1983 FIAT UNO check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 51 of 303

2
System type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . “No loss” with radiator and integral expansion tank. Electric cooling
fan, belt-driven coolant pump, thermostat on cylinder head
General
Radiator fan cuts in . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90 to 94ºC (194 to 201ºF)
Radiator fan switches off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85 to 89ºC (185 to 192ºF)
Thermostat opens:
903 cc engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85 to 89ºC (185 to 192ºF)
1116 cc and 1301 cc engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83 to 87ºC (181 to 188.6ºF)
Fully open:
903 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100ºC (212ºF)
1116 cc and 1301 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95ºC (203ºF)
Expansion tank pressure cap rating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.78 bar (11 lbf/in2)
Coolant
Capacity:
903 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.6 litre (8.1 pint)
1116 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.0 litre (10.6 pint)
1301 cc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6.2 litre (10.9 pint)
Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ethylene glycol based antifreeze
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Temperature sender switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49 36
Coolant pump mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34 25
Alternator adjuster and mountings nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49 36
Chapter 2 Cooling and heating systems
For modifications, and information applicable to later models, see Supplement at end of manual
Coolant mixtures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Coolant pump - removal, overhaul and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Cooling system - draining, flushing and refilling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Cooling system sensors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Description and maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Drivebelt - tensioning and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Fault finding - cooling and heating . . . . . . . . . . . . See end of ChapterHeater - dismantling, overhaul and reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Heater unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Heating and ventilation system - description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Radiator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Radiator fan thermostatic switch - removal, checking and refitting . 5
Radiator fan - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Thermostat - removal, testing and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2•1
Specifications Contents
1 Description and
maintenance
1
1The cooling system consists of a
front-mounted radiator with built-in expansion
tank, a coolant pump (belt-driven from the
crankshaft pulley) and a thermostatically-
controlled electric cooling fan.
2In order to assist rapid warm-up, athermostat is located in a housing at the
left-hand end of the cylinder head. The hose
connections to the thermostat housing vary
according to model.
3The heater is supplied with coolant from the
engine and incorporates a matrix and blower
with the necessary controls.
4The throttle valve plate block of the
carburettor is coolant-heated as a means of
improving fuel atomisation.
5Maintenance is minimal as in theory no
coolant should ever be lost from theexpansion tank. Regularly check that the
coolant level is between 50.0 and 70.0 mm
(1.97 and 2.8 in) above the MIN mark on the
tank with the engine cold. The need for
regular topping up will indicate a leak
somewhere in the system. If one cannot be
found suspect an internal leak in the engine
although this is usually confirmed by a rise in
the engine oil level and water on the dipstick
(photo). Any topping-up should be done using
an antifreeze mixture (see Section 3), not plain
water.
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
Page 52 of 303

6Avoid unscrewing the expansion tank cap
when the engine is hot, but if this must be
done, cover the cap with a cloth to avoid
scalding by escaping steam.
7Periodically, check the condition of all
coolant hoses and tighten the clips.
2 Cooling system- draining,
flushing and refilling
1
1Set the heater temperature lever to
maximum.
2Unscrew the cap from the expansion tank.
3Disconnect the radiator bottom hose and
unscrew the cylinder block drain plug (1116
cc and 1301 cc engines) and allow the coolant
to drain. Refer to photo 29.21B, page 64.
4If the system is in good condition with no
sign of rust or dirt in the drained coolant, then
it may be refilled immediately. If the system
has been neglected and the antifreeze has notbeen regularly renewed and there is evidence
of rust and sediment in the drained liquid then
flush the system through with a cold water
hose.
5If the radiator should appear to be clogged,
it may be necessary to remove it (Section 7)
invert it and reverse flush it using a cold water
hose. If, after a reasonable period the water
still does not run clear, the radiator should be
flushed with a good proprietary cleaning
system. Extensive damage should be repaired
by a specialist or the unit exchanged for a
new or reconditioned radiator.
6Reconnect the bottom hose and screw in
the drain plug.
7Remove the plug (B) (Fig. 2.2) from the
bleed hole in the heater hose.
8Remove the plug (D) (Fig. 2.3) from the
bleed hole in the expansion tank.
9Pour antifreeze mixture slowly into the filler
neck of the expansion tank until it is seen to
come out of the expansion tank plug hole.
Screw in the plug.
10Add further coolant until it is seen todribble out of the hole in the heater hose.
Screw in the plug.
11Top up the expansion tank to the
specified level and screw on the tank cap.
12Start the engine and run it until the cooling
fan cuts in. Switch off, allow to cool and top
up if necessary to the specified mark on the
expansion tank.
3 Coolant mixtures
1In cold climates, antifreeze is needed for
two reasons. In extreme cases, if the coolant
in the engine freezes solid it could crack the
cylinder block or head. But also in cold
weather, with the circulation restricted by the
thermostat, and any warm water that is
getting to the radiator being at the top, the
bottom of the radiator could freeze, and so
block circulation completely, making the
coolant trapped in the engine boil.
2The antifreeze should be mixed in the
proportions advocated by the makers,
according to the climate. There are two levels
of protection. The first cuts risk of damage, as
the antifreeze goes mushy before freezing.
The second, valid all year round, is the
corrosion protection it offers - see below. The
normal proportion in a temperate climate to
provide maximum protection against freezing
and corrosion is 50% antifreeze and
50% water.
3Use only ethylene glycol based antifreeze
and preferably soft water.
4Antifreeze should be left in through the
summer. It has an important secondary
function, to act as an inhibitor against
corrosion. In the cooling system are many
different metals, in particular the aluminium of
the cylinder head. In contact with the coolant
this sets up electrolytic corrosion,
accentuated by any dirt in the system. This
corrosion can be catastrophically fast.
5After about two years, the effectiveness of
the antifreeze’s inhibitor is used up. It must
then be discarded, and the system refilled
with new coolant.
6In warm climates free from frost, an
2•2 Cooling and heating systems
Fig. 2.3 Plug (D) in expansion tank (Sec 2)Fig. 2.2 Plug (B) in heater hose (Sec 2)
1.5 Expansion tank cap
Fig. 2.1 Cooling system on 903 cc engine (Sec 1)
Page 53 of 303

inhibitor should be used. Again, a reputable
make giving full protection must be chosen
and renewed every two years. Inhibitors with
dyes are useful for finding leaks, and on some
makes the dye shows when the inhibiting
ability is finished.
4 Thermostat-
removal, testing and refitting
1
1The thermostat assembly is mounted on the
flywheel end of the cylinder block.
2Unfortunately, the thermostat/housing is a
complete unit and failure of the thermostat will
necessitate the purchase of the complete
component (photo).
3If the thermostat/housing is removed from
the engine, it can be suspended in water and
the water heated to check out its opening
temperature. Movement of the thermostat
valve can be observed to some extent
through the openings in the housing.
4When refitting, always use a new gasket at
its mounting face (photo).
5 Radiator fan thermostatic
switch- removal, checking
and refitting
1
1Drain the cooling system.
2If the thermostatic switch is being removed
because the fan is not operating and the
switch is suspect, check the fan fuse first,
before removing the switch.3To remove the switch, disconnect the leads
from the terminals and unscrew the switch.
4Connect a test bulb and battery across the
switch terminals and then immerse the
sensing part of the switch in a container of
water. Heat the water and, using a
thermometer, check the temperature of the
water when the bulb lights up, indicating the
switch is functioning. The switch should
operate at approximately 194ºF (90ºC). Allow
the water to cool and check that the switch
cuts out at 185ºF (85ºC). Renew a faulty
switch.
5Refitting of the switch is the reverse of the
removal procedure. Always fit a new O-ring on
the switch.
6 Radiator fan-
removal and refitting
1
1Disconnect the electrical leads from the
radiator fan motor.
2Unbolt the fan mounting struts from the
radiator and lift the complete assembly away.
3Refitting is a reversal of removal.
7 Radiator-
removal and refitting
1
1Drain the cooling system.
2Disconnect the electrical leads from the
radiator fan motor and thermostatic switch.3Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
radiator (photos).
4Release the clips from the top of the
radiator and withdraw the radiator complete
with fan from the engine compartment
(photos).
5The radiator is of combined plastic/metal
construction and any repair should be left to
specialists. In an emergency however, minor
leaks from the radiator may be cured by using
a radiator sealant with the radiator in situ.
6Refitting is a reversal of removal. Fill the
cooling system as described in Section 2.
8 Drivebelt-
tensioning and renewal
1
1The drivebelt for the alternator and coolant
pump is correctly tensioned if it deflects
through 10.0 mm (0.39 in) under moderate
thumb pressure at the mid point of the longest
run of the belt.
2To tighten the belt, release the mounting
and adjuster nuts on the alternator and prise
the alternator away from the engine. Tighten
the nuts when the belt is taut and then
re-check the tension as previously described.
Never over-tension a belt or the coolant pump
or alternator bearings may be damaged.
3Check the condition of the belt at regular
intervals. If frayed or cracked, renew it in the
following way.
4Release the alternator mounting and
adjuster nuts and push the alternator fully in
Cooling and heating systems 2•3
7.3A Radiator top hose4.4 Fitting thermostat housing
(1116 cc engine)4.2 Thermostat housing
7.4B Removing radiator/fan assembly7.4A Radiator fixing clip7.3B Radiator hose to thermostat housing
2
Page 54 of 303

towards the engine. Slip the belt off the
pulleys. If this is difficult, turn the crankshaft
pulley using a spanner on its retaining nut
while pressing the belt over the edge of the
pulley rim. Use this method to fit the new belt
after first having engaged it with the coolant
pump and alternator pulley grooves.
5Tension the belt as previously described.
6The tension of a new belt should be
checked and adjusted after the first few
hundred miles of running.
9 Coolant pump- removal,
overhaul and refitting
4
Note: The design of the pump differs between
the 903 cc and the other two engines, but the
removal, overhaul and refitting operations are
essentially similar.
1To gain access to the coolant pump, open
the bonnet and remove the air cleaner.
2Slacken the alternator pivot and adjustment
nuts, push the alternator in towards the
engine and slip the drivebelt from the coolant
pump pulley. Unplug and remove the
alternator.3Drain the cooling system as previously
described.
4Disconnect the hoses from the coolant
pump, also the metal coolant transfer pipe
(photo).
5Unscrew and remove the coolant pump
securing bolts, and lift the pump from the
engine. Peel away and discard the old gasket.
6Clean away external dirt.
7The pump is likely to need overhaul for
worn or noisy bearings, or if the gland is
leaking. There is a drain hole between the
gland and the bearings to prevent
contamination of the bearing grease by leaks,
and possible damage to the bearings. Glandleaks are usually worse when the engine is not
running. Once started, a leak is likely to get
worse quickly, so should be dealt with soon.
Worn bearings are likely to be noted first due
to noise. To check them, the pulley should be
rocked firmly, when any free movement can
be felt despite the belt. But if the bearings are
noisy, yet there is not apparently any free
play, then the belt should be removed so the
pump can be rotated by hand to check the
smoothness of the bearings.
8Dismantling and assembly of the pump
requires the use of a press, and it is preferable
to fit a new pump.
9For those having the necessary facilities,
overhaul can be carried out as follows.
10Remove the retaining nuts and separate
the two halves of the pump.
11The pump shaft is an interference fit in the
impeller, bearings, and pulley boss. How the
pump is dismantled depends on whether only
the gland needs renewing or the bearings as
well, and what puller or press is available to
get everything apart.
12Assuming complete dismantling is
required, proceed as follows. Supporting it
close in at the boss, press the shaft out of the
pulley. Pull the impeller off the other end of
the shaft.
13Take out the bearing stop screw.
14From the impeller end, press the shaft
with the bearings out of the cover half of the
housing.
15Press the shaft out of the bearings, take
off the spacer, the circlip, and the shouldered
ring.
16Do not immerse the bearings in cleaning
2•4 Cooling and heating systems
1 Pump body
2 Pump cover
3 Impeller
4 Connector for hose from
outlet to pump
5 Seal
6 Gasket7 Circlip
8 Bearing shoulder washer
9 Inner seal
10 Inner bearing
11 Bearing retainment screw
and lock washer12 Spacer
13 Outer seal
14 Outer bearing
15 Lock washer
16 Pulley
17 Pump shaft
Fig. 2.5 Sectional views of 1116 cc and 1301 cc engine coolant pump (Sec 9)
Fig. 2.4 Sectional view of 903 cc engine coolant pump (Sec 9)
9.4 Coolant distribution tube at rear of
pump
1 Pump cover
2 Bearing spacer
3 Bearing stop screw
4 Cover nuts
5 Lifting bracket
6 Housing
7 Impeller
8 Gland (seal)
9 Circlip
10 Gasket
11 Shouldered ring
12 Grommets
13 Bearing
14 Pulley
15 Shaft
Page 55 of 303

fluid. They are “sealed”. Liquid will get in, but
a thorough clean will be impracticable, and it
will be impossible to get new grease in.
17Check all the parts, get a new gland, two
new grommets, (1116 cc and 1301 cc) and a
new gasket. Scrape all deposits out of the
housing and off the impeller.
18To reassemble, start by inserting the new
grommets (1116 cc and 1301 cc) in the
grooves by each bearing. Fit the circlip to the
shaft, then the shouldered ring, bearings and
spacer. Fit the shaft and bearing assembly
into the cover. Fit the stop screw. Press on
the pulley.
19Fit the new gland (seal), seating it in its
location in the cover. Press the impeller onto
the shaft. The impeller must be put on part
way, and then the housing held in place to see
how far the impeller must go down the shaft
to give the correct clearance, which is 0.8 to
1.3 mm (0.03 to 0.05 in) as shown in Figs. 2.4
and 2.5.
20The impeller clearance can be checked
through the coolant passage in the side of the
pump.
21Refitting is a reversal of the removal
process, but use a new flange gasket and
tension the drivebelt as described in Section 8
(photo).
22Refill the cooling system.
10 Cooling system sensors
1A coolant temperature sender switch is
located in the cylinder head (above No. 1
spark plug) on 903 cc engines and adjacent to
No. 2 spark plug on 1116 cc and 1301 cc
engines.
2The switch operates the coolant
temperature gauge and an excessive
temperature warning lamp.
3On some models, a level sensor is screwed
into the side of the expansion tank. This
sensor consists of a pair of reed switches
within a capsule which are kept closed by the
strong magnetic flux generated by the
hydrostatic force inspired by the action of the
coolant against the float.
4If the coolant level drops then the magneticflux is weakened and the switches open.
5In the event of a fault developing, before
assuming that the cause is the sensor, check
all connecting wiring.
11 Heating and ventilation
system- description
1The heater is centrally mounted under the
facia and is of fresh air type.2Air is drawn in through the grille at the base
of the windscreen. It then passes through the
coolant heated matrix when it can then be
distributed through selective outlets
according to the setting of the control levers.
3A booster fan is provided for use when the
car is stationary or is travelling too slowly to
provide sufficient air ram effect.
4Fresh air outlets are provided at each end
and centrally on the facia panel.
12 Heater unit-
removal and refitting
1
1Drain the cooling system.
2Disconnect the heater hoses at the engine
compartment rear bulkhead.
3Working within the car under the facia
panel, disconnect the leads from the
heater blower by pulling the connecting plug
apart.
4If a radio is fitted, disconnect the
aerial, earth, speaker and power leads from
it.
Cooling and heating systems 2•5
Fig. 2.6 Checking impeller clearance
(Sec 9)9.21 Fitting coolant pump (1116 cc engine)
Fig. 2.7 Heater and ventilation system (Sec 11)
A Fresh air inlet flap
B Air distribution flap
C Coolant valveD Blower
E MatrixF Control levers
G Footwell air duct
2
Page 62 of 303
Engine idle speed
At normal operating temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 to 850 rev/min
CO percentage at idle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.5 maximum
Torque wrench settingsNm lbf ft
Exhaust manifold nuts (903 cc) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 15
Exhaust and intake manifold nuts (1116 cc, 1301 cc) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 20
Fuel pump nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28 20
Carburettor mounting nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 18
3•4 Fuel system
2.11B Air cleaner mounting bracket and
pipe clip2.11A Air cleaner mounting studs (1116 cc)2.9 Crankcase vent hose at air cleaner
1 Description and
maintenance
1
1The fuel system consists of a rear-mounted
fuel tank, a mechanically-operated fuel pump
and a carburettor and air cleaner.
2On all engines except the 1301 cc a single
venturi downdraught carburettor is fitted. On
the 1301 cc version, a dual barrel carburettor
is fitted.
3Maintenance consists of periodically
checking the condition and security of the fuel
hoses to the pump and carburettor. The fuel
pump cannot be cleaned or repaired and in
the event of a fault developing, the pump
must be renewed.
4On ES versions, an electronic fuel cut-out
device is fitted which reduces fuel
consumption on overrun, see Chapter 9,
Section 33.
2 Air cleaner- servicing,
removal and refitting
1
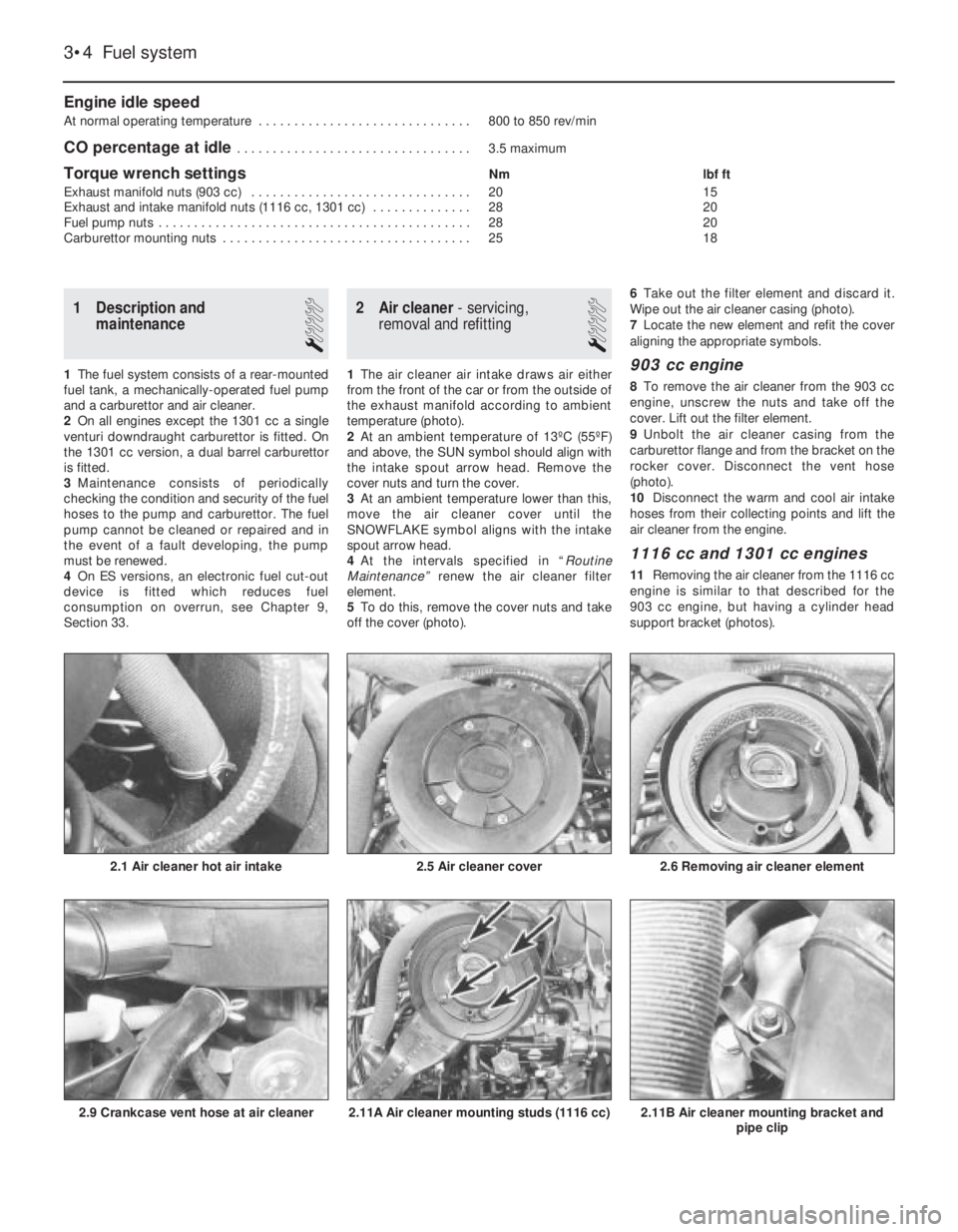
1The air cleaner air intake draws air either
from the front of the car or from the outside of
the exhaust manifold according to ambient
temperature (photo).
2At an ambient temperature of 13ºC (55ºF)
and above, the SUN symbol should align with
the intake spout arrow head. Remove the
cover nuts and turn the cover.
3At an ambient temperature lower than this,
move the air cleaner cover until the
SNOWFLAKE symbol aligns with the intake
spout arrow head.
4At the intervals specified in “Routine
Maintenance” renew the air cleaner filter
element.
5To do this, remove the cover nuts and take
off the cover (photo).6Take out the filter element and discard it.
Wipe out the air cleaner casing (photo).
7Locate the new element and refit the cover
aligning the appropriate symbols.903 cc engine
8To remove the air cleaner from the 903 cc
engine, unscrew the nuts and take off the
cover. Lift out the filter element.
9Unbolt the air cleaner casing from the
carburettor flange and from the bracket on the
rocker cover. Disconnect the vent hose
(photo).
10Disconnect the warm and cool air intake
hoses from their collecting points and lift the
air cleaner from the engine.
1116 cc and 1301 cc engines
11Removing the air cleaner from the 1116 cc
engine is similar to that described for the
903 cc engine, but having a cylinder head
support bracket (photos).
2.6 Removing air cleaner element
2.5 Air cleaner cover2.1 Air cleaner hot air intake
Page 65 of 303

7 Carburettor idle speed and
mixture- adjustment
4
1All carburettors have their mixture
adjustment set in production. The screw is
fitted with a tamperproof cap.
2Under normal circumstances, only the idle
speed screw need be adjusted to set the
engine idle speed to the specified level.
3Before attempting to adjust the idle speed
or mixture, it is important to have the ignition
and valve clearances correctly set and the
engine at normal operating temperature with
the air cleaner fitted.
4Where the mixture must be adjusted, prise
out the tamperproof plug and turn the mixture
screw in to weaken or out to enrich the
mixture until the engine runs smoothly without
any tendency to “hunt”.
5Ideally an exhaust gas analyser should be
used to make sure that the CO level is within
the specified range.
6Once the mixture has been correctly set,
re-adjust the idle speed screw.
8 Carburettor-
removal and refitting
2
1Remove the air cleaner.
2Disconnect the flow and return fuel hoses
from the carburettor and plug them.3Disconnect the coolant hoses from the
carburettor throttle valve plate block.
Provided the cooling system is cold and not
under pressure there should be almost no loss
of coolant. Tie the hoses up as high as
possible with a piece of wire.
4Disconnect the vacuum and vent hoses
from the carburettor.
5Disconnect the throttle and choke controls
from the carburettor.
6Unscrew the mounting flange nuts and lift
the carburettor from the intake manifold
(photo).
7Refitting is a reversal of removal. Use a new
flange gasket and make sure that the fuel
return hose is routed above the air cleaner
intake.
9 Carburettor
(Weber 32 ICEV 50/250/1)-
servicing and adjustment
4
1The carburettor top cover with float may be
removed without the need to withdraw the
carburettor from the manifold. The other
adjustments described will require removal of
the carburettor.
2Unscrew the filter plug from the top cover,
clean the filter screen and refit it.
3Extract the top cover fixing screws, lift the
cover and tilt it to unhook it from the
diaphragm capsule link rod.
4Access to the fuel inlet needle valve isobtained by carefully tapping out the float arm
pivot pin. Take care, the pivot pin pillars are
very brittle.
5Check that the needle valve body is tight
otherwise fuel can bypass the needle valve
and cause flooding.
Float adjustment
6Reassemble and check the float setting. Do
this by holding the top cover vertically so that
the float hangs down under its own weight.
Measure dimension (A) (Fig. 3.10) which
should be between 1 0.50 and 11.10 mm
(0.41 to 0.44 in) with the gasket in position. If
necessary, bend the float arm tab to adjust.
7Now check the float travel which should be
45.0 mm (1.77 in). If adjustment is required,
bend the end of the float arm.
Accelerator pump stroke
8Using a twist drill as a gauge, open the
throttle valve plate through 3.5 mm (0.138 in).
9Turn the nut on the accelerator pump rod
until it just makes contact with the pump
control lever.
Fast idle adjustment
10With the choke valve plate fully closed by
means of the control lever, the throttle valve
Fuel system 3•7
Fig. 3.9 Fuel return hose correctly located
(Sec 8)
8.6 Carburettor mounting flange nut8.2 Fuel hose at carburettor
Fig. 3.10 Float setting diagram (Weber 32 ICEV 50/250) (Sec 9)
A = 10.5 to 11.0 mm (0.41 to 0.44 in) B = 45.0 mm (1.77 in)Fig. 3.11 Accelerator pump setting diagram
(Weber 32 ICEV 50/250) (Sec 9)
X = 3.5 mm (0.138 in)
3
Page 67 of 303

pump jet and give ten full strokes of the
throttle lever, pausing between each stroke to
allow fuel to finish dripping.
8The total volume of fuel collected should be
between 2.5 and 4.5 cc. Adjust the nut on the
pump control and if necessary to increase or
decrease the volume of fuel ejected.
Fast idle adjustment
9With the choke valve plate fully closed, the
throttle valve plate should be open to give a
dimension (X) (Fig. 3.18) of between 0.90 and
1.0 mm (0.035 to 0.039 in). Use a twist drill of
suitable diameter to measure the gap. If
necessary, adjust by means of the screw and
locknut.
Anti-flooding device
10Close the choke valve plate by means of
the control lever. At the same time, push the
lean out valve rod towards the valve.
11There should be a gap (X) (Fig. 3.19)
between the edge of the choke valve plateand the carburettor throat of between 4.75
and 5.25 mm (0.187 to 0.207 in). Adjust if
necessary by means of the screw and locknut
on the lean out valve.
11 Carburettors (Weber 32 ICEE/
250 and Solex C32 DISA 14)-
description and adjustment
4
1One of these carburettors is used on
903 cc ES engines. They are very similar to
the Weber 32 ICEV 50/250 and Solex
C32 DISA 11 already described in this
Chapter except that a fuel cut-out solenoid
valve is fitted in association with the Digiplex
ignition system (see Chapters 4 and 9).
2The solenoid valve cuts off the supply of
fuel to the carburettor whenever the
accelerator pedal is released during overrun
conditions.
3A fuel cut-out device control unit receives
information regarding engine speed from the
static ignition control unit.
4A throttle butterfly switch relays informationthat the accelerator pedal is in the released
state.
5At certain minimum idle speeds during
deceleration, the fuel cut-out solenoid valve is
re-energised so that engine idling is
maintained without the tendency to cut out.
6The Solex type control unit varies the fuel
cut-out point according to the deceleration
value.Fault testing
7Should a fault develop, connect a test lamp
between the fuel cut-out solenoid switch and
a good earth.
8Connect a reliable tachometer to the engine
in accordance with the maker’s instructions.
9Start the engine and raise its speed to
between 3000 and 4000 rev/min, then fully
release the accelerator pedal.
10The test lamp should only go out during
the period when the accelerator pedal is
released. Should the test lamp remain on all
the time, or never come on, check the throttle
switch earth and the solenoid switch
connections.
11Disconnect the multi-plug from the control
unit. Switch on the ignition and check that a
test lamp connected between contact 7 of the
multi-plug and earth will illuminate. If it does
not, there is an open circuit from connection
15/54 of the fuel cut-off switch.
12Switch off the ignition and check for
continuity between contact 3 of the multiplug
and earth. An ohmmeter will be required for
this test.
13If there is no continuity (ohmmeter shows
infinity), check all the system earth
connections. Also check that the wiring plug
under the control unit is properly connected.
14Finally, check the engine speed signal. To
do this, a tachometer must be connected to
the single socket under the control unit within
the engine compartment.
15If the tachometer registers correctly then
this confirms that the electronic ignition
Fuel system 3•9
Fig. 3.18 Fast idle adjustment diagram (Solex C32 DISA 11)
(Sec 10)
X = 0.90 to 1.0 mm (0.035 to 0.039 in)Fig. 3.19 Anti-flooding device adjustment diagram
(Solex C32 DISA 11) (Sec 10)
X = 4.75 to 5.25 mm (0.187 to 0.207 in)
Fig. 3.21 Sectional view of fuel cut-off
switch (Solex C32 DISA 14) (Sec 11)
Fig. 3.20 Moving lean out valve rod
(Solex C32 DISA 11) (Sec 10)
X = 4.75 to 5.25 mm (0.187 to 0.207 in)
3