1983 FIAT UNO chapter 13
[x] Cancel search: chapter 13Page 145 of 303

mounted on the front end of the crankshaft
and driven by it.
11The flexible toothed timing belt drives thecamshaft and the coolant pump from a
sprocket on the front end of the crankshaft.
The belt is tensioned by an
eccentrically-mounted pulley.
12The distributor and the fuel pump
(carburettor models) are driven from the
flywheel end of the camshaft. The fuel pump
on fuel injection models is an integral unit
combined with the fuel gauge sender unit and
immersed in the fuel tank.
PART B:
OPERATIONS POSSIBLE
WITH ENGINE IN CAR
Valve clearances - adjustment
1The operations are similar to those
described in Chapter 1, Section 26, but note
that the special tools referred to have differentpart numbers for the FlRE engine -
1860443000 and 1887001000 (photos).
2Remember that the clearance for inlet and
exhaust valves differs see Specifications at
the beginning of this Supplement.
3Counting from the timing cover end of the
engine, the valve sequence is as follows.
Inlet 2-4-5-7
Exhaust 1-3-6-8
Timing belt - renewal #
4Remove the air cleaner.
5Slacken and remove the alternator
drivebelt, then remove the spark plugs.
6Unbolt and remove the timing belt cover.
Note the bolt located at the bottom of the
cover, this can be easily overlooked (photo).
7Unbolt and remove the crankshaft pulley
(photo).
13•20 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
5B.7 Unscrewing the crankshaft pulley
bolts5B.6 Timing cover lower fixing bolt
removal5B.1B Using a modified C-spanner and
screwdriver to remove a shim
5B.1A Checking a valve clearance
Fig. 13.3 Longitudinal sectional view of the 999 and 1108 cc
engine (Sec 5A)Fig. 13.4 999 and 1008 cc engine lubrication system (Sec 5A)
Page 148 of 303

depressurize the fuel system, before
disconnecting the fuel pipes and removing the
throttle body, as described in Section 9D.
34Disconnect the coolant and vacuum
hoses from the cylinder head and inlet
manifold (photo).
35Disconnect the electrical lead from the
coolant temperature switch, the LT leads from
the distributor and the idle cut-off solenoid
lead.
36Remove the distributor cap, disconnect
the plug leads and place the cap and leads to
one side of the engine compartment.
37Unbolt and remove the timing belt cover.
38Set No. 4 piston to TDC and then release
the timing belt tensioner and slip the belt from
the camshaft and coolant pump sprockets.
39Unbolt and remove the inlet manifold,
complete with carburettor, or throttle body as
applicable.
40Unbolt the exhaust manifold from the
cylinder head and tie it to one side of the
engine compartment; the downpipe bracket
will have to be disconnected.
41Unscrew the cylinder head bolts, a half
turn at a time in the reverse order to that
shown in Fig. 1.30 of Chapter 1. When the
bolts are free, remove them with their
washers.
42Lift the cylinder head from the block. If it is
stuck tight, insert pieces of wood into the
exhaust or inlet ports and use them as levers
to “rock” the head off the block. On no
account drive levers into the gasket joint orattempt to tap the head sideways as it is
located on positioning dowels.
43Remove and discard the cylinder head
gasket and both manifold gaskets.
44The cylinder head can be dismantled after
removing the camshaft and cam followers as
described in the preceding sub-Section.
45Further dismantling and decarbonising are
described in Chapter 1, Section 39. Note that
single valve springs are used.
46If the valves have been ground in, the
valve clearances will require adjusting, as
described previously. This should be done
before the cylinder head is refitted to the
engine.
47Before refitting the assembled cylinder
head, make sure that the head and block
mating surfaces are perfectly clean, and that
the block bolt holes have been cleared of any
oil.
48The camshaft sprocket timing mark must
be aligned with the one on the cylinder head.
49The new gasket should not be removed
from its nylon cover until required for use. Fit
the gasket dry to perfectly clean surfaces.
50Place the gasket on the cylinder block so
that the word ALTO can be read from above
(photos).
51Lower the cylinder head onto the block so
that it locates on the positioning dowels
(photo).
52The cylinder head bolts must have clean
threads, dipped in engine oil and allowed to
drain for thirty minutes. Screw the bolts infinger-tight and then tighten them in the
sequence shown in Fig. 1.30 of Chapter 1,
and in the stages specified (see Specification)
(photos).
53Refit the inlet manifold and carburettor
using a new gasket.
54Reconnect the exhaust manifold using a
new gasket. Tighten all nuts to the specified
torque. Reconnect the exhaust downpipe
bracket.
55Reconnect the timing belt and tension it
as described earlier.
56Refit the timing belt cover and the
distributor cap and camshaft cover.
57Reconnect all hoses, electrical leads and
controls.
58Fit the air cleaner.
59Fill and bleed the cooling system.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•23
5B.50A Cylinder head gasket5B.34 Inlet manifold coolant hose (A) and
brake servo vacuum hose (B)5B.32 Disconnecting the throttle cable
5B.52B Typical disc for angular tightening
of cylinder head bolts
5B.50B Cylinder head gasket top surface
marking
5B.52A Inserting a cylinder head bolt5B.51 Fitting the cylinder head
13
Page 151 of 303
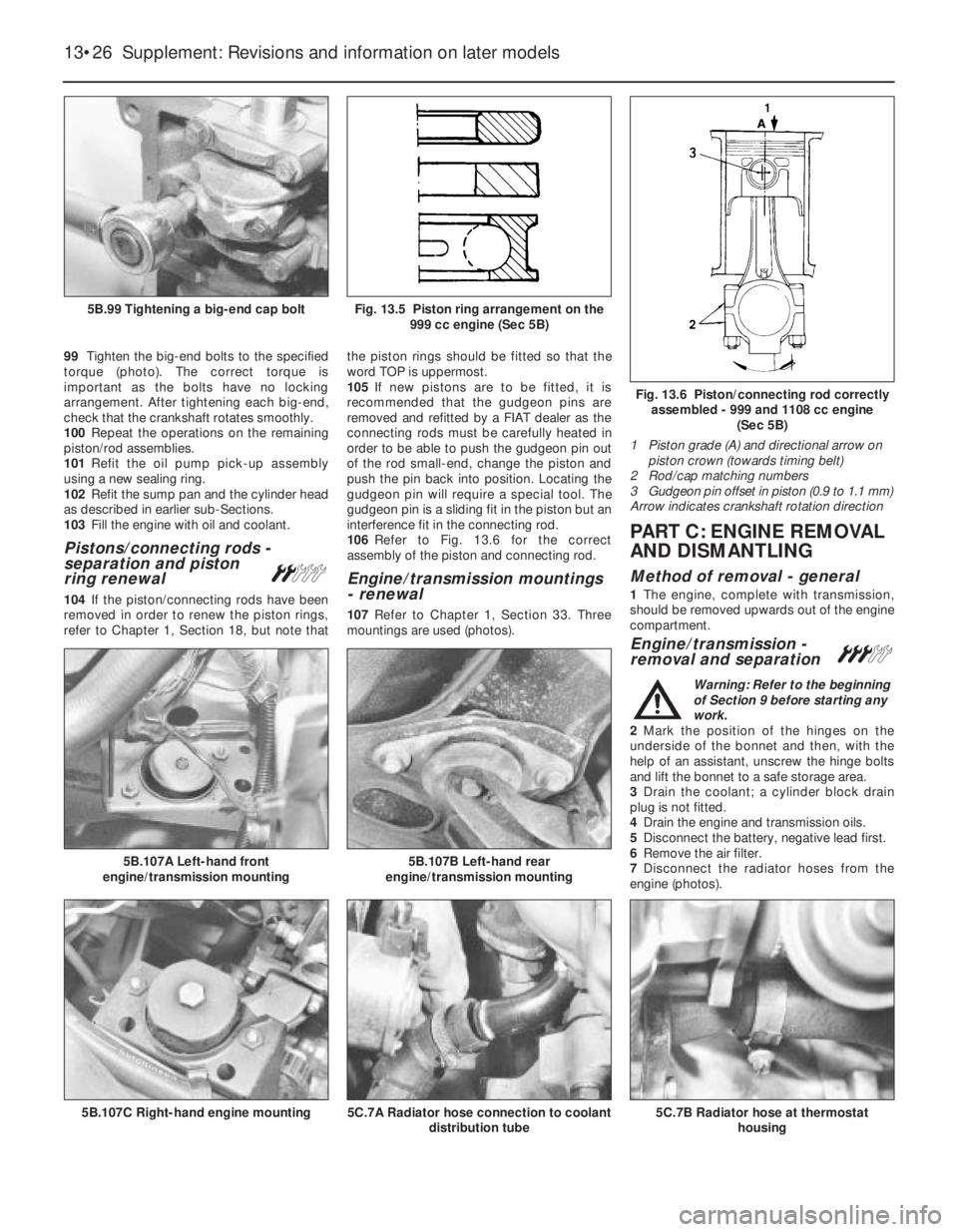
99Tighten the big-end bolts to the specified
torque (photo). The correct torque is
important as the bolts have no locking
arrangement. After tightening each big-end,
check that the crankshaft rotates smoothly.
100Repeat the operations on the remaining
piston/rod assemblies.
101Refit the oil pump pick-up assembly
using a new sealing ring.
102Refit the sump pan and the cylinder head
as described in earlier sub-Sections.
103Fill the engine with oil and coolant.
Pistons/connecting rods -
separation and piston
ring renewal
ª
104If the piston/connecting rods have been
removed in order to renew the piston rings,
refer to Chapter 1, Section 18, but note thatthe piston rings should be fitted so that the
word TOP is uppermost.
105If new pistons are to be fitted, it is
recommended that the gudgeon pins are
removed and refitted by a FIAT dealer as the
connecting rods must be carefully heated in
order to be able to push the gudgeon pin out
of the rod small-end, change the piston and
push the pin back into position. Locating the
gudgeon pin will require a special tool. The
gudgeon pin is a sliding fit in the piston but an
interference fit in the connecting rod.
106Refer to Fig. 13.6 for the correct
assembly of the piston and connecting rod.
Engine/transmission mountings
- renewal
107Refer to Chapter 1, Section 33. Three
mountings are used (photos).
PART C: ENGINE REMOVAL
AND DISMANTLING
Method of removal - general
1The engine, complete with transmission,
should be removed upwards out of the engine
compartment.
Engine/transmission -
removal and separation #
Warning: Refer to the beginning
of Section 9 before starting any
work.
2Mark the position of the hinges on the
underside of the bonnet and then, with the
help of an assistant, unscrew the hinge bolts
and lift the bonnet to a safe storage area.
3Drain the coolant; a cylinder block drain
plug is not fitted.
4Drain the engine and transmission oils.
5Disconnect the battery, negative lead first.
6Remove the air filter.
7Disconnect the radiator hoses from the
engine (photos).
13•26 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
5C.7B Radiator hose at thermostat
housing5C.7A Radiator hose connection to coolant
distribution tube5B.107C Right-hand engine mounting
5B.107B Left-hand rear
engine/transmission mounting5B.107A Left-hand front
engine/transmission mounting
Fig. 13.6 Piston/connecting rod correctly
assembled - 999 and 1108 cc engine
(Sec 5B)
1 Piston grade (A) and directional arrow on
piston crown (towards timing belt)
2 Rod/cap matching numbers
3 Gudgeon pin offset in piston (0.9 to 1.1 mm)
Arrow indicates crankshaft rotation direction
Fig. 13.5 Piston ring arrangement on the
999 cc engine (Sec 5B)5B.99 Tightening a big-end cap bolt
Page 154 of 303

can be lowered to rest on the exhaust and
bodymember.
34Continue to raise the engine and the
transmission until it can be removed from the
engine compartment and placed on the work
surface (photo).
35Clean the exterior of the engine and
transmission by steam cleaning or using a
water soluble solvent.
36Unbolt and remove the starter motor.
37Unscrew the flywheel housing-to-engine
flange bolts. Note the location of the engine
lifting lug.
38Unbolt and remove the lower cover plate
from the flywheel housing.
39Pull the transmission from the engine. It is
located by two hollow dowels and one stud
(photo).
Dismantling - general
40Refer to Chapter 1, Section 14.
Complete dismantling#
Warning: Refer to the beginning
of Section 9 before starting any
work.
41Unbolt and remove the camshaft cover.
42Unbolt and remove the timing belt cover.
43Remove the distributor (Section 10).
44Remove the hot air collector and the
exhaust manifold.
45Release, disconnect and remove the
coolant distribution pipe from the rear of the
coolant pump.46Unscrew and discard the oil filter
cartridge.
47Unbolt the thermostat housing, discard
the joint gasket.
48Remove the fuel pump, together with its
insulator block and actuating pushrod, if
applicable.
49Remove the carburettor, or throttle body,
as appropriate.
50Remove the inlet manifold and discard the
joint gasket.
51Remove the alternator and its drivebelt
and withdraw the engine oil dipstick.
52Unbolt and remove the crankshaft pulley.
53Unbolt and remove the timing belt
tensioner.
54Remove the timing belt.
55Unbolt and remove the coolant pump.
56Remove the cylinder head.
57Remove and discard the cylinder head
gasket.
58Remove the clutch.
59Lock the flywheel starter ring gear teeth
and remove the crankshaft sprocket bolt and
sprocket.
60Unbolt and remove the sump pan,
then the exhaust pipe support bracket
(photos).
61Prevent rotation of the crankshaft by
locking the starter ring gear teeth and then
unbolt and remove the flywheel. The flywheel
can only be fitted in one position as it is
located on a dowel.
62Remove the engine rear plate. Note thesmall socket-headed screw which holds the
timing index plate (photo).
63Unbolt and remove the oil pump pick-up
assembly, followed by the oil pump itself.
64Turn the engine on its side and remove
the piston/connecting rod assemblies.
65Stand the engine on its cylinder block
machined face, and then unbolt and remove
the crankshaft rear oil seal retainer. Discard
the gasket.
66Note the markings on the main bearing
caps. One line on the cap nearest the timing
belt, then two, C for centre cap, then three
and four (photo).
67The caps will only fit one way round.
68Unbolt the main bearing caps, removing
them with the shell bearings.
69Lift the crankshaft from the crankcase and
remove the bearing half shells from the
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•29
5C.39 Separating the engine and
transmission5C.34 Lifting out the engine and
transmission5C.32 Right-hand engine mounting
brackets on body and engine
5C.66 Main bearing cap markings
5C.60A Removing the sump pan
5C.62 Unscrewing socket-head screw
from timing index plate5C.60B Exhaust pipe support bracket
attached to crankcase
13
Page 155 of 303
crankcase. If the shells are to be used again,
keep them with their respective bearing caps.
70The thrust washers which control
crankshaft endfloat are located in the
crankcase, and retained by the turned-over
edges of the centre main bearing shell.
71The engine is now fully stripped.
Examination and renovation
72The procedures for the following items are
essentially as described in Chapter 1, Sec-
tion 18.
Cylinder block and crankcase
Crankshaft and bearings
Flywheel
Oil seals and gaskets
Cylinder head
73Using a straight-edge, check the cylinder
head gasket surface for distortion. If it
exceeds the specified tolerance, it must be
surface ground by your dealer.74Refer to Chapter 1, Section 39, for
dismantling and renovation operations. Note
that single valve springs are fitted.
Oil pump
75Checking operations are described in
sub-Section B.
Pistons and connecting rods
76Refer to sub-Section B.
77If one or more connecting rods are
changed, it is important that its weight is
identical to that of the original. Use an
accurate balance to weigh them and remove
metal if necessary from the new rod in the
areas indicated in Fig. 13.7.
Camshaft and cam followers
78If the camshaft journals or bearings show
any sign of wear or scoring, then the
camshaft, or cylinder head, or both must be
renewed.
79The cam followers should be checked for
ovality using a micrometer. Unless unworn
they should be renewed.
Timing belt tensioner and timing belt
80The tensioner is a lubricant-sealed pulley,
and it should be tested for smooth and quiet
operation by turning it with the fingers. Any
evidence of roughness or rattle will indicate
the need for a new assembly (photo).81The timing belt should be inspected at
regular intervals for correct adjustment and
condition (see Section 3 or “Routine
maintenance” at the beginning of the Manual).
If there is evidence of worn teeth, cracking or
fraying, or oil contamination, renew the belt.
The vehicle manufacturers recommend that
the belt is renewed whenever it is removed,
and it should certainly be renewed at the
intervals specified in Section 3 or the main
“Routine maintenance” section at the
beginning of this Manual as a precautionary
measure against belt breakage and
consequent expensive engine damage.
PART D:
ENGINE REASSEMBLY AND
REFITTING
Reassembly - general
1Refer to Chapter 1, Section 19.
Complete reassembly#
2With the cylinder block/crankcase standing
on the work surface, fit the bearing half shells
into their crankcase seats (photo). Make sure
that the seats are perfectly clean as dirt or grit
trapped under the shell will cause binding
when the crankshaft is turned.
3The centre bearing crankcase web
incorporates the thrust washers held by the
lips of the bearing shell (photo).
4Oil the shells and lower the crankshaft into
the crankcase (photo).
5Fit the bearing shells into the main bearing
caps, again making sure that the shell seats
are perfectly clean (photo).
13•30 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
5D.5 Main bearing cap and shell5D.4 Fitting the crankshaft5D.3 Crankshaft thrust washer at centre
bearing
5D.2 Main bearing shell in crankcase
Fig. 13.8 Checking a cam follower for
ovality - 999 and 1108 cc engine (Sec 5C)
Fig. 13.7 Metal removing areas (arrowed)
on connecting rod - 999 and 1108 cc
engine (Sec 5C)
5C.80 Timing belt tensioner
Page 157 of 303
tighten the sprocket bolt to the specified
torque (photos).
17Refit the clutch to the flywheel asdescribed in Chapter 5. Make sure that the
driven plate is centralised.
18Fit the cylinder head.
19Refit the coolant pump. A conventional
gasket is not used at the joint face, but apply
a continuous bead of RTV silicone instant
gasket 3.0 mm in diameter to the pump
mating surface. Allow at least one hour for
curing before permitting coolant to contact it.
20Fit the timing belt rear cover, then the
timing belt tensioner and lock in its retracted
position (photo).
21Fit and tension the timing belt as
described in sub-Section B.
22Bolt on the crankshaft pulley (photo).
23Refit the alternator and drivebelt (photo).
24Refit the engine oil dipstick.
25Using a new gasket, bolt on the inletmanifold, tightening the nuts to the specified
torque (photos).
26Refit the carburettor, or throttle body, as
appropriate.
27Fit the fuel pump, insulator block and
actuating rod, if applicable. Make sure that a
new gasket is placed on each side of the
pump insulator block.
28Using a new gasket, bolt on the
thermostat housing.
29Oil the sealing ring of a new oil filter
cartridge and screw it into position using hand
pressure only (photo).
30Refit the coolant distribution pipe to the
rear of the coolant pump. Use a new seal
(photo).
31Using a new gasket, bolt on the exhaust
manifold (photo).
13•32 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
5D.31 Exhaust manifold5D.30 Coolant distribution pipe5D.29 Oil filter cartridge and mounting
base
5D.25B Fitting the inlet manifold5D.25A Inlet manifold gasket5D.23 Alternator and drivebelt
5D.22 Crankshaft pulley installation
5D.20 Fitting the timing belt rear cover5D.16B Tightening the crankshaft sprocket
bolt5D.16A Crankshaft sprocket showing
integral key
Page 158 of 303

32Fit the hot air collector plate for the air
cleaner (photo).
33Refer to Section 10 and fit the distributor.
34Bolt on the timing belt cover.
35Fit the camshaft cover, using a new
gasket unless the original one is in perfect
condition.
Engine/transmission -
reconnection and refitting#
36Locate the engine in an upright position
on wooden blocks to allow for the greater
depth of the transmission flywheel housing
when it is joined to the engine.
37Make sure that the clutch driven plate has
been centralised, offer the transmission to the
engine and locate the flywheel housing on the
single stud and dowels.
38Tighten the connecting bolts to specifiedtorque, having located the lifting eye (photo).
39Bolt on the starter motor.
40Refit the cover plate to the flywheel
housing, but do not insert the lower bolts at
this stage as they retain the support bracket
for the gearchange rod.
41The engine and transmission are now
ready for refitting. The operations are a direct
reversal of the operations described earlier,
but observe the following points.
42Have the engine/transmission perfectly
horizontal and suspended on the hoist.
43Lower it into position very slowly until it is
possible to engage the driveshaft inboard
joints with the transmission.
44Continue lowering until the driveshafts
can be fully engaged and the mountings
reconnected. Remove the hoist.
45Tighten all nuts and bolts to the specifiedtorque. Note the method shown for
connecting the gearchange rod ball socket
using pliers (photo).
46Refill the engine with oil and coolant and
replenish the transmission oil.
Initial start-up after major
overhaul
47Refer to Chapter 1, Section 45.
6 Engine-
1301 cc Turbo ie
PART A: GENERAL
Description
1This engine is similar in design to the
1301 cc engine described in Chapter 1, but
the fuel and ignition systems are different, and
a turbocharger, oil cooler and intercooler are
fitted.
2Many dimensions and tolerances have
been altered for this engine, and reference
should be made to the Specifications at the
beginning of this Supplement.
3Operations which differ from those
described in Chapter 1 are given in the
following sub-Sections.
Lubrication system - description
4The lubrication system differs from the
non-Turbo 1301 cc engine in the following
respects.
5An oil cooler is fitted, which comprises a
matrix with inlet and outlet hoses connected
to the oil filter cartridge mounting base.
6A thermostatic control switch is fitted,
which diverts the oil flow through the matrix
only at oil temperatures above 84ºC (183ºF).
Note that a faulty switch will require renewal
of the complete oil filter mounting base.
7Special oil spray nozzles are located in the
crankcase main bearing webs, to cool the
underside of the pistons.
8The ball-type valves in the nozzles open
when the engine oil pressure reaches 1.2 bars
(17.4 lbf/in
2).
9An oil pressure sender unit is screwed into
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•33
5D.45 Connecting ball socket type
gearchange rod5D.38 Lifting eye on flywheel housing
flange5D.32 Air cleaner hot air collector plate
Fig. 13.10 Cutaway view of the 1301 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 6A)
13
Page 159 of 303

the crankcase to operate the oil pressure
gauge. In addition, a low oil pressure switch
screwed into the camshaft oil gallery actuates
a warning light on the instrument panel in theevent of the pressure dropping dangerously
low (photo).
10Oil supply/return ducts provide the
turbocharger lubrication.
PART B:
OPERATIONS POSSlBLE
WITH ENGINE IN CAR
Camshaft and camshaft
carrier - removal and
refitting
#
Warning: Refer to the beginning
of Section 9 before starting any
work.
1Disconnect the battery, negative lead first.
2Disconnect its leads and unbolt the
distributor from the end of the camshaft, and
place it to one side.
3Disconnect the air intake hose from the
throttle valve housing.
4Disconnect the short throttle control cable
from its sector.
5Remove the throttle cable support bracket.
6Disconnect the earth leads from the
camshaft cover.
7Refer to Section 9, Part C of this
Supplement and remove the following
components.
Supplementary air valve
Inlet manifold with fuel pressure regulator
and excess pressure safety switch
Injector cooling duct
8Disconnect the wiring plug from the
Microplex ignition anti-knock sensor.
9Carry out the operations described in
Chapter 1, Section 27, paragraphs 4 to 12.
10Refitting is a reversal of removal, referring
to Section 28 of Chapter 1 for the timing belt
refitting procedure, and to Chapter 1, Sec-
tion 27, paragraphs 15 to 18.
Cylinder head -
removal and refitting#
11Carry out the operations described in
paragraphs 4 to 9 in the preceding
sub-Section, then refer to Chapter 1, Section
29, but ignore all references to the
carburettor.
12Note the distributor mounting cover.
13Four additional cylinder head bolts are
used on these engines, adjacent to the spark
plugs (photo). Note that their tightening torque
differs from the other cylinder head bolts - see
Specifications. These four bolts are tightened
13•34 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
1 Oil pick-up strainer
2 Oil pump
3 Oil pressure relief valve
4 Oil filter cartridge
5 Main oil gallery6 Camshaft oil feed
7 Low oil pressure switch
8 Engine oil cooler
9 Filter mounting base
10 Turbocharger oil feed11 Turbocharger oil return
12 Oil pressure sender unit
13 Oil temperature sender
unit
14 Piston oil spray nozzle
Fig. 13.12 Piston oil spray nozzle locations - 1301 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 6A)
Letters denote cylinder bore grade
Fig. 13.11 1301 cc Turbo ie engine lubrication system (Sec 6A)
6A.9 Oil pressure sender unit