you turn off the engine but still turn the steering
wheel. Use
OFF if you must have your vehicle in motion while the engine
is off (for example,
if your vehicle is being pushed).
RUN: This is the position for driving.
START This starts your engine.
NOTICE:
If your key seems stuck in “LOCK” and you can’t turn it, be
sure it is all the way in. If it is, then turn the steering wheel left
and right while you turn the key hard. But turn the key only
with your hand. Using
a tool to force it could break the key or
service.
the ignition switch. If none of this works, then your vehicle needs
2-16
Page 91 of 348

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Horn
Press the pad in the
center
of the steering
wheel
to sound the
horn.
Tilt Wheel (Option)
A tilt steering wheel
allows
you to adjust
the steering wheel
before
you drive.
You can also raise it to the highest level to give your legs more room when
you enter and exit the vehicle.
To tilt the wheel, hold the steering wheel and pull the lever. Move the
steering wheel to a comfortable level, then release the lever to lock the
wheel
in place.
Do not adjust the steering wheel while driving.
2-37
Page 159 of 348

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Your Driving and the Road
Section
Here you'll find information about driving on different kinds of roads and in
varying weather conditions . We've also included many other useful tips on
driving
.
Defensive Driving ..................... ................. 4-2
DrunkenDriving ........................................... 4-2
Braking ................................................ 4-5
Steering Tips ............................................ 4-8
Control
of a Vehicle
Steering
................................................ 4-8
Passing
............................................... 4-10
Loss of Control ......................................... 4-11
Driving Guidelines
......................................... 4-12
Off-Road Driving With Your Four-wheel Vehicle
............... 4-13
DrivingatNight ........................................... 4-24
Driving
in the Rain ........................................ 4-25
Freeway Driving
........................................... 4-8
Hill and Mountain Roads
.................................... 4-30
Winter Driving
............................................ 4-32
CityDriving
.............................................. 4-27
Recreational Vehicle Towing (Four-wheel Drive Only)
........... 4-35
TowingaTrailer
........................................... 4-37
4-1
Page 165 of 348

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine As you brake, your computer keeps receiving updates on wheel speed and
controls braking pressure accordingly.
Remember: Anti-lock doesn’t change the time
you need to get your foot up
to the brake pedal. If you get too close to the vehicle
in front of you, you
won’t have time to apply your brakes
if that vehicle suddenly slows or
stops. Always leave enough room up ahead
to stop, even though you have
anti-lock brakes.
To Use Four-wheel Anti-Lock
Don’t pump the brakes. Just hold the brake pedal down and let anti-lock
work for
you. You may feel the brakes vibrate, or you may notice some
noise, but this is normal.
Braking in Emergencies
Use your anti-lock braking system when you need to. With anti-lock, you
can steer and brake at
the same time. In many emergencies, steering can
help you more than even the very best braking.
4-7
Page 166 of 348

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Power Steering
If you lose power steering assist because the engine stops or the system is
not functioning, you can steer but it will take much more effort.
Steering Tips
Driving on Curves
It’s important to take curves at a reasonable speed.
A lot
of the “driver lost control” accidents mentioned on the news happen
on curves. Here’s why:
Experienced driver or beginner, each
of us is subject to the same laws of
physics when driving on curves. The traction of the tires against the road
surface makes it possible for the vehicle to change its path when you turn
the front wheels. If there’s
no traction, inertia will keep the vehicle going in
the same direction. If you’ve ever tried to steer
a vehicle on wet ice, you’ll
understand this.
The traction you can get in a curve depends on the condition of your tires
and the road surface, the angle at which the curve
is banked, and your
speed. While you’re
in a curve, speed is the one factor you can control.
Suppose you’re steering through a sharp curve. Then
you suddenly
accelerate. Both control systems
- steering and acceleration - have to do
their work where the tires meet the road. Adding the sudden acceleration
can demand too much
of those places. You can lose control,
What should you do
if this ever happens? Ease up on the accelerator pedal,
steer
the vehicle the way you want it to go, and slow down.
Speed limit signs near curves warn that
you should adjust your speed. Of
course, the posted speeds are based
on good weather and road conditions.
Under less favorable conditions you’ll want
to go slower.
If you need to reduce your speed as you approach a curve, do it before you
enter the curve, while your front wheels are straight ahead.
Try
to adjust your speed so you can “drive” through the curve. Maintain a
reasonable, steady speed. Wait to accelerate until you are out of the curve,
and then accelerate gently into
the straightaway.
4-8
Page 168 of 348
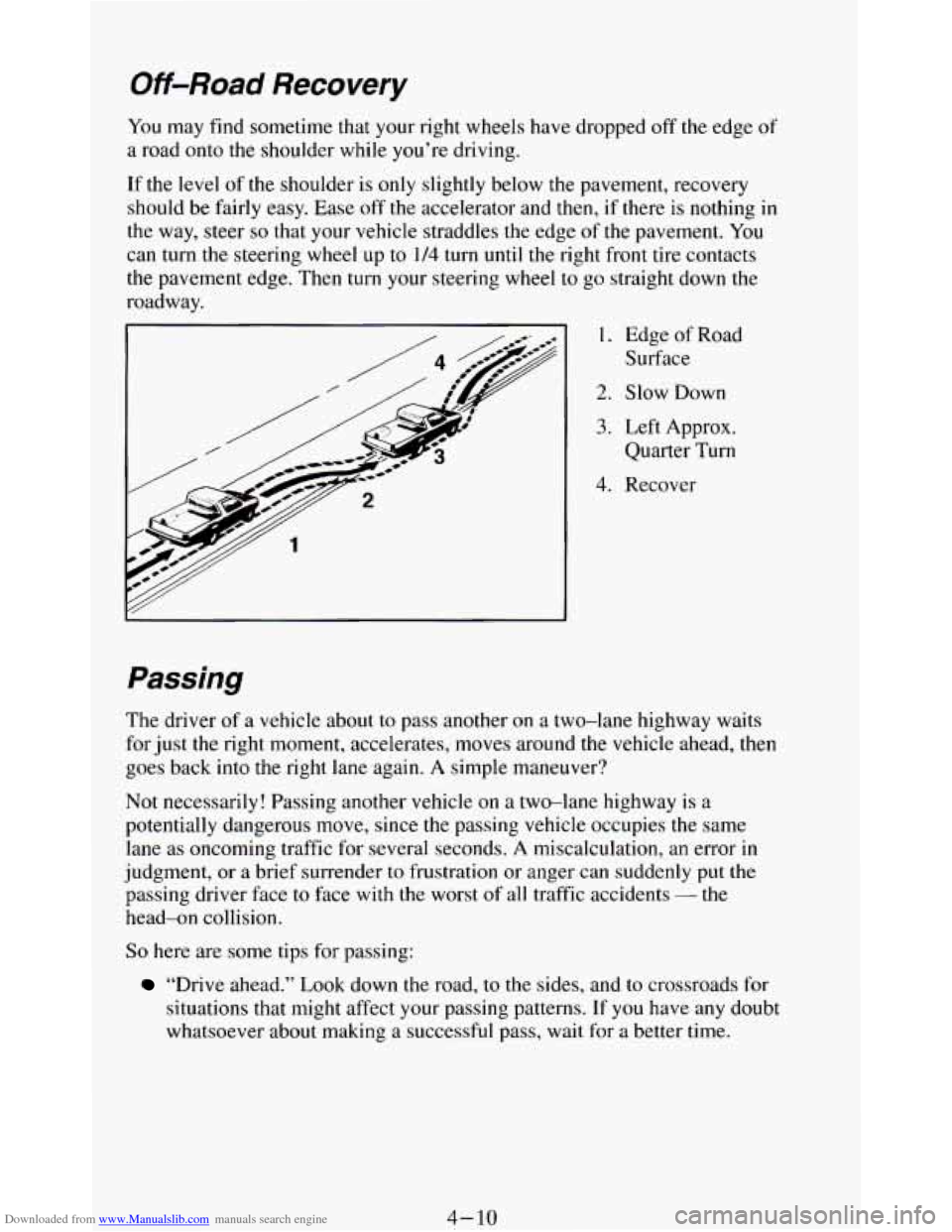
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Off-Road Recovery
You may find sometime that your right wheels have dropped off the edge of
a road onto the shoulder while you’re driving.
If the
level of the shoulder is only slightly below the pavement, recovery
should be fairly easy. Ease
off the accelerator and then, if there is nothing in
the way, steer so that your vehicle straddles the edge of the pavement. You
can turn the steering wheel up to
1/4 turn until the right front tire contacts
the pavement edge. Then turn your steering wheel to go straight down the
roadway.
1. Edge of Road
Surface
2. Slow Down
3. Left Approx.
Quarter Turn
4. Recover
Passing
The driver of a vehicle about to pass another on a two-lane highway waits
for just the right moment, accelerates, moves around
the vehicle ahead, then
goes back into the right lane again. A simple maneuver?
Not necessarily! Passing another vehicle on a two-lane highway is a
potentially dangerous move, since the passing vehicle occupies the same
lane as oncoming traffic for several seconds.
A miscalculation, an error in
judgment, or a brief surrender to frustration or anger can suddenly put the
passing driver face to face with the worst of all traffic accidents - the
head-on collision.
So here are some tips for passing:
“Drive ahead.” Look down the road, to the sides, and to crossroads for
situations that might affect your passing patterns. If
you have any doubt
whatsoever about making a successful pass, wait for a better time.
4- 10