Page 119 of 391
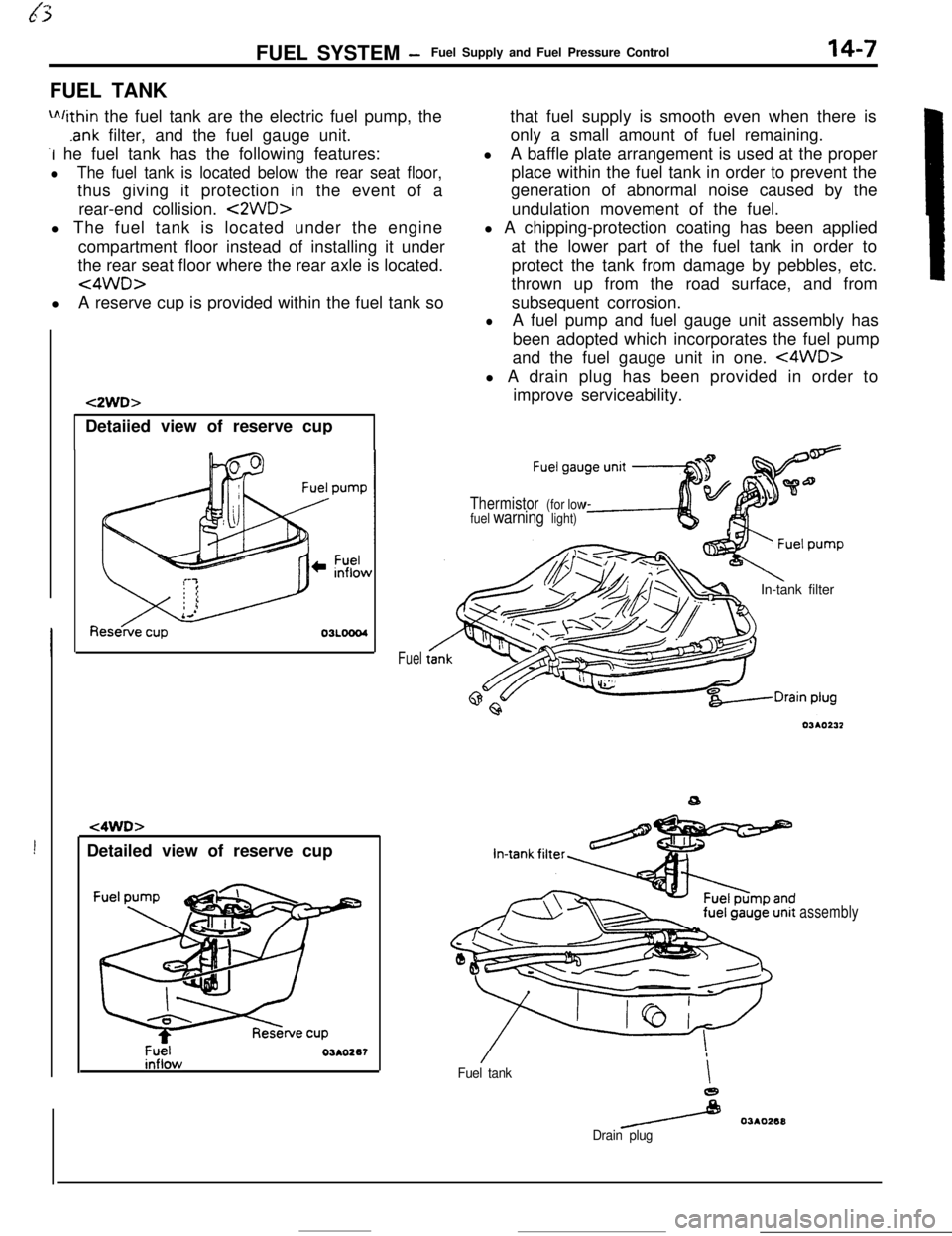
FUEL SYSTEM -Fuel Supply and Fuel Pressure Control14-7FUEL TANK
m/ithin the fuel tank are the electric fuel pump, the
.ank filter, and the fuel gauge unit.
-I he fuel tank has the following features:
lThe fuel tank is located below the rear seat floor,thus giving it protection in the event of a
rear-end collision.
<2WD>l The fuel tank is located under the engine
compartment floor instead of installing it under
the rear seat floor where the rear axle is located.
<4WD>lA reserve cup is provided within the fuel tank so
!Detailed view of reserve cup
t2WD>Detaiied view of reserve cup
t4WD>
Fuel03AO267
Fuelthat fuel supply is smooth even when there is
only a small amount of fuel remaining.
lA baffle plate arrangement is used at the proper
place within the fuel tank in order to prevent the
generation of abnormal noise caused by the
undulation movement of the fuel.
l A chipping-protection coating has been applied
at the lower part of the fuel tank in order to
protect the tank from damage by pebbles, etc.
thrown up from the road surface, and from
subsequent corrosion.
lA fuel pump and fuel gauge unit assembly has
been adopted which incorporates the fuel pump
and the fuel gauge unit in one.
<4WD>l A drain plug has been provided in order to
improve serviceability.
Thermistor (for low
fuel warning light)In-tank filter
Fuel tankI
e
/ 03AO268
Drain plug
assembly
Page 201 of 391
.-_. -
17-8REAR SUSPENSION <4WD> - Geneal information
REAR SUSPENSION <4WD>GENERAL INFORMATION
Rl7BEThe rear suspension is a newly developed double
wishbone independent suspension with a toe-in
correction feature utilizing compliance of thebushing to external force, and provides
excellesteering stability and a good ride.
The special features of this suspension include
l Optimum adjustment of suspensiongeometry
l Optimum adjustment of alignment
change
0 Passive toe-in correction function
l Optimum combination of spring constant,
shock absorber damping force. andbushing characteristics
l Elastic support of the doubleanti-vibration croSsmemberl Improvement of straight-forward
motion stability
0 Improvement of cornering
stability
l Improvement of steerability
l Good balance ofride andsteering stability
( , , :l Low noise and
low vibrationCONSTRUCTION DIAGRAM
absorber
Trailing arm
.
12AC
Page 202 of 391
_ -. ..__ .-
REAR SUSPENSION
<4WD> - Geneal (nformation
THREE SIDE VIEWS
Trailil
12AOll
SPECiFiCATiONSItems
Suspension system
Coil springWire dia. x O.D.
x free lengthmm (in.)Coil spring identification
colourSpring constantN/mm
(kg/mm. Ibs.An.1
Shock absorberType
Max. lengthmm
(in.)Min. length
mm (in.)Stroke
mm (in.)
Damping force (at 0.3
m/set. (0.9 ft./sec.)l
Expansion
N (kg. Ibs.)Contraction
N (kg, Ibs.)Wheel alignment
Toe-in (left/right wheel difference)mm (in.)
CamberSpecifications
Double wishbone tvpe
11.0x106x332.5(.43x4.17x13.1)
Purple x 125.0
(2.50, 140)Hydraulic, cylindrical double-acting
We
568 (22.4)380
(15.0)
188 (7.4)900
(90. 198)300
(30.66)3.6
f 3 (.14 2 .I21
-1”33’ + 30’
Page 203 of 391
REAR SUSPENSION <4WD> - Wheel Alignment
WHEEL ALIGNMENT
This rear suspension has a toe and camber adjustment mechanism.
TOE ADJUSTMENT
Section A-A
Iv’ ‘PI I
12AOllOI12AOO58I-Toe can be adjusted by turning the trailing arm
attaching bolt at the crossmember and trailing arm
connection.
,CAMBER ADJUSTMENT
I
(-1 cam&r @L Y i+) camber 7\\
__cc \
----7--w
’ --
12AcoEl
e /Adjusting cam&\\Adjusting
(eccentric
Section A-ACamber can be adjusted by turning the upper arm
attaching bolt at the crossmember and upper arm
connection..
Page 230 of 391
MANUAL TRANSAXLE <4WD> - General Information
MANUAL TRANSAXLE <4WD>
GENERAL INFORMATION
W5M33 transaxle is a transaxle for 4WD, having
center differential mounted on the output shaft ofwheels. Using the viscous coupling as a device for
the conventional front
wheeledrive type transaxle solimiting differential of the center differential, this
as to distribute drive power to the front and reartransaxle is a full time 4WD type and provides
improved traction and easy drive.
SPECIFICATIONS
Item
Transaxle model
We
Gear ratio
1 St
2nd
3rd4th5th
Reverse
Primary reduction ratio
(number of gear teeth)
Front differential gear ratio
(number of teeth)Specifications
W5M33-2-NPZS
5-speed constant-mesh cable controlled type3.083
1.684
7.1150.833
0.666
3.166
1.275 (37/29).
3.866 (58/l
51
Transfer gear ratio(number of teeth)1.090 (24/22)
Speedometer gear ratio
Oil quantity
liter (qts.)
Transaxle
Transfer
Dry weight ic kg (Ibs.)
29 I36
2.3 (2.43)0.6
(0.63)
64.0(141)
Page 231 of 391
--.-.--_ _ _-MANUAL TRANSAXLE
<4WD> - General Information
SECTIONAL VIEWN5M3321-7Clutch housing
1st speed gear
Input shaft
-Drive bevel gear
\r
l!
.IBearing retainer\
St-1
w
.
I,..\\I \ I I
2nd speed synchronizer assembly
2nd speed gear
3rd speed gear
3rd-4th speed synchronizer assembly
I4th speed gear
I5th speed gear
5th speed
intermediate gear
shaft
Center differential
Front differentialViscdus coupling
wMool4
Page 232 of 391
_.c.
21-8MANUAL TRANSAXLE <4WD> - General Information4WD SYSTEM
Viscous couplingCenter differential
cous coupling
kCenth differential
I
IFro& differential
Rear differential
I
I
I [[lll,i, ‘- h-
1 p’f’ ,* , l/i\
/IViscous couplingL
(Option)
3
2210105CONSTRUCTION
OF THE 4WD SYSTEM
The 4WD system configuration and a section of the
center differential are shown above.The viscous coupling for the center differential is
The center differential is placed on the center shaftlocated on rear side of center differential.This
and engine power is transmitted to the front andarrangement makes the entire transaxle simpler a
rear drive shafts by means of a concentric dual shaftmore compact. Differential limiting by the
centc,construction.differential viscous coupling takes place between
the center differential case and the center shaft
(rear wheel drive shaft).
Page 233 of 391

-MANUAL TRANSAXLE
<4WD> - General information
21-9
wer flow is as shown in the chart below. The
.ire power from the engine is first transmitted
through the input shaft and intermediate gear to the
center differential.
The center differential which distributes power to
the front and rear wheels normally operates at a 50
to 50 ratio. As the differential always transmits more
power to the lighter load side, there may be the
case, for example, when one axle is spinning, the
total drive force of the vehicle reduces.
In order to prevent this, the viscous coupling limits
differential action of the center differential accordingto the rotating speed difference between the center
differential case and the center shaft, thereby
securing drive force.
Half of the drive power distributed by the center
differential is transmitted through the front differen-
tial to the front’ drive shaft.
The other half of the drive power distributed by the
center differential is transmitted through the trans-
fer, the propeller shaft and the rear differential to the
rear drive shaft.
DRIVEN BEVEL
REARDIFF~;MfTIAL
,