1989 FORD FIESTA fuel pump
[x] Cancel search: fuel pumpPage 125 of 296

1 General information andprecautions
General information
The fuel system consists of a fuel tank
(mounted under the body, beneath the rear
seats), fuel hoses, an electric fuel pump
mounted in the fuel tank, and a central fuel
injection (CFi) system. Fuel is supplied from the tank by an integral
electric fuel pump (and combined fuel gauge
sender unit). The fuel is passed through an in-
line filter within the engine compartment, then
to the fuel injection unit. The fuel is maintained
at the required operating pressure by a
pressure regulator unit. The CFi unit itself is a relatively simple
device when compared with a conventional
carburettor. Fuel is injected by a single
solenoid valve (fuel injector) which is mounted
centrally on top of the unit. It is this feature
which gives the system CFi (or Central Fuel
injection) its name (see illustration).The injector is energised by an electrical
signal sent from the EEC IV engine
management module. When energised, the
injector pintle is lifted from its seat, and
atomised fuel is delivered into the inlet
manifold under pressure. The electrical
signals take two forms of current - a high
current to open the injector, and a low current
to hold it open for the duration required. At
idle speed, the injector is pulsed at every
other inlet stroke, rather than with every
stroke as during normal operation.
The air-to-fuel mixture ratio is regulated by
the EEC IV module, based on inputs from the
various engine sensors. No adjustments to
the fuel mixture are possible.
The throttle plate control motor (mounted
on the side of the CFi unit) regulates the idle
speed by reacting to the signals sent by the
EEC IV module. The signals are calculated by
the values and information provided from the
engine sensors. When the throttle position
sensor indicates that the throttle is closed, the
module enters the idle speed mode or
dashpot mode (according to engine speed).
The module maintains the idle speed at a constant value, making minor adjustments as
necessary for different loads and conditions.
The base idle speed can only be adjusted by a
dealer or fuel injection specialist with the
necessary equipment to link up to the engine
management module.
To prevent the engine from running on (or
dieseling) when it is switched off, the EEC IV
module sends a signal to the throttle plate
control motor, to fully close the throttle plate
and return it to its preset position ready for
restarting. When the ignition is switched on
to restart the engine, the motor repositions
the throttle plate to the position required
according to the prevailing conditions. The EEC IV module is the heart of the entire
engine management system, controlling the
fuel injection, ignition and emissions control
systems. The module receives information
from various sensors to determine engine
temperature, speed and load, and the
quantity of air entering the engine. The
sensors also inform the module of throttle
position, inlet air temperature and exhaust gas
oxygen content. All the information supplied
to the module is computed and compared
with pre-set values stored in it’s memory, to
determine the required period of injection. Information on crankshaft position and
engine speed is generated by the distributor
on pre-1990 CVH engine models, or by a
crankshaft position sensor on all other
models. The inductive head of the crankshaft
position sensor runs just above the engine
flywheel and scans a series of 36 protrusions
on the flywheel periphery. As the crankshaft
rotates, the sensor transmits a pulse to the
system’s ignition module every time a
protrusion passes it. There is one missing
protrusion in the flywheel periphery at a point
corresponding to 90º BTDC. The ignition
module recognises the absence of a pulse
from the crankshaft position sensor at this
point to establish a reference mark for
crankshaft position. Similarly, the time interval
between absent pulses is used to determine
engine speed. This information is then fed to
the EEC IV module for further processing. Engine temperature information is supplied
by the coolant temperature sensor. This
component is an NTC (Negative Temperature
Coefficient) thermistor - that is, a semi-
conductor whose electrical resistance
decreases as its temperature increases. It
provides the EEC IV module with a constantly-
varying (analogue) voltage signal,
corresponding to the temperature of the
engine coolant. This is used to refine the
calculations made by the module, when
determining the correct amount of fuel
required to achieve the ideal air/fuel mixture
ratio. Inlet air temperature information is supplied
by the inlet air temperature sensor. This
component is also an NTC thermistor - see
the previous paragraph - providing the EEC IV
module with a signal corresponding to the
temperature of air passing into the engine.
4B•2 Fuel system - central fuel injection engines
1.3 Exploded view of the CFi unit
1 Fuel injector assembly
2 Fuel pressure regulator
assembly 3 Fuel feed connector
4 Intake air temperature
sensor 5 Throttle-plate control
motor
6 Throttle position sensor
7 Fuel injector wiring
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 126 of 296

This is used to refine the calculations made by
the module, when determining the correct
amount of fuel required to achieve the ideal
air/fuel mixture ratio.A throttle position sensor is mounted on the
end of the throttle valve spindle, to provide
the EEC IV module with a constantly-varying
(analogue) voltage signal corresponding to the
throttle opening. This allows the module to
register the driver’s input when determining
the amount of fuel required by the engine. Road speed is monitored by the vehicle
speed sensor. This component is a Hall-effect
generator, mounted on the transmission’s
speedometer drive. It supplies the EEC IV
module with a series of pulses corresponding
to the vehicle’s road speed, enabling the
module to control features such as the fuel
shut-off on overrun. A manifold absolute pressure sensor
measures inlet manifold vacuum, and supplies
this information to the module for calculation
of engine load at any given throttle position. Where power steering is fitted, a pressure-
operated switch is screwed into the power
steering system’s high-pressure pipe. The
switch sends a signal to the EEC IV module to
reduce engine speed should the power
steering fluid pressure become excessively
high. Certain later engines may be fitted with a
heater in the inlet manifold. This is controlled
by the EEC IV module to ensure that, even
before the effect of the coolant heating
becomes apparent, the manifold is warmed-
up. This prevents fuel droplets condensing in
the manifold, thus improving driveability and
reducing exhaust emissions when the engine
is cold.
The oxygen sensor in the exhaust system
provides the EEC IV module with constant
feedback - “closed-loop” control - which
enables it to adjust the mixture to provide the
best possible conditions for the catalytic
converter to operate.
Precautions
Warning: Petrol is extremely
flammable - great care must be
taken when working on any part
of the fuel system. Do not
smoke or allow any naked flames or
uncovered light bulbs near the work area.
Note that gas powered domestic
appliances with pilot flames, such as
heaters, boilers and tumble dryers, also
present a fire hazard - bear this in mind if
you are working in an area where such
appliances are present. Always keep a
suitable fire extinguisher close to the work
area and familiarise yourself with its
operation before starting work. Wear eye
protection when working on fuel systems
and wash off any fuel spilt on bare skin
immediately with soap and water. Note
that fuel vapour is just as dangerous as
liquid fuel; a vessel that has just been
emptied of liquid fuel will still contain vapour and can be potentially explosive.
Petrol is a highly dangerous and volatile
liquid, and the precautions necessary
when handling it cannot be overstressed.
Many of the operations described in this
Chapter involve the disconnection of fuel
lines, which may cause an amount of fuel
spillage. Before commencing work, refer
to the above Warning and the information
in “Safety first” at the beginning of this
manual. When working with fuel system
components, pay particular attention to
cleanliness - dirt entering the fuel system
may cause blockages which will lead to
poor running.
Note: Residual pressure will remain in the fuel
lines long after the vehicle was last used,
when disconnecting any fuel line, it will be
necessary to depressurise the fuel system as
described in Section 2 .
2 Fuel system-
depressurisation
1
Note: Refer to the warning note in Section 1
before proceeding.
Warning: The following
procedure will merely relieve the
pressure in the fuel system -
remember that fuel will still be present in
the system components, and take
precautions accordingly before
disconnecting any of them.
1 The fuel system referred to in this Chapter
is defined as the fuel tank and tank-mounted
fuel pump/fuel gauge sender unit, the fuel
filter, the fuel injector, fuel pressure regulator,
and the metal pipes and flexible hoses of the
fuel lines between these components. All
these contain fuel, which will be under
pressure while the engine is running and/or
while the ignition is switched on.
2 The pressure will remain for some time after
the ignition has been switched off, and must
be relieved before any of these components is
disturbed for servicing work.
3 The simplest depressurisation method is to
disconnect the fuel pump electrical supply by
removing the fuel pump fuse (No 19) and
starting the engine; allow the engine to idle
until it dies through lack of fuel pressure. Turn
the engine over once or twice on the starter to
ensure that all pressure is released, then
switch off the ignition; do not forget to refit the
fuse when work is complete.
4 Note that, once the fuel system has been
depressurised and drained (even partially), it
will take significantly longer to restart the
engine - perhaps several seconds of cranking
- before the system is refilled and pressure
restored.
3 Fuel lines and fittings -
general information
Note: Refer to the warning note in Section 1
before proceeding.
Disconnecting and connecting
quick-release couplings
1 Quick-release couplings are employed at
many of the unions in the fuel feed and return
lines.
2 Before disconnecting any fuel system
component, relieve the residual pressure in
the system (see Section 2), and equalise tank
pressure by removing the fuel filler cap.
Warning: This procedure will
merely relieve the increased
pressure necessary for the
engine to run - remember that
fuel will still be present in the system
components, and take precautions
accordingly before disconnecting any of
them.
3 Release the protruding locking lugs on each
union, by squeezing them together and
carefully pulling the coupling apart. Use rag to
soak up any spilt fuel. Where the unions are
colour-coded, the pipes cannot be confused.
Where both unions are the same colour, note
carefully which pipe is connected to which,
and ensure that they are correctly
reconnected on refitting.
4 To reconnect one of these couplings, press
them together until the locking lugs snap into
their groove. Switch the ignition on and off
five times to pressurise the system, and check
for any sign of fuel leakage around the
disturbed coupling before attempting to start
the engine.
Checking
5 Checking procedures for the fuel lines are
included in Chapter 1.
Component renewal
6 If any damaged sections are to be renewed,
use original-equipment replacement hoses or
pipes, constructed from exactly the same
material as the section being replaced. Do not
install substitutes constructed from inferior or
inappropriate material; this could cause a fuel
leak or a fire.
7 Before detaching or disconnecting any part
of the fuel system, note the routing of all
hoses and pipes, and the orientation of all
clamps and clips. Replacement sections must
be installed in exactly the same manner.
8 Before disconnecting any part of the fuel
system, be sure to relieve the fuel system
pressure (see Section 2), and equalise tank
pressure by removing the fuel filler cap. Also
disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead -
see Chapter 5A, Section 1. Cover the fitting
being disconnected with a rag, to absorb any
fuel that may spray out.
Fuel system - central fuel injection engines 4B•3
4B
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 127 of 296

4 Air cleaner assembly and airinlet components -
removal and refitting
1
Note: Air cleaner element renewal and air
cleaner temperature control system checks
(where applicable) are described in Chapter 1.
Air cleaner assembly
1 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
2 Undo the retaining bolts and partially lift the
air cleaner from the CFi unit, so that the hose
and wiring connections to the underside of
the air cleaner body are accessible.
3 Note their connections and routings, then
detach the wiring and hoses from the
underside of the air cleaner.
4 Lift the air cleaner clear from the CFi unit.
5 Refit in the reverse order of removal.
6 Renew any hoses that are perished or
cracked, and ensure that all fittings are
securely and correctly reconnected.
Air inlet components
7 The air cleaner inlet spout and related
components are removed with the air cleaner
assembly as described above.
5 Accelerator cable - removal,
refitting and adjustment
1
Removal
1 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
2 Fold back the carpet and insulation in the
driver’s footwell to gain access to the
accelerator pedal.
3 Detach the accelerator cable from the
pedal.
4 Remove the air cleaner assembly as
described in Section 4.
5 Working at the throttle housing end of the
cable, pivot the throttle quadrant by hand to
release the tension from the cable, then
detach the inner cable nipple from the throttle
lever.
6 Detach the outer cable from the
adjuster/support bracket, then remove the
cable.
Refitting and adjustment
7 Refit in the reverse order of removal. When
the cable is reconnected at each end, have an
assistant depress the accelerator, and check
that the throttle fully opens and shuts without
binding. Ensure that there is a small amount of
slack in the inner cable when the throttle is
fully released. If adjustment is required,
release the outer cable retaining clip from the
cable at the adjustment/support bracket, slide
the cable through the adjuster grommet to the
point required, then refit the retaining clip to
secure it in the set position.
6 Accelerator pedal -
removal and refitting
1
Refer to Part A, Section 5.
7 Fuel pump/fuel pressure -
checking
3
Note: Refer to the warning note in Section 1
before proceeding.
Fuel pump operation check
1 Switch on the ignition, and listen for the fuel
pump (the sound of an electric motor running,
audible from beneath the rear seats). Assuming
there is sufficient fuel in the tank, the pump
should start and run for approximately one or
two seconds, then stop, each time the ignition
is switched on. Note:If the pump runs
continuously all the time the ignition is switched
on, the electronic control system is running in
the backup (or “limp-home”) mode referred to
by Ford as “Limited Operation Strategy” (LOS).
This almost certainly indicates a fault in the
EEC IV module itself, and the vehicle should
therefore be taken to a Ford dealer for a full test
of the complete system, using the correct
diagnostic equipment; do not waste time or risk
damaging the components by trying to test the
system without such facilities.
2 Listen for fuel return noises from the fuel
pressure regulator. It should be possible to
feel the fuel pulsing in the regulator and in the
feed hose from the fuel filter.
3 If the pump does not run at all, check the
fuse, relay and wiring (see Chapter 12). Check
also that the fuel cut-off switch has not been
activated and if so, reset it.
Fuel pressure check
4 A fuel pressure gauge will be required for this
check and should be connected in the fuel line
between the fuel filter and the CFi unit, in
accordance with the gauge maker’s instructions.
5 Start the engine and allow it to idle. Note
the gauge reading as soon as the pressure
stabilises, and compare it with the figures
given for regulated fuel pressure in the
Specifications . If the pressure is high, check
for a restricted fuel return line. If the pressure
is low, renew the fuel pressure regulator. 6
Switch off the engine, and check that after
one minute, the hold pressure has not fallen
below that specified. If it has, check the seals
on the fuel injector (see Section 14) and renew
them if they appear in any way suspect. If the
seals are okay, then the fuel pressure
regulator or CFi unit are suspect.
7 Carefully disconnect the fuel pressure
gauge, depressurising the system first as
described in Section 2.
8 Run the engine, and check that there are no
fuel leaks.
8 Fuel tank - removal,
inspection and refitting
3
Proceed as described in Part A, Section 8, but
before disconnecting the battery, relieve the
residual pressure in the fuel system (see Sec-
tion 2), and equalise tank pressure by removing
the fuel filler cap. Note also that it will be
necessary to release any additional ventilation
tubes from their retaining clips, and to reposition
or remove the underbody heat shields on certain
models for access to the tank retaining bolts.
9 Fuel pump/fuel gauge
sender unit - removal and
refitting
3
Note: Refer to the warning note in Section 1
before proceeding. Ford specify the use of their
service tool 23-026 (a large box spanner with
projecting teeth to engage the fuel pump/sender
unit retaining ring’s slots) for this task. While
alternatives are possible, in view of the difficulty
experienced in removing and refitting the
pump/sender unit, it is strongly advised that the
correct tool is obtained before starting work.
Removal
1 A combined fuel pump and fuel gauge
sender unit are located in the top face of the
fuel tank. The combined unit can only be
detached and withdrawn from the tank after
the tank is released and lowered from
under the vehicle. Refer to Section 8 and
remove the fuel tank, then proceed as follows.
2 With the fuel tank removed, the
pump/sender unit can be unscrewed using
the special tool (see illustration) .
3 Withdraw the unit upwards from the tank
(see illustration) , and detach the seal ring.
9.3 Fuel pump (A) and sender unit (B)
4B•4 Fuel system - central fuel injection engines
9.2 Ford Special tool engaged on the fuel
pump/sender unit
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 128 of 296
The seal ring must be renewed whenever the
pump/sender unit is withdrawn from the tank.
Refitting
4Refit in the reverse order of removal. Lightly
coat the new unit seal ring with grease to ease
fitting, and ensure that the seal is not
distorted as the unit is fitted into position.
Insert the unit so that the lug of the unit is in
engagement with the slot in the tank aperture,
then turn the unit to lock and secure.
10 Fuel tank ventilation tube -
removal and refitting
3
Refer to Part A, Section 10, but note that on
models with evaporative emission control, the
ventilation tube connects to the combined
roll-over/anti-trickle-fill valve assembly but,
instead of venting to atmosphere, a further
tube runs the length of the vehicle to a carbon
canister in the front right-hand corner of the
engine compartment. Further information on the evaporative
emission control system is contained in Part E
of this Chapter.
11 Fuel tank filler pipe -
removal and refitting
3
Refer to Part A, Section 11.
12 Fuel cut-off switch -
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
2 Remove the left-hand sill scuff plate as
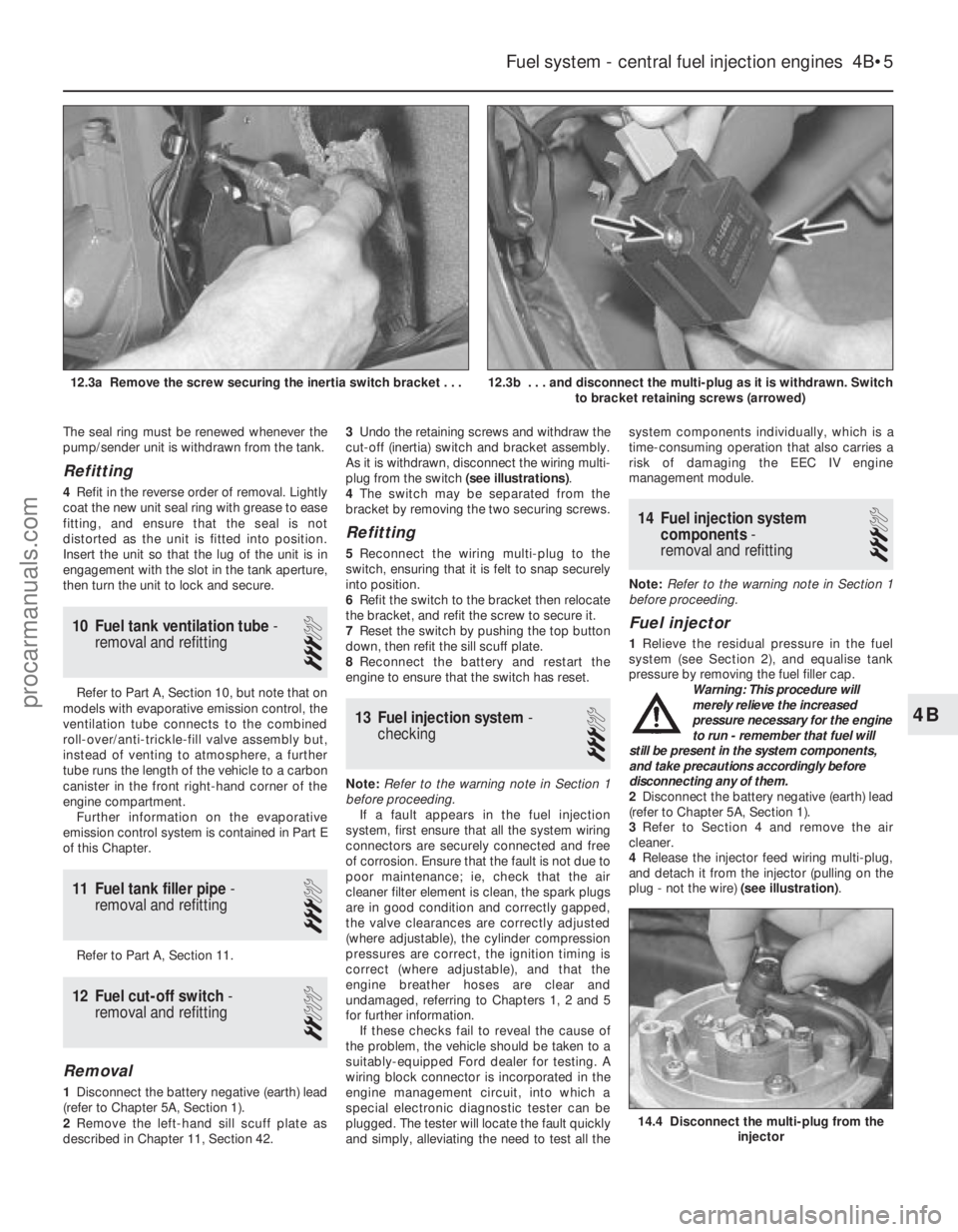
described in Chapter 11, Section 42. 3
Undo the retaining screws and withdraw the
cut-off (inertia) switch and bracket assembly.
As it is withdrawn, disconnect the wiring multi-
plug from the switch (see illustrations).
4 The switch may be separated from the
bracket by removing the two securing screws.
Refitting
5 Reconnect the wiring multi-plug to the
switch, ensuring that it is felt to snap securely
into position.
6 Refit the switch to the bracket then relocate
the bracket, and refit the screw to secure it.
7 Reset the switch by pushing the top button
down, then refit the sill scuff plate.
8 Reconnect the battery and restart the
engine to ensure that the switch has reset.
13 Fuel injection system -
checking
3
Note: Refer to the warning note in Section 1
before proceeding. If a fault appears in the fuel injection
system, first ensure that all the system wiring
connectors are securely connected and free
of corrosion. Ensure that the fault is not due to
poor maintenance; ie, check that the air
cleaner filter element is clean, the spark plugs
are in good condition and correctly gapped,
the valve clearances are correctly adjusted
(where adjustable), the cylinder compression
pressures are correct, the ignition timing is
correct (where adjustable), and that the
engine breather hoses are clear and
undamaged, referring to Chapters 1, 2 and 5
for further information. If these checks fail to reveal the cause of
the problem, the vehicle should be taken to a
suitably-equipped Ford dealer for testing. A
wiring block connector is incorporated in the
engine management circuit, into which a
special electronic diagnostic tester can be
plugged. The tester will locate the fault quickly
and simply, alleviating the need to test all the system components individually, which is a
time-consuming operation that also carries a
risk of damaging the EEC IV engine
management module.
14 Fuel injection system
components -
removal and refitting
3
Note: Refer to the warning note in Section 1
before proceeding.
Fuel injector
1 Relieve the residual pressure in the fuel
system (see Section 2), and equalise tank
pressure by removing the fuel filler cap.
Warning: This procedure will
merely relieve the increased
pressure necessary for the engine
to run - remember that fuel will
still be present in the system components,
and take precautions accordingly before
disconnecting any of them.
2 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
3 Refer to Section 4 and remove the air
cleaner.
4 Release the injector feed wiring multi-plug,
and detach it from the injector (pulling on the
plug - not the wire) (see illustration).
Fuel system - central fuel injection engines 4B•5
12.3b . . . and disconnect the multi-plug as it is withdrawn. Switch
to bracket retaining screws (arrowed)12.3a Remove the screw securing the inertia switch bracket . . .
14.4 Disconnect the multi-plug from the injector
4B
1595Ford Fiesta Remakeprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 134 of 296

4C
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
General
System type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . Electronic Fuel injection (EFi) with turbocharger on RS Turbo models
Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . 1.6 litre CVH engines
Fuel grade
Fuel octane requirement:Engines without catalytic converter* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95 RON unleaded or 97 RON leaded
Engines with catalytic converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95 RON unleaded (leaded fuel must notbe used)
*Refer to dealer for latest recommendations
Fuel system data
Idle speed and mixture settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Fuel pump pressure - engine not running . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.0 bars minimum
Regulated fuel pressure - engine running at idle speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.3 to 2.5 bars
Hold pressure - engine stopped after two minutes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Not less than 0.8 bars below regulated pressure
Turbocharger
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Garrett AiResearch T02
Boost pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . 0.47 to 0.51 bars
Chapter 4 Part C:
Fuel system - electronic fuel injection engines
Accelerator cable - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Accelerator pedal - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Air cleaner assembly and air inlet components - removal and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . . 4
Air cleaner element renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See Chapter 1
Exhaust system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See Chapter 1
Fuel cut-off switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Fuel filter renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . \
. . . . .See Chapter 1
Fuel injection system - checking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Fuel injection system components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . 14
Fuel lines and fittings - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Fuel pump/fuel gauge sender unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . 9
Fuel pump/fuel pressure - checking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Fuel system - depressurisation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Fuel tank - removal, inspection and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 Fuel tank filler pipe - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Fuel tank ventilation tube - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
General fuel system checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See Chapter 1
General information and precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Idle speed and mixture check and adjustment . . . . . . . .See Chapter 1
Idle speed control valve cleaning and maintenance . . . .See Chapter 1
Inlet manifold - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Intercooler - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Turbocharger - general information and precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Turbocharger - removal, examination and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Turbocharger boost control valve - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . 18
Turbocharger boost pressure - checking and adjustment . . . . . . . . 19
Underbody fuel/brake line check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See\
Chapter 1
Underbonnet check for fluid leaks and hose condition . .See Chapter 1
4C•1
Specifications Contents
Easy,
suitable for
novice with little
experience Fairly easy,
suitable
for beginner with
some experience Fairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,
suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanic Very difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 135 of 296

Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Idle speed control valve bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 to 5 3 to 4
Fuel pressure regulator bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 to 12 6 to 9
Fuel rail bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . 20 to 26 15 to 19
Inlet air temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 to 25 15 to 18
Inlet manifold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . . 16 to 20 12 to 15
Oxygen sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .\
. . . . . . . . 50 to 70 37 to 52
Intercooler-to-radiator bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 to 6 3 to 5
Boost control valve screws . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.2 to 2.7 1.5 to 2
Exhaust manifold heatshield bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 to 26 16 to 19
Exhaust manifold-to-engine nuts (non-Turbo models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 to 17 11 to 13
Exhaust manifold-to-engine nuts (Turbo models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 to 31 21 to 23
Exhaust manifold-to-turbocharger bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 to 28 15 to 21
Turbocharger-to-exhaust downpipe nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35 to 47 26 to 35
Turbocharger cooling pipe banjo union bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 to 29 17 to 22
Turbocharger oil feed and return line couplings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 to 20 11 to 15
4C•2 Fuel system - electronic fuel injection engines
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
1 General information and
precautions
General information
The fuel system consists of a fuel tank
(mounted under the body, beneath the rear
seats), fuel hoses, an electric fuel pump
mounted in the fuel tank, and an electronic
fuel injection system. Fuel is supplied under pressure from the
fuel pump to the fuel distributor rail mounted
on top of the inlet manifold (see illustration).
The fuel rail acts as a pressurised fuel
reservoir for the fuel injectors. The electro-
mechanical injectors have only “on” or “off”
positions, the volume of fuel being injected to meet the engine operating conditions being
determined by the length of time that the
injectors are opened. The volume of fuel
required for one power stroke is determined
by the EEC IV engine management module,
and is divided by two equal amounts. The first
half of the required volume is injected into the
static air ahead of the inlet valve one complete
engine revolution before the inlet valve is due
to open. After one further revolution, the inlet
valve opens and the required fuel volume is
injected into the air flow being drawn into the
cylinder. The fuel will therefore be consistently
injected to two inlet valves simultaneously at a
particular crankshaft position.
The volume of air drawn into the engine is
governed by the air filter unit and other
variable operating factors. These variables are
assessed by the EEC IV module and the corresponding signals are produced to
actuate the injectors accordingly.
The engine base idle speed can be
adjusted (if required), by turning the adjuster
screw (covered by a tamperproof cap) in the
throttle housing. Provision for adjusting the
fuel mixture is made by the mixture screw in
the potentiometer unit mounted on the
bulkhead. An idle speed control valve, itself controlled
by the EEC-IV engine management module,
stabilises the engine idle speed under all
conditions by the opening of an auxiliary air
passage which bypasses the throttle. Apart
from a base-idle speed adjustment, no
adjustments to the operational idle speed can
be made. The EEC IV module is the heart of the entire
engine management system, controlling the
fuel injection, ignition and emissions control
systems. The module receives information
from various sensors to determine engine
temperature, speed and load, and the
quantity of air entering the engine. The
sensors also inform the module of throttle
position, inlet air temperature and, on models
with catalytic converters, exhaust gas oxygen
content. All the information supplied to the
module is computed and compared with
pre-set values stored in it’s memory, to
determine the required period of injection.
Information on crankshaft position and
engine speed is generated by a crankshaft
position sensor. The inductive head of the
sensor runs just above the engine flywheel
and scans a series of 36 protrusions on the
flywheel periphery. As the crankshaft
rotates, the sensor transmits a pulse to the
system’s ignition module every time a
protrusion passes it. There is one missing
protrusion in the flywheel periphery at a point
corresponding to 90° BTDC. The ignition
module recognises the absence of a pulse
from the crankshaft position sensor at this
point to establish a reference mark for
crankshaft position. Similarly, the time interval
between absent pulses is used to determine
engine speed. This information is then fed to
the EEC IV module for further processing.
1.2 General view of the 1.6 litre EFi fuel injection system arrangement\
1 Throttle housing
2 Upper inlet manifold section
3 Wiring loom connector
4 Intake air temperature sensor 5 Wiring harness ducting
6 Fuel rail
7 Lower section of inlet
manifold
8 Cylinder head 9 Fuel injector
10
Fuel pressure regulator
11 Vacuum hose
12 Air inlet duct
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 137 of 296

11On non-Turbo models, disconnect the
flexible hose between the air cleaner lid and
the air inlet duct.
12 On Turbo models, disconnect the idle
speed control valve air bypass hose from the
air inlet duct and the flexible hose between
the air inlet duct and intercooler (see
illustration) .
13 Undo the two retaining bolts, and remove
the air inlet duct from the rocker cover.
14 Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure.
5 Accelerator cable - removal,
refitting and adjustment
1
Removal
1 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
2 Remove the air inlet components as
described in Section 4.
3 Fold back the carpet and insulation in the
driver’s footwell to gain access to the
accelerator pedal.
4 Detach the accelerator cable from the
pedal.
5 Working at the throttle housing end of the
cable, pivot the throttle quadrant by hand to
release the tension from the cable, then
detach the inner cable nipple from the throttle
lever (see illustration) .
6 Detach the outer cable from the
adjuster/support bracket, then remove the
cable.
Refitting and adjustment
7 Refit in the reverse order of removal. When
the cable is reconnected at each end, have an assistant depress the accelerator, and check
that the throttle fully opens and shuts without
binding. Ensure that there is a small amount of
slack in the inner cable when the throttle is
fully released. If adjustment is required,
release the outer cable retaining clip from the
cable at the adjustment/support bracket, slide
the cable through the adjuster grommet to the
point required, then refit the retaining clip to
secure it in the set position.
6 Accelerator pedal
-
removal and refitting
1
Refer to Part A, Section 5.
7 Fuel pump/fuel pressure -
checking
3
Note: Refer to the warning note in Section 1
before proceeding.
Fuel pump operation check
1 Switch on the ignition, and listen for the fuel
pump (the sound of an electric motor running,
audible from beneath the rear seats). Assuming
there is sufficient fuel in the tank, the pump
should start and run for approximately one or
two seconds, then stop, each time the ignition
is switched on. Note:If the pump runs
continuously all the time the ignition is switched
on, the electronic control system is running in
the backup (or “limp-home”) mode referred to
by Ford as “Limited Operation Strategy” (LOS).
This almost certainly indicates a fault in the
EEC IV module itself, and the vehicle should
therefore be taken to a Ford dealer for a full test of the complete system, using the correct
diagnostic equipment; do not waste time or risk
damaging the components by trying to test the
system without such facilities.
2
Listen for fuel return noises from the fuel
pressure regulator. It should be possible to
feel the fuel pulsing in the regulator and in the
feed hose from the fuel filter.
3 If the pump does not run at all, check the
fuse, relay and wiring (see Chapter 12). Check
also that the fuel cut-off switch has not been
activated and if so, reset it.
Fuel pressure check
4 A fuel pressure gauge will be required for
this check and should be connected in the
fuel line between the fuel filter and the fuel rail,
in accordance with the gauge maker’s
instructions.
5 Disconnect the wiring from the E-DIS
ignition coil and the fuel injectors.
6 Switch the ignition on and off twice, and
check that the pump pressure is as listed in
the Specifications .
7 If the pressure is not as specified, check the
fuel system for leaks or damage. If the system
appears okay, renew the fuel pump.
8 Reconnect the wiring to the ignition coil and
fuel injectors.
9 If the pump pressure was satisfactory, start
the engine and allow it to idle. Disconnect the
vacuum hose at the fuel pressure regulator,
and plug the hose. Note the gauge reading as
soon as the pressure stabilises, and compare
it with the figures given for regulated fuel
pressure in the Specifications.
10 If the regulated fuel pressure is not as
specified, remove the plug from the top of the
fuel pressure regulator, and using a suitable
Allen key, adjust the pressure regulator as
necessary.
11 Switch off the engine, and check that the
fuel pressure stays at the specified hold
pressure for two minutes after the engine is
turned off.
12 Carefully disconnect the fuel pressure
gauge, depressurising the system first as
described in Section 2. Reconnect the ignition
coil and fuel injector wiring.
13 Run the engine, and check that there are
no fuel leaks.
4C•4 Fuel system - electronic fuel injection engines
5.45 Accelerator cable retention
arrangement at the throttle linkage
4.12 Air intake, turbocharger and intercooler details on Turbo models
1595Ford Fiesta Remake
1 Fresh air intake
2 Air cleaner lid
3 Turbocharger
4 Intercooler
5 Air inlet duct
6 Throttle housing
7 Inlet manifold
8 (Hitachi-built) idle
speed control valveprocarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su
Page 138 of 296

8 Fuel tank- removal,
inspection and refitting
3
Proceed as described in Part A, Section 8,
but before disconnecting the battery, relieve
the residual pressure in the fuel system (see
Section 2), and equalise tank pressure by
removing the fuel filler cap.
9 Fuel pump/fuel gauge sender unit - removal and
refitting
3
Refer to Part B, Section 9.
10 Fuel tank ventilation tube -
removal and refitting
3
Refer to Part A, Section 10, but note that on
models with evaporative emission control, the
ventilation tube connects to the combined
roll-over/anti-trickle-fill valve assembly but,
instead of venting to atmosphere, a further
tube runs the length of the vehicle to a carbon
canister in the front right-hand corner of the
engine compartment.
Further information on the evaporative
emission control system is contained in Part E
of this Chapter.
11 Fuel tank filler pipe -
removal and refitting
3
Refer to Part A, Section 11.
12 Fuel cut-off switch -
removal and refitting
1
Refer to Part B, Section 12.
13 Fuel injection system -
checking
3
Refer to Part B, Section 13
14 Fuel injection system components - removal and
refitting
3
Note: Refer to the warning note in Section 1
before proceeding.
Fuel rail and injectors
Note: For simplicity, and to ensure that the
necessary absolute cleanliness on reassembly,
the following procedure describes the removal
of the fuel rail assembly, complete with the
injectors and pressure regulator, so that
the injectors can be serviced individually on a clean work surface. It is also possible to remove
and refit an individual injector, once the fuel
system has been depressurised and the battery
has been disconnected. If this approach is
followed, read through the complete
procedure, and work as described in the
relevant paragraphs, depending on the amount
of preliminary dismantling required. Be careful
not to allow any dirt to enter the system.
1
Relieve the residual pressure in the fuel
system (see Section 2), and equalise tank
pressure by removing the fuel filler cap. Warning: This procedure will
merely relieve the increased
pressure necessary for the engine
to run - remember that fuel will
still be present in the system components,
and take precautions accordingly before
disconnecting any of them.
2 Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(refer to Chapter 5A, Section 1).
3 Disconnect the HT lead connectors from the
spark plugs, and release the leads from their
locating grooves in the air inlet duct. Position
them out of the way. On Turbo models, undo the
two screws and remove the HT lead bracket.
4 Remove the air inlet components as
described in Section 4.
5 Unscrew the retaining nuts and the bolt,
and detach the accelerator cable support
bracket at the throttle housing.
6 Disconnect the wiring connector from the
throttle position sensor.
7 Unscrew the four retaining bolts, and
remove the throttle housing and its mating
face gasket (see illustration) .
8 Disconnect the wiring multi-plug from the
engine coolant temperature sensor and the
inlet air temperature sensor.
9 Disconnect the wiring multi-plugs from the
fuel injectors, then undo the two retaining
bolts and detach the wiring harness from the
fuel rail (see illustrations) .
10 Unscrew the fuel supply pipe at the fuel
rail. Plug the rail and pipe, to prevent further
fuel spillage and the possible ingress of dirt.
11 Disconnect the fuel return and vacuum
pipes from the pressure regulator, and catch
any fuel spillage in a clean cloth.
12 Unscrew the fuel rail securing bolts, and
carefully withdraw the rail (complete with
injectors) from the engine (see illustrations).
Fuel system - electronic fuel injection engines 4C•5
14.9b . . . unbolt the wiring harness . . .
14.9a Disconnect the wiring multi-plug
from each injector . . .14.7 Throttle housing retaining boltlocations (arrowed)
4C
1595Ford Fiesta Remake 14.12a Remove the fuel rail retaining
bolts . . .
14.9c . . . and remove the completeharness
procarmanuals.com
http://vnx.su