1993 CHEVROLET DYNASTY warning
[x] Cancel search: warningPage 277 of 2438

WARNING: WHEN BLEEDING THE MODULATOR
ASSEMBLY WEAR SAFETY GLASSES. A CLEAR
BLEED TUBE MUST BE ATTACHED TO THE
BLEEDER SCREWS AND SUBMERGED IN A CLEAR
CONTAINER FILLED PART WAY WITH CLEAN
BRAKE FLUID. DIRECT THE FLOW OF BRAKE
FLUID AWAY FROM THE PAINTED SURFACES OF
THE VEHICLE. BRAKE FLUID AT HIGH PRESSURE
MAY COME OUT OF THE BLEEDER SCREWS,
WHEN OPENED.
When bleeding the Modulator Assembly. The fol-
lowing bleeding sequence MUSTbe followed to in-
sure complete and adequate bleeding of the brakes
hydraulic system. The Modulator Assembly can be
bled using a Manual bleeding procedure or standard
Pressure Bleeding Equipment. If the brake system is to be bled using pressure
bleeding equipment. Refer to Bleeding Brake System,
in the Service Adjustments section at the beginning
of this group, for proper equipment usage and proce-
dures.
MODULATOR ASSEMBLY BLEEDING SEQUENCE
1 SECONDARY SUMP
(1) Put a bleeder tube on the Secondary Sump
bleeder screw (Fig. 1). (2) Use a pressure bleeder, or have an assistant,
apply light and constant pressure on the brake pedal.
Loosen the Secondary Sump bleeder screw (Fig. 1). (3) Using the DRB II select the Actuate Valves
test mode. Then actuate the LF Build/Decay Valve. (4) Bleed the Secondary Sump. Until a clear air
free flow of brake fluid is evident in the clear hose
and no air bubbles appear in the container, or the
brake pedal bottoms. (5) Tighten the bleeder screw and release the
brake pedal. (6) Repeat steps 2 through 5 until a clear air free
flow of brake fluid is coming out of the Secondary
Sump bleeder screw. (7) Next select and actuate the RR Build/Decay
Valve. Again repeat steps 2 through 5 until a clean
air free flow of brake fluid is coming out of the Sec-
ondary Sump bleeder screw.
2 PRIMARY SUMP
(1) Put a bleeder tube on the Primary Sump
bleeder screw (Fig. 1). (2) Use a pressure bleeder, or have an assistant,
apply light and constant pressure on the brake pedal.
Loosen the Primary Sump bleeder screw (Fig. 1). (3) Using the DRB II select the Actuate Valves
test mode. Then actuate the RF Build/Decay Valve. (4) Bleed the Primary Sump. Until a clear air free
flow of brake fluid is evident in the clear hose and no
air bubbles appear in the container, or the brake
pedal bottoms. (5) Tighten the bleeder screw and release the
brake pedal. (6) Repeat steps 2 through 5 until a clear air free
flow of brake fluid is coming out of the Primary
Sump bleeder screw. (7) Next select and actuate the LR Build/Decay
Valve. Again repeat steps 2 through 5 until a clean
air free flow of brake fluid is coming out of the Pri-
mary Sump bleeder screw.
3 PRIMARY ACCUMULATOR
(1) Put a bleeder tube on the Primary Accumulator
bleeder screw. (Fig. 1) (2) Use a pressure bleeder, or have an assistant,
apply light and constant pressure on the brake pedal.
Loosen the Primary Accumulator bleeder screw (Fig.
1). (3) Using the DRB II select the Actuate Valves
test mode. Then actuate the RF/LR Isolation Valve. (4) Bleed the Primary Accumulator. Until a clear
air free flow of brake fluid is evident in the clear
hose and no air bubbles appear in the container, or
the brake pedal bottoms. (5) Tighten the bleeder screw and release the
brake pedal.
Fig. 1 Bleeding ABS Modulator Assembly
Ä ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 127
Page 280 of 2438
junction block. Torque both lower mounting bracket
bolts to 28 N Im (250 in. lbs.)
(4) Reinstall the 4 hydraulic brake tubes to the
Modulator Assembly and torque the fittings to 16
N Im (145 in. lbs.).
(5) Reconnect the 10 way Modulator assembly con-
nector, and the delta P switch connector. (6) Lower the vehicle and install the 2 master cyl-
inder supply tubes to the Modulator Assembly.
Torque the Modulator Assembly fittings and the
master cylinder fittings to 16 N Im (145 in.lbs.).
(7) Torque the Modulator to fender splash shield
attaching bolt to 28 N Im (250 in. lbs.)
(8) Bleed the brake system. Refer to the Bleeding
Bendix Anti 6 Brake System in this section of the
manual for proper bleeding procedure. (9) Reinstall the acid shield and battery tray. Re-
install battery and connect battery cables.
MASTER CYLINDER AND POWER BOOSTER
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
If the Master Cylinder or the Power Booster need
to be serviced or replaced. Refer to Master Cylinder
or Power Brake Service section in this group of the
service manual. After servicing the Master Cylinder. Refer back to
this section of the service manual. For the appropri-
ate procedure and sequence, used to bleed the base
and ABS portion of the brake system
PROPORTIONING VALVES (FIG. 5)
CAUTION: Proportioning valves should never be
disassembled.
REMOVAL (1) Remove brake tube and fitting from proportion-
ing valve. (2) Remove proportioning valve from Modulator
Assembly.
INSTALLATION (1) Install proportioning valve on Modulator As-
sembly and tighten to 40 N Im (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install brake tube on proportioning valve.
Tighten tube nut to 15 N Im (11 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Bleed the affected brake line, see Bleeding Ben-
dix Anti Lock 6 Brake System in this section of the
manual.
ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS
CONTROLLER ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (CAB)
REMOVAL
(1) Turn vehicle ignition off. (2) Disconnect the wiring harness connectors from
the Anti-Lock relays (Fig. 6). Relays will be removed
as part of the (CAB) bracket. (3) Disconnect the wiring harness 60 way connec-
tor (Fig. 6) from the Controller Anti-Lock Brake
Module (CAB). VERIFY THAT THE VEHICLE
IGNITION IS OFF BEFORE REMOVING THE
60 WAY CONNECTOR. (4) Remove the 2 (CAB) module bracket, to frame
rail mounting bolts (Fig. 6) (5) Remove the (CAB) module from the vehicle.
(6) Remove the 3 (CAB) to bracket mounting
screws and remove the (CAB) from the mounting
bracket (Fig. 7).
INSTALLATION
The Controller Anti-Lock Brake (CAB) module in-
stallation is done in the reverse order of removal.
REMOVAL/INSTALLATION OF SYSTEM AND WARNING LAMP RELAY
The System and Warning Lamp relay are both ser-
viced together as an assembly, with the mounting
bracket. They are mounted to a separate bracket that
is attached to the (CAB) bracket assembly (Fig. 8).
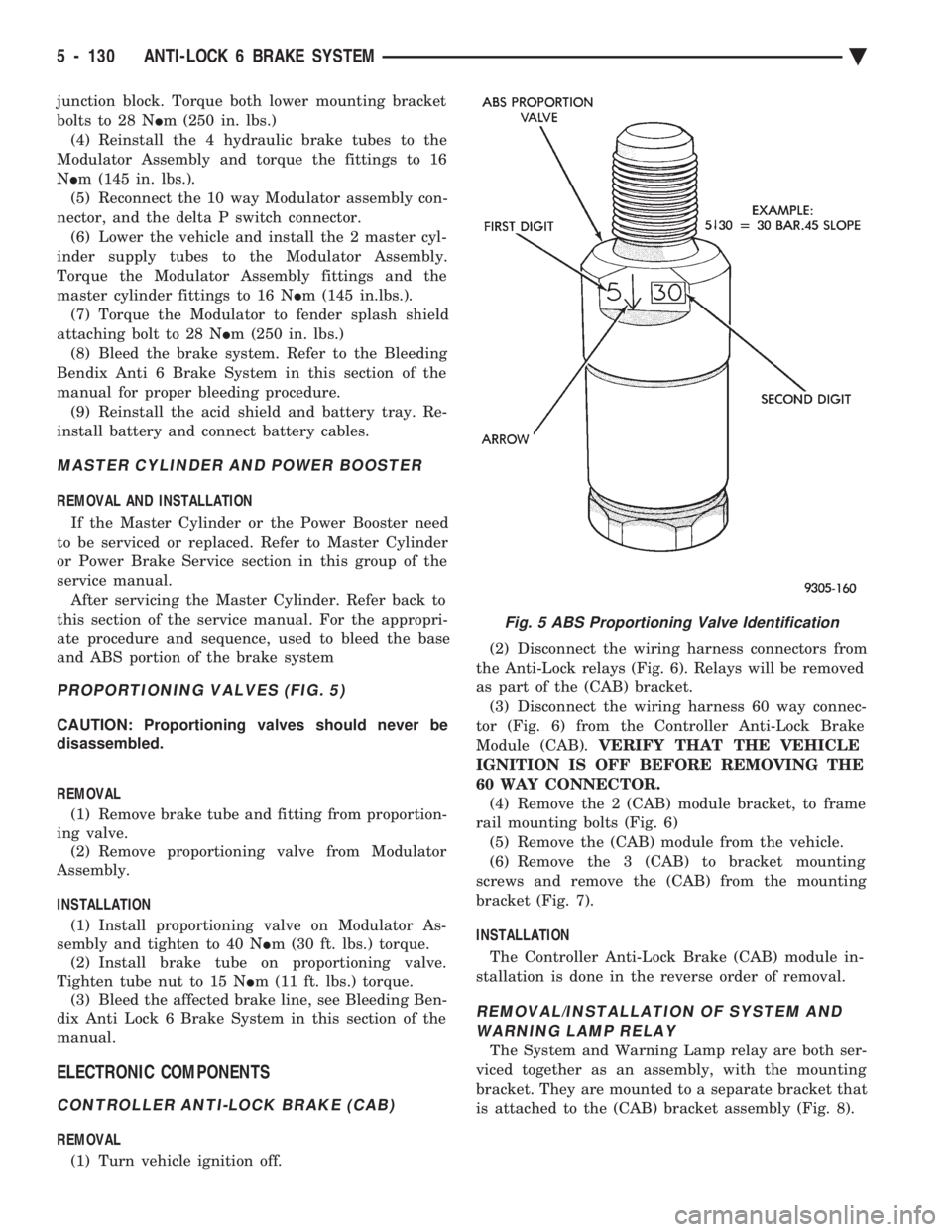
Fig. 5 ABS Proportioning Valve Identification
5 - 130 ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 281 of 2438
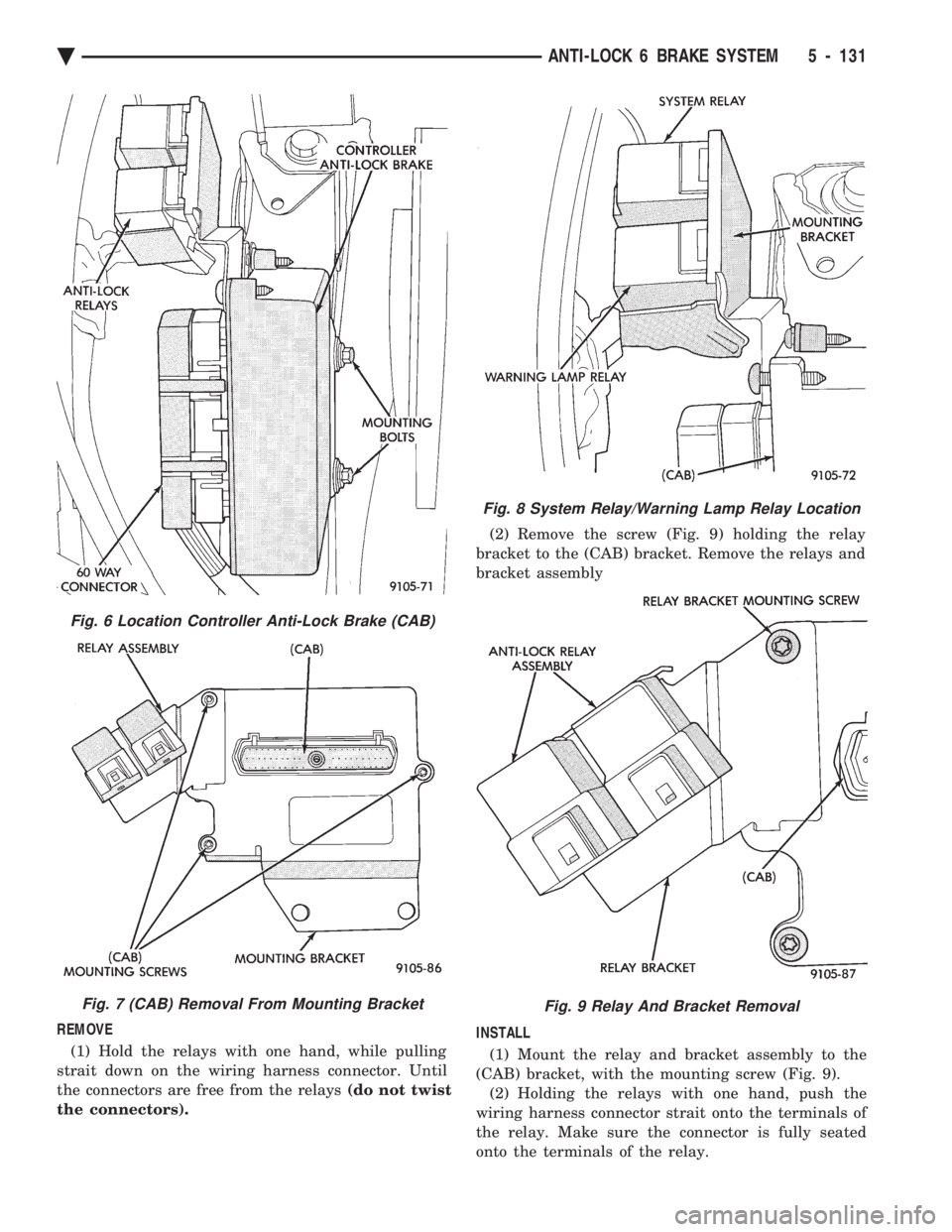
REMOVE (1) Hold the relays with one hand, while pulling
strait down on the wiring harness connector. Until
the connectors are free from the relays (do not twist
the connectors). (2) Remove the screw (Fig. 9) holding the relay
bracket to the (CAB) bracket. Remove the relays and
bracket assembly
INSTALL
(1) Mount the relay and bracket assembly to the
(CAB) bracket, with the mounting screw (Fig. 9). (2) Holding the relays with one hand, push the
wiring harness connector strait onto the terminals of
the relay. Make sure the connector is fully seated
onto the terminals of the relay.
Fig. 6 Location Controller Anti-Lock Brake (CAB)
Fig. 7 (CAB) Removal From Mounting Bracket
Fig. 8 System Relay/Warning Lamp Relay Location
Fig. 9 Relay And Bracket Removal
Ä ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 131
Page 287 of 2438

BRAKES
CONTENTS
page page
BENDIX ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM ...... 12
GENERAL INFORMATION .................. 1 HYDRAULIC SYSTEM CONTROL VALVES . . . 10
SERVICE ADJUSTMENTS
.................. 3
GENERAL INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references may be made to
a particular vehicle by letter or number designation.
A chart showing the break down of these designa-
tions is included in the Introduction Section at the
front of this service manual. Standard brake equipment consists of:
² Double pin floating caliper disc front brakes.
² Rear automatic adjusting drum brakes.
² Differential valve with a brake warning switch.
² Master cylinder.
² Vacuum power booster.
² Double pin floating caliper rear disc brakes are
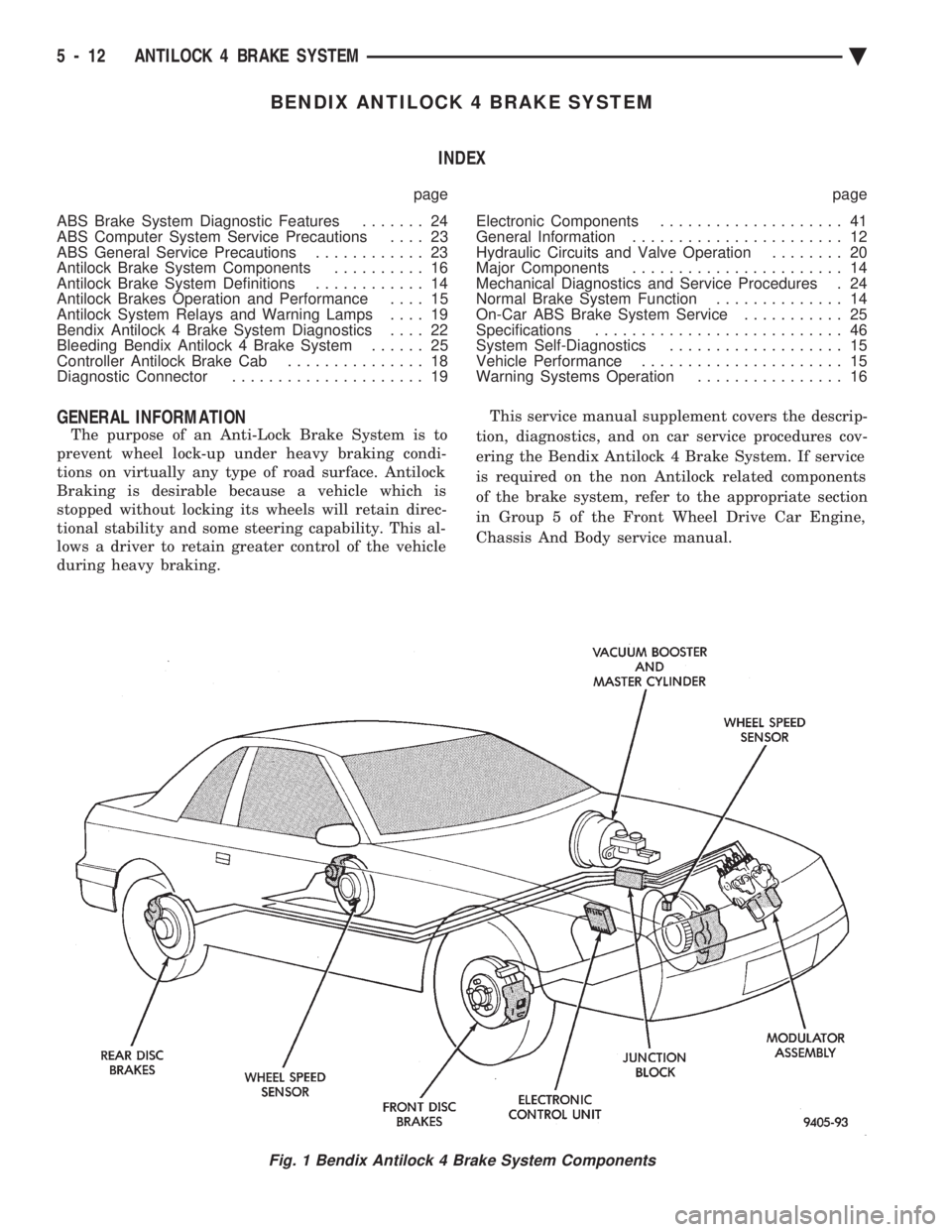
available on some models. The Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System, uses the fol-
lowing standard brake system components. Master
cylinder, power booster, caliper assemblies, braking
discs, pedal assembly, brake lines and hoses. The
unique parts of the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System
consists of the following components, modulator as-
sembly, unique proportioning valves, unique junction
block, wheel speed sensors, tone wheels, and elec-
tronic control unit. These components will be de-
scribed in detail in the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake
System section in this service manual supplement. The hydraulic system, (Fig. 1) on the Bendix Anti-
lock 4 brake system is diagonally split. Diagonally
split hydraulic brake systems, have the left front and
right rear brakes on one hydraulic system and the
right front and left rear on the other. A diagonally
split hydraulic brake system, will maintain half of
the vehicles braking capability if there is a failure in
either half of the hydraulic system. The Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System uses two
types of brake line fittings and tubing flares on the
modulator assembly (Fig. 1). The different types are
the ISO style and double wall style with their corre-
sponding fittings at different joint locations. See (Fig.
2) for specific joint locations and type of tubing
flares. CAUTION: When servicing a vehicle, sheet metal
screws, bolts or other metal fastener cannot be in-
stalled in a shock tower to take the place of any
original plastic clip. Also, NO holes can be drilled
into the front shock tower in the area shown in (Fig.
3), for installation of any metal fasteners into the
shock tower.
Because of minimum clearance in this area, (Fig.
3) installation of metal fasteners could damage the
coil spring coating and lead to a corrosion failure of
the spring. If a plastic clip is missing, lost or broken
during servicing a vehicle, replace only with the
equivalent part listed in the Mopar parts catalog.
Fig. 1 Identifying Hydraulic Brake Tubing Flares
Ä BRAKES 5 - 1
Page 296 of 2438

HYDRAULIC SYSTEM CONTROL VALVES INDEX
page page
General Information ....................... 10
Hydraulic System Service Procedures ......... 11 Pressure Differential Warning Light Switch
...... 10
GENERAL INFORMATION
All models equipped with a Bendix Antilock 4 Brake
System have 2 screw-in type proportioning valves.
There is 1 valve for each individual rear wheel hydrau-
lic brake line. The proportioning valves are mounted
directly into the rear brake outlet ports of the modula-
tor assembly (Fig. 1).
The proportioning valves limit brake pressure to the
rear brakes after a certain pressure (split point) is
reached. This improves front to rear brake balance
during normal braking. Screw-in proportioning valves can be identified by
numbers stamped on the body of the valve. The first
digit represents the slope, the second digit represents
the split (cut-in) point, and the arrow represents the
flow direction of the valve. Be sure numbers listed
on a replacement valve are the same as on the
valve that is being removed. See (Fig. 2) for detail of
the valve identification.
PRESSURE DIFFERENTIAL WARNING LIGHT
SWITCH
The hydraulic brake system, on vehicles equipped
with the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System is split
diagonally. The left front and right rear brakes are on
one hydraulic system, and the right front and left
rear are on another. Both systems are routed
through, and hydraulically separated by the Pressure
Differential Switch (Fig. 3) mounted in the hydraulic brake tube junction block. The function of the Pressure
Differential Switch is to alert the driver of a malfunc-
tion in the brake hydraulic system.
If hydraulic pressure is lost in one system, the
warning light switch will activate the RED brake
warning light on the instrument panel, when the brake
pedal is depressed. At this point the brakes hydraulic
system requires immediate service. However, since the
brake systems are split diagonally the vehicle will
retain 50% of its stopping capability in the event of a
failure in either half. The warning light switch is the latching type. It
will automatically center itself after the repair is
made and the brake pedal is depressed.
Fig. 1 Rear Brake Proportioning Valve Location On Modulator Assembly
Fig. 2 ABS PROPORTIONING VALVE IDENTIFICA- TION
Fig. 3 Pressure Differential Warning Light Switch InJunction Block.
5 - 10 BRAKES Ä
Page 297 of 2438

The instrument panel bulb can be checked each
time the ignition switch is turned to the start posi-
tion or the parking brake is set.
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM SERVICE PROCEDURES
BRAKE WARNING SYSTEM
CHECKING BRAKE WARNING SWITCH UNIT
The Red Brake Warning light will come on when the
parking brake is applied with the ignition key turned
ON. The same light will also illuminate should one of
the two service brake hydraulic systems fail.
CAUTION:Make sure air does not enter the hydraulic
system during this test procedure. See bleeding with-
out a pressure bleeder at the beginning of this section
for master cylinder fluid level checking procedures.
To test the service brake warning system lamp.
Raise vehicle on a hoist and open a wheel cylinder
bleeder while a helper depresses the brake pedal and
observes the warning light.
If light fails to come on, inspect for a burned out bulb,
disconnected socket, or a broken or disconnected wire at
the switch. If the bulb is not burned out and the wire
continuity is not interrupted. Check the service brake
warning switch operation with a test lamp between the
switch terminal and a known good ground. Be sure to
fill master cylinder and bleed brake system after correc-
tion has been made, if necessary.
TESTING ANTILOCK PROPORTIONING VALVES
(1) Install one gauge and (TEE) between modula-
tor assembly and male end (Inlet) of proportioning
valve (Fig. 4). (2) Install second gauge at female end (Outlet) of
proportioning valve (Fig. 4).
(3) Have a helper exert pressure on brake pedal to
obtain and hold required pressure reading on the
valve inlet gauge. (4) Check reading on outlet gauge. If inlet and out-
let pressures do not agree with the following chart,
replace the valve. See (Fig. 3) for proportioning valve
identification.
BENDIX ANTILOCK 4 PROPORTIONING VALVE APPLICATIONS
BENDIX ANTILOCK 4 PROPORTIONING VALVE PRESSURES
Fig. 4 Tube Connections for ABS
Ä BRAKES 5 - 11
Page 298 of 2438
BENDIX ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM INDEX
page page
ABS Brake System Diagnostic Features ....... 24
ABS Computer System Service Precautions .... 23
ABS General Service Precautions ............ 23
Antilock Brake System Components .......... 16
Antilock Brake System Definitions ............ 14
Antilock Brakes Operation and Performance .... 15
Antilock System Relays and Warning Lamps .... 19
Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System Diagnostics .... 22
Bleeding Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System ...... 25
Controller Antilock Brake Cab ............... 18
Diagnostic Connector ..................... 19 Electronic Components
.................... 41
General Information ....................... 12
Hydraulic Circuits and Valve Operation ........ 20
Major Components ....................... 14
Mechanical Diagnostics and Service Procedures . 24
Normal Brake System Function .............. 14
On-Car ABS Brake System Service ........... 25
Specifications ........................... 46
System Self-Diagnostics ................... 15
Vehicle Performance ...................... 15
Warning Systems Operation ................ 16
GENERAL INFORMATION
The purpose of an Anti-Lock Brake System is to
prevent wheel lock-up under heavy braking condi-
tions on virtually any type of road surface. Antilock
Braking is desirable because a vehicle which is
stopped without locking its wheels will retain direc-
tional stability and some steering capability. This al-
lows a driver to retain greater control of the vehicle
during heavy braking. This service manual supplement covers the descrip-
tion, diagnostics, and on car service procedures cov-
ering the Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System. If service
is required on the non Antilock related components
of the brake system, refer to the appropriate section
in Group 5 of the Front Wheel Drive Car Engine,
Chassis And Body service manual.
Fig. 1 Bendix Antilock 4 Brake System Components
5 - 12 ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 302 of 2438

(2) The voltage output from each of the wheel
speed sensors is verified to be within the correct op-
erating range. If a vehicle is not set in motion within 3 minutes
from the time the ignition switch is turned to the on
position. The solenoid valve test is bypassed but the
pump/motor is activated briefly to verify that it is op-
erating correctly.
WARNING SYSTEMS OPERATION
The ABS system uses an Amber Antilock Warning
Lamp, located in the instrument cluster. The purpose
of the warning lamp is discussed in detail below. The Amber Antilock Warning Light will turn on
whenever the CAB detects a condition which results
in a shutdown of the Antilock brake system. The
Amber Antilock Warning Lamp is normally on until
the CAB completes its self tests and turns the lamp
off (approximately 1-2 seconds). When the Amber
Antilock Warning Light is on, only the Antilock
brake function of the brake system if affected. The
standard brake system and the ability to stop the car
will not be affected when only the Amber Antilock
Warning Light is on.
NORMAL OPERATION OF WARNING LAMP
With ignition key turned to the Crank position, the
Red Brake Warning Lamp and Amber Antilock
Warning Lamp will turn on as a bulb check. The
Amber Antilock Warning Lamp will stay on for 1-2
seconds then turn off, once verification of Antilock
Brake System self diagnosis is completed.
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The following is a detailed description of the Ben-
dix Antilock 4 Brake System components. For infor-
mation on servicing the Four Wheel Disc Brake
System, see the standard Brake section in the Front
Wheel Drive Car, chassis service manual.
MODULATOR ASSEMBLY
WARNING: THE ONLY COMPONENTS OF THE
MODULATOR ASSSEMBLY THAT ARE SERVICE-
ABLE, ARE THE 2 PROPORTIONING VALVES,
BLEED SCREWS AND THREAD SAVERS. THE RE-
MAINING COMPONENTS OF THE MODULATOR AS-
SEMBLY ARE NOT INTENDED TO BE
SERVICEABLE ITEMS. NO ATTEMPT SHOULD BE
MADE TO REMOVE OR SERVICE ANY OTHER COM-
PONENTS OF THE MODEULATOR ASSEMBLY.
The Modulator Assembly (Fig. 1) is located under
the battery tray and is covered with an acid shield.
The Modulator Assembly contains the following com-
ponents for controlling the Antilock brake system. 4
Build/Decay Valves, 4 Shuttle Orifices, 2 Fluid
Sumps, 2 Accumulators, and a Pump/Motor assem- bly. Also attached to the Modulator Assembly are 6
brake tubes which are connected to a 12 way junc-
tion block. The junction block (Fig. 2) is mounted to
the left frame rail below the master cylinder in the
same location as the non ABS equipped combination
valve. The wheel brake lines are attached to the sys-
tem via the connector block.BUILD/DECAY VALVES
There are 4 Build/Decay valves, one for each
wheel. In the released position they provide a fluid
path direct to the wheel brakes. In the actuated (de-
cay) position, they provide a fluid path from the
wheel brakes to the sump. The Build/Decay valves
are spring loaded in the released (build) position.
SHUTTLE ORIFICE
There are 4 Shuttle Orifice Valves, one for each
wheel. The Shuttle Orifice Valve is a hydraulically
actuated valve which shuttles when the Build/Decay
valve is actuated. Actuating of the Build/Decay valve
causes a pressure differential to be created across the
Shuttle Orifice Valve. This acts like placing an ori-
Fig. 1 Modulator Assembly
Fig. 2 Antilock Brake Junction Block
5 - 16 ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä