1993 CHEVROLET DYNASTY turn signal
[x] Cancel search: turn signalPage 1801 of 2438

desired MAP value. Under idle conditions, the PCM
adjusts the idle air control motor to maintain a de-
sired engine speed.
AIR CONDITIONING (A/C) CLUTCH RELAYÐPCM
OUTPUT
The PCM operates the air conditioning clutch relay
ground circuit. The radiator fan relay supplies bat-
tery power to the solenoid side of the A/C clutch re-
lay. The air conditioning clutch relay will not
energize unless the radiator fan relay energizes. The
PCM energizes the radiator fan relay when the air
conditioning or defrost switch is put in the ON posi-
tion and the low pressure and high pressure switches
close. With the engine operating, the PCM cycles the air
conditioning clutch on and off when the A/C switch
closes with the blower motor switch in the on posi-
tion. When the PCM senses low idle speeds or wide
open throttle through the throttle position sensor, it
de-energizes the A/C clutch relay. The relay contacts
open, preventing air conditioning clutch engagement. The A/C clutch relay is mounted to the inner
fender panel, next to the drivers side strut tower
(Fig. 11).
AUTO SHUTDOWN (ASD) RELAY AND FUEL PUMP
RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM operates the auto shutdown (ASD) relay
and fuel pump relay through one ground path. The
PCM operates the relays by switching the ground
path on and off. Both relays turn on and off at the
same time. The ASD relay connects battery voltage to the fuel
injector and ignition coil. The fuel pump relay con-
nects battery voltage to the fuel pump and oxygen
sensor heating element. The PCM turns the ground path off when the igni-
tion switch is in the Off position. Both relays are off.
When the ignition switch is in the On or Crank po-
sition, the PCM monitors the camshaft position sen-
sor (distributor pick-up) signal to determine engine
speed and ignition timing (coil dwell). If the PCM
does not receive a camshaft position sensor signal
when the ignition switch is in the Run position, it
de-energizes both relays. Battery voltage is not sup-
plied to the fuel injector, ignition coil, fuel pump and
oxygen sensor heating element. The ASD relay and fuel pump relay are mounted
on the drivers side fender well, next to the strut
tower (Fig. 11).
DUTY CYCLE EVAP PURGE SOLENOIDÐPCM
OUTPUT
The duty cycle EVAP purge solenoid regulates the
rate of vapor flow from the EVAP canister to the
throttle body. The powertrain control module oper-
ates the solenoid. During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the so-
lenoid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged.
The PCM de-energizes the solenoid during open loop
operation. The engine enters closed loop operation after it
reaches a specified temperature and the time delay
ends. During closed loop operation, the PCM ener-
gizes and de-energizes the solenoid approximately 5
to 10 times per second, depending upon operating
conditions. The PCM varies the vapor flow rate by
changing solenoid pulse width. Pulse width is the
amount of time the solenoid energizes. A rubber boot covers the EVAP purge solenoid.
The solenoid and bracket attach to the EVAP canis-
Fig. 12 EVAP Purge Solenoid
Fig. 11 Relay Identification
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 61
Page 1802 of 2438

ter mounting studs (Fig. 12). The top of the solenoid
has the word TOP on it. The solenoid will not oper-
ate unless it is installed correctly.
DATA LINK CONNECTORÐPCM OUTPUT
The data link connector provides the technician
with the means to connect the DRBII scan tool to di-
agnosis the vehicle.
FUEL INJECTORÐPCM OUTPUT
The Fuel Injectors are electric solenoids driven by
the PCM (Fig. 13). Based on sensor inputs, the PCM
determines when and how long the fuel injector
should operate. The amount of time an injector fires
is referred to as injector pulse width. The auto shut-
down (ASD) relay supplies battery voltage to the in-
jector. The PCM supplies the ground path. By
switching the ground path on and off, the PCM ad-
justs injector pulse width.
When the PCM supplies a ground path, a spring
loaded needle or armature lifts from its seat and fuel
flows through the injector orifice. Fuel is constantly supplied to the injector at regu-
lated 380 Kpa (55 psi). Unused fuel returns to the
fuel tank.
GENERATOR FIELDÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM regulates the charging system voltage
within a range of 12.9 to 15.0 volts. Refer to Group
8A for charging system information.
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTORÐPCM OUTPUT
The idle speed stepper motor is mounted on the
throttle body and is controlled by the PCM (Fig. 9).
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed through the idle
air control motor to compensate for engine load or
ambient conditions. The throttle body has an air bypass passage that
provides air for the engine at idle (the throttle blade is closed). The idle air control motor pintle protrudes
into the air bypass passage and regulates air flow
through it. The PCM adjusts engine idle speed by moving the
idle air control motor pintle in and out of the bypass
passage. The adjustments are based on inputs the
PCM receives from the throttle position sensor, speed
sensor (distributor pick-up coil), coolant temperature
sensor, and various switch operations (brake, park/
neutral, air conditioning). Deceleration die out is also
prevented by increasing airflow when the throttle is
closed quickly.
IGNITION COILÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM provides a ground contact (circuit) for en-
ergizing the ignition coil. When the PCM breaks the
contact, the energy in the coil primary transfers to
the secondary causing the spark. The PCM will de-
energize the ASD relay if it does not receive an input
from the distributor pick-up. Refer to Auto Shutdown
(ASD) Relay/Fuel Pump RelayÐPCM Output in this
section for relay operation. The ignition coil is mounted on the hot box next to
the thermostat housing (Fig. 14).
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR (CHECK ENGINE)
LAMPÐPCM OUTPUT
The malfunction indicator lamp (instrument panel
Check Engine lamp) comes on each time the ignition
key is turned ON and stays on for 3 seconds as a
bulb test. The malfunction indicator lamp warns the
operator that the PCM has entered a Limp-in mode.
During Limp-in-Mode, the PCM attempts to keep the
system operational. The malfunction indicator lamp
signals the need for immediate service. In limp-in
Fig. 13 Fuel Injector
Fig. 14 Ignition Coil
14 - 62 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1811 of 2438

the PCM to store diagnostic trouble codes for other
systems. For example, a fuel pressure problem will not
register a fault directly, but could cause a rich or lean
condition. This could cause the PCM to store an oxygen
sensor diagnostic trouble code. Fuel Pressure - The vacuum assisted fuel pressure
regulator controls fuel system pressure. The PCM
cannot detect a clogged fuel pump inlet filter, clogged
in-line fuel filter, stuck open regulator, or a pinched
fuel supply or return line. However, these could result
in a rich or lean condition causing the PCM to store an
oxygen sensor diagnostic trouble code. Secondary Ignition Circuit - The PCM cannot
detect an inoperative ignition coil, fouled or worn spark
plugs, ignition cross firing, or open spark plug cables. Engine Timing - The PCM cannot detect an incor-
rectly indexed timing belt, camshaft sprocket and
crankshaft sprocket. However, these could result in a
rich or lean condition causing the PCM to store an
oxygen sensor diagnostic trouble code. Cylinder Compression - The PCM cannot detect
uneven, low, or high engine cylinder compression. Exhaust System - The PCM cannot detect a
plugged, restricted or leaking exhaust system. Fuel Injector Mechanical Malfunctions - The
PCM cannot determine if a fuel injector is clogged, the
needle is sticking or if the wrong injector is installed.
However, these could result in a rich or lean condition
causing the PCM to store an oxygen sensor diagnostic
trouble code. Excessive Oil Consumption - Although the PCM
monitors exhaust stream oxygen content when the
system is in closed loop, it cannot determine excessive
oil consumption. Throttle Body Air Flow - The PCM cannot detect a
clogged or restricted air cleaner inlet or filter element. Evaporative System - The PCM cannot detect a
disconnected (open vacuum line) restricted, plugged or
loaded evaporative purge canister. Vacuum Assist - The PCM cannot detect leaks or
restrictions in the vacuum circuits of vacuum assisted
engine control system devices. However, these could
cause the PCM to store a MAP sensor diagnostic
trouble code and cause a high idle condition. PCM System Ground - The PCM cannot determine
a poor system ground. However, one or more diagnostic
trouble codes may be generated as a result of this
condition. PCM Connector Engagement - The PCM may not
be able to determine spread or damaged connector
pins. However, it might store diagnostic trouble codes
as a result of spread connector pins.HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The PCM compares input signal voltages from each
input device with established high and low limits for the
device. If the input voltage is not within limits and other
criteria are met, the PCM stores a diagnostic trouble code
in memory. Other diagnostic trouble code criteria might
include engine RPM limits or input voltages from other
sensors or switches that must be present before verifying
a diagnostic trouble code condition.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A diagnostic trouble code indicates the powertrain
control module (PCM) has recognized an abnormal
condition in the system. Abnormal conditions are usu-
ally shorted or open circuits.
The technician can display diagnostic trouble codes in
two ways. The first way is to cycle the ignition switch and
count the number of times the malfunction indicator lamp
(check engine lamp on the instrument panel) flashes on
and off. The DRBII scan tool provides the second method
of displaying diagnostic trouble codes. Diagnostic trouble
codes indicate the results of a circuit failure, but do not
directly identify the failed component.
For a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes, refer to
the charts at the end of this section.
OBTAINING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
USING DRBII SCAN TOOL
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR BLOCK
WHEELS BEFORE PERFORMING ANY TEST ON AN
OPERATING ENGINE. (1) Connect DRBII scan tool to the data link (diag-
nostic) connector located in the engine compartment,
next to the PCM (Fig. 1). (2) If possible, start the engine and cycle the A/C
switch if applicable. Shut off the engine. (3)
Turn the ignition switch on, access Read Fault
Screen. Record all the diagnostic trouble codes shown on
the DRBII scan tool. [Observe the malfunction indicator
lamp (check engine lamp) on the instrument panel. The
lamp should light for 2 seconds then go out (bulb check)].
To erase diagnostic trouble codes, use the Erase
Trouble Code data screen on the DRBII scan tool.
USING THE MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (1) Cycle the ignition key On - Off - On - Off - On
within 5 seconds. (2) Count the number of times the malfunction indi-
cator lamp (check engine lamp on the instrument
panel) flashes on and off. The number of flashes
represents the trouble code. There is a slight pause be-
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 71
Page 1825 of 2438

² Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
² Oxygen Sensor
² SCI Receive
² Speed Control System Controls
² Throttle Position Sensor
² Vehicle Speed Sensor
PCM Outputs:
² Air Conditioning Clutch Relay
² Generator Field
² Idle Air Control Motor
² Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay
² Barometric Read Solenoid
² Canister Purge Solenoid
² Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine Lamp)
² Data Link Connector
² Fuel Injectors
² Ignition Coil
² Radiator Fan Relay
² Speed Control Solenoids
² Tachometer Output
² Wastegate Solenoid
Based on inputs it receives, the PCM adjusts fuel
injector pulse width, idle speed, ignition spark ad-
vance, ignition coil dwell and canister purge opera-
tion. The PCM regulates operation of the cooling fan,
A/C and speed control systems. The PCM changes
generator charge rate by adjusting the generator
field. The PCM adjusts injector pulse width (air-fuel ra-
tio) based on the following inputs.
² battery voltage
² engine coolant temperature
² exhaust gas content
² engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
² manifold absolute pressure
² throttle position
The PCM adjusts ignition timing based on the fol-
lowing inputs.
² engine coolant temperature
² knock sensor
² engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
² manifold absolute pressure
² throttle position
The Automatic Shut Down (ASD) and Fuel Pump
relays are mounted externally, but turned on and off
by the PCM through the same circuit. The camshaft position sensor and crankshaft posi-
tion sensor signals are sent to the PCM. If the PCM
does not receive both signals within approximately
one second of engine cranking, it deactivates the
ASD relay and fuel pump relay. When these relays
are deactivated, power is shut off to the fuel injector,
ignition coil, oxygen sensor heating element and fuel
pump. The PCM contains a voltage converter that
changes battery voltage to a regulated 8.0 volts. The
8.0 volts power the camshaft position sensor, crank- shaft position sensor and vehicle speed sensor. The
PCM also provides a 5.0 volts supply for the coolant
temperature sensor, manifold absolute pressure sen-
sor and throttle position sensor.
AIR CONDITIONING SWITCH SENSEÐPCM INPUT
When the air conditioning or defrost switch is put
in the ON position and the low pressure and high
pressure switches are closed, the PCM receives an in-
put for air conditioning. After receiving this input,
the PCM activates the A/C compressor clutch by
grounding the A/C clutch relay. The PCM also ad-
justs idle speed to a scheduled RPM to compensate
for increased engine load.
BATTERY VOLTAGEÐPCM INPUT
The PCM monitors the battery voltage input to de-
termine fuel injector pulse width and generator field
control. If battery voltage is low the PCM will in-
crease injector pulse width (period of time that the
injector is energized).
BRAKE SWITCHÐPCM INPUT
When the brake switch is activated, the PCM re-
ceives an input indicating that the brakes are being
applied. After receiving this input, the PCM vents
the speed control servo. Venting the servo turns the
speed control system off. The brake switch is
mounted on the brake pedal support bracket.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM INPUT
Fuel injection synchronization and cylinder identi-
fication are provided through the camshaft position
sensor (Fig. 3). The sensor generates pulses. The
pulse are the input sent to the PCM. The PCM inter-
prets the camshaft position sensor input along with
the crankshaft position sensor input to determine
crankshaft position. The PCM uses crankshaft posi-
tion sensor input to determine injector sequence and
ignition timing.
Fig. 3 Camshaft Sensor
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 85
Page 1829 of 2438
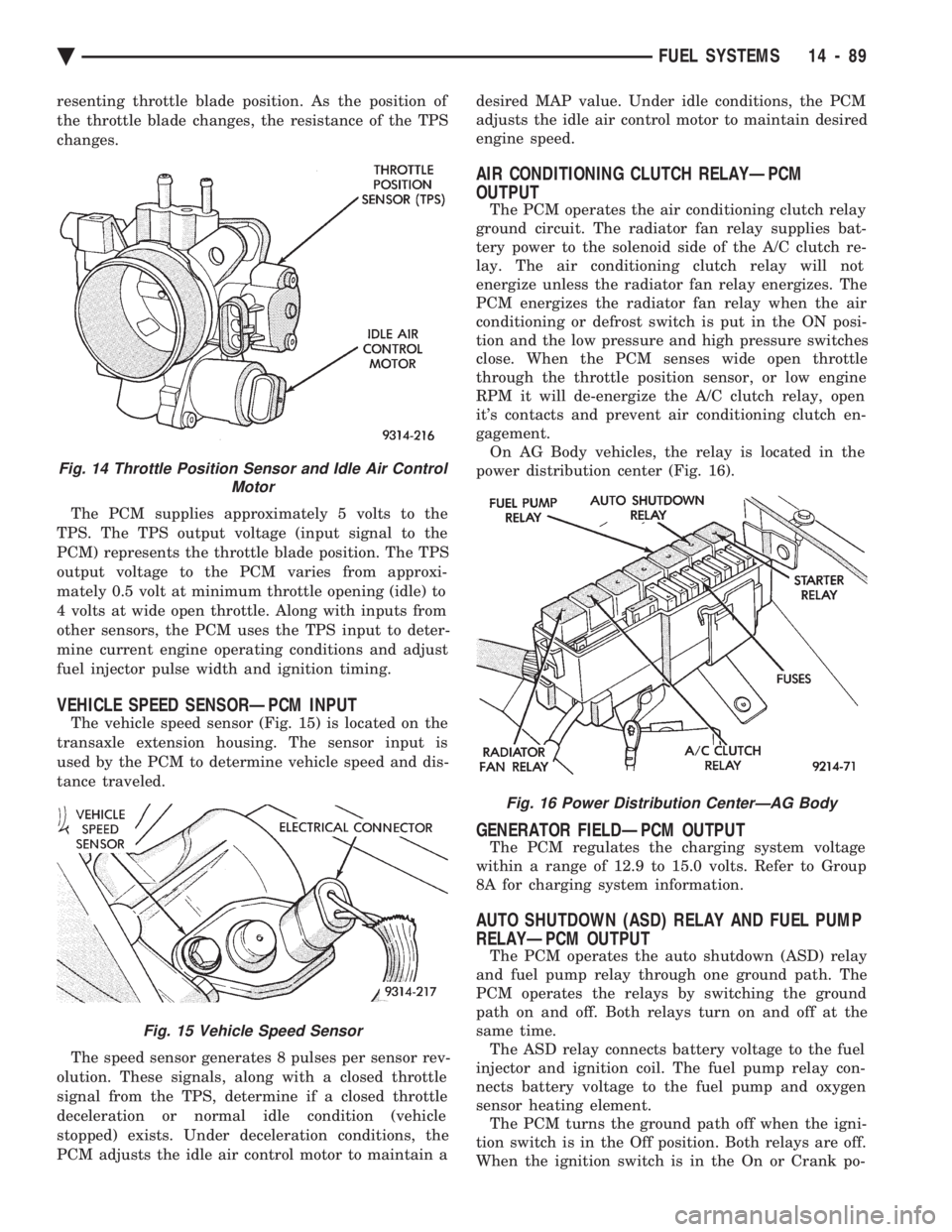
resenting throttle blade position. As the position of
the throttle blade changes, the resistance of the TPS
changes. The PCM supplies approximately 5 volts to the
TPS. The TPS output voltage (input signal to the
PCM) represents the throttle blade position. The TPS
output voltage to the PCM varies from approxi-
mately 0.5 volt at minimum throttle opening (idle) to
4 volts at wide open throttle. Along with inputs from
other sensors, the PCM uses the TPS input to deter-
mine current engine operating conditions and adjust
fuel injector pulse width and ignition timing.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The vehicle speed sensor (Fig. 15) is located on the
transaxle extension housing. The sensor input is
used by the PCM to determine vehicle speed and dis-
tance traveled.
The speed sensor generates 8 pulses per sensor rev-
olution. These signals, along with a closed throttle
signal from the TPS, determine if a closed throttle
deceleration or normal idle condition (vehicle
stopped) exists. Under deceleration conditions, the
PCM adjusts the idle air control motor to maintain a desired MAP value. Under idle conditions, the PCM
adjusts the idle air control motor to maintain desired
engine speed.
AIR CONDITIONING CLUTCH RELAYÐPCM
OUTPUT
The PCM operates the air conditioning clutch relay
ground circuit. The radiator fan relay supplies bat-
tery power to the solenoid side of the A/C clutch re-
lay. The air conditioning clutch relay will not
energize unless the radiator fan relay energizes. The
PCM energizes the radiator fan relay when the air
conditioning or defrost switch is put in the ON posi-
tion and the low pressure and high pressure switches
close. When the PCM senses wide open throttle
through the throttle position sensor, or low engine
RPM it will de-energize the A/C clutch relay, open
it's contacts and prevent air conditioning clutch en-
gagement. On AG Body vehicles, the relay is located in the
power distribution center (Fig. 16).
GENERATOR FIELDÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM regulates the charging system voltage
within a range of 12.9 to 15.0 volts. Refer to Group
8A for charging system information.
AUTO SHUTDOWN (ASD) RELAY AND FUEL PUMP
RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM operates the auto shutdown (ASD) relay
and fuel pump relay through one ground path. The
PCM operates the relays by switching the ground
path on and off. Both relays turn on and off at the
same time. The ASD relay connects battery voltage to the fuel
injector and ignition coil. The fuel pump relay con-
nects battery voltage to the fuel pump and oxygen
sensor heating element. The PCM turns the ground path off when the igni-
tion switch is in the Off position. Both relays are off.
When the ignition switch is in the On or Crank po-
Fig. 14 Throttle Position Sensor and Idle Air Control Motor
Fig. 15 Vehicle Speed Sensor
Fig. 16 Power Distribution CenterÐAG Body
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 89
Page 1830 of 2438

sition, the PCM monitors the crankshaft position and
camshaft position sensor signals to determine engine
speed and ignition timing (coil dwell). If the PCM
does not receive the crankshaft position sensor and
camshaft position sensor signals when the ignition
switch is in the Run position, it de-energizes both re-
lays. When the relays are de-energized, battery volt-
age is not supplied to the fuel injector, ignition coil,
fuel pump and oxygen sensor heating element. The ASD relay and fuel pump relay are located in
the power distribution center (Fig. 16).
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTORÐPCM OUTPUT
The idle air control motor is mounted on the throt-
tle body (Fig. 14). The PCM operates the motor. The
PCM adjusts engine idle speed through the idle air
control motor to compensate for engine load or ambi-
ent conditions. The throttle body has an air bypass passage that
provides air for the engine at idle (the throttle blade
is closed). The idle air control motor pintle protrudes
into the air bypass passage and regulates air flow
through it. The PCM adjusts engine idle speed by moving the
idle air control motor pintle in and out of the bypass
passage. The adjustments are based on inputs the
PCM receives. The inputs are from the throttle posi-
tion sensor, camshaft position sensor, crankshaft po-
sition sensor, coolant temperature sensor, and
various switch operations (brake and air condition-
ing). Deceleration die out is also prevented by in-
creasing airflow when the throttle is closed quickly
after a driving (speed) condition.
BAROMETRIC READ SOLENOIDÐPCM OUTPUT
The barometric pressure read solenoid is spliced
into the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
vacuum hose (Fig. 12). The barometric read solenoid
switches the pressure supply to the MAP sensor from
either barometric pressure (atmospheric) or manifold
vacuum. The PCM operates the solenoid. Atmospheric pressure is periodically supplied to
the MAP sensor to measure barometric pressure.
This occurs at closed throttle, once per throttle clo-
sure but no more often than once every 3 minutes
and within a specified RPM band. Barometric infor-
mation is used primarily for boost control and start
fuel enrichment at various altitudes.
CANISTER PURGE SOLENOIDÐPCM OUTPUT
Vacuum for the Evaporative Canister is controlled
by the Canister Purge Solenoid (Fig. 17). The sole-
noid is controlled by the PCM. The PCM operates the solenoid by switching the
ground circuit on and off. When grounded, the sole-
noid energizes and prevents vacuum from reaching
the evaporative canister. When not energized the so-
lenoid allows vacuum to flow to the canister. During warm-up and for a specified time period after
hot starts the PCM grounds the purge solenoid.
Vacuum does not operate the evaporative canister
valve. The PCM removes the ground to the solenoid when
the engine reaches a specified temperature and the
time delay interval has occurred. When the solenoid is
de-energized, vacuum flows to the canister purge
valve. Vapors are purged from the canister and flow to
the throttle body. The purge solenoid will also be energized during
certain idle conditions, in order to update the fuel
delivery calibration.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (CHECK
ENGINE)ÐPCM OUTPUT
The malfunction indicator lamp (instrument panel
Check Engine lamp) comes on each time the ignition
key is turned ON and stays on for 3 seconds as a bulb
test. The malfunction indicator lamp warns the opera-
tor that the PCM has entered a Limp-in mode. During
Limp-in-Mode, the PCM attempts to keep the system
operational. The malfunction indicator lamp signals
the need for immediate service. In limp-in mode, the
PCM compensates for the failure of certain components
that send incorrect signals. The PCM substitutes for
the incorrect signals with inputs from other sensors. Signals that can trigger the malfunction indi-
cator lamp (Check Engine Lamp).
² Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
² Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
² Throttle Position Sensor
² Battery Voltage Input
² An Emissions Related System
² Charging system
The malfunction indicator lamp can also be used to
display diagnostic trouble codes. Cycle the ignition
switch on, off, on, off, on, within five seconds and any
Fig. 17 EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid and Waste- gate Control Solenoid
14 - 90 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1832 of 2438

noid is energized. The solenoid mounts to the passen-
ger side inner fender panel, next to the strut tower
(Fig. 17).
MODES OF OPERATION
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to the output devices. For example,
the PCM must calculate a different injector pulse
width and ignition timing for idle than it does for wide
open throttle (WOT). There are several different modes
of operation that determine how the PCM responds to
the various input signals. There are two different areas of operation, OPEN
LOOP and CLOSED LOOP. During OPEN LOOP modes, the PCM receives input
signals and responds according to preset PCM pro-
gramming. Input from the oxygen (O
2) sensor is not
monitored during OPEN LOOP modes. During CLOSED LOOP modes, the PCM does moni-
tor the oxygen (O
2) sensor input. This input indicates
to the PCM whether or not the calculated injector pulse
width results in the ideal air-fuel ratio of 14.7 parts air
to 1 part fuel. By monitoring the exhaust oxygen
content through the O
2sensor, the PCM can fine tune
the injector pulse width to achieve optimum fuel
economy combined with low emissions. The 2.2L Turbo III multi-port fuel injection system
has the following modes of operation:
² Ignition switch ON - Zero RPM
² Engine start-up
² Engine warm-up
² Cruise (Idle)
² Acceleration
² Deceleration
² Wide Open Throttle
² Ignition switch OFF
The engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up, and
wide open throttle modes are OPEN LOOP modes. The
acceleration, deceleration, and cruise modes, with the
engine at operating temperature are CLOSED
LOOP modes (under most operating conditions).
IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE
When the ignition switch activates the fuel injection
system the following actions occur:
²
The PCM calculates basic fuel strategy by determining
atmospheric air pressure from the MAP sensor input.
² The PCM monitors the coolant temperature sensor
and throttle position sensor input. The PCM modifies
fuel strategy based on this input. When the key is in the ON position and the engine is
not running, the auto shutdown (ASD) relay and fuel
pump relay are not energized. Therefore battery volt-
age is not supplied to the fuel pump, ignition coil, fuel
injector or oxygen sensor heating element.
ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. The following actions
occur when the starter motor is engaged. If the PCM receives the camshaft position and crank-
shaft position sensor signals, it energizes the auto
shutdown (ASD) relay and fuel pump relay. These
relays supply battery voltage to the fuel pump, fuel
injectors, ignition coil, and oxygen sensor heating ele-
ment. If the PCM does not receive the camshaft posi-
tion sensor and crankshaft position sensor signals
within approximately one second, it de-energizes the
ASD relay and fuel pump relay. The PCM energizes all injectors until it determines
crankshaft position from the camshaft position sensor
and crankshaft position sensor signals. The PCM de-
termines crankshaft position within 1 engine revolu-
tion. After determining crankshaft position, the PCM be-
gins energizing the injectors in sequence. The PCM
adjusts injector pulse width and controls injector syn-
chronization by turning the individual ground paths to
the injectors On and Off. When the engine idles within 664 RPM of its target
RPM, the PCM compares current MAP sensor value
with the atmospheric pressure value received during
the Ignition Switch On (zero RPM) mode. If the PCM
does not detect a minimum difference between the two
values, it sets a MAP fault into memory. Once the ASD and fuel pump relays have been
energized, the PCM:
² Determines injector pulse width based on coolant
temperature, manifold absolute pressure (MAP) and
the number of engine revolutions since cranking was
initiated.
² Monitors the coolant temperature sensor, camshaft
position sensor, crankshaft position sensor, MAP sen-
sor, and throttle position sensor to determine correct
ignition timing.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE
This is a OPEN LOOP mode. The following inputs
are received by the PCM:
² engine coolant temperature
² knock sensor
² manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
² engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
² throttle position
² A/C switch
² battery voltage
The PCM provides a ground path for the injectors to
precisely control injector pulse width (by switching the
ground on and off). The PCM adjusts engine idle speed
through the idle air control motor. Also, the PCM
regulates ignition timing.
14 - 92 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1844 of 2438

SYSTEM TESTS
Apply parking brake and/or block wheels be-
fore performing idle check or adjustment, or any
engine running tests.
OBTAINING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
(1) Connect DRBII scan tool to the data link connec-
tor (Fig. 1). (2) Start the engine if possible, cycle the trans mis-
sion selector and the A/Cswitch if applicable. Shut off
the engine. (3) Turn the ignition switch on, access Read Fault
Screen. Record all the fault messages shown on the
DRBII scan tool. Observe the malfunction indicator
lamp (check engine lamp on the instrument panel). The
lamp should light for 2 seconds then go out (bulb
check). Diagnostic trouble code erasure: access erase
diagnostic trouble code data.
STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs used by the powertrain control
module (PCM) have only two recognized states, HIGH
and LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize
the difference between a selected switch position ver-
sus an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective
switch. If the display changes, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM is functional. From the state
display screen access either State Display Inputs and
Outputs or State Display Sensors.
STATE DISPLAY INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and access
the State Display screen. Then access Inputs and
Outputs. The following is a list of the engine control
system functions accessible through the Inputs and
Outputs screen. Speed Control Resume
Brake Switch
Speed Control On/Off
Speed Control Set
A/C Switch Sense
S/C Vent Solenoid S/C Vacuum Solenoid
A/C Clutch Relay
Baro Read Solenoid
Wastegate Solenoid
Auto Shutdown Relay
Radiator Fan Relay
Purge Solenoid
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine Lamp)
STATE DISPLAY SENSORS
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the State Display screen. Then access Sensor
Display. The following is a list of the engine control
system functions accessible through the Sensor Dis-
play screen. Oxygen Sensor Signal
Coolant Temperature
Coolant Temp Sensor
Throttle Position
Minimum Throttle
Knock Sensor Signal
Battery Voltage
MAP Sensor Reading
Idle Air Control Motor Position
Adaptive Fuel Factor
Barometric Pressure
Min Airflow Idle Spd (speed)
Engine Speed
DIS Sensor Status
Fault #1 Key-On Info
Module Spark Advance
Cyl 1 Knock Retard
Cyl 2 Knock Retard
Cyl 3 Knock Retard
Cyl 4 Knock Retard
Boost Pressure Goal
Charge Temperature
Charge Temp Sensor
Speed Control Target
Fault #2 Key-on Info
Fault #3 Key-on Info
Speed Control Status
Charging System Goal
Theft Alarm Status
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DESCRIPTION (CON'T)
14 - 104 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä