1990 MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 138 of 391

Page 145 of 391
FUEL SYSTEM- Fuel Injection Control14-33
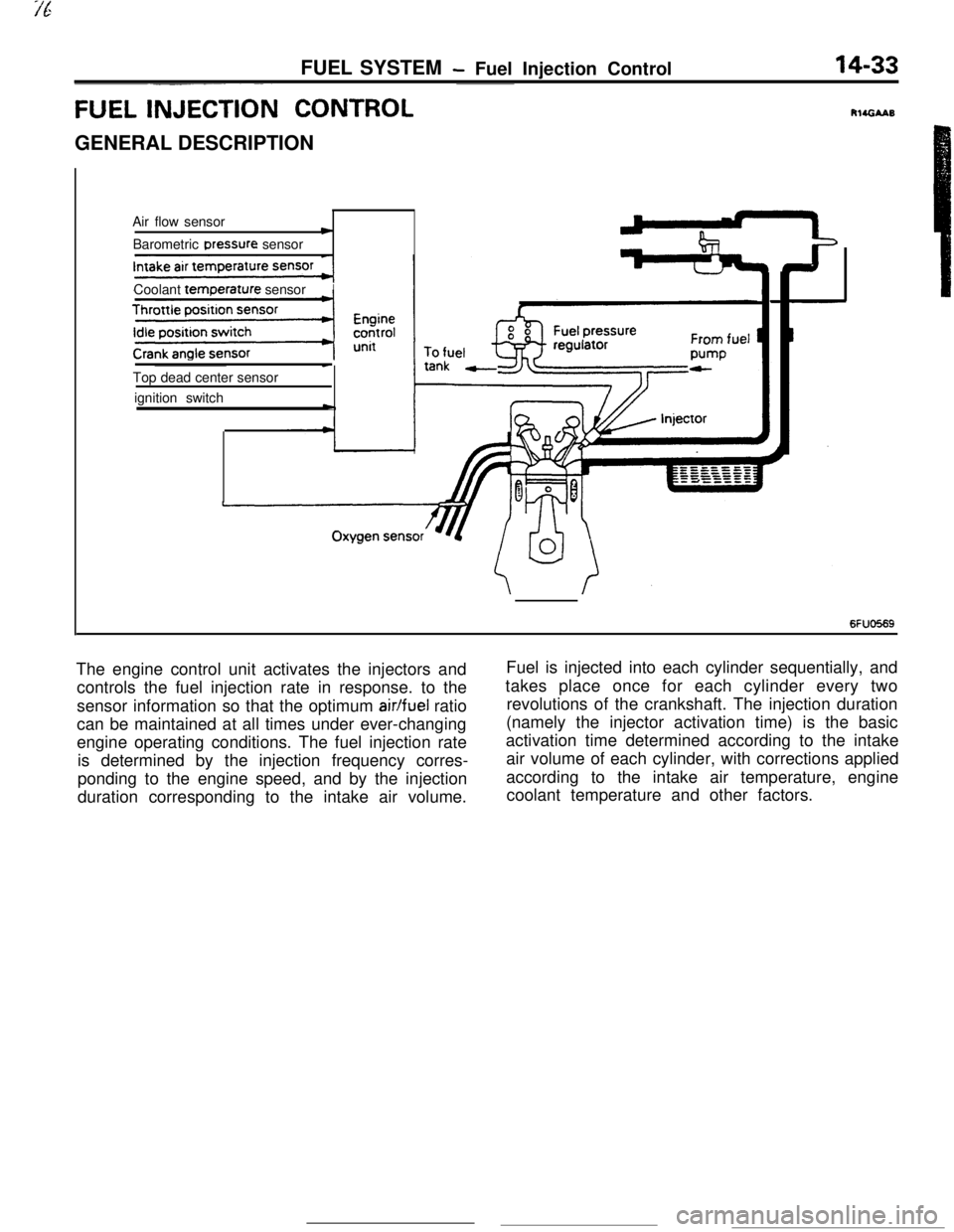
FUEL INJECTI& CONTROLGENERAL DESCRIPTION
Air flow sensor
cBarometric Dressure sensor
Coolant
temr3erature sensorITop dead center sensor
ignition switch
-
c
6FUO569The engine control unit activates the injectors andFuel is injected into each cylinder sequentially, and
controls the fuel injection rate in response. to thetakes place once for each cylinder every two
sensor information so that the optimum
air/fuel ratiorevolutions of the crankshaft. The injection duration
can be maintained at all times under ever-changing(namely the injector activation time) is the basic
engine operating conditions. The fuel injection rateactivation time determined according to the intake
is determined by the injection frequency corres-air volume of each cylinder, with corrections applied
ponding to the engine speed, and by the injectionaccording to the intake air temperature, engine
duration corresponding to the intake air volume.coolant temperature and other factors.
Page 148 of 391

14-36FUEL SYSTEM- Fuel lniection Control
SFUOSlS
RESISTOR
co,.of the injector.
Because the injector must respond instantly to fuel-injection
signals, the number of windings of the coil is reduced in order
to facilitate current rise when the current is flowing in the coil.
By doing so, the resistance of the injector coil becomes smaller
and a greater amount of current can flow, with the result that
the calorific value of the injector coil becomes greater, and
1overheating occurs.
For this reason, for turbocharger-equipped models (which have
low resistance of the injector coil), a resistor is provided
between the power supply (+) and the injector in order to
regulate the amount of current flowing in the coil.
FUEL INJECTION TIMING (INJECTOR AC-
TIVATION TIMING)
The fuel injection timing in multipoint fuel injection
has two modes, sequential and simultaneous. In
sequential injection, fuel is injected into each
cyl-inder sequentially throughout the entire normaloperating range including idling; in simultaneous
injection, fuel is injected simultaneously into all
cylinders during starting and acceleration.
Sequential Injection
r
No. 1cylinder
TDC sensor signal
Crank angle
sensor signal
No. 1 cylinder
No. 3 cylinder
No. 4 cylinder
No. 2 cylinder
In sequential injection, the’ injectors are activated foreach cylinder on the combustion stroke of the
piston. The No. 1 cylinder TDC signal is the
refer-
ence signal for sequential injection. The signal
represents the compression stroke in the No.
1cylinder and, with that timing as a reference, fuel isinjected into the cylinders in the order of
No.2,No.
1, No.3, and No.4. The injection for each
cylinder is synchronized with the crank angle
sen-sor’s 5” BTDC signal. Fuel is injected in each
cylinder once for every two revolutions of the
crankshaft.
-
Page 158 of 391

.
14-46FUEL SYSTEM- Idle Speed Control
The rotor rotates in either direction by angular step increments
corresponding to the number of pulses coming from the en
?control unit, causing the pintle to extend or retract. As
pintle retracts or extends, the gap it forms between the
sea:changes, controlling the bypass air flow. The relationship
between the pintle extension or retraction movement and
bypass air flow rate is as shown at the left.
Number of pulse
7F UW(Control relay
@iI---
unit
Battery power is supplied first to the control relay,
then to the idle speed control servo coil, then to theservo activation signal to turn the power transistor
engine control unit.on and thus forms the coil grounding circuit. As the
The engine control unit uses the idle speed controlcoils are sequentially energized, the magnet rotor of
the idle speed control servo is caused to rotate.
Page 159 of 391

FUEL SYSTEM- Idle Speed Control14-47Operating Principles of Stepper Motor
Stator ICoil Al and
A2 e
Stator II
Fig. A7FUO43Fig. B6FUO519The stepper motor construction is as shown in Fig.
A. Its operating principles are explained below, with
reference to the schematic Fig.
8.STEP “0”
Engine controlunitPower
Coil B 1Coil
B2
I6FU0520
- Stator IStator
II
U
LdStep o 1 23When coils Al and
Bl are energized the upperhalves of stators I and
II are N poles and their lower
halves are
S poles. Thus, their N poles and S polesattract the
S poles and N poles of rotor magnets.
respectively, and the rotor is held stationary.
Page 161 of 391

FUEL SYSTEM -Idle Speed Control14-49
Servo ControlServo control includes feedback control and position
ontrol. In feedback control, the engine control uniti;onstantly calculates the actual idle speed, and if
the
value differs from the target idle speed, the unit
drives the stepper motor to adjust actual speed to
Feedback ControlWhile the engine runs at idle speed, the stepper
motor is activated to keep the engine speed at the
preset target idle speed by controlling the bypass air
volume.
The target idle speed that is optimum for each
operating condition (including air conditioner switch
ON/OFF) has been preset. This engine speed
feedback control is provided under stabilized idling
conditions and not when any of the following
conditions occur.
l When the vehicle is moving at 2.5 km/h (1.6
mph) or more.the target value. In position control, the idle speed
control
is adjusted to the target position to cope
with air conditioner and other load changes. Position
control is also performed when cranking the engine
and decelerating.
lWhen the idle switch is turned from OFF to ON,
and while the idle switch is in the OFF position.
lWhen the air conditioner switch is turned from
ON to OFF, or vice versa.
l When power steering oil pressure switch is
turned from ON to OFF, or vice versa.
l When the ignition switch is turned from ST to
IG, or vice versa.
l While the dash pot control is in operation.
lWhen the inhibitor switch is switched from “N”
range to “D” range or vice versa.
If-1Air conditioner switch
Idle speed
control servo
r------ -- -‘,
(N range)4* I-I
BI
8
IL -L
- !5ysr motor 1I
zIdle upIStepper motor 7Engine
PII2. I.1Coolant temperature
tL.---m--v--JJ
Engine speed
I6Fuo6oo
Servo Drive Steps
(1) If there is a difference between the target and actual idle
speeds, the servo is activated the number of angular steps
corresponding to the difference, thereby extending or
.retracting the pintle to control the amount of bypass air, and
adjusts the actual idle speed to the target value.
Difference between the target
and actual idle speed fpm6FUO699I
Time sec.
c
6FUO76!The sewo drive steps during idle speed feedback Control
van/ as shown at the left.
Page 163 of 391

FUEL SYSTEM -Idle Speed Control14-51
_ 0 (32)80 (175)Coolant temperature “C (“F)6FUO2653
ATarget position during operation
of the power steering systemIDLE CONTROL SERVO POSITION CONTROL WHEN THE
ENGINE IS IDLING
(1) Basic position
The basic position is preset as a map value Optimized
according to the engine coolant temperature. The idle
speed control servo is activated to conform to this position,
thereby maintaining the optimum idle speed.
This basic position of the idle control servo
diiectlycorresponds to the basic idle speed described earlier.
1II
0(32)
80(176)Coolant temperature
“C VW6FUO291Servo position
during operation of
the air conditioner
0(32)
80(176)Coolant temperature “C (“F)6FUO757
1L)760 (30)Barometric pressure mmHg
(in.Hg)BFUlOlC(2) Servo position during shift to “D” range
For models equipped with the automatic
transaxle.when
the position of the shift lever is anywhere other than the
“P” or “N” range, the servo position is increased in
proportion to the load of the torque-converter.
(3) Idle control servo position during operation of the power
steering system
When the power steering oil pressure switch is turned on
because the steering wheel is being turned while
thevehicle is stationary, the servo position is changed to
correspond to the increased power steering pump load.
(4) Servo position while the air conditioner is being operated
When the air conditioner switch is turned on, the servo
position is changed to correspond to the increased air
conditioner load.
(5) High altitude compensation
A correction is performed by increasing the opening of the
idle speed control servo to allow increasing bypass air flow
in order to compensate for the loss of intake air volume
(asmeasured by weight) caused by a reduction in intake air
density due to a drop in barometric pressure at increased
altitude.
(6) “Training” function
A “training” function that enters a value based upon the
engine rpm and the target rpm into the memon/,
andcorrects the servo position according to this value, is
provided in order to obtain an even higher degree of
precision of position control.
Page 164 of 391

--
14-52FUEL SYSTEM - Idle Speed Control
4
Start of deceleration
DLhq ON
position
I*2 to 6
Time sec.6FUO295
II)
0(32180(176)Temperature “C 1°F)6FUO29t
CONTROL WHEN THE ENGINE SPEED IS UNUSUALLY LOWThe followi
gcontrols are provided when the engine speecfalls below
i5;D rpm after the engine has been fully warmed-up
[with engine coolant temperature more than
55°C (131”F)].
(1) During feedback control
The idle speed control servo is activated immediately by a
particular number of angular steps which represent the
feedback correction.
(2) During servo position control
The idle speed control servo is activated to conform to
aposition corresponding to an increased number of steps
(46
steps).DASH POT CONTROL
Control is provided to dampen the extending motion of the
pintle from a certain opening degree, thereby absorbing
deceleration shocks.
(1) Control while cruising
While cruising or racing, the idle speed control servo is
activated to further open the bypass air path corresponding
to the dash pot position which is more open than the idle
position.The idle speed control servo is activated in this way when
the following conditions are met.
l Engine speed 500 rpm or higher
l Idle position switch in the OFF position
The dash pot position is dependent on the throttle valve
opening map value.,
(2) Control during deceleration
When the vehicle is decelerated from a cruising or racing
speed, the idle speed control servo is activated to close the
bypass air path gradually from the dash pot position so that
the intake air volume is not abruptly reduced, thereby
dampening deceleration shocks.
The idle speed control servo is activated when either one of
the following conditions are met.
lWhen the throttle position sensor output voltage drops
l When the idle switch is turned on.
CONTROL WHEN STARTING
While the engine is being cranked, the idle speed control servo
is controlled to provide optimum bypass air volume for starting.
Immediately after the ignition switch is turned on, idle speed
servo position control is provided to achieve the optimum
_
position.