1993 CHEVROLET DYNASTY engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 1770 of 2438

The PCM removes the ground to the solenoid when
the engine reaches a specified temperature and the
time delay interval has occurred. When the solenoid is
de-energized, vacuum flows to the canister purge
valve. Vapors are purged from the canister and flow to
the throttle body. The purge solenoid is also energized during certain
idle conditions to update the fuel delivery calibration.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (CHECK
ENGINE)ÐPCM OUTPUT
The Malfunction Indicator lamp (instrument panel
Check Engine lamp) comes on each time the ignition
key is turned ON and stays on for 3 seconds as a bulb
test. The malfunction indicator lamp warns the opera-
tor that the PCM has entered a Limp-in mode. During
Limp-in-Mode, the PCM attempts to keep the system
operational. The malfunction indicator lamp signals
the need for immediate service. In limp-in mode, the
PCM compensates for the failure of certain components
that send incorrect signals. The PCM substitutes for
the incorrect signals with inputs from other sensors. Signals that can trigger the Malfunction Indi-
cator Lamp.
² Coolant Temperature Sensor
² Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
² Throttle Position Sensor
² Battery Voltage Input
² An Emissions Related System
² Charging system
The malfunction indicator lamp can also be used to
display diagnostic trouble codes. Cycle the ignition
switch on, off, on, off, on, within five seconds and any
diagnostic trouble codes stored in the PCM will be
displayed. Refer to the 2.2L/2.5L Single Point Fuel
InjectionÐOn-Board Diagnostics section in this group.
DATA LINK CONNECTORÐPCM OUTPUT
The data link connector provides the technician with
the means to connect the DRBII scan tool to diagnosis
the vehicle.
ELECTRIC ELECTRONIC GAS
RECIRCULATIONÐPCM OUTPUT
The electronic exhaust gas recirculation transducer
(EET) is a back pressure transducer/electric vacuum
solenoid assembly (Fig. 13). The EET assembly mounts
above the EGR valve (Fig. 14).
The solenoid turns the vacuum supply to the trans-
ducer on and off. The electric vacuum solenoid portion
of the EET energizes when the PCM provides a ground
path. When the solenoid energizes, vacuum is pre-
vented from flowing to the transducer. When the sole-
noid de-energizes, vacuum flows to the transducer. The
solenoid energizes during engine warm-up, closed
throttle (idle or cruise), wide open throttle, and rapid
acceleration/deceleration. If the solenoid wire con-
nector is disconnected, the EGR valve will oper-
ate at all times.
Fig. 12 EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid
Fig. 13 Electronic EGR Recirculation Transducer
Fig. 14 EGR Valve and Electric EGR Transducer
14 - 30 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1771 of 2438

FUEL INJECTORÐPCM OUTPUT
The Fuel Injector is an electric solenoid operated
by the PCM (Fig. 15).
Based on sensor inputs, the PCM determines when
and how long the fuel injector should operate. The
amount of time the injector fires is referred to as in-
jector pulse width. The auto shutdown (ASD) relay
supplies battery voltage to the injector. The PCM
supplies the ground path. By switching the ground
path on and off, the PCM adjusts injector pulse
width. When the PCM supplies a ground path, a
spring loaded needle or armature lifts from its seat.
Fuel flows through the orifice and deflects off the
sharp edge of the injector nozzle. The resulting fuel
sprays forms a 45É cone shaped pattern before enter-
ing the air stream in the throttle body. Fuel is supplied to the injector constantly at regu-
lated 270 Kpa (39 psi). Unused fuel returns to the
fuel tank.
GENERATOR FIELDÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM regulates the charging system voltage
within a range of 12.9 to 15.0 volts. Refer to Group
8A for charging system information.
IGNITION COILÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM provides a ground contact (circuit) for en-
ergizing the ignition coil. When the PCM breaks the
contact, the energy in the coil primary transfers to
the secondary causing the spark. The PCM will de-
energize the ASD relay if it does not receive an input
from the distributor pick-up. Refer to Auto Shutdown
(ASD) Relay/Fuel Pump RelayÐPCM Output in this
section for relay operation. The ignition coil is mounted on the hot box next to
the thermostat housing (Fig. 16).
PART THROTTLE UNLOCK SOLENOIDÐPCM
OUTPUT
Three-speed automatic transaxles use a part throt-
tle unlock solenoid. The PCM controls the lock-up of
the torque convertor through the part throttle unlock
solenoid. The transaxle is locked up only in direct
drive mode. Refer to Group 21 for transaxle informa-
tion.
RADIATOR FAN RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
The radiator fan is energized by the PCM through
the radiator fan relay. The PCM grounds the radia-
tor fan relay when engine coolant reaches a predeter-
mined temperature. For more information, refer to
Group 7, Cooling Systems. On AC, AG and AJ models, the radiator fan relay
is located in the power distribution center. Refer to
the Wiring and Component Identification section of
Group 8W. On AA and AP models, the radiator fan relay is
mounted on the drivers side fender well, next to the
strut tower (Fig. 10).
SPEED CONTROL SOLENOIDSÐPCM OUTPUT
The speed control vacuum and vent solenoids are
operated by the PCM. When the PCM supplies a
ground to the vacuum and vent solenoids, the speed
control system opens the throttle blade. When the
PCM supplies a ground only to the vent solenoid, the
throttle blade holds position. When the PCM removes
the ground from both the vacuum and vent solenoids,
the throttle blade closes. The PCM balances the two
solenoids to maintain the set speed. Refer to Group
8H for speed control information.
Fig. 15 Fuel Injector
Fig. 16 Ignition Coil
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 31
Page 1772 of 2438

TACHOMETERÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies engine RPM to the instrument
panel tachometer. Refer to Group 8 for tachometer
information.
MODES OF OPERATION
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to the output devices. For example,
the PCM must calculate a different injector pulse
width and ignition timing for idle than it does for wide
open throttle (WOT). There are several different modes
of operation that determine how the PCM responds to
the various input signals. There are two different areas of operation, OPEN
LOOP and CLOSED LOOP. During OPEN LOOP modes, the PCM receives input
signals and responds according to preset PCM pro-
gramming. Input from the oxygen (O
2) sensor is not
monitored during OPEN LOOP modes. During CLOSED LOOP modes, the PCM does moni-
tor the oxygen (O
2) sensor input. This input tells the
PCM if the calculated injector pulse width results in an
air-fuel ratio of 14.7 to 1. By monitoring the exhaust
oxygen content, the can PCM fine tune injector pulse
width for optimum fuel economy and low emissions. The single point fuel injection system has the follow-
ing modes of operation:
² Ignition switch ON - Zero RPM
² Engine start-up
² Engine warm-up
² Cruise (Idle)
² Acceleration
² Deceleration
² Wide Open Throttle
² Ignition switch OFF
The engine start-up (cranking), engine warm-up, and
wide open throttle modes are OPEN LOOP modes. The
acceleration, deceleration, and cruise modes, with the
engine at operating temperature are CLOSED
LOOP modes (under most operating conditions).
IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE
When the single point fuel injection system is acti-
vated by the ignition switch, the following actions
occur:
² The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure from
the MAP sensor input to calculate basic fuel strategy.
² The PCM monitors the coolant temperature sensor
and throttle position sensor inputs. The PCM modifies
fuel strategy based on these inputs. When the key is in the ON position and the engine is
not running, the (ASD) and fuel pump relays are not
energized. Therefore, battery voltage is not supplied to
the fuel pump, ignition coil, fuel injector or oxygen
sensor heating element. ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. The following actions
occur when the starter motor is engaged. If the PCM receives a distributor signal it energizes
the auto shutdown (ASD) relay and fuel pump relay to
supply battery voltage to the fuel injector, ignition coil
and oxygen sensor heating element. If the PCM does
not receive a distributor input, it de-energizes the ASD
and fuel pump relays after approximately one second. When the engine idles within 664 RPM of the target
RPM, the PCM compares the current MAP value with
the atmospheric pressure value it received during the
Ignition Switch On (Zero RPM) Mode. If a minimum
difference between the two is not detected, a MAP
sensor fault is set into memory. Once the ASD relay and fuel pump relay have ener-
gized, the PCM:
² Supplies a ground path to the injector. The injector
is pulsed four times per engine revolution instead of
the normal two pulses per revolution.
² Determines injector pulse width based on coolant
temperature, MAP sensor input, throttle position, and
the number of engine revolutions since cranking was
initiated.
² Monitors the coolant temperature sensor, distribu-
tor pick-up, MAP sensor, and throttle position sensor to
determine correct ignition timing.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE
This is a OPEN LOOP mode. The following inputs
are received by the PCM:
² coolant temperature
² manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
² engine speed (distributor pick-up)
² throttle position
² A/C switch
² battery voltage
The PCM provides a ground path for the injector to
precisely control injector pulse width (by switching the
ground on and off) and fires the injector twice per
engine revolution. The PCM regulates ignition timing.
It also adjusts engine idle speed through the idle air
control motor.
CRUISE OR IDLE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature this is
a CLOSED LOOP mode. During cruising speed and at
idle the following inputs are received by the PCM:
² coolant temperature
² manifold absolute pressure
² engine speed
² throttle position
² exhaust gas oxygen content
² A/C control positions
² battery voltage
14 - 32 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1773 of 2438

The PCM provides a ground path for the injector to
precisely control injector pulse width and fires the in-
jector twice per engine revolution. The PCM controls
engine idle speed and ignition timing. The PCM con-
trols the air/fuel ratio according to the oxygen con-
tent in the exhaust gas.
ACCELERATION MODE This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. The PCM recog-
nizes an abrupt increase in throttle position or MAP
pressure as a demand for increased engine output
and vehicle acceleration. The PCM increases injector
pulse width in response to increased fuel demand.
DECELERATION MODE This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During decelera-
tion the following inputs are received by the PCM:
² coolant temperature
² manifold absolute pressure
² engine speed
² throttle position
² exhaust gas oxygen content
² A/C control positions
² battery voltage
The PCM may receive a closed throttle input from
the throttle position sensor (TPS) at the same time it
senses an abrupt decrease in manifold pressure from
the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor. This
indicates a hard deceleration. The PCM may reduce
injector firing to once per engine revolution. This
helps maintain better control of the air-fuel mixture
(as sensed through the O
2sensor).
During a deceleration condition, the PCM grounds
the exhaust gas recirculation transducer (EET) sole-
noid. EGR stops when the PCM grounds the solenoid.
WIDE OPEN THROTTLE MODE This is an OPEN LOOP mode. During wide open
throttle operation, the following inputs are received
by the PCM:
² coolant temperature
² manifold absolute pressure
² engine speed
² throttle position
When the PCM senses a wide open throttle condi-
tion through the throttle position sensor (TPS) it
will:
² De-energize the air conditioning relay. This dis-
ables the air conditioning system.
² Provide a ground path for the electric EGR trans-
ducer (EET) solenoid, preventing the EGR system
from functioning. The exhaust gas oxygen content input is not ac-
cepted by the PCM during wide open throttle opera- tion. The PCM will adjust injector pulse width to
supply a predetermined amount of additional fuel.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE
When the ignition switch is turned to the OFF po-
sition, the following occurs:
² All outputs are turned off.
² No inputs are monitored.
² The PCM shuts down.
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
The pressure regulator is a mechanical device lo-
cated at the top of the throttle body (Fig. 17). Its
function is to maintain a constant 270 kPa (39 PSI)
across the fuel injector tip.
The regulator uses a spring loaded rubber dia-
phragm to uncover a fuel return port. When the fuel
pump becomes operational, fuel flows past the injec-
tor into the regulator, and is restricted from flowing
any further by the blocked return port. When fuel
pressure reaches 270 kPa (39 PSI) it pushes on the
diaphragm, compresses the spring, and uncovers the
fuel return port. The diaphragm and spring con-
stantly move from an open to closed position keeping
fuel pressure consistent.
THROTTLE BODY
The throttle body assembly (Fig. 18) is mounted on
top of the intake manifold. It contains the fuel injec-
tor, pressure regulator, throttle position sensor and
idle air control motor. Air flow through the throttle
body is controlled by a cable operated throttle blade
located in the base of the throttle body. The throttle
body itself provides the chamber for metering, atom-
izing, and mixing fuel with the air entering the en-
gine.
Fig. 17 Fuel Pressure Regulator
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 33
Page 1779 of 2438
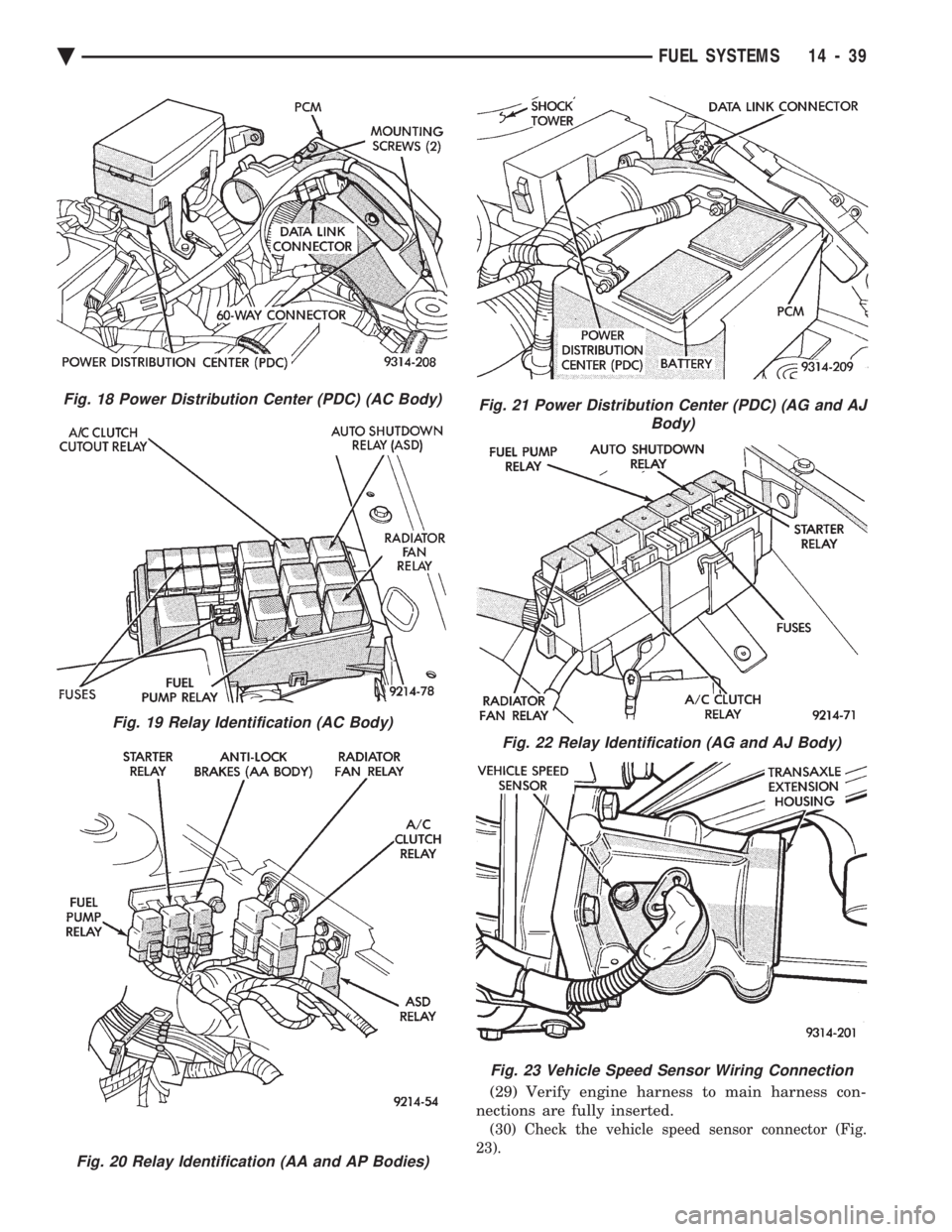
(29) Verify engine harness to main harness con-
nections are fully inserted.
(30) Check the vehicle speed sensor connector (Fig.
23).
Fig. 18 Power Distribution Center (PDC) (AC Body)
Fig. 19 Relay Identification (AC Body)
Fig. 20 Relay Identification (AA and AP Bodies)
Fig. 21 Power Distribution Center (PDC) (AG and AJ Body)
Fig. 22 Relay Identification (AG and AJ Body)
Fig. 23 Vehicle Speed Sensor Wiring Connection
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 39
Page 1780 of 2438

(31) Verify engine ground strap is attached at the
engine and dash panel (Figs. 24 and 25). (32) Verify oxygen sensor electrical connector is at-
tached to the sensor (Fig. 26). (33) Check Hose and Wiring Connections at Fuel
Pump. Check that wiring connector is making con-
tact with terminals on pump.
Fig. 24 Engine Ground Strap at Intake ManifoldFig. 25 Engine Ground Strap to Dash Panel
Fig. 26 Heated Oxygen Sensor Electrical Connection
14 - 40 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1781 of 2438

2.2L/2.5L SINGLE POINT FUEL INJECTIONÐON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS INDEX
page page
60-Way PCM Wiring Connector .............. 46
Circuit Actuation Test Mode ................ 45
Diagnostic Trouble Code Description .......... 42
General Information ....................... 41
High and Low Limits ...................... 42
Ignition Timing Procedure .................. 46 Monitored Circuits
........................ 41
Non-Monitored Circuits .................... 42
State Display Test Mode ................... 45
Systems Test ........................... 45
Throttle Body Minimum Air Flow Check Procedure.46
GENERAL INFORMATION
The powertrain control module (PCM) has been
programmed to monitor many different circuits of the
fuel injection system. If a problem is sensed with a
monitored circuit often enough to indicate an actual
problem, the PCM stores a fault. If the problem is re-
paired or ceases to exist, the PCM cancels the Diag-
nostic Trouble Code after 50 to 100 vehicle key on/off
cycles. Certain criteria must be met for a diagnostic trou-
ble code to be entered into powertrain control module
(PCM) memory. The criteria may be a specific range
of engine RPM, engine temperature, and/or input
voltage to the PCM. It is possible that a diagnostic trouble code for a
monitored circuit may not be entered into memory
even though a malfunction has occurred. This may
happen because one of the diagnostic trouble code
criteria for the circuit has not been met. For exam-
ple , assume that one of the diagnostic trouble code
criteria for a certain sensor circuit is that the engine
must be operating between 750 and 2000 RPM to be
monitored for a diagnostic trouble code. If the sensor
output circuit shorts to ground when engine RPM is
above 2400 RPM (resulting i n a 0 volt input to the
PCM) a diagnostic trouble code will not be entered
into memory. This is because the condition does not
occur within the specified RPM range. There are several operating conditions for which
the PCM does not monitor and set diagnostic trouble
codes. Refer to Monitored Circuits and Non-Moni-
tored Circuits in this section. Stored diagnostic trouble codes can be displayed by
cycling the ignition key On - Off - On - Off - On.
Also, the technician can display fault information us-
ing the DRB II scan tool. The DRBII scan tool con-
nects to the data link connector in the vehicle (Fig.
1,2or3).
MONITORED CIRCUITS
The powertrain control module (PCM) can detect
certain fault conditions in the fuel injection system. Open or Shorted Circuit - The PCM can deter-
mine if the sensor output (input to PCM) is within
proper range, and if the circuit is open or shorted. Output Device Current Flow
- The PCM senses
whether the output devices are hooked up. If there is
a problem with the circuit, the PCM senses whether
the circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted
high. Oxygen Sensor - The PCM can determine if the
oxygen sensor is switching between rich and lean
Fig. 1 Data Link Connector LocationÐAA and AP Vehicles
Fig. 2 Data Link Connector LocationÐAC Vehicles
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 41
Page 1782 of 2438

once the system has entered closed loop. Refer to
Modes of Operation in this section for an explanation
of closed loop operation.
NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor the following circuits,
systems and conditions that could have malfunctions
that result in driveability problems. Diagnostic trou-
ble codes may not be displayed for these conditions.
However, problems with these systems may cause di-
agnostic trouble codes to be displayed for other sys-
tems. For example, a fuel pressure problem will not
register a fault directly, but could cause a rich or
lean condition. This could cause an oxygen sensor
fault to be stored in the PCM. Fuel Pressure - Fuel pressure is controlled by the
fuel pressure regulator. The PCM cannot detect a
clogged fuel pump inlet filter, clogged in-line fuel fil-
ter, or a pinched fuel supply or return line. However,
these could result in a rich or lean condition causing
an oxygen sensor fault. Secondary Ignition Circuit - The PCM cannot
detect an inoperative ignition coil, fouled or worn
spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or open spark plug
cables. Engine Timing - The PCM cannot detect an incor-
rectly indexed timing chain, camshaft sprocket and
crankshaft sprocket. The PCM also cannot detect an
incorrectly indexed distributor. However, these could
result in a rich or lean condition causing an oxygen
sensor fault to be stored in the PCM. Cylinder Compression - The PCM cannot detect
uneven, low, or high engine cylinder compression. Exhaust System
- The PCM cannot detect a
plugged, restricted or leaking exhaust system. Fuel Injector Malfunctions - The PCM cannot
determine if the fuel injector is clogged, the pintle is
sticking or the wrong injector is installed. However,
these could result in a rich or lean condition causing
an oxygen sensor fault to be stored in the PCM. Excessive Oil Consumption - Although the PCM
monitors the exhaust stream oxygen content through
the oxygen sensor when the system is in closed loop,
it cannot determine excessive oil consumption. Throttle Body Air Flow - The PCM cannot detect
a clogged or restricted air cleaner inlet or filter ele-
ment. Evaporative System - The PCM will not detect a
restricted, plugged or loaded evaporative purge can-
ister. Vacuum Assist - Leaks or restrictions in the vac-
uum circuits of vacuum assisted engine control sys-
tem devices are not monitored by the PCM. However,
these could result in a MAP sensor fault being stored
in the PCM. PCM System Ground - The PCM cannot deter-
mine a poor system ground. However, a diagnostic
trouble code may be generated as a result of this con-
dition. PCM Connector Engagement - The PCM cannot
determine spread or damaged connector pins. How-
ever, a diagnostic trouble code may be generated as a
result of this condition.
HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The powertrain control module (PCM) compares in-
put signal voltages from each input device with es-
tablished high and low limits that are programmed
into it for that device. If the input voltage is not
within specifications and other diagnostic trouble
code criteria are met, a diagnostic trouble code will
be stored in memory. Other diagnostic trouble code
criteria might include engine RPM limits or input
voltages from other sensors or switches that must be
present before a fault condition can be verified.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DESCRIPTION
When a diagnostic trouble code appears, it indi-
cates the powertrain control module (PCM) has rec-
ognized an abnormal condition in the system.
Diagnostic trouble codes can be obtained from the
malfunction indicator lamp (instrument panel Check
Engine lamp) on the Instrument Panel or from the
DRBII scan tool. Diagnostic trouble codes indicate
the results of a failure but do not identify the failed
component directly.
Fig. 3 Data Link Connector LocationÐAG and AJ Vehicles
14 - 42 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä