1988 OPEL CALIBRA roof rack
[x] Cancel search: roof rackPage 70 of 525

12•56Wiring diagrams
Key to wiring diagrams for 1992 and later models (continued)
NoDescriptionTrackNoDescriptionTrack
K95Traction control control unit1125 to 1140
K97Headlamps washer pump time delay relay630 to 632
K101Parking position mirror relay774 to 777
K102Park brake shift lock control unit 469 to 471
L1Ignition coil150, 172, 205, 273, 241, 302, 361
L2Ignition coil1000 to 1004, 1054 to 1059
M1Starter105, 106
M2Windshield wiper motor601 to 604
M3Heating blower motor127 to 129
M4Radiator blower motor118, 120, 140, 356, 431, 948, 954, 980
M6Left headlamp wiper motor622 to 624
M7Right headlamp wiper motor 626 to 628
M8Back window wiper motor611 to 613
M10Air conditioning blower motor905 to 908
M11Radiator blower motor136, 434, 962, 984
M13Vectra/Cavalier sun roof motor1172 to 1175
M13.1Sun roof motor1172, 1174
M13.2Timing box microswitch1172
M13.3Timing box microswitch1174
M18Driver door central locking motor807 to 810
M19Left rear door central locking motor821 to 823
M20Right rear door central locking motor825 to 827
M21Fuel pump232, 263, 297, 339, 399, 834, 1098, 1039
M23Alternator blower motor135, 974
M24Headlamps washer pump632
M26Automatic antenna motor798 to 799
M30Driver side outside mirror638 to 641
M31Passenger side outside mirror644 to 647
M32Passenger door central locking motor813 to 816
M33Idle speed actuator285, 286, 317, 318, 381,
382, 1019, 1020, 1075, 1076
M37Tail gate/boot lid central locking motor818 to 821
M39Left headlamp levelling motor 692 to 695
M40Right headlamp levelling motor696 to 699
M41Fuel filler door central locking motor823, 824
M47Driver door window lifter motor867 to 871
M48Passenger door window lifter motor885 to 889
M49Left rear window lifter motor873 to 877
M50Right rear window lifter motor891 to 895
M55Windshield and back window washer pump617
M57Coolant pump134, 970
M60Calibra tailgate central locking motor827, 828
M61Calibra sun roof motor1178 to 1186
M61.1Sun roof motor1179 to 1182
M61.2Relay 11178, 1179
M61.3Relay 21184 to 1186
M62Driver side outside mirror760 to 767
M63Passenger side outside mirror769 to 776
M65TC throttle valve actuator1130 to 1134
M66Idle air stepper motor215 to 218, 250 to 253
P1Fuel indicator704
P2Coolant temperature indicator706
P3Clock862
P4Fuel sensor704
P5Coolant temperature sensor706
P7Tachometer708
P11Airflow meter 285 to 289
P12Coolant temperature sensor282, 381
P13Outside temperature sensor856
P14Distance sensor412, 413
P17Left front revolution sensor1110, 1154
P18Right front revolution sensor1113, 1157
P19Left rear revolution sensor1116, 1160
P20Right rear revolution sensor1119, 1163P21Distance sensor731
P23Intake manifold absolute pressure sensor160, 161, 185, 186,
217 to 219, 250 to 252
P24Engine oil temperature sensor162, 187
P27Left front brake lining sensor740
P28Right front brake lining sensor740
P29Intake manifold temperature sensor382, 1016, 1072
P30Coolant temperature sensor215, 248, 313, 1017, 1073
P32Heated exhaust oxygen sensor294, 295, 331, 332, 391,
392, 1034, 1035, 1093, 1094
P33Exhaust oxygen sensor229, 257
P34Throttle valve potentiometer221 to 223, 280, 281, 253 to 255,
383 to 385, 478, 479, 1018, 1019, 1074, 1075
P35Crankshaft impulse sensor178 to 180, 289 to 291, 248 to 250,
318 to 320, 373 to 375, 1025 to 1027, 1084 to 1086
P38Transmission oil temperature sensor494
P39Trailer bulb test sensor752 to 754
P43Electronic speedometer733
P44Air mass meter393 to 397, 334 to 338,
1037, 1038, 1096, 1097
P45Transmission input revolution sensor490, 491
P46Knock control sensor322, 323, 377, 378,
1022, 1023, 1078, 1079
P47Cylinder identification hall sensor325 to 327, 385 to 387,
1028 to 1030, 1087, 1089
P48Automatic transmission distance sensor488, 489
P50Catalytic converter temperature sensor463, 464
P53Driver side anti-theft warning unit sensor839 to 847
P54Passenger side anti-theft warning unit sensor839 to 847
P55Engine coolant temperature sensor415
P56Knock control sensor II1080, 1081
P57Antenna797
R3Cigarette lighter675
R5Glow plugs418 to 420, 441 to 443
R13Left heated washer nozzle 626
R14Right heated washer nozzle628
R19Radiator blower preresistor120, 140, 945
R22Glow plugs pre-resistor423
R23Driver airbag squib1194
S1Starter switch103 to 106
S1.2Key contact switch783
S2Light switch assy
S2.1Light switch504 to 507
S2.2Passenger compartment lamp switch587
S2.3Instrument lights dimmer728
S3Heating blower switch123 to 130
S4Heated back window & mirror switch654 to 657
S5Turn signal switch assy
S5.2Low beam switch536, 537
S5.3Turn signal switch580 to 582
S5.4Parking lamp switch501, 502
S7Back up lamp switch597, 599
S8Stop lamp switch562
S9Wiper unit switch
S9.2Interval windshield wiper switch601 to 604
S9.5Back window and washer unit wiper switch614 to 616
S10Automatic transmission switch472 to 478
S11Brake fluid control switch712
S13Parking brake switch713
S14Oil pressure switch710
S15Boot lamp switch585
S17Passenger door contact switch590
S20Pressure switch
S20.1Low pressure compressor switch925
Page 71 of 525

Wiring diagrams 12•57
12
Key to wiring diagrams for 1992 and later models (continued)
NoDescriptionTrackNoDescriptionTrack
S20.2High pressure compressor switch925
S20.3High pressure blower compressor switch939
S21Fog lamps switch555 to 557
S22Rear fog lamp switch549 to 551
S24Air conditioning blower switch904 to 911
S29Coolant temperature switch118, 137, 357, 942, 957, 972
S30Left front heating mat switch660 to 662
S31Rear left door contact switch591
S32Rear right door contact switch592
S33Traction control switch1130, 1131
S37Window lifter switch868 to 894
S37.1Left window lifter switch868 to 870
S37.2Right window lifter switch886 to 888
S37.3Left rear window lifter switch874 to 876
S37.4Right rear window lifter switch892 to 894
S37.5Safety switch872, 873
S37.6Window anti-jam off switch890
S37.7Automatic window lifter control877 to 882
S39Left rear door window lifter switch878 to 880
S40Right rear door window lifter switch896 to 898
S41Driver door burglary locking switch800 to 802
S42Passenger door central locking switch805
S44Throttle valve switch316, 317
S47Driver door contact switch593, 594
S52Hazard warning switch569 to 573
S53First gear identification switch372
S55Right front heating mat switch664 to 666
S57Sun roof switch1170 to 1183
S63Computer switch
S63.1Function reset switch856
S63.2Clock hours adjustment switch857
S63.3Function select switch858
S63.4Clock minute adjustment switch859
S64Horn switch672
S68Outside mirror switch assy
S68.1Outside mirror adjustment switch638 to 640, 758 to 762
S68.3Left/right outside mirror switch637 to 641, 759 to 763
S68.4Parking position switch765
S82Washer fluid minimum capacity control switch736
S882 stage coolant temperature switch120, 121, 137, 138, 430, 431
S89Seat belt switch998
S93Coolant minimum capacity control switch737
S95Engine oil minuimum capacity control switch738
S98Headlamps levelling switch691 to 693
S99ZV driver door window lifter switch865
S100ZV passenger door window lifter switch883
S101Compressor switch926 to 928
S102Circulation switch918 to 920
S103Transmission temperature switch350
S104Kickdown switch493
S105Start-up assistance switch495 to 497
S106Economy power program switch492
S109Acceleration revolution pressure switch921
S115Coolant temperature switch487, 488
S116Stop lamp switch564, 565
S117Hydraulic pressure switch346
S120Engine compartment hood (anti-theft warning unit) switch835
S127Calibra tail gate central locking switch831
S128Coolant temperature switch936,937S131Defroster lever limit switch918
U2Computer851 to 862
U4ABS hydroaggregate1102 to 1122, 1146 to 1164
U4.1Pump motor relay1102, 1103, 1146, 1147
U4.2Solenoid valves relay1104, 1105, 1148, 1149
U4.3Pump motor1102,1146
U4.4Diode1105,1149
U4.5Left front solenoid valve1109,1153
U4.6Right front solenoid valve1111,1155
U4.7Rear axle solenoid valve1113,1157
U4.8ABS control unit1106 to 1122, 1150 to 1164
U4.9Solenoid valves plug1109 to 1113, 1153 to 1157
U5Check control display
U5.1Washer fluid minimum capacity telltale741
U5.2Oil minimum capacity telltale740
U5.3Coolant minimum capacity telltale739
U5.4Tail light & low beam telltale738
U5.5Stop light failure telltale737
U5.6Front brake lining telltale736
U12Filter heater
U12.1Temperature switch426, 452
U12.2Filter heater427, 453
U13Automatic transmission
U13.1Solenoid valve (shift 1)481
U13.2Solenoid valve (shift 2)482
U13.3Solenoid valve (lock up control)483
U13.4Solenoid valve (pressure control)484
U17Roof antenna amplifier795
V1Brake fluid test bulb diode712
V8Air conditioning compressor diode926
X1 onWiring connectorsVarious
X10Anti theft warning unit code837
X13Diagnostic link164, 165, 189, 190, 226, 270, 271, 258, 259,
309, 310, 370, 371, 343, 344, 473, 474, 573, 725, 836, 837, 860,
861, 1012, 1013, 1069, 1070, 1118, 1119, 1136, 1162, 1163
X15Octane number plug157, 158, 182, 183, 225, 226,
257, 258, 284, 285
X54Ignition coding plug310, 311, 1014, 1070, 1071
Y1Air conditioning compressor clutch925
Y4Headlamps washer solenoid valve620
Y5Fuel solenoid valve410, 445
Y7Fuel injection valves287 to 294,320 to 327,
384 to 391,1025 to 1032,1078 to 1089
Y10Hall sensor ignition distributor153 to 158
Y11Hot start solenoid valve375, 376
Y12Charging pressure control changeover valve377, 378
Y18Exhaust gas recirculation valve1093
Y23Inductive sensor distributor201 to 208
Y24Distributor (inductive discharge)
Y25Acceleration revolution solenoid valve155, 177
Y30Cold start acceleration solenoid valve 448
Y32Fuel injection valve212, 245
Y33Ignition distributor175 to 177, 268 to 270, 238 to 240,
301 to 303, 360 to 362
Y34Tank ventilation valve293, 331, 332, 379, 380,
1092, 1016, 1017,
Y35Circulation solenoid valve918
Y44Four wheel drive solenoid valve350
Y47Park brake shift lock lifting magnet469
Page 122 of 525

4Pull the cassette storage box or the rubber
mat, as applicable, from the rear of the centre
console to expose the rear securing screw
(see illustration).
5Extract the rear securing screw (see
illustration), then withdraw the rear centre
console section upwards, feeding the gaiter
over the handbrake lever.
6Where applicable, ensure that the battery
negative lead has been disconnected, then
disconnect the wiring plug(s) from the electric
window and/or trip computer switches.
Refitting
7Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Front section
Removal
8Remove the rear centre console section, as
described previously in this Section.
9Remove the gearchange lever, as described
in Chapters 7A or 7B, as applicable. 10Disconnect the battery negative lead, if
not already done.
11Pull the ashtray assembly from the centre
console, and disconnect the wiring plugs from
the cigarette lighter (see illustration).
12Extract the two now-exposed screws
securing the centre console to the facia (see
illustration).
13Working at either side of the centre
console, remove the two lower centre
console-to-facia securing screws, and the two
centre console-to-floor bracket securing
screws (see illustration).
14The front centre console section can now
be withdrawn.
Refitting
15Refitting is a reversal of removal, but feed
the cigarette lighter wiring through the
aperture in the centre console as the centre
console is offered into position.
39Headlining -removal and
refitting
3
Removal
1Where applicable, remove the sunroof
crank drive, as described in Section 34.
2Remove the grab handles from the sides of
the roof (see illustration).
3Remove the sunvisors. On models with
illuminated sunvisor vanity mirrors,
disconnect the battery negative lead, then pull
the lamp wiring from the roof as the sunvisor
is withdrawn and disconnect the wiring plugs.
4On models without a sunroof, disconnect
the battery negative lead (if not already done),
then prise the courtesy lamp and its trim panel
from the roof and disconnect the wiring.
5Open the doors, and prise the
weatherstrips from the tops of the door
apertures.
6Remove the front body pillar and centre
body pillar trim panels, as described in
Section 36.
7Loosen the upper edge of the rear quarter
trim panels, referring to Section 36 if
necessary.
8On Hatchback models, open the tailgate,
and prise the rear trim panel from the roof.
9With the help of an assistant, lower the
headlining from the roof, and withdraw it
through the tailgate on Hatchback models or
through one of the door apertures on Saloon
models.
Bodywork and fittings 11•19
38.4 Pull the cassette storage box from
the console . . .
38.12 Extract the two centre console-to-
facia securing screws38.11 Disconnecting the wiring plugs from
the cigarette lighter
38.3 Pull the grip from the handbrake lever38.2 . . . then extract the front securing
screw
11
38.5 . . . then extract the rear securing
screw
38.13 Unscrewing a side centre console-
to-facia securing screw39.2 Removing a grab handle securing
screw
Page 123 of 525
Refitting
10Refitting is a reversal of removal, but
where applicable, refit the sunroof crank drive,
as described in Section 34.
40Seats (without tensioners) -
removal and refitting
3
Front seats
Removal
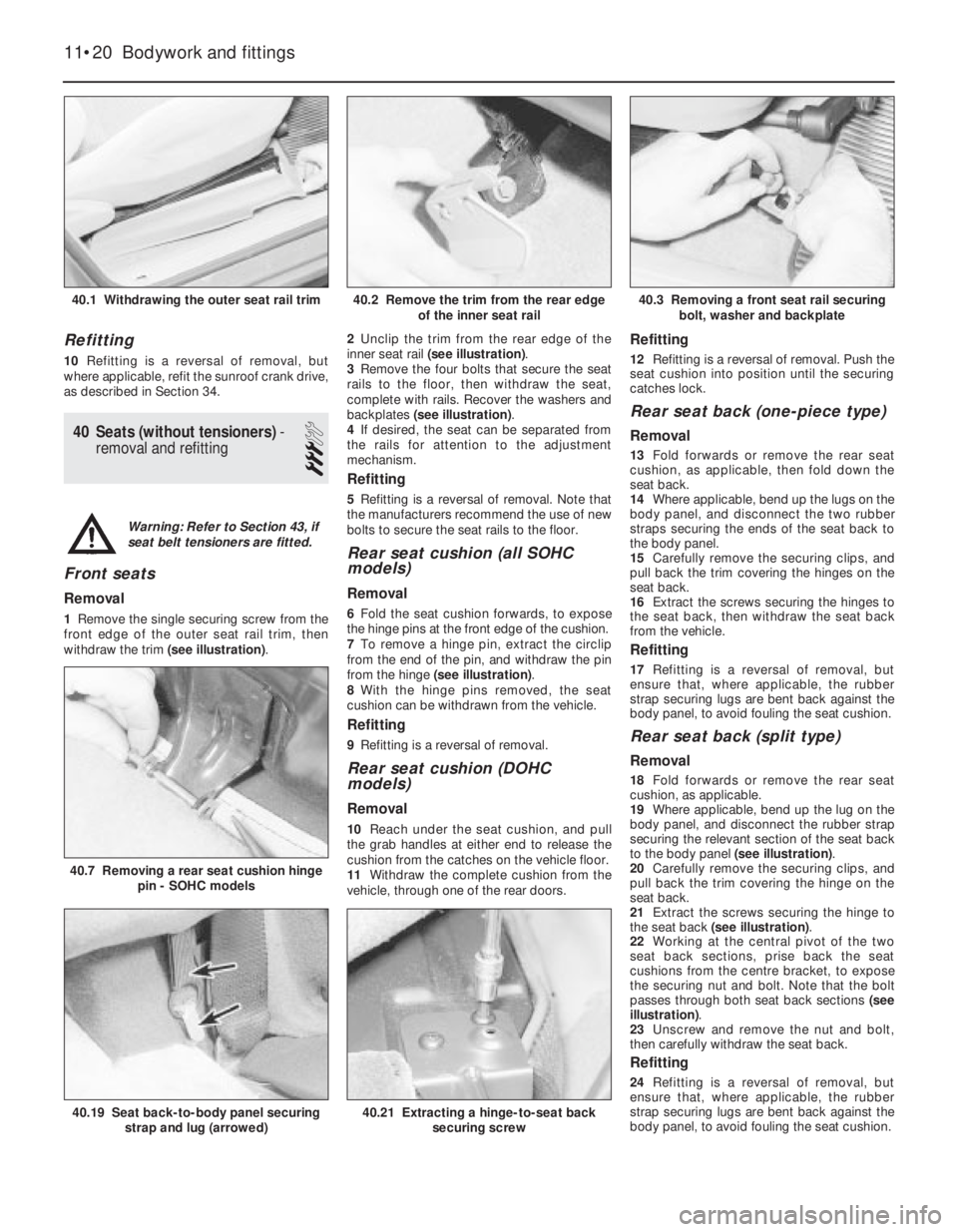
1Remove the single securing screw from the
front edge of the outer seat rail trim, then
withdraw the trim (see illustration).2Unclip the trim from the rear edge of the
inner seat rail (see illustration).
3Remove the four bolts that secure the seat
rails to the floor, then withdraw the seat,
complete with rails. Recover the washers and
backplates (see illustration).
4If desired, the seat can be separated from
the rails for attention to the adjustment
mechanism.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal. Note that
the manufacturers recommend the use of new
bolts to secure the seat rails to the floor.
Rear seat cushion (all SOHC
models)
Removal
6Fold the seat cushion forwards, to expose
the hinge pins at the front edge of the cushion.
7To remove a hinge pin, extract the circlip
from the end of the pin, and withdraw the pin
from the hinge (see illustration).
8With the hinge pins removed, the seat
cushion can be withdrawn from the vehicle.
Refitting
9Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Rear seat cushion (DOHC
models)
Removal
10Reach under the seat cushion, and pull
the grab handles at either end to release the
cushion from the catches on the vehicle floor.
11Withdraw the complete cushion from the
vehicle, through one of the rear doors.
Refitting
12Refitting is a reversal of removal. Push the
seat cushion into position until the securing
catches lock.
Rear seat back (one-piece type)
Removal
13Fold forwards or remove the rear seat
cushion, as applicable, then fold down the
seat back.
14Where applicable, bend up the lugs on the
body panel, and disconnect the two rubber
straps securing the ends of the seat back to
the body panel.
15Carefully remove the securing clips, and
pull back the trim covering the hinges on the
seat back.
16Extract the screws securing the hinges to
the seat back, then withdraw the seat back
from the vehicle.
Refitting
17Refitting is a reversal of removal, but
ensure that, where applicable, the rubber
strap securing lugs are bent back against the
body panel, to avoid fouling the seat cushion.
Rear seat back (split type)
Removal
18Fold forwards or remove the rear seat
cushion, as applicable.
19Where applicable, bend up the lug on the
body panel, and disconnect the rubber strap
securing the relevant section of the seat back
to the body panel (see illustration).
20Carefully remove the securing clips, and
pull back the trim covering the hinge on the
seat back.
21Extract the screws securing the hinge to
the seat back (see illustration).
22Working at the central pivot of the two
seat back sections, prise back the seat
cushions from the centre bracket, to expose
the securing nut and bolt. Note that the bolt
passes through both seat back sections (see
illustration).
23Unscrew and remove the nut and bolt,
then carefully withdraw the seat back.
Refitting
24Refitting is a reversal of removal, but
ensure that, where applicable, the rubber
strap securing lugs are bent back against the
body panel, to avoid fouling the seat cushion.
11•20Bodywork and fittings
40.1 Withdrawing the outer seat rail trim40.3 Removing a front seat rail securing
bolt, washer and backplate
40.7 Removing a rear seat cushion hinge
pin - SOHC models
40.21 Extracting a hinge-to-seat back
securing screw40.19 Seat back-to-body panel securing
strap and lug (arrowed)
40.2 Remove the trim from the rear edge
of the inner seat rail
Warning: Refer to Section 43, if
seat belt tensioners are fitted.
Page 240 of 525

REF
Overall length: *
Saloon models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4432 mm
Hatchback models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4352 mm
Overall width: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1876 mm
Overall height (unladen): *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1400 mm
Wheelbase: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2600 mm
Track:
Front: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1426 mm
Rear: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1423 mm
Ground clearance (minimum): *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .120 mm
Weights
Kerb weight: *
Dependent on model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1098 ± 101 kg
Maximum gross vehicle weight: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Refer to VIN plate
Maximum roof rack load: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100 kg
Maximum towing hitch downward load: *
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75 kg
Maximum towing weight: *
Trailer with brakes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1175 ± 175 kg
Trailer without brakes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .550 ± 50 kg
* Exact details depend upon model and specification.
Refer to owners handbook.
Dimensions and Weights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•1
Conversion Factors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•2
Buying Spare Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•3
Vehicle Identification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•3
General Repair Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•4
Jacking and Vehicle Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•5Radio/cassette unit Anti-theft System . . . . . . . .REF•5
Tools and Working Facilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•6
MOT Test Checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•8
Fault Finding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•12
Glossary of Technical Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•20
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .REF•25
Reference REF•1
Dimensions and Weights
Page 243 of 525

REF•4General Repair Procedures
Whenever servicing, repair or overhaul work
is carried out on the car or its components, it is
necessary to observe the following procedures
and instructions. This will assist in carrying out
the operation efficiently and to a professional
standard of workmanship.
Joint mating faces and gaskets
When separating components at their
mating faces, never insert screwdrivers or
similar implements into the joint between the
faces in order to prise them apart. This can
cause severe damage which results in oil
leaks, coolant leaks, etc upon reassembly.
Separation is usually achieved by tapping
along the joint with a soft-faced hammer in
order to break the seal. However, note that this
method may not be suitable where dowels are
used for component location.
Where a gasket is used between the mating
faces of two components, ensure that it is
renewed on reassembly, and fit it dry unless
otherwise stated in the repair procedure. Make
sure that the mating faces are clean and dry,
with all traces of old gasket removed. When
cleaning a joint face, use a tool which is not
likely to score or damage the face, and remove
any burrs or nicks with an oilstone or fine file.
Make sure that tapped holes are cleaned
with a pipe cleaner, and keep them free of
jointing compound, if this is being used, unless
specifically instructed otherwise.
Ensure that all orifices, channels or pipes
are clear, and blow through them, preferably
using compressed air.
Oil seals
Oil seals can be removed by levering them
out with a wide flat-bladed screwdriver or
similar implement. Alternatively, a number of
self-tapping screws may be screwed into the
seal, and these used as a purchase for pliers
or some similar device in order to pull the seal
free.
Whenever an oil seal is removed from its
working location, either individually or as part
of an assembly, it should be renewed.
The very fine sealing lip of the seal is easily
damaged, and will not seal if the surface it
contacts is not completely clean and free from
scratches, nicks or grooves.
Protect the lips of the seal from any surface
which may damage them in the course of
fitting. Use tape or a conical sleeve where
possible. Lubricate the seal lips with oil before
fitting and, on dual-lipped seals, fill the space
between the lips with grease.
Unless otherwise stated, oil seals must be
fitted with their sealing lips toward the
lubricant to be sealed.
Use a tubular drift or block of wood of the
appropriate size to install the seal and, if the
seal housing is shouldered, drive the seal
down to the shoulder. If the seal housing is
unshouldered, the seal should be fitted with its
face flush with the housing top face (unless
otherwise instructed).
Screw threads and fastenings
Seized nuts, bolts and screws are quite a
common occurrence where corrosion has set
in, and the use of penetrating oil or releasing
fluid will often overcome this problem if the
offending item is soaked for a while before
attempting to release it. The use of an impact
driver may also provide a means of releasing
such stubborn fastening devices, when used
in conjunction with the appropriate
screwdriver bit or socket. If none of these
methods works, it may be necessary to resort
to the careful application of heat, or the use of
a hacksaw or nut splitter device.
Studs are usually removed by locking two
nuts together on the threaded part, and then
using a spanner on the lower nut to unscrew
the stud. Studs or bolts which have broken off
below the surface of the component in which
they are mounted can sometimes be removed
using a proprietary stud extractor. Always
ensure that a blind tapped hole is completely
free from oil, grease, water or other fluid
before installing the bolt or stud. Failure to do
this could cause the housing to crack due to
the hydraulic action of the bolt or stud as it is
screwed in.
When tightening a castellated nut to accept
a split pin, tighten the nut to the specified
torque, where applicable, and then tighten
further to the next split pin hole. Never slacken
the nut to align the split pin hole, unless stated
in the repair procedure.
When checking or retightening a nut or bolt
to a specified torque setting, slacken the nut
or bolt by a quarter of a turn, and then
retighten to the specified setting. However,
this should not be attempted where angular
tightening has been used.
For some screw fastenings, notably cylinder
head bolts or nuts, torque wrench settings are
no longer specified for the latter stages of
tightening, “angle-tightening” being called up
instead. Typically, a fairly low torque wrench
setting will be applied to the bolts/nuts in
the correct sequence, followed by one or
more stages of tightening through specified
angles.
Locknuts, locktabs and washers
Any fastening which will rotate against a
component or housing in the course of
tightening should always have a washer
between it and the relevant component or
housing.
Spring or split washers should always be
renewed when they are used to lock a critical
component such as a big-end bearing
retaining bolt or nut. Locktabs which are
folded over to retain a nut or bolt should
always be renewed.
Self-locking nuts can be re-used in non-
critical areas, providing resistance can be felt
when the locking portion passes over the bolt
or stud thread. However, it should be noted
that self-locking stiffnuts tend to lose theireffectiveness after long periods of use, and in
such cases should be renewed as a matter of
course.
Split pins must always be replaced with new
ones of the correct size for the hole.
When thread-locking compound is found on
the threads of a fastener which is to be re-
used, it should be cleaned off with a wire
brush and solvent, and fresh compound
applied on reassembly.
Special tools
Some repair procedures in this manual
entail the use of special tools such as a press,
two or three-legged pullers, spring
compressors, etc. Wherever possible, suitable
readily-available alternatives to the
manufacturer’s special tools are described,
and are shown in use. Unless you are highly-
skilled and have a thorough understanding of
the procedures described, never attempt to
bypass the use of any special tool when the
procedure described specifies its use. Not
only is there a very great risk of personal injury,
but expensive damage could be caused to the
components involved.
Environmental considerations
When disposing of used engine oil, brake
fluid, antifreeze, etc, give due consideration to
any detrimental environmental effects. Do not,
for instance, pour any of the above liquids
down drains into the general sewage system,
or onto the ground to soak away. Many local
council refuse tips provide a facility for waste
oil disposal, as do some garages. If none of
these facilities are available, consult your local
Environmental Health Department for further
advice.
With the universal tightening-up of
legislation regarding the emission of
environmentally-harmful substances from
motor vehicles, most current vehicles have
tamperproof devices fitted to the main
adjustment points of the fuel system. These
devices are primarily designed to prevent
unqualified persons from adjusting the fuel/air
mixture, with the chance of a consequent
increase in toxic emissions. If such devices are
encountered during servicing or overhaul, they
should, wherever possible, be renewed or
refitted in accordance with the vehicle
manufacturer’s requirements or current
legislation.
Note: It is
antisocial and
illegal to dump
oil down the
drain. To find
the location of
your local oil
recycling
bank, call this
number free.
Page 246 of 525
Tools and Working Facilities REF•7
REF
Special tools
The tools in this list are those which are not
used regularly, are expensive to buy, or which
need to be used in accordance with their
manufacturers’ instructions. Unless relatively
difficult mechanical jobs are undertaken
frequently, it will not be economic to buy
many of these tools. Where this is the case,
you could consider clubbing together with
friends (or joining a motorists’ club) to make a
joint purchase, or borrowing the tools against
a deposit from a local garage or tool hire
specialist. It is worth noting that many of the
larger DIY superstores now carry a large
range of special tools for hire at modest rates.
The following list contains only those tools
and instruments freely available to the public,
and not those special tools produced by the
vehicle manufacturer specifically for its dealer
network. You will find occasional references
to these manufacturers’ special tools in the
text of this manual. Generally, an alternative
method of doing the job without the vehicle
manufacturers’ special tool is given. However,
sometimes there is no alternative to using
them. Where this is the case and the relevant
tool cannot be bought or borrowed, you will
have to entrust the work to a dealer.
MValve spring compressor
MValve grinding tool
MPiston ring compressor
MPiston ring removal/installation tool
MCylinder bore hone
MBalljoint separator
MCoil spring compressors (where applicable)
MTwo/three-legged hub and bearing puller
MImpact screwdriver
MMicrometer and/or vernier calipers
MDial gauge
MStroboscopic timing light
MDwell angle meter/tachometer
MUniversal electrical multi-meter
MCylinder compression gauge
MHand-operated vacuum pump and gauge
MClutch plate alignment set
MBrake shoe steady spring cup removal tool
MBush and bearing removal/installation set
MStud extractors
MTap and die set
MLifting tackle
MTrolley jack
Buying tools
Reputable motor accessory shops and
superstores often offer excellent quality tools
at discount prices, so it pays to shop around.
Remember, you don’t have to buy the most
expensive items on the shelf, but it is always
advisable to steer clear of the very cheap
tools. Beware of ‘bargains’ offered on market
stalls or at car boot sales. There are plenty of
good tools around at reasonable prices, but
always aim to purchase items which meet the
relevant national safety standards. If in doubt,
ask the proprietor or manager of the shop for
advice before making a purchase.
Care and maintenance of tools
Having purchased a reasonable tool kit, it is
necessary to keep the tools in a clean and
serviceable condition. After use, always wipe
off any dirt, grease and metal particles using a
clean, dry cloth, before putting the tools away.
Never leave them lying around after they have
been used. A simple tool rack on the garage
or workshop wall for items such as
screwdrivers and pliers is a good idea. Store
all normal spanners and sockets in a metal
box. Any measuring instruments, gauges,
meters, etc, must be carefully stored where
they cannot be damaged or become rusty.
Take a little care when tools are used.
Hammer heads inevitably become marked,
and screwdrivers lose the keen edge on their
blades from time to time. A little timely
attention with emery cloth or a file will soon
restore items like this to a good finish.
Working facilities
Not to be forgotten when discussing tools
is the workshop itself. If anything more than
routine maintenance is to be carried out, a
suitable working area becomes essential.
It is appreciated that many an owner-
mechanic is forced by circumstances to
remove an engine or similar item without the
benefit of a garage or workshop. Having done
this, any repairs should always be done under
the cover of a roof.
Wherever possible, any dismantling should
be done on a clean, flat workbench or table at
a suitable working height.
Any workbench needs a vice; one with a jaw
opening of 100 mm is suitable for most jobs.
As mentioned previously, some clean dry
storage space is also required for tools, as well
as for any lubricants, cleaning fluids, touch-up
paints etc, which become necessary.
Another item which may be required, and
which has a much more general usage, is an
electric drill with a chuck capacity of at least 8
mm. This, together with a good range of twist
drills, is virtually essential for fitting
accessories.
Last, but not least, always keep a supply of
old newspapers and clean, lint-free rags
available, and try to keep any working area as
clean as possible.
Stroboscopic timing light Stud extractor setCompression tester
Dial test indicator (“dial gauge”)Micrometer set