1988 OPEL CALIBRA fuel
[x] Cancel search: fuelPage 9 of 525

4If adjustment is necessary, release the
clamp screw and turn the cam plate in the
desired direction. Tighten the clamp screw,
and recheck the pump delivery (see
illustration).
Removal
5Proceed as described in Section 17,
paragraphs 1 and 2.
6Thoroughly clean all external dirt from the
area around the accelerator pump housing.
7Remove the four securing screws and lift off
the accelerator pump cover. Recover the
diaphragm, spring, valve retainer and valve.
Note the orientation of the valve retainer.
Refitting
8Clean the mating faces of the cover and
housing.
9Check the condition of the valve, and renew
if necessary.
10Begin refitting by locating the valve, valve
retainer and spring in the housing. Note that
the valve retainer can only be fitted in one
position. The larger diameter of the spring
should rest against the valve retainer.
11Locate the diaphragm on the housing,
ensuring that the spring is correctly seated,
and refit the cover. Tighten the cover securing
screws progressively to avoid distorting the
diaphragm (see illustration).
12Further refitting is a reversal of removal.
19Automatic choke unit -
removal, refitting and
adjustment
3
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding. A
tachometer and an exhaust gas analyser will
be required to check the idle speed and
mixture on completion. If the coolant housing
is removed, new O-rings will be required for
refitting
Removal
1Proceed as described in Section 17,
paragraphs 1 and 2.
2Note the position of the bi-metal housing
alignment marks as an aid to refitting, if
necessary making additional marks for clarity,
then remove the three securing screws and lift
off the bi-metal housing. Place the housing to
one side, taking care not to strain the coolant
hoses or electric choke heater wiring.
3Remove the three screws securing the
choke housing to the carburettor body, and
withdraw the choke assembly, taking care not
to bend the choke operating rod.
4If it is necessary to remove the bi-metal
housing for renewal, continue as follows;
otherwise go on to paragraph 8.
5Identify the automatic choke coolant hose
locations as an aid to refitting, then
disconnect the hoses. Be prepared for
coolant spillage, and either plug the hoses, or
secure them with their ends facing upwards,
to prevent further loss of coolant.
6Disconnect the wiring from the electric
choke heater, and withdraw the bi-metal
housing.
7The coolant housing can be separated from
the bi-metal housing by unscrewing the
central securing bolt. Recover the O-rings
from under the bolt head, and from the rim of
the coolant housing.
Refitting
8Begin refitting by locating the choke
assembly on the carburettor body, ensuring
that the lever on the choke assembly engages
with the choke operating rod. Tighten the
three securing screws.
9Check and if necessary adjust the choke
valve gap and the fast idle cam position, as
described in paragraphs 15 to 19, of this
Section.10Connect the bi-metal spring to the choke
lever, position the bi-metal housing on the
choke housing, and loosely fit the securing
screws. Align the marks on the bi-metal
housing and the choke housing as noted
during removal, then tighten the securing
screws.
11Where applicable, refit the coolant
housing to the bi-metal housing, using new O-
rings if necessary, and reconnect the coolant
hoses and electric choke heater wiring.
12Further refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
13If the coolant hoses have been
disconnected, check the coolant level, as
described in Chapter 3.
14Check and if necessary adjust the fast idle
speed, as described in paragraphs 25 to 34,
of this Section.
Adjustment
Choke valve gap
15With the bi-metal housing removed as
described in paragraphs 2 to 4, of this
Section, continue as follows.
16Press the choke operating lever fully
clockwise, and retain it in position with a
rubber band.
17Move the throttle lever to the fully open
position, and measure the choke valve gap
between the lower side of the choke plate and
the wall of the primary barrel. Check that the
gap is as given in the Specifications.
18If necessary, adjust the choke valve gap
by bending the “adjuster segment (2)” If the
gap is too small, enlarge gap “B”, by levering
with a screwdriver. If the gap is too large,
decrease gap “B” using a pair of pliers (see
illustration).
19If no further adjustments are to be carried
out, refit the bi-metal housing, as described in
paragraphs 10 to 14, of this Section.
Fuel and exhaust systems - carburettor models 4A•9
18.11 Carburettor accelerator pump components
1 Cover with operating lever
2 Diaphragm
3 Spring4 Valve
5 Air passage
18.4 Accelerator pump delivery adjustment: “+” to
increase, “-” to reduce
4A
Page 10 of 525
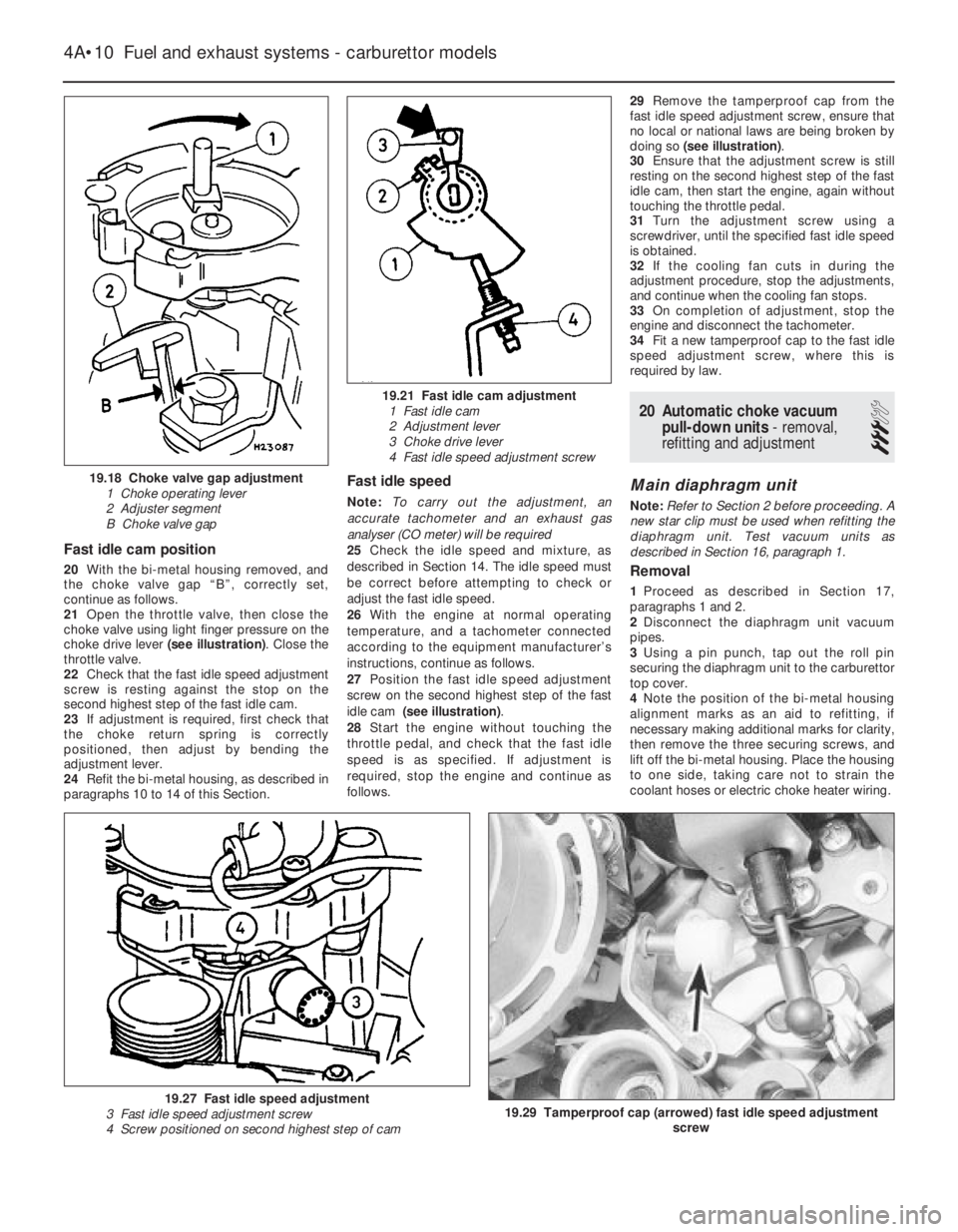
Fast idle cam position
20With the bi-metal housing removed, and
the choke valve gap “B”, correctly set,
continue as follows.
21Open the throttle valve, then close the
choke valve using light finger pressure on the
choke drive lever (see illustration). Close the
throttle valve.
22Check that the fast idle speed adjustment
screw is resting against the stop on the
second highest step of the fast idle cam.
23If adjustment is required, first check that
the choke return spring is correctly
positioned, then adjust by bending the
adjustment lever.
24Refit the bi-metal housing, as described in
paragraphs 10 to 14 of this Section.
Fast idle speed
Note: To carry out the adjustment, an
accurate tachometer and an exhaust gas
analyser (CO meter) will be required
25Check the idle speed and mixture, as
described in Section 14. The idle speed must
be correct before attempting to check or
adjust the fast idle speed.
26With the engine at normal operating
temperature, and a tachometer connected
according to the equipment manufacturer’s
instructions, continue as follows.
27Position the fast idle speed adjustment
screw on the second highest step of the fast
idle cam (see illustration).
28Start the engine without touching the
throttle pedal, and check that the fast idle
speed is as specified. If adjustment is
required, stop the engine and continue as
follows.29Remove the tamperproof cap from the
fast idle speed adjustment screw, ensure that
no local or national laws are being broken by
doing so (see illustration).
30Ensure that the adjustment screw is still
resting on the second highest step of the fast
idle cam, then start the engine, again without
touching the throttle pedal.
31Turn the adjustment screw using a
screwdriver, until the specified fast idle speed
is obtained.
32If the cooling fan cuts in during the
adjustment procedure, stop the adjustments,
and continue when the cooling fan stops.
33On completion of adjustment, stop the
engine and disconnect the tachometer.
34Fit a new tamperproof cap to the fast idle
speed adjustment screw, where this is
required by law.
20Automatic choke vacuum
pull-down units - removal,
refitting and adjustment
3
Main diaphragm unit
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding. A
new star clip must be used when refitting the
diaphragm unit. Test vacuum units as
described in Section 16, paragraph 1.
Removal
1Proceed as described in Section 17,
paragraphs 1 and 2.
2Disconnect the diaphragm unit vacuum
pipes.
3Using a pin punch, tap out the roll pin
securing the diaphragm unit to the carburettor
top cover.
4Note the position of the bi-metal housing
alignment marks as an aid to refitting, if
necessary making additional marks for clarity,
then remove the three securing screws, and
lift off the bi-metal housing. Place the housing
to one side, taking care not to strain the
coolant hoses or electric choke heater wiring.
4A•10Fuel and exhaust systems - carburettor models
19.18 Choke valve gap adjustment
1 Choke operating lever
2 Adjuster segment
B Choke valve gap
19.21 Fast idle cam adjustment
1 Fast idle cam
2 Adjustment lever
3 Choke drive lever
4 Fast idle speed adjustment screw
19.29 Tamperproof cap (arrowed) fast idle speed adjustment
screw19.27 Fast idle speed adjustment
3 Fast idle speed adjustment screw
4 Screw positioned on second highest step of cam
Page 11 of 525

5Remove the three screws securing the
choke assembly to the carburettor body.
Allow the choke assembly to drop down, but
do not disconnect the choke linkage.
6Remove the star clip that secures the
diaphragm unit to the carburettor top cover,
and withdraw the diaphragm unit.
Refitting
7Refitting is a reversal of removal, but use a
new star clip to secure the diaphragm unit to
the carburettor top cover. Before refitting the
air box to the top of the carburettor, check
and if necessary adjust the choke pull-down,
as follows.
Vacuum pull-down
Adjustment
8With the air cleaner or air box removed from
the top of the carburettor, as described in
Section 17, paragraph 2, continue as follows.
9Note the position of the bi-metal housing
alignment marks as an aid to refitting, if
necessary making additional marks for clarity,
then remove the three securing screws, and
lift off the bi-metal housing. Place the housing
to one side, taking care not to strain the
coolant hoses or electric choke heater wiring.
10Position the fast idle speed adjustment
screw on the highest step of the fast idle cam,
and check that the choke valve is closed.
11Move the pull-down arm towards the
diaphragm unit by pushing on the adjustment
screw until resistance is felt. Hold the arm in
this position.
12Using a drill shank of appropriate
diameter, or a similar item, measure the
clearance between the lower side of the
choke plate and the wall of the primary barrel
(see illustrations). Check that the clearance
is as given for the “small” choke pull-down
gap in the Specifications.
13If adjustment is necessary, turn the
adjustment screw in the appropriate direction,
using an Allen key, until the clearance is
correct.14Now push the pull-down arm towards the
diaphragm unit as far as its stop, and hold the
arm in this position.
15As before measure the clearance between
the lower side of the choke plate and the wall
of the primary barrel. Check that the
clearance is as given for the “large” choke
pull-down gap in the Specifications.
16If adjustment is necessary, turn the
adjustment screw in the appropriate direction
until the clearance is correct.
17Connect the bi-metal spring to the choke
lever, position the bi-metal housing on the
choke housing and loosely fit the securing
screws. Align the marks on the bi-metal
housing and the choke housing as noted
during removal, then tighten the securing
screws.
18Refit the air box to the top of the
carburettor on completion.
Secondary pull-down solenoid
Removal
19This unit operates in conjunction with the
main diaphragm unit.
20To remove the solenoid unit, first continue
as described in Section 17, paragraphs 1 and
2.
21Disconnect the diaphragm unit vacuum
pipe.22Disconnect the wiring plug, then unscrew
the securing screw, and withdraw the
solenoid unit and its mounting bracket from
the carburettor. Note that the securing screw
also secures the wiring plug earth lead (see
illustration).
Refitting
23Refitting is a reversal of removal, but
ensure that the wiring plug earth lead is in
place under the solenoid bracket securing
screw.
21Carburettor filter -removal
and refitting
3
Removal
1A small tubular filter gauze is fitted into the
carburettor top cover’s fuel inlet union to
remove any particles of dirt from the fuel.
2To ensure a clean fuel supply and to
prevent the risk of misfiring, poor starting or
other problems due to a restricted fuel supply,
this filter must be cleaned and/or renewed at
the interval specified in Chapter 1.
3To reach the filter, remove the air cleaner or
air box, as applicable, then disconnect and
plug the hose from the fuel pump or vapour
separator to the top cover union.
4Remove the filter by hooking it out with a
small screwdriver, or by snaring it with a long
thin screw (3 mm thread size, screwed
approximately 5 mm into the filter).
5If the filter is blocked or heavily fouled, or if
it is torn, distorted or damaged in any way, it
must be renewed. If it is fit for further use,
clean it using a jet of compressed air or by
brushing away particles of dirt with an old soft
toothbrush. Then flushing it in clean solvent,
taking care not to allow any overspray to get
into your eyes; if petrol is used, take care to
prevent the risk of fire.
Fuel and exhaust systems - carburettor models 4A•11
20.12B Checking the vacuum pull-down gap using a twist drill
20.22 Secondary choke pull-down
solenoid securing screw and earth lead
20.12A Choke vacuum pull-down adjustment
1 Adjustment screw 2 Diaphragm unit A Twist drill
4A
Page 12 of 525

Refitting
6On refitting the filter, press it into the union
until it catches (see illustration). The
remainder of the reassembly procedure is the
reverse of removal.
22Throttle valve dashpot
(automatic models) -
adjustment
2
1Remove the air cleaner or air box, refer to
Section 3.
2Ensure that the lever (see illustration)is in
the idling position.
3Slacken the locknut and unscrew the
dashpot until a gap of 0.05 mm (0.002 in)
exists between the lever and the dashpot tip.
Then screw the dashpot downwards 2.5 full
turns and tighten the locknut.
4Refit all removed components.
23Throttle position sensor
(automatic transmission
models) - removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery earth lead.
2Disconnect the wiring plug from the sensor.
3Either unscrew the two securing screws
and withdraw the sensor from its bracket, or
unbolt the bracket.
Refitting
4Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure, noting the following points.
a)Install the sensor when the throttle valve
is fully closed and ensure that the
adapter, “1” (see illustration),seats
correctly on the throttle valve spindle.
b)Tighten the screws carefully.
24Idle speed increase valve -
testing
2
1Certain models are fitted with an idle speed
increase valve that is attached to the side of
the carburettor.
2To test the operation of this valve first
remove the air filter and vacuum hose.
3With the valve’s plug connected, have
someone turn the ignition on (but do not start
the engine). A mechanical shifting noise
should be heard. If not replace the unit.
4After refitting replace the vacuum hose and
air filter.
25Idle cut-off solenoid (1.8 litre
models) - description and
testing
2
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
Description
1On 1.8 litre models, the carburettor is fitted
with an idle cut-off solenoid. This is an
electrically operated valve, which interrupts
the idle mixture circuit when the ignition isswitched off, thus preventing the engine from
running-on (see illustration).
2The idle cut-off solenoid is energised all the
time that the ignition is switched on. A
defective solenoid, or a break in its power
supply, will cause the engine to stall or idle
roughly, although it will run normally at speed.
Testing
3If the operation of the solenoid is suspect,
first check that battery voltage is present at
the solenoid terminal when the ignition is
switched on. Use a 12 volt test lamp or similar
test device.
4If no voltage is present, then the fault lies in
the wiring to the solenoid. If voltage is
present, the solenoid can be tested as
follows.
5With the solenoid unscrewed from the
carburettor, connect the body of the solenoid
to the negative terminal of a 12 volt battery.
When the battery positive terminal is
connected to the solenoid centre terminal,
there should be an audible click, and the
needle at the tip of the solenoid should
retract.
6A defective idle cut-off solenoid must be
renewed.
26Inlet manifold - removal and
refitting
3
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding. A
new manifold gasket must be used on refitting
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Drain the cooling system, as described in
Chapter 3.
3Proceed as described in Section 13,
paragraphs 2 to 7 inclusive, ignoring the
reference to coolant spillage in paragraph 5.
4A•12Fuel and exhaust systems - carburettor models
21.6 Refitting the carburettor fuel filter
23.4 Throttle position sensor - models with automatic
transmission
1 Adapter 2 Sensor22.2 Adjusting the throttle valve dashpot - models with
automatic transmission
1 Lever2 Locknut3 Dashpot
Page 13 of 525

4Disconnect the coolant hose from the rear
of the manifold (see illustration).
5Where applicable, disconnect the camshaft
cover breather hose from the rear of the
manifold (see illustration).
6Unscrew the union and disconnect the
brake servo vacuum hose from the manifold.
7On 1.4 and 1.6 litre models, disconnect the
wiring from the temperature gauge sender.
8Unscrew and remove the top alternator
mounting nut and bolt.
9On 1.4 and 1.6 litre models, disconnect and
remove the stub hose that connects the
crankcase breather tube to the rear of the
camshaft housing.
10Make a final check to ensure that all
relevant hoses, pipes and wires have been
disconnected.
11Unscrew the securing nuts, and withdraw
the manifold from the cylinder head (see
illustration). Note the position of the rear
engine lifting bracket, which is secured by one
of the manifold nuts, and recover the manifoldgasket.
12It is possible that some of the manifold
studs may be unscrewed from the cylinder
head when the manifold securing nuts are
unscrewed. In this event, the studs should be
screwed back into the cylinder head once the
manifold has been removed, using two
manifold nuts locked together.
13If desired, the carburettor can be removed
from the manifold, referring to Section 13, if
necessary.
Refitting
14Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
15If the carburettor has been removed from
the manifold, refit it, using a new gasket.
16If the alternator mounting bracket has
been unbolted from the manifold, refit it
before refitting the manifold, as access to the
securing bolt is extremely limited once the
manifold is in place.
17Refit the manifold using a new gasket,and ensure that the engine lifting bracket is in
place under the relevant manifold nut. Tighten
the nuts to the specified torque.
18Ensure that all relevant hoses, pipes and
wires are correctly reconnected.
19Refill the cooling system, as described in
Chapter 3.
20Check the throttle cable free play and
adjust if necessary, as described in Section
11.
21If the carburettor has been disturbed,
check and if necessary adjust the idle speed
and mixture, as described in Section 14.
Fuel and exhaust systems - carburettor models 4A•13
26.5 . . .and the camshaft cover breather
hose (arrowed) from the inlet manifold -
1.6 litre model
26.11 Withdrawing the inlet manifold -
1.6 litre model
26.4 Disconnecting the coolant hose . . .
4A
25.1 Carburettor idle cut-off solenoid
(arrowed) - 1.8 litre models
Page 20 of 525
3To remove the cigarette lighter assembly,
simply pull it from the illumination ring
assembly. If desired, the illumination ring
assembly can be removed, by pulling it from
the housing after depressing the retaining
clips.
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of removal.
16Clock - removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Using a thin-bladed screwdriver, carefully
prise the clock from the facia panel.
3Disconnect the wiring plugs and withdraw
the clock (see illustration).
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of removal.
17Heated front seats - general
2
Heating pads are fitted to the front seats of
some models. Before attempting to remove a
seat so equipped, disconnect the battery and
the leads from the heating pad.
18Instrument panel -removal
and refitting
3
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the steering wheel, (Chapter 10).
3Remove the steering column shrouds, and
the instrument panel upper and lower trim
panels, (Chapter 11).
4Remove the single upper, and two lower,
instrument panel securing screws (see
illustration).
5Carefully withdraw the instrument panel,
and disconnect the speedometer cable and
the two wiring plugs. Note that the
speedometer cable is retained by a clip, which
must be pressed towards the speedometer to
release the cable (see illustration).6If desired, the instrument panel can be
dismantled, with reference to Section 19.
Refitting
7Refitting is a reversal of removal, but ensure
that the speedometer cable is not kinked or
twisted between the instrument panel and the
bulkhead as the panel is refitted.
19Instrument panel
components - removal and
refitting
3
1With the instrument panel removed, as
described in Section 18, continue as follows.
Panel illumination and warning
lamp bulbs
Removal
2Twist the relevant bulbholder clockwise,
and withdraw it from the printed circuit board
on the rear of the instrument panel (see
illustration).
3The bulbs are integral with the bulbholders,
and must be renewed as a unit.
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Voltage stabiliser
Removal
5Remove the single securing screw from the
rear of the instrument panel, then pull the
voltage stabiliser from the contacts on the
printed circuit board (see illustration).
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Fuel and temperature gauges -
“low series” models
Removal
7Pull the trip meter reset pin from the front of
the panel.
8Release the two retaining clips at the top of
the panel, and remove the panel shroud (see
illustration).
9Unscrew the two securing nuts, and
withdraw the relevant gauge through the front
of the instrument panel.
12•6Body electrical systems
16.3 Disconnecting the wiring plugs from
the clock
18.5 Disconnecting an instrument panel
wiring plug. Note speedometer cable
retaining clip (arrowed)
19.8 Removing the instrument panel
shroud19.5 Instrument panel voltage stabiliser
(arrowed)19.2 Withdrawing an instrument panel
illumination lamp bulb
18.4 Unscrewing a lower instrument panel
securing screw
Page 21 of 525

Refitting
10Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Fuel and temperature gauge
assembly -“high series” models
11The procedure is as described in
paragraphs 7 to 10 inclusive, except that the
gauge assembly is secured by four nuts.
Tachometer
12The procedure is as described in
paragraphs 7 to 10 inclusive except that the
tachometer is secured by three nuts (see
illustration).
Speedometer
Removal
13Proceed as described in paragraphs 7
and 8.
14Extract the four securing screws from the
rear of the panel (see illustration).
Refitting
15Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Printed circuit board
Removal
16Remove all bulbs and instruments, and
the voltage stabiliser, as described previously
in this Section.
17Carefully peel the printed circuit board
from the instrument panel.
Refitting
18Refitting is a reversal of removal, but
ensure that the printed circuit board is seated
correctly on the rear of the instrument panel.
20Trip computer components -
removal and refitting
2
1Disconnect the battery lead.
Display module
Removal
2Using a thin-bladed screwdriver, carefully
prise the module from the facia panel.
3Disconnect the wiring plug and withdraw
the module.
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Display module illumination bulb
Removal
5Remove the display module, as described
previously in this Section.
6Using a length of rubber sleeving of similar
diameter, or an alternator tool, extract the
bulb by inserting the tool through the hole in
the side of the display module (see
illustration).
Refitting
7Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Operating switch
Removal
8Remove the rear section of the centre
console, as described in Chapter 11.
9Release the wiring plug from the switch
using a screwdriver.
10Lift the switch, then pull it down and out
from the centre console.
Refitting
11Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Outside air temperature sensor
Removal
12The sensor is located at the left-hand end
of the front bumper (see illustration).
13Prise the cover cap from the bumper, then
unclip the sensor, and disconnect the wiring
plug.
Refitting
14Refitting is a reversal of removal.
21Check control system
components - removal and
refitting
3
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
Warning lamp bulbs
2The warning lamp bulbs are located in the
instrument panel, and removal and refitting
are described in Section 19.
Control module
Removal
3The control module is located behind the
passenger side of the facia, above the
glovebox.
4Remove the glovebox assembly, as
described in Chapter 11.
5Disconnect the control module wiring plug,
then release the control module from its
mounting and withdraw the unit.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Coolant level sensor
Removal
7The coolant level sensor is integral with the
coolant expansion tank cap.
8Disconnect the wiring from the top of the
cap, then unscrew the cap and withdraw it
from the expansion tank.
9If faulty, the complete cap assembly must
be renewed.
Refitting
10Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Washer fluid level sensor
Removal
11The sensor is mounted in the side of the
fluid reservoir.
12Disconnect the wiring from the sensor,
then unscrew the sensor from the fluid
reservoir. If the fluid level is above the level of
the sensor, be prepared for fluid spillage.
Refitting
13Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Body electrical systems 12•7
20.6 Removing the trip computer display
module illumination bulb20.12 Trip computer outside air
temperature sensor location (arrowed)
19.14 Speedometer securing screws
(arrowed)19.12 Tachometer securing nuts (arrowed)
12
Page 30 of 525
Centre console-mounted
switches
Removal
5The switches must be removed as a
complete assembly, and cannot be
dismantled. If one of the switches is faulty, the
complete assembly must be renewed.
6Remove the rear section of the centre
console, as described in Chapter 11.
7Release the securing clips, and withdraw
the switch assembly through the top of the
centre console.
Refitting
8Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Operating motors
9Remove the door window regulator, as
described in Chapter 11.
10To remove the motor assembly from the
front door window regulator, unscrew the
three motor securing nuts, and the single
screw securing the pulse pick-up unit to the
regulator assembly. Withdraw the motor,
complete with the pulse pick-up unit. Note
that if the motor or pick-up unit is/are faulty,
the two components must be renewed as an
assembly, as no spare parts are available (see
illustration).
11The motor assembly fitted to the rear door
window regulator is an integral part of the
regulator, and no attempt should be made at
dismantling. If faulty, the complete
motor/regulator assembly must be renewed,
as no spares are available.
45Electric window controls -
programming
1
1Whenever the battery is disconnected, or any
of the electric window components are removed,
on completion of work, the electric window
controls must be programmed as follows.
2Close all doors, and switch on the ignition.
3Close one of the windows by pressing the
relevant operating switch. Press and hold the
switch for a further five seconds after the
relevant window has fully closed.4Repeat the procedure for the remaining
window(s).
46Central door locking
components -removal and
refitting
3
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
Electronic control module
Removal
2The module is mounted in the driver’s
footwell, behind the side trim panel.
3Remove the driver’s footwell side trim
panel, as described in Chapter 11.
4Unscrew the two securing nuts, and lift the
module from the body panel (see
illustration).
5Depress the retaining clip to release the
wiring plug, then withdraw the module.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Operating switch
Removal
7The operating switch takes the form of a
microswitch, mounted inside the door at the
rear of the exterior handle assembly.8Remove the door inner trim panel, as
described in Chapter 11.
9Peel back the plastic insulating sheet
sufficiently to gain access to the exterior
handle.
10Unclip the microswitch from the rear edge
of the exterior handle assembly, and
disconnect the switch wiring plug from the
door wiring harness, then withdraw the switch
(see illustration).
Refitting
11Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Door lock operating motor
Removal
12Remove the door lock, as described in
Chapter 11.
13Disconnect the lock operating rod from
the motor.
14Remove the two securing screws, and
withdraw the motor from the lock assembly.
Refitting
15Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Tailgate/boot lid lock operating
motor
Removal
16On Hatchback models, extract the
securing screws and remove the rear tailgate
trim panel.
17Remove the two securing screws, and
manipulate the motor to disconnect the lock
operating rod.
18Withdraw the motor and disconnect the
wiring plug (see illustration).
Refitting
19Refitting is a reversal of removal.
Fuel filler flap lock operating
motor
Removal
20Remove the right-hand rear quarter trim
panels, as described in Chapter 11.
21Disconnect the wiring plug from the rear
of the motor (see illustration).
12•16Body electrical systems
44.10 Front door electric window motor
securing nuts and pulse pick-up securing
screw (arrowed)
46.10 Central door locking operating
microswitch (arrowed) in driver’s door46.18 Disconnecting the wiring plug from
the tailgate lock operating motor -
Hatchback model46.4 Unscrewing a central door locking
control module securing nut