1988 OPEL CALIBRA torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 2 of 525

16 SV engine
Idle speed
Manual transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .925 ±25 rpm
Automatic transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .825 ±25 rpm (in ‘park’ or ‘neutral’)
Idle mixture (CO content) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.5 to 1.5%
Fast idle speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2000 to 2400 rpm
Choke valve gap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.5 to 3.5 mm
Choke pull-down gap:
Up to 1990:
“Small” . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.3 to 1.7 mm
“Large” . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.9 to 2.3 mm
From 1990:
“Small” . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.5 to 1.7 mm
“Large” . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.0 to 2.2 mm
Idle fuel jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Idle air bleed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .132.5
PrimarySecondary
Venturi diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20.0 mm24.0 mm
Main jet:
Up to 1990 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .X95X105
From 1990 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .X92.5X105
18 SV engine
Idle speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .925 ±25 rpm
Idle mixture (CO content) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .0.5 to 1.5%
Fast idle speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1900 to 2300 rpm
Choke valve gap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1.5 to 3.5 mm
Choke pull-down gap:
“Small” . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2.2 ±0.2 mm
“Large” . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3.3 ±0.2 mm
Idle fuel jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42.5
Idle air bleed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .132.5
PrimarySecondary
Main jet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .107.5125
Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Exhaust manifold nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2216
Exhaust downpipe-to-manifold bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Exhaust fixings except flexible joint bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Exhaust flexible joint bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .129
Fuel pump bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1813
Fuel tank mounting strap bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
Inlet manifold nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2216
1General description
The fuel system on all carburettor models
comprises a fuel tank, a fuel pump, a vapour
separator (1.6 and 1.8 litre models only), a
downdraught carburettor, and a thermostati-
cally-controlled air cleaner.
The fuel tank is mounted under the rear of
the vehicle, forward of the rear suspension.
The tank is ventilated to the atmosphere, and
has a simple filler pipe and a fuel gauge
sender unit.
The fuel pump is a mechanical diaphragm
type, actuated by a pushrod bearing on the
camshaft.
The fuel vapour separator is used to
stabilise the fuel supply to the carburettor.
Vapour is purged from the carburettor fuel
supply, thus improving hot starting qualities.
The carburettor is a Pierburg 2E3 type, a full
description of which is given in Section 12.The air cleaner has a wax or vacuum-
controlled air inlet supplying a blend of hot
and cold air to suit the prevailing engine
operating conditions. A fuller description is
given in Section 4.
All engines available within the Cavalier
range can be operated on unleaded petrol -
see Chapter 5.
2Fuel system - precautions
1Certain adjustment points in the fuel system
are protected by tamperproof caps, plugs or
seals. In some territories, it is an offence to
drive a vehicle with broken or missing
tamperproof seals. Before disturbing a
tamperproof seal, check that no local or
national laws will be broken by doing so, and
fit a new tamperproof seal after adjustment is
complete, where required by law. Do not
break tamperproof seals on a vehicle that is
still under warranty.2When working on fuel system components,
scrupulous cleanliness must be observed,
and care must be taken not to introduce any
foreign matter into fuel lines or components.
Carburettors in particular are delicate
instruments, and care should be taken not to
disturb any components unnecessarily.
Before attempting work on a carburettor,
ensure that the relevant spares are available.
Full overhaul procedures for carburettors have
not been given in this Chapter. Complete
stripdown of a carburettor is unlikely to cure a
fault that is not immediately obvious, without
introducing new problems. If persistent
problems are met, it is recommended that the
advice of a Vauxhall dealer or carburettor
specialist is sought. Most dealers will be able
to provide carburettor re-setting and servicing
facilities, and if necessary it should be
possible to buy a reconditioned carburettor.
3Refer to Chapter 5, for precautions to be
observed when working on vehicles fitted with
an engine management system.
4A•2Fuel and exhaust systems - carburettor models
Page 4 of 525

4Unscrew the two securing bolts, and
withdraw the pump from the camshaft
housing (see illustration).
5Recover the plastic insulating block.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal, but ensure
that the fuel hoses are reconnected to their
correct locations as noted during removal,
and tighten the securing bolts to the specified
torque.
7Run the engine and check for leaks on
completion. If leakage is evident, stop the
engine immediately and rectify the problem
without delay. Note that the engine may take
a longer time than usual to start when the
pump has been removed, as the pump refills
with fuel.
7Fuel tank - removal,
examination and refitting
4
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Siphon out any remaining fuel in the tank
through the filler pipe. Siphon the fuel into a
clean metal container that can be sealed.
3Chock the front wheels, then jack up the
rear of the vehicle, and support securely on
axle stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle
Support”) placed under the body side
members.
4Disconnect the exhaust system front
flexible joint. Suspend the front section of the
exhaust system with wire or string from the
underbody.
5Disconnect the rear section of the exhaust
system from its rubber mountings, and allow it
to rest on the rear suspension torsion beam. It
is advisable to support the rear section of the
exhaust at its front end, with wire or string
from the underbody, to avoid straining the
system.
6Unclip the handbrake cable from the
bracket on the left-hand fuel tank securing
strap.
7Disconnect the fuel hoses from the fuel
level sender unit located in the right-hand side
of the fuel tank. Make a note of the hosepositions for use when refitting. Be prepared
for fuel spillage, and take adequate fire
precautions. Plug the open ends of the hoses,
to prevent dirt ingress and further fuel loss.
8Disconnect the wiring plug from the fuel
level sender unit.
9Disconnect the filler and vent hoses from
the rear of the fuel tank.
10Support the weight of the fuel tank on a
jack with an interposed block of wood.
11Unscrew the securing bolts from the tank
mounting straps, then remove the straps and
lower the tank sufficiently to enable the
disconnection of the remaining vent hose.
12With the aid of an assistant, withdraw the
tank sideways from the right-hand side of the
vehicle. Note that as the tank is withdrawn,
some residual fuel may be released.
Examination
13If the tank contains sediment or water, it
may be cleaned out using two or three rinses
with clean fuel. Shake vigorously using
several changes of fuel, but before doing so,
remove the fuel level sender unit, as
described in Section 8. This procedure should
be carried out in a well-ventilated area, and it
is vital to take adequate fire precautions -
refer to the “Safety first!” Section at the
beginning of this manual for further details.
14Any repairs to the fuel tank should be
carried out by a professional. Do not under
any circumstances attempt to weld or solder a
fuel tank. Removal of all residual fuel vapour
requires several hours of specialist cleaning.
Refitting
15Refitting is a reversal of removal, ensuring
that all hoses are reconnected to their correct
locations as noted during removal.
16On completion, fill the fuel tank, then run
the engine and check for leaks. If leakage is
evident, stop the engine immediately and
rectify the problem without delay. Note that
the engine may take a longer time than usual
to start when the fuel tank has been removed,
as the pump refills with fuel.
8Fuel level sender unit -
removal and refitting
3
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Siphon out any remaining fuel in the tank
through the filler pipe. Siphon the fuel into a
clear metal container that can be sealed.
3Chock the front wheels, then jack up the rear
of the vehicle, and support securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
placed under the body side members.
4The sender unit is located in the right-hand
side at the fuel tank.
5Make alignment marks on the sender unit
and the fuel tank, so that the sender unit can
be refitted in its original position.6Disconnect the fuel hoses from the sender
unit. Be prepared for fuel spillage, and take
adequate fire precautions. Plug the open ends
of the hoses, to prevent dirt ingress and
further fuel loss.
7Disconnect the wiring plug from the fuel
level sender unit.
8To remove the sender unit, engage a flat
piece of metal as a lever between two of the
slots on the sender unit rim, and turn it anti-
clockwise.
9Withdraw the unit carefully, to avoid
bending the float arm.
10Recover the sealing ring.
Refitting
11Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
12Examine the condition of the sealing ring,
and renew if necessary.
13Ensure that the marks made on the
sender unit and fuel tank before removal are
aligned.
14Ensure that the hoses are reconnected to
their correct locations as noted during
removal.
15On completion, fill the fuel tank, then run
the engine and check for leaks. Also check
that the fuel gauge reads correctly. If leakage
is evident, stop the engine immediately and
rectify the problem without delay. Note that
the engine may take a longer time than usual
to start when the sender unit has been
removed, as the fuel pump refills with fuel.
9Fuel vapour separator (1.6
and 1.8 litre models) -
removal and refitting
3
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
Removal
1The fuel vapour separator is located on a
bracket attached to the side of the
carburettor.
2Note the locations of the three fuel hoses,
labelling them if necessary for use when
refitting, then disconnect the hoses from the
vapour separator. Be prepared for fuel
spillage, and take adequate fire precautions.
Plug the open ends of the hoses, to prevent
dirt ingress and further fuel spillage.
3Remove the two securing screws, and lift
the vapour separator from its bracket.
4Check the body of the separator for cracks
or leaks before refitting, and renew if
necessary.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal, but ensure
that the three fuel hoses are connected to
their correct locations as noted during
removal.
6Run the engine and check the hose
connections for leaks on completion. If
leakage is evident, stop the engine
immediately and rectify the problem without
delay.
4A•4Fuel and exhaust systems - carburettor models
6.4 Withdrawing the fuel pump and plastic
insulating block - 1.6 litre model
Page 13 of 525

4Disconnect the coolant hose from the rear
of the manifold (see illustration).
5Where applicable, disconnect the camshaft
cover breather hose from the rear of the
manifold (see illustration).
6Unscrew the union and disconnect the
brake servo vacuum hose from the manifold.
7On 1.4 and 1.6 litre models, disconnect the
wiring from the temperature gauge sender.
8Unscrew and remove the top alternator
mounting nut and bolt.
9On 1.4 and 1.6 litre models, disconnect and
remove the stub hose that connects the
crankcase breather tube to the rear of the
camshaft housing.
10Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant hoses, pipes and wires have been
disconnected.
11Unscrew the securing nuts, and withdraw
the manifold from the cylinder head (see
illustration). Note the position of the rear
engine lifting bracket, which is secured by one
of the manifold nuts, and recover the manifoldgasket.
12It is possible that some of the manifold
studs may be unscrewed from the cylinder
head when the manifold securing nuts are
unscrewed. In this event, the studs should be
screwed back into the cylinder head once the
manifold has been removed, using two
manifold nuts locked together.
13If desired, the carburettor can be removed
from the manifold, referring to Section 13, if
necessary.
Refitting
14Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
15If the carburettor has been removed from
the manifold, refit it, using a new gasket.
16If the alternator mounting bracket has
been unbolted from the manifold, refit it
before refitting the manifold, as access to the
securing bolt is extremely limited once the
manifold is in place.
17Refit the manifold using a new gasket,and ensure that the engine lifting bracket is in
place under the relevant manifold nut. Tighten
the nuts to the specified torque.
18Ensure that all relevant hoses, pipes and
wires are correctly reconnected.
19Refill the cooling system, as described in
Chapter 3.
20Check the throttle cable free play and
adjust if necessary, as described in Section
11.
21If the carburettor has been disturbed,
check and if necessary adjust the idle speed
and mixture, as described in Section 14.
Fuel and exhaust systems - carburettor models 4A•13
26.5 . . .and the camshaft cover breather
hose (arrowed) from the inlet manifold -
1.6 litre model
26.11 Withdrawing the inlet manifold -
1.6 litre model
26.4 Disconnecting the coolant hose . . .
4A
25.1 Carburettor idle cut-off solenoid
(arrowed) - 1.8 litre models
Page 15 of 525

12
Wiper blades
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 ins. Champion X-4803
Fuses
Rating:
Red . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 A
Blue . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15 A
Yellow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 A
Green . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 A
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Airbag unit to steering wheel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Airbag control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7
Brackets, passenger airbag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 16
Passenger airbag to bracket . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 6
Steering to column . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 18
Chapter 12
Body electrical systems
Aerial - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Aerial mast, electric - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Airbag - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Airbag contact unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Airbag control unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
Airbag unit, drivers side - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .56
Airbag unit, passengers side - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Anti-theft alarm - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Anti-theft alarm system components - removal and refitting . . . . . . .54
Bracket, passenger airbag unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . .60
Brake lamp switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Central door locking components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . .46
Check control system components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . .21
Cigarette lighter - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Clock - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Courtesy lamp switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Direction indicator/lighting switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . .5
Electric door mirror switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Electric window components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Electric window controls - programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Electrical fault-finding - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Exterior lamp bulbs - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Facia panel switches - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Front indicator lamp unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Front foglamp - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Fuses and relays - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
General information and precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Handbrake “on” warning lamp switch - removal and refitting . . . . . .13
Headlamp aim adjustment motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . .26
Headlamp dim-dip system - general, removal and refitting . . . . . . . .28
Headlamp unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Headlamp washer fluid non-return valve - removal and refitting . . . .43Headlamp wiper motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Headlamps - alignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Heated front seats - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Horn(s) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Ignition switch and lock cylinder - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . .4
Instrument panel - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Instrument panel components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Interior lamp bulbs - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Interior lamps - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Luggage compartment lamp switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . .11
Number plate lamp - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Oil pressure warning lamp switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . .14
Radio/cassette player - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Rear lamp unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Reversing lamp switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See Chapter 7A
Side repeater lamp - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Speakers - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Speedometer cable - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Steering wheel (with airbag) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Sunroof motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Sunroof operating switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Tailgate wiper motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Trip computer components - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Wash/wipe switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Washer fluid reservoir - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Washer nozzles - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Washer pump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Windscreen wiper motor and linkage - removal and refitting . . . . . . .38
Wiper arms - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
Wiper blades - renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Wiring diagrams - general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
12•1
Specifications Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
Page 34 of 525

56Airbag unit, drivers side -
removal and refitting
4
Note:On power steering models in particular,
it will be advantageous to jack up the front of
the car and support it on axle stands placed
under the body side members, so that the
steering wheel can be turned more easily.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead and
cover the battery terminal. Wait a minimum of 1
minute.
2With the steering wheel positioned in the
straight-ahead position, turn it 90°clockwise
so that the left-hand spoke is accessible from
the rear.
3Using a Torx type socket, undo the first
airbag retaining bolt from the rear of the
steering wheel (see illustration).
4Turn the steering wheel 180°anti-clockwise
so that the right-hand spoke is accessible
from the rear.
5Undo the second retaining bolt from the
rear of the steering wheel.
6Return the steering wheel to the
straight-ahead position then carefully lift up
the airbag unit.
7Disconnect the wiring plug and remove the
airbag from the car.
Refitting
8Refitting is a reversal of removal.
57Steering wheel (with airbag)
-removal and refitting
4
Note: Read warning at the beginning of
Section 55, before starting work. A
two-legged puller will be required for this
operation. Note also that the steering wheel is
a very tight fit on the shaft.
Removal
1Remove the airbag unit as described
previously.
2Ensure that the steering wheel is in the
straight ahead position.
3From the centre of the steering wheel
unscrew the two screws securing the airbag
contact unit.4Using a screwdriver, prise back the tabs on
the lockwasher securing the steering wheel
retaining nut.
5Unscrew and remove the steering wheel
retaining nut and the lockwasher.
6Make alignment marks between the
steering wheel and the end of the column
shaft.
7A suitably small two-legged puller must
now be fitted to the steering wheel in order to
pull it from the column shaft.
8Once the steering wheel has been released
from the column shaft, disconnect the horn
wiring and remove the steering wheel.
Refitting
9Begin refitting by positioning the steering
wheel on the column shaft, ensuring that the
marks made on removal are aligned, and that
the wheel correctly engages with the airbag
contact unit. It may be necessary to tap the
steering wheel fully home on the column shaft
using a metal tube and socket.
10Reconnect the horn wiring.
11Refit the lockwasher and the steering
wheel retaining nut, and tighten the nut to the
specified torque. Bend up the lockwasher to
secure.
12Refit the two screws securing the airbag
contact unit.
13Refit the airbag as described previously.
58Airbag contact unit -removal
and refitting
4
Note: Read warning at the beginning of
Section 55, before starting work.
Removal
1Remove the airbag and the steering wheel
as described previously.
2Remove the steering column upper and
lower shrouds, referring to Chapter 10, if
necessary.
3Disconnect the contact unit wiring plug
below the steering column and withdraw the
contact unit from the column, noting its fitted
position as a guide to reassembly (see
illustration).
Refitting
4Before refitting the contact unit, ensure that
the front wheels are in the straight-ahead
position.
5Place the contact unit on the column in the
correct position as noted during removal.
6Route the wiring harness under the steering
column lock/ignition switch and connect the
wiring plug.
7Refit the steering column shrouds.
8Refit the steering wheel and airbag as
described previously.
59Airbag unit, passengers side
- removal and refitting
4
Note: Read warning at the beginning of
Section 55, before starting work.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery, cover the terminals
and wait at least 1 minute.
2Remove the glovebox assembly. Refer to
Chapter 11, for further details if necessary.
3Remove the right hand ventilation air duct.
12•20Body electrical systems
58.3 Airbag contact unit retaining screws
56.3 Airbag, steering wheel and contact unit details
Warning: Read warning at the
beginning of Section 55, before
starting work.
Warning: Stand the unit with the
cover uppermost and do not
expose it to heat sources in
excess of 100ºC. Do not attempt
to open or repair the airbag unit, or apply
any voltage to it. Do not use any airbag
unit that is visibly damaged or has been
tampered with.
Page 89 of 525

Distributor
Direction of rotor arm rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Anti-clockwise (viewed from cap)
Firing order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-3-4-2 (No 1 cylinder at timing belt end of engine)
Dwell angle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Automatically controlled by electronic module (not adjustable)
Ignition timing
14 NV . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5°BTDC
16 SV, X 16 SZ, C 16 NZ, C 16 NZ2 and C 18 NZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10°BTDC *
18 SV and 2.0 litres models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 12°BTDC *
* Ignition timing electronically controlled no adjustment possible
Spark plugs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .See Chapter 1 Specifications
Torque wrench settingNmlbf ft
Alternator mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Camshaft phase sensor disc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Camshaft phase sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1511
‘Compact’ series alternator lower mounting bolt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3526
‘Compact’ series alternator upper mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2015
DIS module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Inductive pulse pick-up to block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Spark plugs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Starter motor mounting bracket-to-cylinder block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
Starter motor mounting:
1.4 and 1.6 litre models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2518
1.8 and 2.0 litre models:
Engine side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4533
Transmission side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7555
1Electrical system - general
1The electrical system is of the 12 volt
negative earth type, and consists of a 12 volt
battery, alternator with integral voltage
regulator, starter motor, and related electrical
accessories, components and wiring.
2The battery is of the maintenance-free
“sealed for life” type, and is charged by an
alternator, which is belt-driven from the
crankshaft pulley. The starter motor is of the
pre-engaged type, incorporating an integral
solenoid. On starting, the solenoid moves the
drive pinion into engagement with the flywheel
ring gear before the starter motor is
energised. Once the engine has started, a
one-way clutch prevents the motor armature
being driven by the engine until the pinion
disengages from the flywheel.
3It is necessary to take extra care when
working on the electrical system, to avoid
damage to semi-conductor devices (diodes
and transistors), and to avoid the risk of
personal injury. Along with the precautions
given in the “Safety first!” Section at the
beginning of this manual, take note of the
following points when working on the system.4Always remove rings, watches, etc. before
working on the electrical system. Even with
the battery disconnected, discharge could
occur if a component live terminal is earthed
through a metal object. This could cause a
shock or nasty burn.
5Do not reverse the battery connections.
Components such as the alternator, or any
other component having semi-conductor
circuitry, could be irreparably damaged.
6If the engine is being started using jump
leads and a slave battery, connect the
batteries positive to positive and negative to
negative. This also applies when connecting a
battery charger.
7Never disconnect the battery terminals, or
alternator multi-plug connector, when the
engine is running.
8The battery leads and alternator wiring
must be disconnected before carrying out any
electric welding on the vehicle.
9Never use an ohmmeter of the type
incorporating a hand-cranked generator for
circuit or continuity testing.
2Ignition system - general
1The ignition system is responsible for
igniting the air/fuel mixture in each cylinder at
the correct moment, in relation to engine
speed and load. A number of different types
of ignition systems are fitted to models within
the range. Ranging from a basic breakerless
electronic system, to a fully integrated engine
management system controlling both ignition
and fuel injection systems. Each system isdescribed in further detail later in this Section.
2The ignition system is based on feeding low
tension voltage from the battery to the coil,
where it is converted to high tension voltage.
The high tension voltage is powerful enough
to jump the spark plug gap in the cylinders
many times a second under high compression
pressures, providing that the system is in
good condition. The low tension (or primary)
circuit consists of the battery, the lead to the
ignition switch. The lead from the ignition
switch to the low tension coil windings and
the supply terminal on the electronic module.
The lead from the low tension coil windings to
the control terminal on the electronic module.
The high tension (or secondary) circuit
consists of the high tension coil windings, the
HT (high tension) lead from the coil to the
distributor cap, the rotor arm, the HT leads to
the spark plugs, and the spark plugs.
3The system functions in the following
manner. Current flowing through the low
tension coil windings produces a magnetic
field around the high tension windings. As the
engine rotates, a sensor produces an
electrical impulse that is amplified in the
electronic module and used to switch off the
low tension circuit.
4The subsequent collapse of the magnetic
field over the high tension windings produces
a high tension voltage, which is then fed to the
relevant spark plug through the distributor
cap and rotor arm. The low tension circuit is
automatically switched on again by the
electronic module, to allow the magnetic field
to build up again before the firing of the next
spark plug. The ignition is advanced and
retarded automatically, to ensure that the
spark occurs at the correct instant with the
engine speed and load.
5•2Engine electrical systems
Caution: Before carrying out
any work on the vehicle
electrical system, read through
the precautions given in the
“Safety first!” Section at the beginning of
this manual, and in Section 3 of this
Chapter.
Page 93 of 525
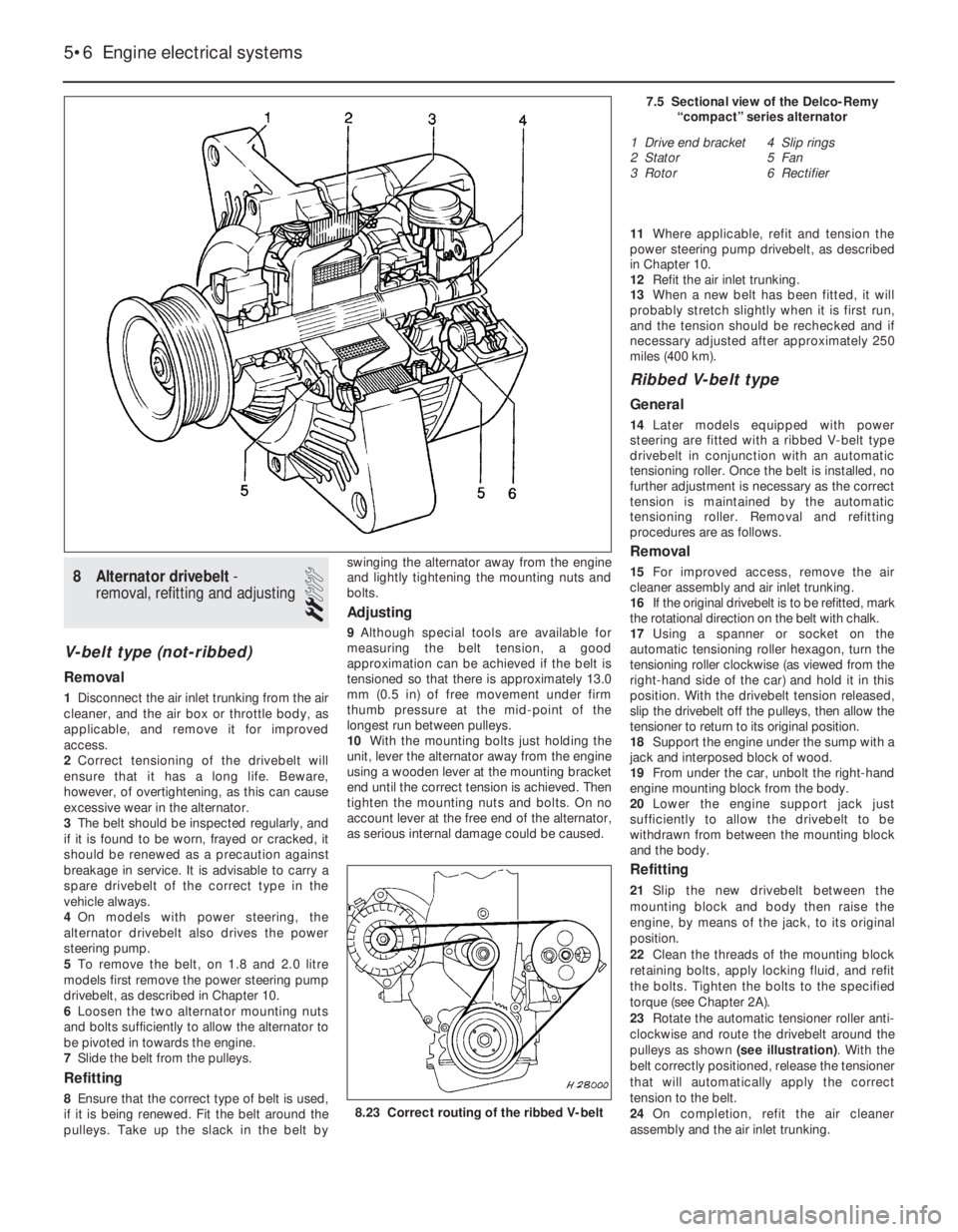
8Alternator drivebelt -
removal, refitting and adjusting
2
V-belt type (not-ribbed)
Removal
1Disconnect the air inlet trunking from the air
cleaner, and the air box or throttle body, as
applicable, and remove it for improved
access.
2Correct tensioning of the drivebelt will
ensure that it has a long life. Beware,
however, of overtightening, as this can cause
excessive wear in the alternator.
3The belt should be inspected regularly, and
if it is found to be worn, frayed or cracked, it
should be renewed as a precaution against
breakage in service. It is advisable to carry a
spare drivebelt of the correct type in the
vehicle always.
4On models with power steering, the
alternator drivebelt also drives the power
steering pump.
5To remove the belt, on 1.8 and 2.0 litre
models first remove the power steering pump
drivebelt, as described in Chapter 10.
6Loosen the two alternator mounting nuts
and bolts sufficiently to allow the alternator to
be pivoted in towards the engine.
7Slide the belt from the pulleys.
Refitting
8Ensure that the correct type of belt is used,
if it is being renewed. Fit the belt around the
pulleys. Take up the slack in the belt byswinging the alternator away from the engine
and lightly tightening the mounting nuts and
bolts.
Adjusting
9Although special tools are available for
measuring the belt tension, a good
approximation can be achieved if the belt is
tensioned so that there is approximately 13.0
mm (0.5 in) of free movement under firm
thumb pressure at the mid-point of the
longest run between pulleys.
10With the mounting bolts just holding the
unit, lever the alternator away from the engine
using a wooden lever at the mounting bracket
end until the correct tension is achieved. Then
tighten the mounting nuts and bolts. On no
account lever at the free end of the alternator,
as serious internal damage could be caused.11Where applicable, refit and tension the
power steering pump drivebelt, as described
in Chapter 10.
12Refit the air inlet trunking.
13When a new belt has been fitted, it will
probably stretch slightly when it is first run,
and the tension should be rechecked and if
necessary adjusted after approximately 250
miles (400 km).
Ribbed V-belt type
General
14Later models equipped with power
steering are fitted with a ribbed V-belt type
drivebelt in conjunction with an automatic
tensioning roller. Once the belt is installed, no
further adjustment is necessary as the correct
tension is maintained by the automatic
tensioning roller. Removal and refitting
procedures are as follows.
Removal
15For improved access, remove the air
cleaner assembly and air inlet trunking.
16If the original drivebelt is to be refitted, mark
the rotational direction on the belt with chalk.
17Using a spanner or socket on the
automatic tensioning roller hexagon, turn the
tensioning roller clockwise (as viewed from the
right-hand side of the car) and hold it in this
position. With the drivebelt tension released,
slip the drivebelt off the pulleys, then allow the
tensioner to return to its original position.
18Support the engine under the sump with a
jack and interposed block of wood.
19From under the car, unbolt the right-hand
engine mounting block from the body.
20Lower the engine support jack just
sufficiently to allow the drivebelt to be
withdrawn from between the mounting block
and the body.
Refitting
21Slip the new drivebelt between the
mounting block and body then raise the
engine, by means of the jack, to its original
position.
22Clean the threads of the mounting block
retaining bolts, apply locking fluid, and refit
the bolts. Tighten the bolts to the specified
torque (see Chapter 2A).
23Rotate the automatic tensioner roller anti-
clockwise and route the drivebelt around the
pulleys as shown (see illustration). With the
belt correctly positioned, release the tensioner
that will automatically apply the correct
tension to the belt.
24On completion, refit the air cleaner
assembly and the air inlet trunking.
5•6Engine electrical systems
7.5 Sectional view of the Delco-Remy
“compact” series alternator
1 Drive end bracket
2 Stator
3 Rotor4 Slip rings
5 Fan
6 Rectifier
8.23 Correct routing of the ribbed V-belt
Page 94 of 525

9Alternator-removal and
refitting
3
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding
Except ‘compact’ series
alternators
Removal
1Disconnect the battery leads.
2Disconnect the air trunking from the air
cleaner, and the air box or throttle body, as
applicable, and remove it for improved
access.
3Disconnect the wiring plug, or disconnect
the wires from their terminals on the rear of
the alternator, noting their locations (see
illustration).
4Remove the drivebelt, (Section 8).
5Unscrew the two mounting bolts and nuts
and recover any washers and insulating
bushes, noting their locations. Note the earth
strap attached to the top mounting bolt (see
illustration).
6Withdraw the alternator, taking care not to
knock or drop it, as this can cause irreparable
damage.
Refitting
7Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
8Ensure that the earth lead is in place on the
top mounting bolt.
9Refit and tension the drivebelt, (Section 8).
‘Compact’ series alternators
Removal
10Disconnect the battery negative lead.
11Remove the air inlet trunking and, if
necessary for improved access, the air
cleaner assembly.
12Mark the rotational direction on the
alternator drivebelt with chalk.
13Using a spanner or socket on the
automatic tensioning roller hexagon turn the
tensioning roller clockwise (as viewed from
the right-hand side of the car) and hold it in
this position. With the drivebelt tension
released, slip the drivebelt off the alternator
pulley, then allow the tensioner to return to its
original position.14Disconnect the electrical cable
connections at the rear of the alternator.
15Undo and remove the alternator lower
mounting bolt, and slacken both upper bolts
that secure the alternator mounting brackets
to the engine.
16Undo and remove both bolts that secure
the alternator to its mounting brackets, noting
the location of the different length bolts.
Swing the brackets clear and remove the
alternator from the engine.
Refitting
17Refitting is a reversal of removal. Tighten
the mounting bolts to the specified torque,
and refit the drivebelt as described in
Section 8.
10Alternator -testing
5
Due to the specialist knowledge and
equipment required to test or service an
alternator, it is recommended that if a fault is
suspected, the vehicle is taken to a dealer or a
specialist. Information is limited to the
inspection and renewal of the brushes.
Should the alternator not charge, or the
system be suspect, the following points may
be checked before seeking further assistance:
a)Check the drivebelt tension, as described
in Section 8
b)Check the condition of the battery and its
connections -see Section 5c)Inspect all electrical cables and
connections for condition and security
Note that if the alternator is found to be
faulty, it may prove more economical to buy a
factory-reconditioned unit, rather than having
the existing unit overhauled.
11Alternator brushes -removal,
inspection and refitting
3
Removal
Delco-Remy type (except ‘compact’
series)
1Remove the alternator, as described in
Section 9
2Scribe a line across the drive end housing
and the slip ring end housing, to ensure
correct alignment when reassembling.
3Unscrew the three through-bolts, and prise
the drive end housing and rotor away from the
slip ring end housing and stator (see
illustration).
4Check the condition of the slip rings, and if
necessary clean with a rag or very fine glass
paper (see illustration).
5Remove the three nuts and washers
securing the stator leads to the rectifier, and
lift away the stator assembly (see
illustration).
Engine electrical systems 5•7
11.3 Separating the drive end housing
from the slip ring end housing - Delco-
Remy alternator
11.4 Alternator slip rings (arrowed) -
Delco-Remy alternator
11.5 Delco-Remy alternator
A Stator lead securing nuts
B Brush holder/voltage regulator
securing screws
9.5 Disconnecting the earth lead from the
top alternator mounting bolt9.3 Disconnecting the wires from the
terminals on the rear of the alternator -
Delco-Remy alternator
5