1983 FIAT UNO check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 163 of 303

9Turn the engine clockwise using a suitable
socket on the crankshaft pulley bolt, until the
exhaust valve of No 1 cylinder (valve No 1) is
fully closed; ie the cam lobe is pointing
directly upwards. Alternatively, the engine can
be turned by jacking up one front corner of
the vehicle and supporting it securely on an
axle stand (apply the handbrake and chock
the diagonally-opposite rear wheel before
jacking), engaging top gear and turning the
raised roadwheel in the forward direction of
travel. In both cases, it will be easier to turn
the engine if the spark plugs are removed, but
if this is done, take care not to allow dirt or
other foreign matter to enter the spark plug
holes.
10Insert a feeler gauge of the correct
thickness between the cam follower shim and
the heel of the No 1 cam lobe (photo). If
necessary, increase or reduce the thickness
of the feeler gauge until it is a firm sliding fit.
Record the thickness of the feeler gauge,
which will represent the valve clearance for
this particular valve.
11Turn the crankshaft, and repeat the
procedure for the remaining valves, recording
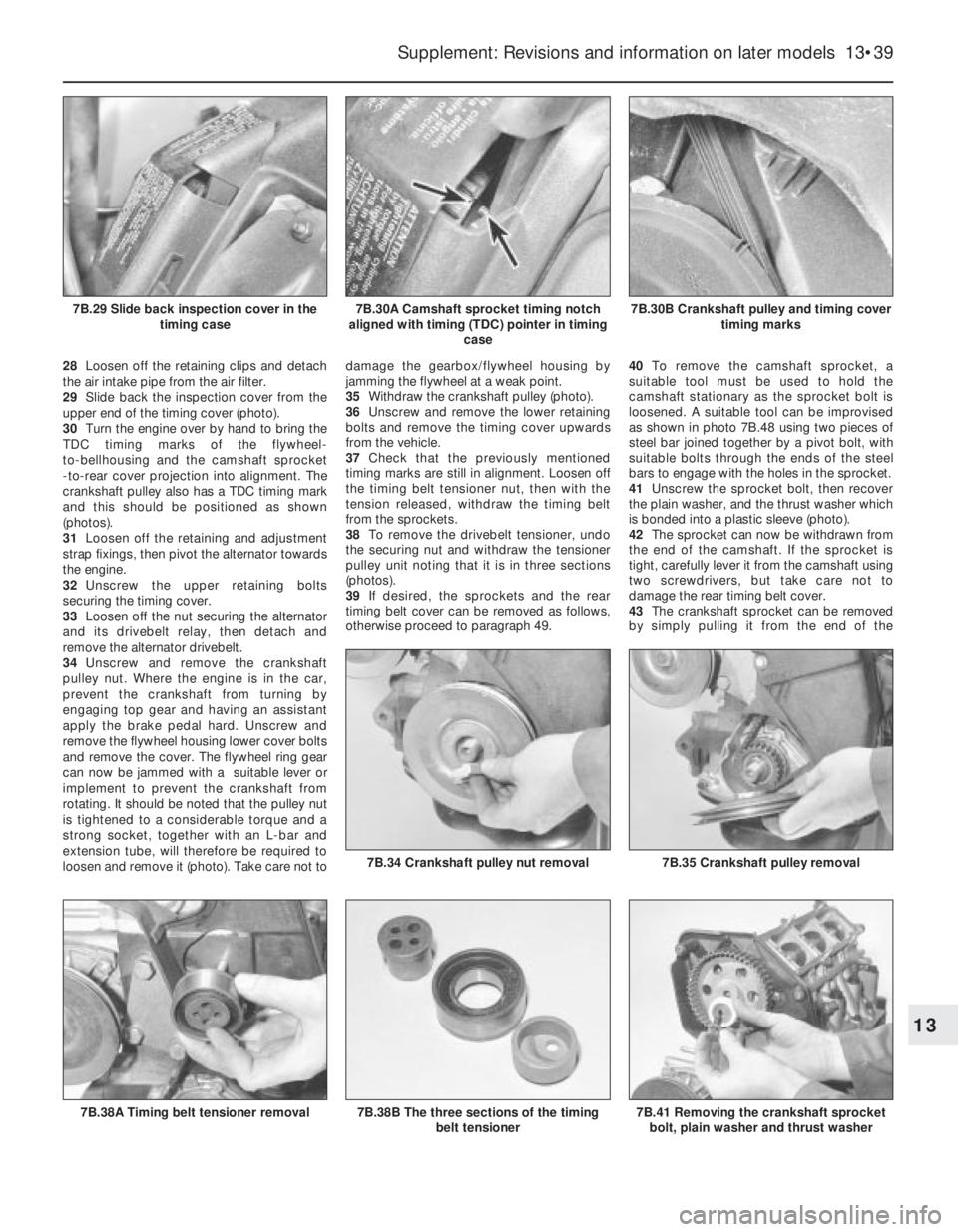
their respective clearances. Note that the
clearance for inlet and exhaust valves differs.
12If a clearance is incorrect, the relevant
cam follower shim must be removed, and a
thicker or thinner shim must be fitted to
achieve the correct clearance. To remove a
shim proceed as follows.
13Turn the crankshaft until the relevant cam
lobe is pointing directly upwards.
14The cam follower must now be depressed
in order to extract the shim. FIAT special tool
No 1860642000 is available for this purpose,
but alternatively a suitable tool can be
improvised (photo). The tool should locate on
the rim of the cam follower, leaving enough
room for the shim to be prised out by means
of the cut-outs provided in the cam follower
rim. Depress the cam follower by turning the
crankshaft as described previously until the
relevant cam lobe is pointing directly
downwards, then fit the tool between the
camshaft and the edge of the cam follower to
retain the cam follower in the depressed
position.
15Ensure that the tool is securely located, asthere is a risk of personal injury if the tool is
dislodged whilst the cam follower is
depressed, then turn the crankshaft until the
relevant cam lobe is pointing directly
upwards, leaving sufficient room to extract
the shim (photo). A pair of angle-nosed pliers
will greatly ease removal of the shim.
16Once the shim has been extracted,
establish its thickness. The thickness in mm
should be stamped into the face of the shim,
although it is possible for wear to obliterate
the number, in which case the use of a metric
micrometer is the only way to accurately
establish the thickness.
17Refer to the clearance recorded for the
valve concerned. If the clearance recorded
was larger than that specified, a thicker shim
must be fitted, and if the clearance recorded
was smaller than that specified, a thinner shim
must be fitted. The required thickness of shim
can be
calculated as follows.
Sample calculation - clearance too large:
Desired clearance (A) 0.40 mm
Measured clearance (B) 0.45 mm
Difference (B - A) + 0.05 mm
Original shim thickness 3.40 mm
Required shim thickness 3.40 + 0.05 =
3.45 mm
Sample calculation - clearance too small:
Desired clearance (A) 0.50 mm
Measured clearance (B) 0.35 mm
Difference (B - A) 0.15 mm
Original shim thickness 4.55 mm
Required shim thickness 4.55 - 0.15 =
4.40 mm
18Shims are available in thicknesses from
3.20 to 4.70 mm, in steps of 0.05 mm. Note
that if several shims have to be changed, they
can often be interchanged, thus avoiding the
need by buy more new shims than are
necessary.
19The shims should be fitted to the cam
followers with the stamped thickness marking
against the face of the cam follower.
20After fitting a shim, rotate the crankshaft
as described previously until the relevant cam
lobe is pointing directly downwards (resting
on the shim), then carefully remove the tool
used to retain the follower in the depressed
position.21Re-check each relevant valve clearance
after fitting the shim.
22On completion, where applicable, lower
the vehicle to the ground.
23Refit the camshaft cover, using a new
gasket.
24On the ie engine, reconnect the hoses and
refit the air cleaner unit.
25On the Turbo ie engine, reconnect the air
hose and the accelerator cable.
Timing belt tensioner
and sprockets -
removal and refitting
#
Note: The timing belt must be renewed after
removal: never refit a used drivebelt. When
fitting the new timing belt it will need to be
correctly tensioned and to achieve this the
manufacturers specify the use of special tools
1860745200 (18760745300 on Turbo model)
and 1860745100. If these tools are not readily
available, an approximate setting can be
made, but in this instance it is strongly
recommended that the car be taken to a FIAT
dealer at the earliest opportunity to have the
belt tension checked and correctly set using
the recommended tools.
26Loosen off the front right-hand side wheel
bolts, then raise and support the car at the
front end on axle stands. Remove the front
right-hand roadwheel.
27Remove the underwing shield from the
right-hand wheel arch to allow access to the
lower timing cover and alternator fixings (photo).
13•38 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
7B.27 Underwing shield (A) showing
central compression pin (B) and retaining
clip (C). Drive pin through clip to remove
7B.15 Removing a shim from a cam
follower7B.14 Special tool for retaining cam
follower in depressed position7B.10 Measuring a valve clearance
(No 2 valve shown)
Page 164 of 303
28Loosen off the retaining clips and detach
the air intake pipe from the air filter.
29Slide back the inspection cover from the
upper end of the timing cover (photo).
30Turn the engine over by hand to bring the
TDC timing marks of the flywheel-
to-bellhousing and the camshaft sprocket
-to-rear cover projection into alignment. The
crankshaft pulley also has a TDC timing mark
and this should be positioned as shown
(photos).
31Loosen off the retaining and adjustment
strap fixings, then pivot the alternator towards
the engine.
32Unscrew the upper retaining bolts
securing the timing cover.
33Loosen off the nut securing the alternator
and its drivebelt relay, then detach and
remove the alternator drivebelt.
34Unscrew and remove the crankshaft
pulley nut. Where the engine is in the car,
prevent the crankshaft from turning by
engaging top gear and having an assistant
apply the brake pedal hard. Unscrew and
remove the flywheel housing lower cover bolts
and remove the cover. The flywheel ring gear
can now be jammed with a suitable lever or
implement to prevent the crankshaft from
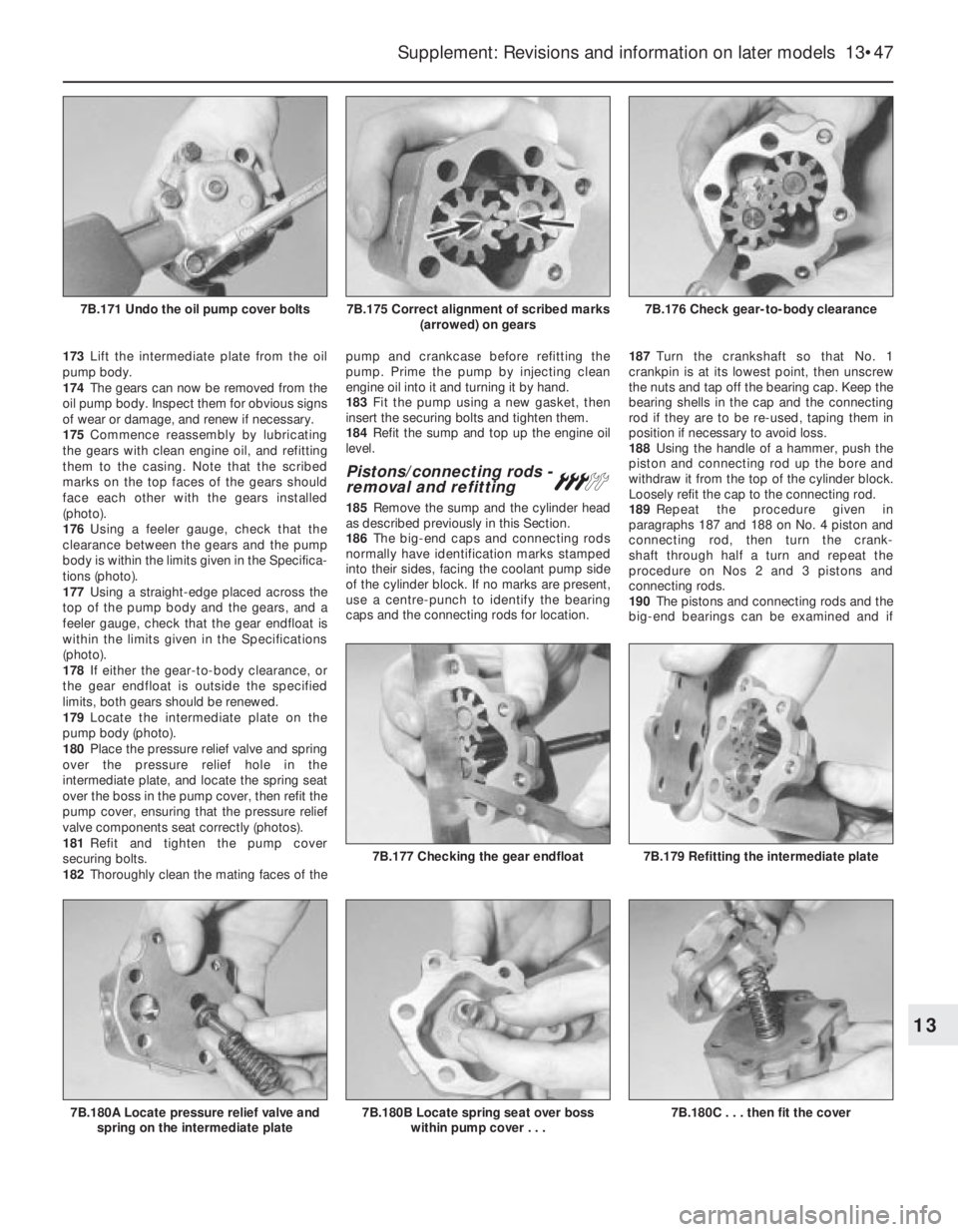
rotating. It should be noted that the pulley nut
is tightened to a considerable torque and a
strong socket, together with an L-bar and
extension tube, will therefore be required to
loosen and remove it (photo). Take care not todamage the gearbox/flywheel housing by
jamming the flywheel at a weak point.
35Withdraw the crankshaft pulley (photo).
36Unscrew and remove the lower retaining
bolts and remove the timing cover upwards
from the vehicle.
37Check that the previously mentioned
timing marks are still in alignment. Loosen off
the timing belt tensioner nut, then with the
tension released, withdraw the timing belt
from the sprockets.
38To remove the drivebelt tensioner, undo
the securing nut and withdraw the tensioner
pulley unit noting that it is in three sections
(photos).
39If desired, the sprockets and the rear
timing belt cover can be removed as follows,
otherwise proceed to paragraph 49.40To remove the camshaft sprocket, a
suitable tool must be used to hold the
camshaft stationary as the sprocket bolt is
loosened. A suitable tool can be improvised
as shown in photo 7B.48 using two pieces of
steel bar joined together by a pivot bolt, with
suitable bolts through the ends of the steel
bars to engage with the holes in the sprocket.
41Unscrew the sprocket bolt, then recover
the plain washer, and the thrust washer which
is bonded into a plastic sleeve (photo).
42The sprocket can now be withdrawn from
the end of the camshaft. If the sprocket is
tight, carefully lever it from the camshaft using
two screwdrivers, but take care not to
damage the rear timing belt cover.
43The crankshaft sprocket can be removed
by simply pulling it from the end of the
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•39
7B.30B Crankshaft pulley and timing cover
timing marks7B.30A Camshaft sprocket timing notch
aligned with timing (TDC) pointer in timing
case7B.29 Slide back inspection cover in the
timing case
7B.41 Removing the crankshaft sprocket
bolt, plain washer and thrust washer7B.38B The three sections of the timing
belt tensioner
7B.35 Crankshaft pulley removal7B.34 Crankshaft pulley nut removal
7B.38A Timing belt tensioner removal
13
Page 166 of 303

thumb and forefinger at the centre of the run
between the auxiliary shaft sprocket and the
camshaft sprocket. Using this method it
should just be possible to twist the belt
through 90º using moderate pressure.
55To adjust the tension, loosen off the
tensioner pulley nut then insert two rods (or
screwdrivers) into position in the pulley holes
and position a lever between them.
56Gently lever the tensioner pulley in the
required direction to set the tension as
described, then initially tighten the pulley nut
to lock the tensioner in the required position.
57Remove the tools from the tensioner,
recheck the tension and then tighten the
tensioner pulley nut securely.
58Rotate the crankshaft clockwise through
two complete turns using a socket or spanner
on the crankshaft pulley nut, then recheck the
belt tension. To avoid the possibility of
unscrewing the pulley nut, remove the spark
plugs to enable the engine to be turned over
easier.
59If further adjustment is required, repeat
the previously mentioned procedures. If in
doubt, err on the slightly tight side when
adjusting the tension. If the belt is set too
loose, it may jump off the sprockets resulting
in serious damage.
60Remove the crankshaft pulley retaining
nut, fit the timing belt cover, then refit and
tighten the pulley nut to the specified torque
setting.
61Refit the remaining components in the
reverse order of removal. Tighten the retaining
nuts/bolts to the specified torque settings
where given. Adjust the tension of the
alternator drivebelt as described in Section 8.
Adjustment using FIAT special
tools
62Assemble the special tools and fit them to
the belt tensioner pulley as shown in
Fig. 13.16. When fitted, the tool rod must be
as vertical as possible and it is important to
note that no sliding weights must be attached
to tool No. 1860745100.
63Slacken the tensioner pulley nut, if not
already done. Rotate the crankshaft clockwise
through two complete turns using a socket or
spanner on the crankshaft pulley nut. The
special tool rod may move from the vertical asthe engine is turned over, in which case the
joint will need to be re-adjusted to return the
rod to the vertical and the operation repeated.
64With the two revolutions of the crankshaft
completed, tighten the belt tensioner pulley
nut securely and remove the special tools.
65Remove the crankshaft pulley retaining
nut, fit the timing belt cover, then refit and
tighten the pulley nut to its specified torque
setting.
66Refit the remaining components in the
reverse order of removal. Tighten the retaining
nuts/bolts to the specified torque settings
where given. Adjust the tension of the
alternator drivebelt as described in Sec-
tion 8.
Camshaft front oil seal -
renewal#
67The camshaft front oil seal may be
renewed with the engine in the vehicle, and
the camshaft in situ, as follows.
68Remove the timing belt and the camshaft
sprocket as described previously in this
Section.
69Punch or drill a small hole in the centre of
the exposed oil seal. Screw in a self-tapping
screw, and pull on the screw with pliers to
extract the seal.
70Clean the oil seal seat with a wooden or
plastic scraper.
71Lubricate the lips of the new seal with
clean engine oil, and drive it into position until
it is flush with the housing, using a suitable
socket or tube. Take care not to damage the
seal lips during fitting. Note that the seal lips
should face inwards.
72Refit the camshaft sprocket and thetiming belt as described previously in this
Section.
Camshaft, housing and
followers -
removal and refitting
#
Note: The engine must be cold when
removing the camshaft housing. Do not
remove the camshaft housing from a hot
engine. New camshaft housing and camshaft
cover gaskets must be used on refitting.
73If the engine is still in the vehicle,
disconnect the battery negative lead.
74Refer to paragraphs 3 to 7 in this part of
this Section for details and remove the
camshaft cover.
75Remove the camshaft sprocket and timing
belt as described previously in this Section.
76Remove the three securing nuts and the
single securing bolt, and withdraw the upper
section of the rear timing belt cover.
77Unscrew the camshaft housing securing
bolts. There are seven bolts which are
accessible from outside the camshaft
housing, and five shorter bolts which are
accessible from inside the housing (these
bolts are normally covered by the camshaft
cover). Note that each bolt is fitted with two
washers (photo).
78Carefully lift the camshaft housing from
the cylinder head. Be prepared for the cam
followers to drop from their bores in the
camshaft housing as the camshaft housing is
lifted, and ensure that the cam followers are
identified for position so that they can be
refitted in their original positions (this can be
achieved by placing each cam follower over
its relevant valve in the cylinder head).
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•41
Fig. 13.16 FIAT special tool No. 1860745100 (A) for timing belt adjustment shown fitted to
the tensioner pulley - 1372 cc ie and Turbo ie engines (Sec 7B)
Use with adapter No. 1860745200 on 1372 cc ie engines and No. 1860745300 on 1372 cc
Turbo ie engines
7B.77 Removing one of the camshaft
housing shorter securing bolts
13
Page 168 of 303

98Commence reassembly by liberally oiling
the bearings in the housing, and the oil seal lip.
99Carefully insert the camshaft into the
housing from the blanking plate/distributor
end, taking care to avoid damage to the
bearings.
100Refit the blanking plate using a new
gasket.
101Refit the camshaft housing as described
previously in this Section.
Cylinder head
(1372 cc ie engine) -
removal and refitting
#
Note: The following instructions describe
cylinder head removal and refitting leaving the
camshaft, manifolds and associated items in situ
In the head. If required, these items can be
removed separately. When removing the
cylinder head the engine must be cold - do not
remove the head from a hot engine. A new
cylinder head gasket and any associated gaskets
must be used during reassembly. FIAT specify
that the main cylinder head bolts should be
renewed after they have been used (ie tightened)
four times. If in any doubt as to the number of
times that they have been used renew them as a
precaution against possible failure.
Warning: Refer to the beginning
of Section 9 before starting any
work.
102Depressurise the fuel supply system as
described in Section 9 of this Chapter.
103Disconnect the battery negative lead.
104Drain the engine coolant as described in
Section 8.
105Remove the air cleaner unit as described
in Section 9.
106Remove the timing belt as described
previously in this Section.107Disconnect the crankcase ventilation
hose from the cylinder head and the SPi
injector unit.
108Disconnect the accelerator cable at the
engine end.
109Detach the engine idle speed check
actuator lead, the inlet manifold vacuum
sensor lead, the coolant temperature sensor
lead, the injector supply lead, the throttle
position switch lead and the distributor cap
(with HT leads). Position them out of the way.
110Disconnect the brake servo hose from
the manifold.
111Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
thermostat and the inlet manifold.
112Slowly release the fuel supply and return
hose retaining clips and detach the hoses
from the injector unit housing and
connections. Catch any fuel spillage in a clean
cloth and plug the hoses to prevent the
ingress of dirt and further fuel loss.
113Unbolt and detach the exhaust downpipe
from the manifold.
114Loosen off the cylinder head retaining
bolts in a progressive manner, reversing the
sequence shown in Fig. 13.17. When all of the
bolts are loosened off, extract them and
collect the washers.
115Check that all fittings and associated
attachments are clear of the cylinder head,
then carefully lift the head from the cylinder
block. If necessary tap the head lightly with a
soft-faced mallet to free it from the block, but
do not lever it free between the joint faces.
Note that the cylinder head is located on
dowels.116Recover the old cylinder head gasket and
discard it.
117Clean the cylinder head and block mating
surfaces by careful scraping. Take care not to
damage the cylinder head - it is manufactured in
light alloy and is easily scored. Cover the coolant
passages and other openings to prevent dirt and
carbon from falling into them. Mop out all the oil
from the cylinder head bolt holes - if oil is left in
them, hydraulic pressure, caused when the bolts
are refitted, could cause the block to crack.
118If required the cylinder head can be
dismantled and overhauled as described in
paragraphs 129 to 131 of this Section.
119The new gasket must be removed from
its protective packing just before it is fitted.
Do not allow any oil or grease to come into
contact with the gasket. Commence refitting
the cylinder head by locating the new gasket
on the cylinder block so that the word “ALTO”
is facing up (photo).
120With the mating faces scrupulously
clean, refit the cylinder head into position and
engage it over the dowels. Refer to the note at
the beginning of this part of the Section, then
refit the ten main cylinder head bolts and
washers. Screw each bolt in as far as possible
by hand to start with. Do not fit the smaller
(M8 x 1.25) bolts at this stage (photos).
121The bolts must now be tightened in stages
and in the sequence shown in Fig. 13.17. Refer
to the specified torque wrench settings and
tighten all bolts to the Stage 1 torque, then
using a suitable angle gauge, tighten them to
the second stage, then the third stage (photos).
122With the main cylinder head bolts fully
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•43
7B.120B . . . and engage the positioning
dowels in their holes7B.120A Lower the cylinder head onto the
block . . .7B.119 Locating a new cylinder head
gasket on the cylinder block (engine
shown on dismantling stand)
7B.121A Tighten main cylinder head bolts
to specified torque . . .Fig. 13.17 Cylinder head bolt tightening
sequence on the 1372 cc ie and Turbo ie
engines (Sec 7B)
13
7B.121B . . . and then through the specified
angle
Page 169 of 303

tightened, refit the five smaller (M8 x 1.25)
bolts adjacent to the line of the spark plug
holes and tighten them to their specified
torque wrench setting (photo).
123Reconnect the associated fittings to the
cylinder head in the reverse order of removal.
Ensure that the mating faces of the exhaust
manifold-to-downpipe are clean and fit a new
gasket when reconnecting.
124Ensure that all wiring connections are
cleanly and securely made.
125Top up the engine oil and coolant levels
as required on completion.
Cylinder head
(1372 cc Turbo ie engine)
- removal and refitting
#
126Proceed as described in paragraphs 102
to 125 above for the non-Turbo model, but
note the following differences.127The cylinder head cannot be removed
and refitted with the manifolds and
turbocharger fitted. It is therefore first
necessary to detach and remove the inlet
manifold, then the turbocharger and the
exhaust manifold as described in Section 9.
128The ignition distributor is mounted on the
side of the engine, not the rear end of the
cylinder head as on the “ie” engine. It is
therefore only necessary to disconnect the HT
leads from the spark plugs.
Cylinder head - inspection
and renovation¢
Note: Refer to a dealer for advice before
attempting to carry out valve grinding or seat
recutting operations. These operations may
not be possible for the DIY mechanic due to
the fitment of hardened valve seats for use
with unleaded petrol.129Use a straight-edge to check the cylinder
head gasket surface for distortion. If it
exceeds the specified tolerance, it must be
resurfaced by a FIAT dealer or automotive
engineer.
130Refer to Section 39 in Chapter 1 for the
general details on dismantling and renovating
operations on the cylinder head but note that
there is a spring seat and a flat washer fitted
between the cylinder head and the valve
springs (photos).
Crankshaft front oil seal -
removal and renewal#
131Remove the timing belt as described
earlier in this Section. Note that as mentioned
previously, the timing belt will need to be
renewed during reassembly.
132Referring to Fig. 13.18, loosen off the bolt
indicated from the timing belt rear cover.
13•44 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
7B.130H . . . the outer spring . . .7B.130G . . . the inner spring . . .7B130F . . . locate the spring seat . . .
7B.130E Refit the flat washer . . .7B.130D . . . and drive it into position7B.130C . . . locate stem oil seal . . .
7B.130B Valve assembly - 1372 cc engine;
insert valve into guide . . .7B.130A Inlet (A) and exhaust (B) valves
and associate components - 1372 cc
engine7B.122 Tighten the smaller cylinder head
bolts to their specified torque setting
Page 171 of 303

new oil seal, ensuring that it is correctly
orientated, and drive it squarely into position.
149Refit all disturbed components.
Flywheel - removal,
inspection and refitting#
150If not already done, remove the clutch as
described in Chapter 5.
151Prevent the flywheel from turning by
jamming the ring gear teeth, or by bolting a
strap between the flywheel and the cylinder
block.
152Make alignment marks on the flywheel
and the end of the crankshaft, so that the
flywheel can be refitted in its original position.
153Unscrew the securing bolts and remove
the washer plate, then withdraw the flywheel.
Do not drop it, it is very heavy.
154With the flywheel removed, the ring gear
can be examined for wear and damage.
155If the ring gear is badly worn or has
missing teeth it should be renewed. The old
ring gear can be removed from the flywheel by
cutting a notch between two teeth with a
hacksaw and then splitting it with a cold
chisel. Wear eye protection when doing this.
156Fitting of a new ring gear requires heating
the ring to a temperature of 80ºC (176ºF). Do
not overheat, or the hard-wearing properties
will be lost. The gear has a chamfered inner
edge which should fit against the shoulder on
the flywheel. When hot enough, place the gear
in position quickly, tapping it home ifnecessary, and let it cool naturally without
quenching in any way.
157Ensure that the mating faces are clean,
then locate the flywheel on the rear of the
crankshaft, aligning the previously made
marks on the flywheel and crankshaft.
158Fit the washer plate, and insert the
securing bolts, then prevent the flywheel from
turning as described in paragraph 151 whilst
the bolts are tightened progressively to the
specified torque setting in a diagonal
sequence (photos).
159If applicable, refit the clutch as described
in Chapter 5.
Sump -
removal and refittingÁ
160Drain the engine oil from the sump as
described in Chapter 1.
161Disconnect the lead from the engine oil
level sensor in the sump.
162Unscrew and remove the bolts retaining the
gear linkage mounting bracket (where applicable)
and the clutch housing lower cover bolts.
Remove the cover from the clutch housing.
163Unscrew and remove the sump retaining
bolts and nuts and lower the sump from the
crankcase. Recover the gasket.
164Clean all traces of old gasket from the
sump, crankcase and both oil seal housing
mating surfaces.
165Commence reassembly by applying
sealing compound (FIAT No. 5882442 orequivalent) to the joints between the
crankshaft front and rear oil seal housings and
the mating face of the crankcase (photo).
166Locate the new gasket in position on the
crankcase then fit the sump. As it is fitted it
will need to be twisted to avoid fouling the oil
pump unit. Refit the retaining bolts and nuts
and tighten them to the specified torque
(photos).
167Check that the sump drain plug is refitted
and fully tightened. If the engine is in the car,
top up the engine oil level.
Oil pump - removal,
checking and refittingª
168Drain the engine oil and remove the
sump as described in the previous
sub-Section.
169Unscrew the retaining bolts then
withdraw the oil pump and intake pipe/filter
from its location within the crankcase.
Remove the gasket.
170If oil pump wear is suspected, first check
the cost and availability of new parts and the
cost of a new pump. Then examine the pump
as described below and decide whether
renewal or repair is the best course of action.
171Unscrew the three securing bolts and
remove the oil pump cover (photo). Note that
as the cover is removed, the oil pressure relief
valve components will be released.
172Recover the oil pressure relief valve,
spring and spring seat.
13•46 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
7B.166C . . . and insert the retaining bolts7B.166B . . . refit the sump . . .7B.166A Locate the new gasket . . .
7B.165 Apply sealant to the front oil seal
housing/cylinder block joint7B.158B . . . tighten the bolts to the
specified torque7B.158A Locate the flywheel, washer plate
and bolts . . .
Page 172 of 303
173Lift the intermediate plate from the oil
pump body.
174The gears can now be removed from the
oil pump body. Inspect them for obvious signs
of wear or damage, and renew if necessary.
175Commence reassembly by lubricating
the gears with clean engine oil, and refitting
them to the casing. Note that the scribed
marks on the top faces of the gears should
face each other with the gears installed
(photo).
176Using a feeler gauge, check that the
clearance between the gears and the pump
body is within the limits given in the Specifica-
tions (photo).
177Using a straight-edge placed across the
top of the pump body and the gears, and a
feeler gauge, check that the gear endfloat is
within the limits given in the Specifications
(photo).
178If either the gear-to-body clearance, or
the gear endfloat is outside the specified
limits, both gears should be renewed.
179Locate the intermediate plate on the
pump body (photo).
180Place the pressure relief valve and spring
over the pressure relief hole in the
intermediate plate, and locate the spring seat
over the boss in the pump cover, then refit the
pump cover, ensuring that the pressure relief
valve components seat correctly (photos).
181Refit and tighten the pump cover
securing bolts.
182Thoroughly clean the mating faces of thepump and crankcase before refitting the
pump. Prime the pump by injecting clean
engine oil into it and turning it by hand.
183Fit the pump using a new gasket, then
insert the securing bolts and tighten them.
184Refit the sump and top up the engine oil
level.
Pistons/connecting rods -
removal and refitting#
185Remove the sump and the cylinder head
as described previously in this Section.
186The big-end caps and connecting rods
normally have identification marks stamped
into their sides, facing the coolant pump side
of the cylinder block. If no marks are present,
use a centre-punch to identify the bearing
caps and the connecting rods for location.187Turn the crankshaft so that No. 1
crankpin is at its lowest point, then unscrew
the nuts and tap off the bearing cap. Keep the
bearing shells in the cap and the connecting
rod if they are to be re-used, taping them in
position if necessary to avoid loss.
188Using the handle of a hammer, push the
piston and connecting rod up the bore and
withdraw it from the top of the cylinder block.
Loosely refit the cap to the connecting rod.
189Repeat the procedure given in
paragraphs 187 and 188 on No. 4 piston and
connecting rod, then turn the crank-
shaft through half a turn and repeat the
procedure on Nos 2 and 3 pistons and
connecting rods.
190The pistons and connecting rods and the
big-end bearings can be examined and if
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•47
7B.176 Check gear-to-body clearance7B.175 Correct alignment of scribed marks
(arrowed) on gears7B.171 Undo the oil pump cover bolts
7B.180C . . . then fit the cover7B.180B Locate spring seat over boss
within pump cover . . .
7B.179 Refitting the intermediate plate7B.177 Checking the gear endfloat
7B.180A Locate pressure relief valve and
spring on the intermediate plate
13
Page 173 of 303

necessary renovated as described later in this
Section.
191Commence refitting as follows.
192Clean the backs of the bearing shells and
the recesses in the connecting rods and
big-end caps.
193Lubricate the cylinder bores with engine
oil.
194Fit a ring compressor to No. 1 piston, theninsert the piston and connecting rod into No. 1
cylinder. With No 1 crankpin at its lowest point,
drive the piston carefully into the cylinder with
the wooden handle of a hammer (photos).
Leave enough space between the connecting
rod and the crankshaft to allow the bearing
shell to be fitted. The piston must be fitted with
the cut-out in the piston crown on the auxiliary
shaft side of the engine, and the cylinder identi-
fication marking on the connecting rod and
big-end cap on the coolant pump side of the
engine - see Fig. 13.21.
195Slide the appropriate bearing shell into
position in the connecting rod big-end, then
pull the connecting rod firmly into position on
the crankpin (photo).
196Press the appropriate bearing shell into
position in the big-end cap (photo).
197Oil the crankpin, then fit the big-end
bearing cap with the cylinder identification
marking on the coolant pump side of the
engine, and tighten the nuts to the specified
torque setting (photos).
198Check that the crankshaft turns freely.
199Repeat the procedure in paragraphs 194
to 198 inclusive on the remaining pistons.
200Refit the cylinder head and the sump.
Pistons/connecting rods -
examination and
renovation
#
201The procedures for inspecting and
renovating the pistons and connecting rod
assemblies are in general the same as thatdescribed for the smaller engines in Sec-
tion 18 of Chapter 1. However, the following
additional points should be noted.
202When renewing a gudgeon pin, first
check the fit in the piston. It should be
possible to fit the gudgeon pin using hand
pressure, but the pin should be a tight enough
fit that it does not drop out under its own
weight. Oversize gudgeon pins are available
as spares if necessary. Use new circlips when
refitting the pistons to the connecting rods.
203Before fitting the pistons to their
connecting rods, weigh each piston and
check that their weights are all within 2.5 g of
each other. If not, the heavier pistons must be
lightened by machining metal from the
underside of the small-end bosses. This
operation must be entrusted to a FIAT dealer
or engine reconditioning specialist.
204The pistons should be fitted to the
connecting rods so that the higher, flat side of
the piston crown is on the side of the
connecting rod with the stamped cylinder
identification number, ie the gudgeon pin is
offset towards the cylinder identification
number see Fig. 13.21.
205The piston rings should be fitted with the
word “TOP” on each ring facing uppermost,
or if no marks are visible, as noted during
removal. If a stepped top compression ring is
being fitted, fit the ring with the smaller
diameter of the step uppermost. The ring end
gaps should be offset 120º from each other.
Use two or three old feeler gauges to assist
13•48 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
7B.197B . . . and tighten the nuts to the
specified torque
Fig. 13.21 Correct orientation of piston
and connecting rod in engine - 1372 cc ie
and Turbo ie engines (Sec 7B)
1 Auxiliary shaft
2 Cylinder identification markings on
connecting rod and big-end cap
Arrow denotes direction of engine rotation
Note offset gudgeon pin
7B.197A . . . then fit the cap . . .7B.196 . . . and big-end bearing cap . . .
7B.195 Assemble the shell bearing to the
connecting rod . . .7B.194B Tapping a piston into its bore7B.194A Fitting a ring compressor to a
piston