1988 OPEL CALIBRA weight
[x] Cancel search: weightPage 161 of 525

d)Disconnect the fuel pump hose and wiring
as described in Section 12.
e)When releasing the tank mounting straps,
note that the fuel filter must either be
moved aside or removed completely,
whichever is most convenient
f)One of the fuel hoses connects to a pipe
in the side of the tank.
DOHC models
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Siphon out any remaining fuel in the tank
through the filler pipe. Siphon the fuel into a
clean metal container that can be sealed.
4Chock the front wheels, then jack up the
rear of the vehicle, and support on axle stands
placed under the body side members (see
“Jacking and Vehicle Support”).
5Open the fuel filler flap, then pull back the
rubber seal to expose the fuel filler pipe
securing screw (see illustration). Remove the
screw.
6Release the fuel tank vent hoses from the
clips on the underbody.
7Support the weight of the fuel tank on a
jack, with an interposed block of wood.
8Unscrew the securing bolts from the tank
mounting straps. Then remove the straps and
lower the tank sufficiently to enable the fuel
hoses, vent hoses and fuel tank sender unit
wiring to be disconnected (see illustration).
9Disconnect the vent hoses and the fuel tank
sender unit wiring. Note the positions of the
vent hoses as an aid to refitting.
10Disconnect the fuel hoses from the tank and
the fuel tank sender unit, making a note of the
hose positions for use when refitting. Be
prepared for fuel spillage, and take adequate fire
precautions. Plug the open ends of the hoses, to
prevent dirt ingress and further fuel loss.
11Lower the fuel tank, and withdraw it from
under the vehicle.
12If the tank contains sediment or water, it
may be cleaned out using two or three rinses
with clean fuel. Shake vigorously using
several changes of fuel, but before doing so,
remove the fuel tank sender unit, as described
in Section 17. This procedure should be
carried out in a well-ventilated area, and it is
vital to take adequate fire precautions - refer
to the “Safety first!” Section at the beginning
of this manual for further details.
Refitting
13Any repairs to the fuel tank should be
carried out by a professional.
14Refitting is a reversal of removal, ensuring
that all hoses are reconnected to their correct
locations as noted during removal.
15On completion, fill the fuel tank, then run
the engine and check for leaks. If leakage is
evident, stop the engine immediately, and
rectify the problem without delay.
17Fuel tank sender unit -
removal and refitting
3
Note:Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
Removal
SOHC models
1Remove the fuel tank, (refer to Section 16),
if necessary. Note that there is only one hose
connected to the sender unit. This must also
be disconnected from the union on the inside
of the unit before it can be withdrawn
completely from the tank (see illustration).
DOHC models
2Remove the fuel tank, as described in
Section 16.
3Make alignment marks on the sender unit
and the fuel tank so that the sender unit can
be refitted in its original position.
4To remove the sender unit, an improvised
tool must be used which engages with thecut-outs in the sender unit retaining ring. The
Vauxhall special tool KM-673 for this purpose
is shown (see illustration).
5Withdraw the unit carefully, to avoid
bending the float arm.
6Recover the sealing ring.
Refitting
7Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
8Renew the sealing ring.
9Ensure that the marks made on sender unit
and fuel tank before removal are aligned.
10Refit the fuel tank, (Section 16).
18Fuel flow damper - removal
and refitting
3
Note:Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
Removal
1The fuel flow damper is located on the fuel
pump bracket under the rear of the vehicle, on
the right-hand side of the spare wheel well or
in front of the fuel tank, depending on model
(see illustration). The damper is positioned in
the fuel feed line between the fuel pump and
the fuel filter, and its purpose is to reduce
pressure fluctuations in the fuel return line,
thus reducing noise levels.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Have a container to hand, to catch the fuel
that will be released as the damper is
removed.
4B•8Fuel and exhaust systems - fuel injection models
16.5 Fuel filler pipe securing screw
(arrowed) - models with semi-trailing arm
rear axles17.1 Fuel level sender unit - models with
semi-independent rear axles
18.1 Fuel flow damper - models with semi-
trailing arm rear axles17.4 Vauxhall special tool KM-673 for
removing fuel level sender units
16.8 Fuel tank mounting - models with
semi-trailing arm rear axles
1 Strap securing bolt 2 Vent hose securing
Page 206 of 525
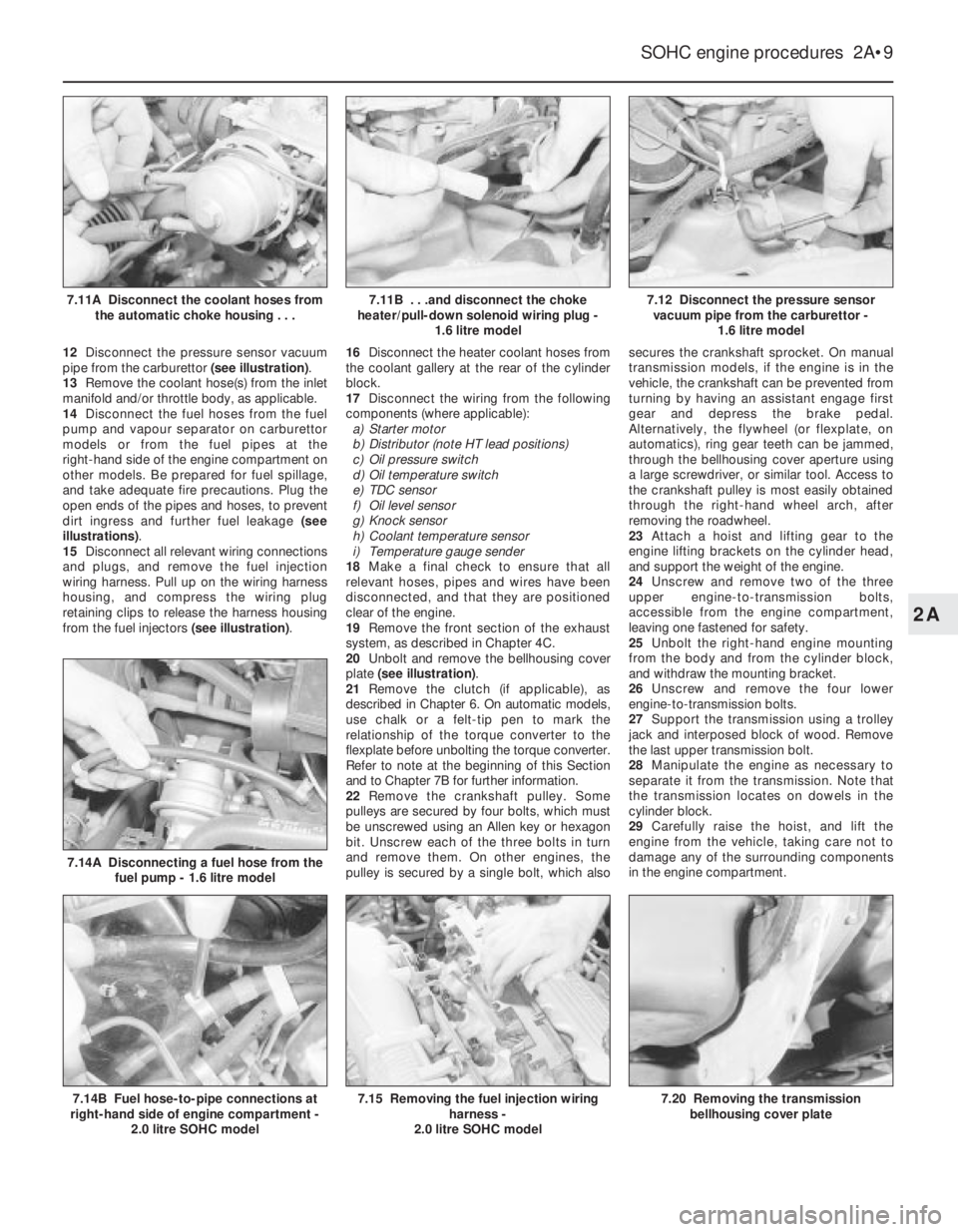
12Disconnect the pressure sensor vacuum
pipe from the carburettor (see illustration).
13Remove the coolant hose(s) from the inlet
manifold and/or throttle body, as applicable.
14Disconnect the fuel hoses from the fuel
pump and vapour separator on carburettor
models or from the fuel pipes at the
right-hand side of the engine compartment on
other models. Be prepared for fuel spillage,
and take adequate fire precautions. Plug the
open ends of the pipes and hoses, to prevent
dirt ingress and further fuel leakage (see
illustrations).
15Disconnect all relevant wiring connections
and plugs, and remove the fuel injection
wiring harness. Pull up on the wiring harness
housing, and compress the wiring plug
retaining clips to release the harness housing
from the fuel injectors (see illustration).16Disconnect the heater coolant hoses from
the coolant gallery at the rear of the cylinder
block.
17Disconnect the wiring from the following
components (where applicable):
a)Starter motor
b)Distributor (note HT lead positions)
c)Oil pressure switch
d)Oil temperature switch
e)TDC sensor
f)Oil level sensor
g)Knock sensor
h)Coolant temperature sensor
i)Temperature gauge sender
18Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant hoses, pipes and wires have been
disconnected, and that they are positioned
clear of the engine.
19Remove the front section of the exhaust
system, as described in Chapter 4C.
20Unbolt and remove the bellhousing cover
plate (see illustration).
21Remove the clutch (if applicable), as
described in Chapter 6. On automatic models,
use chalk or a felt-tip pen to mark the
relationship of the torque converter to the
flexplate before unbolting the torque converter.
Refer to note at the beginning of this Section
and to Chapter 7B for further information.
22Remove the crankshaft pulley. Some
pulleys are secured by four bolts, which must
be unscrewed using an Allen key or hexagon
bit. Unscrew each of the three bolts in turn
and remove them. On other engines, the
pulley is secured by a single bolt, which alsosecures the crankshaft sprocket. On manual
transmission models, if the engine is in the
vehicle, the crankshaft can be prevented from
turning by having an assistant engage first
gear and depress the brake pedal.
Alternatively, the flywheel (or flexplate, on
automatics), ring gear teeth can be jammed,
through the bellhousing cover aperture using
a large screwdriver, or similar tool. Access to
the crankshaft pulley is most easily obtained
through the right-hand wheel arch, after
removing the roadwheel.
23Attach a hoist and lifting gear to the
engine lifting brackets on the cylinder head,
and support the weight of the engine.
24Unscrew and remove two of the three
upper engine-to-transmission bolts,
accessible from the engine compartment,
leaving one fastened for safety.
25Unbolt the right-hand engine mounting
from the body and from the cylinder block,
and withdraw the mounting bracket.
26Unscrew and remove the four lower
engine-to-transmission bolts.
27Support the transmission using a trolley
jack and interposed block of wood. Remove
the last upper transmission bolt.
28Manipulate the engine as necessary to
separate it from the transmission. Note that
the transmission locates on dowels in the
cylinder block.
29Carefully raise the hoist, and lift the
engine from the vehicle, taking care not to
damage any of the surrounding components
in the engine compartment.
SOHC engine procedures 2A•9
7.12 Disconnect the pressure sensor
vacuum pipe from the carburettor -
1.6 litre model
7.20 Removing the transmission
bellhousing cover plate7.15 Removing the fuel injection wiring
harness -
2.0 litre SOHC model7.14B Fuel hose-to-pipe connections at
right-hand side of engine compartment -
2.0 litre SOHC model
7.14A Disconnecting a fuel hose from the
fuel pump - 1.6 litre model
7.11B . . .and disconnect the choke
heater/pull-down solenoid wiring plug -
1.6 litre model7.11A Disconnect the coolant hoses from
the automatic choke housing . . .
2A
Page 207 of 525

30With the engine removed, the
transmission can be supported by placing a
length of wood between the bellhousing and
the front suspension subframe. Once the
wooden support is in place, remove the trolley
jack from under the transmission.
Refitting
Note: New left and right-hand
engine/transmission mounting-to-body bolts
must be used on refitting.
31Use an M10 x 1.25 bottoming tap to clean
the threads in the torque converters threaded
bosses and ensure that new bolts are
available for reassembly, where applicable.
32Support the transmission with a trolley
jack and remove the length of wood from
between the bellhousing and the subframe.
33Support the engine with the hoist and
lifting tackle, and gently lower it into position
in the engine compartment.
34Mate the engine and transmission
together, ensuring that the transmission
locates on the dowels in the cylinder block,
then refit the three upper
engine-to-transmission bolts.
35Tighten all nuts and bolts to their specified
torque wrench settings. When tightening the
torque converter-to-flexplate bolts to their
specified torque wrench settings, a
commercially available adapter will be
required (see illustration).
36If the clutch is still bolted to the flywheel,
ensure that the weight of the transmission is
not allowed to hang on the input shaft as it is
engaged with the clutch friction disc.
37Refit the four lower
engine-to-transmission bolts, but again do not
fully tighten them at this stage.
38Fit the right-hand engine mounting
bracket to the cylinder block, and tighten the
securing bolts to the specified torque.39Manipulate the engine and transmission
as necessary to enable the right-hand engine
mounting-to-body bolts to be fitted, then fit
new bolts and tighten them to the specified
torque.
40Tighten all the engine-to-transmission
bolts to the specified torque, then disconnect
the lifting tackle and hoist from the engine,
and remove the trolley jack from beneath the
transmission.
41Refit the transmission bellhousing cover
plate.
42Refit the clutch, as described in Chapter
6.
43Refit the front section of the exhaust
system, as described in Chapter 4C.
44Refit the crankshaft pulley using a reversal
of the removal procedure described earlier in
paragraph 22, and tighten the securing bolt(s)
to the specified torque.
45Lower the vehicle to the ground.
46Refit all relevant wires, pipes and hoses,
etc., using a reversal of the removal
procedure described earlier.
47Where applicable, refit the power steering
pump, tension the pump drivebelt, and bleed
the hydraulic fluid circuit, as described in
Chapter 10.
48Refit the alternator and tension the
drivebelt, as described in Chapter 5.
49Refit the air cleaner components, referring
to Chapter 4A or 4B, if necessary. On
carburettor models reconnect the hot air hose
to the exhaust manifold hot air shroud.
50Fit a new oil filter (if not already replaced),
and fill the engine with oil, as described in
Chapter 1.
51Refit the radiator and refill the cooling
system, as described in Chapter 3.
52Refit the bonnet as described in Chapter
11.
53Reconnect the battery negative lead.
54Refer to Section 37
8Engine and transmission -
removal, separation,
reconnection and refitting
4
Note: A hoist and lifting tackle will be required
for this operation
Removal
1Proceed as described in Section 7,
paragraphs 1 to 18 inclusive.
2Working in the engine compartment,
remove the gear selector linkage, as
described in Chapters 7A and 7B, as
appropriate.
3On manual transmission models, remove
the retaining clip, then slide the clutch cable
from the release lever, pushing the release
lever back towards the bulkhead if necessary
to allow the cable to be disconnected. On
automatic models disconnect the selector
cable from the actuating lever, then either
unbolt the cable bracket or release the cable
from the bracket. In either case, pull the cablesupport from the bracket on the transmission
casing, then move the cable and secure to
one side out of the way, taking note of its
routing.
4Disconnect the wiring from the reversing
lamp switch, which is located at the front of
the manual transmission casing, above the
left-hand mounting bracket. On automatic
models, disconnect the transmission wiring
by unplugging the five connector plugs from
the various switches, solenoids and sensors.
Release also the wiring from any clips or ties
securing to the vehicle.
5Where applicable, withdraw the automatic
transmission breather hose from under the
battery bracket. Disconnect the oxygen
sensor wiring if fitted.
6Unscrew the securing sleeve, and
disconnect the speedometer cable from the
transmission.
7Unscrew the retaining nut, and disconnect
the earth strap from the transmission
endplate.
8Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant hoses, pipes, wires etc. have been
disconnected, and that they are positioned
clear of the engine and transmission.
9Proceed as described in Section 7,
paragraphs 19 and 22.
10Disconnect the inboard ends of the
driveshafts from the differential, referring to
the relevant paragraphs of Chapter 8. Be
prepared for oil spillage as the driveshafts are
withdrawn, and plug the apertures in the
differential, to prevent further loss of oil and
dirt ingress. Support the driveshafts by
suspending them with wire or string - do not
allow them to hang down under their own
weight.
11Attach a hoist and lifting gear to the
engine lifting brackets on the cylinder head,
and support the weight of the engine.
12Remove the left-hand transmission
mounting completely by unscrewing the two
bolts securing the rubber mounting to the
vehicle, body, and the three bolts securing the
mounting bracket to the transmission (see
illustration).
13Unbolt the right-hand engine mounting
from the body and from the cylinder block,
and withdraw the mounting bracket.
2A•10SOHC engine procedures
8.12 Left-hand transmission mounting
viewed from underside of vehicle7.35 Commercially-available torque
wrench adapter being used to tighten
torque converter bolts
If a tap is not available, cut
two slots into the threads of
one of the old flywheel bolts
and use the bolt to remove
the locking compound from the
threads.
Page 208 of 525

14Working under the vehicle, unscrew and
remove the two nuts securing the
engine/transmission rear mounting to the front
subframe, and the three bolts securing the
mounting bracket to the transmission, then
withdraw the mounting bracket (see
illustrations).
15Carefully swing the engine/transmission
assembly across the engine compartment as
necessary, to allow the assembly to be lifted
vertically from the vehicle by raising the hoist.
Take care not to damage any of the
surrounding components in the engine
compartment.
Separation
16With the engine/transmission assembly
removed, support the assembly on blocks of
wood positioned on a workbench, or failing
that, on a clean area of the workshop floor.
17Clean away any external dirt using
paraffin or a water-soluble solvent and a stiff
brush.
18Unbolt and remove the transmission
bellhousing cover plate.
19Ensure that both engine and transmission
are adequately supported, then unscrew and
remove the engine-to-transmission bolts.
20Carefully withdraw the transmission from
the engine, ensuring that the weight of the
transmission is not allowed to hang on the
input shaft while it is engaged with the clutch
friction disc. Note that the transmission
locates on dowels positioned in the cylinder
block.
21On automatic models unbolt the
transmission bellhousing cover plate (three
bolts), then use chalk or a felt-tip pen to mark
the relationship of the torque converter to the
flexplate before unbolting the torque
converter. Note:If the torque converter is
removed (even partially) from the transmission,
a considerable amount of the fluid inside it will
leak out. To prevent this, when prising the
transmission off its locating dowels and
removing it, be careful to keep the torque
converter pressed firmly into the transmission.
If the transmission is to be removed for some
time, retain the torque converter by bolting a
strip of metal across the bellhousing mating
surface. Applying a spanner to the crankshaft
pulley/sprocket bolt, rotate the crankshaft
until the first bolt appears, then use ascrewdriver or similar to jam the flexplate ring
gear teeth to prevent it from rotating as the
bolt is unscrewed. Unscrew each of the three
bolts in turn and remove them.
Reconnection
22Before beginning the refitting operations,
check that the two original bolts that secured
the left-hand transmission rubber mounting to
the vehicle body rotate freely in their threaded
bores in the body. If necessary, re-cut the
threaded bores using an M10 x 1.25 mm tap.
23Where applicable, if the clutch assembly
has been removed from the flywheel, it will
prove easier to refit after the transmission has
been refitted.
24On automatics, if any fluid was spilled from
the torque converter, be careful to refill it as
much as possible. Wipe clean the converter’s
spigot to prevent damage to the transmission’s
input shaft oil seal as the converter is installed,
and ensure that the converter engages
correctly on the fluid pump shaft.
25If the transmission has been renewed, be
careful to flush clean the radiator fluid cooler
passages. Vauxhall recommend the use of
low-pressure compressed air, but this will
require great care to avoid deforming the
radiator.
26Be very careful to ensure that all
components are scrupulously clean, to avoid
the risk of dirt getting into the system.
27Use an M10 x 1.25 bottoming tap to clean
the threads in the torque converters threaded
bosses and ensure that new bolts are
available for reassembly, where applicable.
28Tighten all nuts and bolts to their specified
torque wrench settings.
29Refer also to Section 7, paragraphs 35
and 36.
30Carefully offer the transmission to the
engine until the bellhousing is located on the
dowels in the cylinder block, then refit the
engine-to-transmission bolts, and tighten
them to the specified torque.
31Refit the transmission bellhousing cover
plate.
Refitting
32Working under the vehicle, refit the rear
engine/transmission mounting to the
transmission, using new locking plates under
the bolt heads, and tighten the bolts to the
specified torque.
33Fit the two bolts securing the engine/
transmission rear mounting to the front
subframe, but do not fully tighten at this stage.
34Fit the right-hand engine mounting
bracket to the cylinder block, and tighten the
securing bolts to the specified torque.
35Fit new right-hand engine
mounting-to-body bolts, but do not fully
tighten them at this stage.
36Fit the left-hand transmission mounting
bracket to the transmission, and tighten the
securing bolts to the specified torque.
37Fit new left-hand transmission
mounting-to-body bolts, and tighten them to
the specified torque.
38Tighten the right-hand engine mounting-
to-body bolts and the engine/transmission
rear mounting-to-front subframe bolts to their
specified torques, then remove the lifting
tackle and hoist from the engine.
39Where applicable, the clutch can now be
fitted, and the transmission input shaft can be
pressed into engagement with the splined hub
of the clutch friction disc, (see Chapter 5).
40Reconnect the inboard ends of the
driveshafts to the differential, with reference
to the relevant paragraphs of Chapter 8, and
using new snap rings.
41Refit the front section of the exhaust
system, as described in Chapter 4C.
42Refit the crankshaft pulley, using a
reversal of the removal procedure described
in Section 7, paragraph 22, and tighten the
securing bolt(s) to the specified torque.
43On automatic models, connect the wires
to the various switches, solenoids and
sensors. Replace the transmission breather
hose and oxygen sensor (if fitted).
44Reconnect the transmission earth strap,
and tighten the securing nut.
45Lower the vehicle to the ground.
46Reconnect the speedometer cable to the
transmission, and tighten the securing sleeve.
47Reconnect the reversing lamp wiring.
48On manual transmission models, refit the
clutch cable to the bracket on the
transmission casing, then reconnect the cable
to the release lever, and adjust the cable as
described in Chapter 6. Ensure that the cable
is routed as noted during removal.
49Refit the gear selector linkage, as
described in Chapter 7A, if applicable.
50Proceed as described in Section 7,
paragraphs 41 to 52 inclusive.
51Top-up the transmission oil level, as
described in Chapters 7A and 7B.
52Adjust the selector cable on completion,
and refill the transmission with fluid (see
above).
53Reconnect the battery negative lead.
54Refer to Section 37
SOHC engine procedures 2A•11
8.14B Rear engine/transmission mounting-
to-transmission bolts (arrowed)8.14A Rear engine/transmission
mounting-to-front subframe nuts
2A
If a tap is not available, cut
two slots into the threads of
one of the old flywheel bolts
and use the bolt to remove
the locking compound from the threads.
Page 209 of 525

9Engine and transmission
mountings - renewal
3
Note: New left and right-hand
engine/transmission mounting-to-body bolts
must be used on refitting
1The engine/transmission assembly is
suspended in the engine compartment on
three mountings, two of which are attached to
the transmission, and one to the engine.
Right-hand mounting
2If not already done, apply the handbrake,
then raise the front of the vehicle, and support
securely on axle stands (see “Jacking and
Vehicle Support”)..
3Attach lifting tackle and a hoist to the
engine lifting brackets on the cylinder head,
and support the weight of the engine.
4Working under the vehicle, unbolt the
engine mounting bracket from the cylinder
block, and unbolt the mounting block from the
body, then withdraw the bracket/mounting
assembly (see illustration).
5Unbolt the mounting block from the
bracket.
6Fit the new mounting block to the bracket,
and tighten the securing bolts to the specified
torque.
7Refit the mounting bracket to the cylinder
block, and tighten the securing bolts to the
specified torque.
8Fit new mounting block-to-body bolts, and
tighten them to the specified torque.
9Disconnect the lifting tackle and hoist from
the engine.
10Lower the vehicle to the ground.
Left-hand mounting
11Proceed as described in paragraphs 2
and 3.
12Working under the vehicle, unbolt the
mounting block from the mounting bracket
and the body (see illustration).13Before fitting the new mounting block,
check that the original engine bolts which
secured the mounting block to the body
rotate freely in their threaded bores in the
body. If necessary, re-cut the threaded bores
using an M10 x 1.25 mm tap.
14Fit the new mounting block to the bracket,
and tighten the securing bolts to the specified
torque.
15Fit new mounting block-to-body bolts,
and tighten them to the specified torque.
16Proceed as described in paragraphs 9
and 10.
Rear mounting
17Proceed as described in paragraphs 2
and 3.
18Working under the vehicle, unbolt the
mounting block from the front subframe and
the mounting bracket.
19Fit the new mounting block to the
subframe and mounting bracket, and tighten
the securing bolts to the specified torque.
20Proceed as described in paragraphs 9
and 10.
10Engine dismantling and
reassembly - general
4
General
1Ideally, the engine should be mounted on a
dismantling stand, but if this is not available,
stand the engine on a strong bench, at a
comfortable working height. Failing this, the
engine will have to be stripped down on the
floor.
2Cleanliness is most important, and if theengine is dirty, it should be cleaned with
paraffin in an upright position.
3Avoid working with the engine directly on a
concrete floor, as grit presents a real source
of trouble.
4If the engine oil appears extremely dirty or
contaminated, avoid inverting the engine until
the sump has been removed. This will prevent
any contaminated “sludge” from entering the
oilways.
5As parts are removed, clean them in a
paraffin bath. Do not immerse parts with
internal oilways in paraffin, as it is difficult to
remove, usually requiring a high pressure
hose. Clean oilways with nylon pipe cleaners.
6It is advisable to have containers available
to hold small items, to prevent loss and
confusion when refitting.
7Always obtain complete sets of gaskets
when the engine is being dismantled. Keep
the old gaskets as they can be used as
patterns to make replacements should new
gaskets not be available.
8Where possible, refit nuts, bolts and
washers to their locations after removal of the
relevant components, as this helps protect
the threads, and will also prove helpful during
reassembly.
9Retain unserviceable components, to
compare them with the new components
supplied.
10Many of the engine components are
secured using socket-headed “Torx” or
“Allen” bolts, and tools will be required to
remove and refit such bolts.
11Read through each relevant Section of
this Chapter carefullybeforebeginning work,
to ensure that any special tools that may be
required are available. Many components
(gaskets, oil seals, and certain bolts) must be
renewed on reassembly; where applicable,
obtain the required new components before
starting work.
12Before beginning a complete strip of the
engine, the following ancillary components
can be removed once the engine has been
removed from the vehicle:
2A•12SOHC engine procedures
9.4 Right-hand engine mounting
1 Mounting block-to-body bolts
2 Mounting bracket-to-cylinder block bolts9.12 Left-hand engine/transmission mounting
1 Mounting block-to-body bolts
2 Mounting block-to-mounting bracket bolts
If a tap is not available, cut
two slots into the threads of
one of the old flywheel bolts
and use the bolt to remove
the locking compound from the threads.
Page 230 of 525

31Refit the previously removed
components, referring to the relevant
Sections of this Chapter.
35Crankshaft and bearings -
examination
4
Examination
1Examine the crankpin and main journal
surfaces for signs of scoring or scratches, and
check the ovality and taper of the crankpins
and main journals. If the bearing surface
dimensions do not fall within the tolerance
ranges given in the Specifications at the
beginning of this Chapter, the crankpins
and/or main journals will have to be reground.
2Big-end and crankpin wear is accompanied
by distinct metallic knocking, particularly
noticeable when the engine is pulling from low
revs, and some loss of oil pressure.
3Main bearing and main journal wear is
accompanied by severe engine vibration rumble
- getting progressively worse as engine rev’s
increase - and again by loss of oil pressure.
4If the crankshaft requires regrinding, take it
to an engine reconditioning specialist, who
will machine it for you and supply the correct
undersize bearing shells.
5Inspect the big-end and main bearing shells
for signs of general wear, scoring, pitting and
scratches. The bearings should be matt grey
in colour. With leadindium bearings, should a
trace of copper colour be noticed, the
bearings are badly worn, as the lead bearing
material has worn away to expose the indium
underlay. Renew the bearings if they are in
this condition, or if there are any signs of
scoring or pitting. You are strongly advised
to renew the bearings - regardless of their
condition at time of major overhaul.
Refitting used bearings is a false economy.
6The undersizes available are designed to
correspond with crankshaft regrind sizes. Thebearings are in fact, slightly more than the
stated undersize, as running clearances have
been allowed for during their manufacture.
7Main and big-end bearing shells can be
identified as to size by the marking on the
back of the shell. Standard size shell bearings
are marked STD or .00, undersize shells are
marked with the undersize such as 0.020 u/s.
This marking method applies only to
replacement bearing shells, and not to those
used during production.
8An accurate method of determining bearing
wear is by using a Plastigage. The crankshaft
is located in the main bearings (and, if
necessary, the big-end bearings), and the
Plastigage filament is located across the
journal. Vauxhall recommend that the
crankshaft journal and bearing shells are
lightly lubricated, to prevent the Plastigage
from tearing as the bearing cap is removed.
The bearing cap should be fitted, and the
bolts tightened to the specified torque. The
cap is then removed, and the width of the
filament is checked against a scale that shows
the bearing running clearance. The clearance
should be compared with that given in the
Specifications.
9Where applicable, check the teeth of the
crankshaft TDC sensor wheel for damage
(see illustration). If evident, the crankshaft
must be renewed.
10Similarly, check the condition of the pins
in the front crankshaft balance weight, which
serve as detect points for the plug-in
diagnostic sensor used by Vauxhall dealers
(see illustration).
36Cylinder block and bores -
examination and renovation
4
Examination
1Examine the cylinder bores for taper,
ovality, scoring and scratches. Start bycarefully examining the top of the cylinder
bores. If they are at all worn, a very slight
ridge will be found on the thrust side. This
marks the top of the piston ring travel. The
owner will have a good indication of the bore
wear before dismantling the engine, or
removing the cylinder head. Excessive oil
consumption, accompanied by blue smoke
from the exhaust, is a sure sign of worn
cylinder bores and piston rings.
2Measure the bore diameter across the
block, and just below any ridge. This can be
done with an internal micrometer or a dial
gauge. Compare this with the diameter of the
bottom of the bore, which is not subject to
wear. If no measuring instruments are
available, use a piston from which the rings
have been removed, and measure the gap
between it and the cylinder wall with a feeler
blade. Refer to the Specifications. If the
cylinder wear exceeds the permitted
tolerances, then the cylinders will need
reboring, in which case note the following
points:
a)Piston and cylinder bores are closely
matched in production. The actual
diameter of the piston is indicated by
numbers on its crown; the same numbers
stamped on the crankcase indicate the
bore diameter
b)After reboring has taken place, the
cylinder bores should be measured
accurately and oversize pistons selected
from the grades available to give the
specified piston-to-bore clearance
c)For grading purposes, the piston diameter
is measured across the bottom of the skirt
3If the wear is marginal and within the
tolerances given, new special piston rings can
be fitted to offset the wear.
4Thoroughly examine the crankcase and
cylinder block for cracks and damage, and
use a piece of wire to probe all oilways and
waterways to ensure that they are
unobstructed.
SOHC engine procedures 2A•33
35.10 Check the condition of the pins (arrowed) in the front
crankshaft balance weight - 2.0 litre SOHC engine35.9 Check the condition of the TDC sensor wheel teeth at the
front of the crankshaft - 2.0 litre SOHC engine
2A
Page 231 of 525

5Note that the rubber plug located next to
the bellhousing flange on the cylinder block
covers the aperture for the installation of a
diagnostic TDC sensor. The sensor, when
connected to a monitoring unit, indicates TDC
from the position of the pins set into the
crankshaft balance weight.
37Examination and renovation
-general
4
General
1With the engine completely stripped, clean all
components and examine them for wear. Each
component should be checked, and where
necessary renewed or renovated, as described
in the relevant Sections of this Chapter.
2Renew main and big-end bearing shells as
a matter of course, unless it is known that
they have had little wear, and are in perfect
condition.
3If in doubt whether to renew a component
that is still just serviceable, consider the time
and effort that will be incurred should the
component fail at an early date after rebuild.
Obviously, the age and expected life of the
vehicle must influence the standards applied.4Gaskets, oil seals and O-rings must all be
renewed as a matter of routine. Flywheel,
cylinder head, and main and big-end bearing
cap bolts must be renewed, because of the
high stress to which they are subjected.
5Renew the engine core plugs while they are
easily accessible, if they show signs of
leakage. Knock out the old plugs with a
hammer and chisel or punch. Clean the plug
seats, smear the new plugs with sealing
compound, and tap them squarely into
position.
38Initial start-up after major
overhaul or repair
2
1Make a final check to ensure that
everything has been reconnected to the
engine, and that no rags or tools have been
left in the engine compartment.
2Check that oil and coolant levels are
correct.
3Start the engine. This may take a little longer
than usual, as fuel is pumped to the engine.
4Check that the oil pressure warning lamp
goes out when the engine starts. This may
take a few seconds as the new oil filter fills
with oil.5Run the engine at a fast tickover, and check
for leaks of oil, fuel and coolant. If a new
camshaft has been fitted, pay careful
attention to the running-in procedure given in
Section 18, paragraphs 17 and 18. Where
applicable, check the power steering and/or
automatic transmission fluid cooler unions for
leakage. Some smoke and odd smells may be
experienced, as assembly lubricants and
sealers burn off the various components.
6Bring the engine to normal operating
temperature. Check the ignition timing, idle
speed and the mixture (where applicable), as
described in Chapter 4A or 4B.
7Allow the engine to cool, then recheck the
oil and coolant levels. Top-up if necessary
8If new bearings, pistons, etc., have been
fitted, the engine should be run-in at reduced
speeds and loads for the first 500 miles (800
km) or so. It is beneficial to change the engine
oil and filter after this mileage.
2A•34SOHC engine procedures
Page 240 of 525

REF
Overall length: *
Saloon models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4432 mm
Hatchback models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4352 mm
Overall width: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1876 mm
Overall height (unladen): *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1400 mm
Wheelbase: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2600 mm
Track:
Front: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1426 mm
Rear: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1423 mm
Ground clearance (minimum): *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .120 mm
Weights
Kerb weight: *
Dependent on model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1098 ± 101 kg
Maximum gross vehicle weight: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Refer to VIN plate
Maximum roof rack load: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100 kg
Maximum towing hitch downward load: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75 kg
Maximum towing weight: *
Trailer with brakes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1175 ± 175 kg
Trailer without brakes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .550 ± 50 kg
* Exact details depend upon model and specification.
Refer to owners handbook.
Dimensions and Weights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•1
Conversion Factors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•2
Buying Spare Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•3
Vehicle Identification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•3
General Repair Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•4
Jacking and Vehicle Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•5Radio/cassette unit Anti-theft System . . . . . . . .REF•5
Tools and Working Facilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•6
MOT Test Checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•8
Fault Finding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•12
Glossary of Technical Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•20
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•25
Reference REF•1
Dimensions and Weights