1993 CHEVROLET DYNASTY oil
[x] Cancel search: oilPage 1832 of 2438

noid is energized. The solenoid mounts to the passen-
ger side inner fender panel, next to the strut tower
(Fig. 17).
MODES OF OPERATION
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to the output devices. For example,
the PCM must calculate a different injector pulse
width and ignition timing for idle than it does for wide
open throttle (WOT). There are several different modes
of operation that determine how the PCM responds to
the various input signals. There are two different areas of operation, OPEN
LOOP and CLOSED LOOP. During OPEN LOOP modes, the PCM receives input
signals and responds according to preset PCM pro-
gramming. Input from the oxygen (O
2) sensor is not
monitored during OPEN LOOP modes. During CLOSED LOOP modes, the PCM does moni-
tor the oxygen (O
2) sensor input. This input indicates
to the PCM whether or not the calculated injector pulse
width results in the ideal air-fuel ratio of 14.7 parts air
to 1 part fuel. By monitoring the exhaust oxygen
content through the O
2sensor, the PCM can fine tune
the injector pulse width to achieve optimum fuel
economy combined with low emissions. The 2.2L Turbo III multi-port fuel injection system
has the following modes of operation:
² Ignition switch ON - Zero RPM
² Engine start-up
² Engine warm-up
² Cruise (Idle)
² Acceleration
² Deceleration
² Wide Open Throttle
² Ignition switch OFF
The engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up, and
wide open throttle modes are OPEN LOOP modes. The
acceleration, deceleration, and cruise modes, with the
engine at operating temperature are CLOSED
LOOP modes (under most operating conditions).
IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE
When the ignition switch activates the fuel injection
system the following actions occur:
²
The PCM calculates basic fuel strategy by determining
atmospheric air pressure from the MAP sensor input.
² The PCM monitors the coolant temperature sensor
and throttle position sensor input. The PCM modifies
fuel strategy based on this input. When the key is in the ON position and the engine is
not running, the auto shutdown (ASD) relay and fuel
pump relay are not energized. Therefore battery volt-
age is not supplied to the fuel pump, ignition coil, fuel
injector or oxygen sensor heating element.
ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. The following actions
occur when the starter motor is engaged. If the PCM receives the camshaft position and crank-
shaft position sensor signals, it energizes the auto
shutdown (ASD) relay and fuel pump relay. These
relays supply battery voltage to the fuel pump, fuel
injectors, ignition coil, and oxygen sensor heating ele-
ment. If the PCM does not receive the camshaft posi-
tion sensor and crankshaft position sensor signals
within approximately one second, it de-energizes the
ASD relay and fuel pump relay. The PCM energizes all injectors until it determines
crankshaft position from the camshaft position sensor
and crankshaft position sensor signals. The PCM de-
termines crankshaft position within 1 engine revolu-
tion. After determining crankshaft position, the PCM be-
gins energizing the injectors in sequence. The PCM
adjusts injector pulse width and controls injector syn-
chronization by turning the individual ground paths to
the injectors On and Off. When the engine idles within 664 RPM of its target
RPM, the PCM compares current MAP sensor value
with the atmospheric pressure value received during
the Ignition Switch On (zero RPM) mode. If the PCM
does not detect a minimum difference between the two
values, it sets a MAP fault into memory. Once the ASD and fuel pump relays have been
energized, the PCM:
² Determines injector pulse width based on coolant
temperature, manifold absolute pressure (MAP) and
the number of engine revolutions since cranking was
initiated.
² Monitors the coolant temperature sensor, camshaft
position sensor, crankshaft position sensor, MAP sen-
sor, and throttle position sensor to determine correct
ignition timing.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE
This is a OPEN LOOP mode. The following inputs
are received by the PCM:
² engine coolant temperature
² knock sensor
² manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
² engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
² throttle position
² A/C switch
² battery voltage
The PCM provides a ground path for the injectors to
precisely control injector pulse width (by switching the
ground on and off). The PCM adjusts engine idle speed
through the idle air control motor. Also, the PCM
regulates ignition timing.
14 - 92 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1835 of 2438

2.2L TURBO III MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTIONÐGENERAL DIAGNOSIS INDEX
page page
Fuel System Diagram ..................... 95 Visual Inspection......................... 95
FUEL SYSTEM DIAGRAM
Refer to the System Operation portion of this sec-
tion for descriptions of the components shown in Fig.
1.
VISUAL INSPECTION
Perform a visual inspection for loose, disconnected,
or misrouted wires and hoses before diagnosing or
servicing the fuel injection system. A visual check
helps save unnecessary test and diagnostic time. A
thorough visual inspection includes the following
checks: (1) Check the ignition coil electrical connections
(Fig. 2). (2) Verify the harness connector is attached to the
canister purge solenoid (Fig. 3). (3) Verify the harness connector is attached to the
wastegate solenoid (Figs. 3).
Fig. 1 Multi-port Fuel Injection Components
Fig. 2 Ignition Coil Electrical Connection
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 95
Page 1836 of 2438

(4) Verify the harness connector is attached to the
MAP sensor (Fig. 4).
(5) Check vacuum hose connections between vac-
uum source and canister purge, wastegate, and baro-
metric read solenoids (Figs. 3 and 4). (6) Verify hoses are securely attached to vapor
canister (Fig. 5).
(7) Verify the generator wiring and belt are cor-
rectly installed and tightened. (8) Check ignition cable routing and attachment
(Fig. 6).
(9) Check oil pressure sending unit electrical con-
nection (Fig. 7).
(10) Check the camshaft position sensor and crank-
shaft position sensor electrical connections (Figs. 7
and 8). (11) Check radiator fan electrical connector.
(12) Check electrical connector at the coolant tem-
perature sensor (Fig. 9). (13) Inspect the engine temperature sensor electri-
cal connection (Fig. 9). (14) Check the power brake booster and speed con-
trol connections (Fig. 10).
Fig. 6 Ignition Cable Mounting and Attachment
Fig. 7 Oil Pressure Sending Unit and Crankshaft Position Sensor
Fig. 3 Solenoid Connections
Fig. 4 Barometric/MAP Solenoid Hose Connections
Fig. 5 Vapor Canister
14 - 96 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1841 of 2438

Secondary Ignition Circuit - The PCM cannot
detect an inoperative ignition coil, fouled or worn spark
plugs, ignition cross firing, or open spark plug cables. Engine Timing - The PCM cannot detect an incor-
rectly indexed timing chain, camshaft sprocket and
crankshaft sprocket. However, these could result in a
rich or lean condition causing an oxygen sensor fault. Cylinder Compression - The PCM cannot detect
uneven, low, or high engine cylinder compression. Exhaust System - The PCM cannot detect a
plugged, restricted or leaking exhaust system. Fuel Injector Malfunctions - The PCM cannot
determine if the fuel injector is clogged, the pintle is
sticking or the wrong injector is installed. However,
these could result in a rich or lean condition causing an
oxygen sensor fault to be stored in the PCM. Excessive Oil Consumption - Although the PCM
monitors exhaust stream oxygen content when the
system is in closed loop, it cannot determine excessive
oil consumption. Throttle Body Air Flow - The PCM cannot detect a
clogged or restricted air cleaner inlet or filter element. Evaporative System - The PCM will not detect a
restricted, plugged or loaded evaporative purge canis-
ter. Vacuum Assist - Leaks or restrictions in the
vacuum circuits of vacuum assisted engine control
system devices are not monitored by the PCM. How-
ever, these could result in a MAP sensor fault being
stored in the PCM. PCM System Ground
- The PCM cannot determine
a poor system ground. However, a diagnostic trouble
code may be generated as a result of this condition. PCM Connector Engagement - The PCM cannot
determine spread or damaged connector pins. How-
ever, a diagnostic trouble code may be generated as a
result of this condition.
HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The powertrain control module (PCM) compares in-
put signal voltages from each input device with estab-
lished high and low limits that are programmed into it
for that device. If the input voltage is not within
specifications and other diagnostic trouble code criteria
are met, a diagnostic trouble code will be stored in
memory. Other diagnostic trouble code criteria might
include engine RPM limits or input voltages from other
sensors or switches that must be present before a fault
condition can be verified.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DESCRIPTION
When a diagnostic trouble code appears, it indicates
the powertrain control module (PCM) has recognized
an abnormal condition in the system. Diagnostic
trouble codes can be obtained from the malfunction
indicator lamp (Check Engine lamp on the instrument
panel) or from the DRBII scan tool. Diagnostic trouble
codes indicate the results of a failure but do not
identify the failed component directly.
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 101
Page 1845 of 2438

Wastegate Duty Cycle
Battery Temperature
Map Sensor Voltage
Vehicle Speed
Oxygen Sensor State
Baro Read Update
MAP Gauge Reading
Throttle Opening (percentage)
Total Spark Advance
CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST MODE
The purpose of the circuit actuation test mode is to
check for the proper operation of output circuits or
devices which the powertrain control module (PCM)
cannot internally recognize. The PCM can attempt to
activate these outputs and allow an observer to ver-
ify proper operation. Most of the tests available in
this mode provide an audible or visual indication of
device operation (click of relay contacts, spray fuel,
etc.). With the exception of an intermittent condition,
if a device functions properly during its test, assume
the device, its associated wiring, and its driver cir-
cuit are in working order.
OBTAINING CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the Actuators screen. The following is a list of
the engine control system functions accessible
through Actuators screens. Stop All Tests
Ignition Coil #1
Ignition Coil #2
Fuel Injector #1
Fuel Injector #2
Fuel Injector #3
Idle Air Control Motor Open/Close
Radiator Fan Relay
A/C Clutch Relay
Auto Shutdown Relay
Purge Solenoid
S/C Serv Solenoids
Generator Field
Tachometer Output
Wastegate Solenoid
Baro Read Solenoid
All Solenoids/Relays
Speed Control Vent Solenoid
Speed Control Vacuum Solenoid
ASD Fuel System Test
Fuel Injector #4
THROTTLE BODY MINIMUM AIR FLOW CHECK
PROCEDURE
(1) Warm the engine in neutral until the cooling
fan has cycled on and off at least once. (2) Shut off engine.
(3) Hook-up Tachometer.
(4) Disconnect the PCV valve hose from the nipple
on the intake manifold. (5) Attach air metering fitting, special tool 6457
(0.125 inch orifice), to the intake manifold PCV nip-
ple. (6) Disconnect 3/16 inch manifold vacuum purge
line from the top of the throttle body. Cap the 3/16
inch throttle body nipple. (7) Connect DRBII scan tool.
(8) Restart engine. Allow engine to idle for at least
one minute. (9) Using the DRBII scan tool, access Min. Airflow
Idle Spd. The following will then occur:
² Idle air control motor will fully close.
² Idle spark advance will become fixed.
² Engine RPM will be displayed on the DRBII scan
tool. (10) Check idle RPM with tachometer, if idle RPM
is within the below specification then the throttle
body minimum airflow is set correctly.
If the idle RPM is not within specification, replace
the throttle body. (11) Shut off engine.
(12) Remove air metering fitting 6457 from the in-
take manifold PCV nipple. Connect the PCV hose to
the nipple. (13) Remove DRBII scan tool.
(14) Disconnect tachometer.
(15) Reconnect purge line to throttle body.
IGNITION TIMING PROCEDURE
Ignition timing cannot be changed or set on the
Turbo III engine. Refer to Group 8D for a description
of the Direct Ignition System (DIS).
60-WAY PCM WIRING CONNECTOR
Refer to the PCM wiring connector diagram (Fig.
2) for information regarding wire colors and cavity
numbers.
IDLE SPECIFICATIONS
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 105
Page 1849 of 2438
FUEL INJECTOR RAIL ASSEMBLY
WARNING: THE 2.2L TURBO III FUEL SYSTEM IS
UNDER A CONSTANT PRESSURE OF APPROXI-
MATELY 380 KPA (55 PSI). PERFORM FUEL PRES-
SURE RELEASE PROCEDURE BEFORE SERVICING
THE FUEL RAIL OR FUEL INJECTORS.
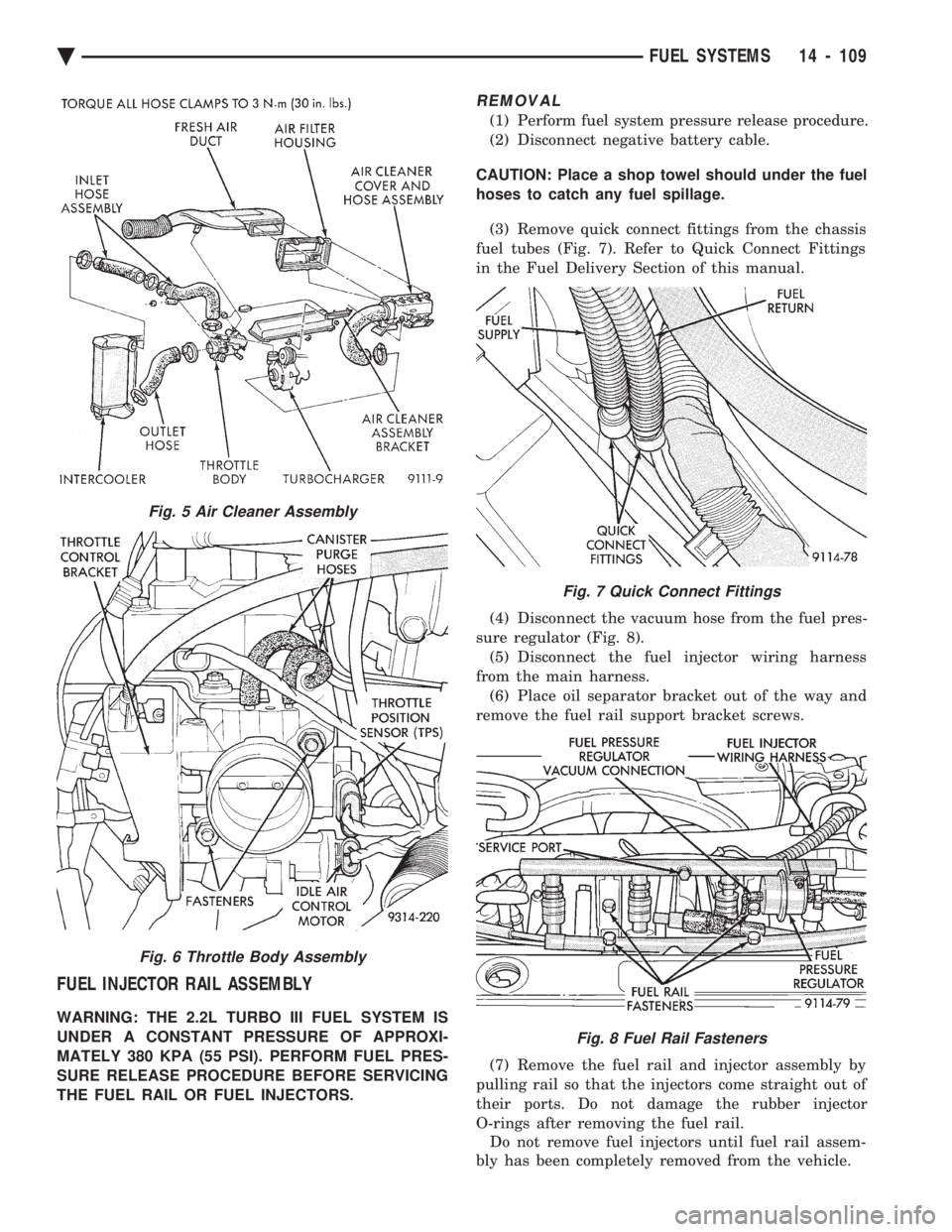
REMOVAL
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable.
CAUTION: Place a shop towel should under the fuel
hoses to catch any fuel spillage. (3) Remove quick connect fittings from the chassis
fuel tubes (Fig. 7). Refer to Quick Connect Fittings
in the Fuel Delivery Section of this manual.
(4) Disconnect the vacuum hose from the fuel pres-
sure regulator (Fig. 8). (5) Disconnect the fuel injector wiring harness
from the main harness. (6) Place oil separator bracket out of the way and
remove the fuel rail support bracket screws.
(7) Remove the fuel rail and injector assembly by
pulling rail so that the injectors come straight out of
their ports. Do not damage the rubber injector
O-rings after removing the fuel rail. Do not remove fuel injectors until fuel rail assem-
bly has been completely removed from the vehicle.
Fig. 7 Quick Connect Fittings
Fig. 8 Fuel Rail Fasteners
Fig. 5 Air Cleaner Assembly
Fig. 6 Throttle Body Assembly
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 109
Page 1850 of 2438

(8) Cover or plug the injector ports with while ser-
vicing the injectors (Fig. 9).
INSTALLATION
(1) Ensure the injectors are seated into the re-
ceiver cup, with the lock ring in place. (2) Ensure the injector wiring connectors are fully
inserted into the fuel injectors. (3) Make sure the injector holes are clean and all
plugs have been removed (Fig. 9). (4) Lubricate the injector O-rings with a drop of
clean engine oil. (5) Install the injector assemblies into their holes
and install the attaching bolts. Draw the fuel rail as-
sembly evenly into the intake manifold, making sure
each injector enters its own hole. The oil separator
bracket must be on top of the fuel rail bracket (Fig.
8). (6) Once all injectors are evenly seated, tighten the
fuel rail attaching bolts to 23 N Im (200 in. lbs.)
torque. (7) Connect the fuel injector wiring harness to the
main harness. (8) Lubricate the ends of the chassis tubes with
clean 30 weight engine oil. (9) Connect fuel hose quick connect fittings to the
chassis fuel tubes. Pull on the fittings to ensure com-
plete connection. Refer to Quick Connect Fittings in the Fuel Deliv-
ery Section of this group. (10) Connect the vacuum hose to the fuel pressure
regulator. (11) Connect negative cable to battery.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized
for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or un-
til the ignition switch is turned to the Off position. (12) With the DRBII scan tool the ASD Fuel Sys-
tem Test to pressurize the fuel system to check for
leaks.
FUEL INJECTORS
Remove the fuel rail to service the injectors. Refer
to Fuel Injector Rail Assembly in this section.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect injector electrical connector from in-
jector. (Fig. 10).
(2) Position fuel rail assembly so that the fuel in-
jectors are easily accessible (Fig. 11).
(3) Remove injector lock ring off the fuel rail and
injector. Pull injector straight out of fuel rail receiver
cup (Fig. 11). (4) Check injector O-ring for damage. If O-ring is
damaged, it must be replaced. If injector is reused, a
protective cap must be installed on the injector tip to
prevent damage. (5) Repeat for remaining injectors.
Fig. 9 Fuel Injector Ports
Fig. 10 Fuel Rail and Injector Assembly
Fig. 11 Servicing Fuel Injectors
14 - 110 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1851 of 2438

INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing an injector, the rubber O-ring
must be lubricated with a drop of clean engine oil to aid
in installation. (2) Being careful not to damage the O-ring, install
injector top end into fuel rail receiver cup. (3) Install injector lock ring by sliding open end into
slot of the injector and onto the receiver cup ridge into
the side slots of ring (Fig. 11). (4) Repeat steps for remaining injectors.
(5) Install injector wiring harness to injectors. Place
harness into retaining clips.
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
WARNING: THE 2.2L TURBO III FUEL SYSTEM IS
UNDER A CONSTANT PRESSURE OF APPROXI-
MATELY 380 KPA (55 PSI). PERFORM FUEL PRES-
SURE RELEASE PROCEDURE BEFORE SERVICING
THE FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR.
REMOVAL
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Disconnect vacuum hose from fuel pressure regu-
lator (Fig. 12).
Place a shop towel under fuel pressure regula-
tor to absorb any fuel spillage. (4) Loosen fuel hose clamp and remove fuel return
hose. (5) Remove fuel pressure regulator mounting nuts.
Remove fuel pressure regulator from rail (Fig. 12).
Check O-Ring for damage. If O-Ring is damaged it
must be replaced.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate O-ring with a drop of clean engine oil.
Install O-ring into the receiver cup on fuel rail. (2) Install fuel pressure regulator mounting nuts.
Tighten nuts to 7 N Im (65 in. lbs.) torque. (3) Connect fuel return hose to pressure regulator.
Tighten hose clamp to 1 N Im (10 in. lbs.) torque (Fig.
12). (4) Install vacuum hose on fuel pressure regulator.
(5) Connect negative cable to battery.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized
for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or un-
til the ignition switch is turned to the Off position. (6) With the DRBII scan tool the ASD Fuel System
Test to pressurize system and check for leaks.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP) SENSOR
SERVICE
(1) Remove vacuum hose from MAP sensor (Fig.
13) (2) Remove MAP sensor mounting screws (Fig. 13).
(3) Remove electrical connector. Remove sensor.
(4) Reverse the above procedure for installation.
WASTEGATE AND CANISTER PURGE SOLENOID
SERVICE
(1) Remove vacuum hoses from sensors (Fig. 14).
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from solenoids
(Fig. 14). (3) Remove solenoid pack mounting nut. Remove
solenoid pack. (4) Depress tab on top of solenoid to be replaced
and slide the solenoid downward out of mounting
bracket. (5) Reverse above procedure to install.
PCM SERVICE
(1) Remove air cleaner duct from PCM.
(2) Remove battery.
(3) Remove PCM mounting screws (Fig. 15).
(4) Disconnect the 60-way wiring connector. Re-
move the PCM. (5) Reverse the above procedure for installation.
Fig. 13 Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
Fig. 12 Servicing Fuel Pressure Regulator
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 111