1983 FIAT UNO checking oil
[x] Cancel search: checking oilPage 127 of 303

Cooling system................................................................................. 8
Part A: 999 cc engine
Description
Maintenance
Thermostat - removal and refitting
Coolant pump - removal and refitting
Part B: 1301 cc Turbo ie engine
Description
Part C: 1372 cc ie and 1372 cc Turbo ie engines
Description
Maintenance
Cooling system - draining, flushing and refilling
Radiator (and cooling fan) - removal and refitting
Thermostat - removal and refitting
Coolant pump - removal and refitting
Coolant pump/alternator drivebelt - checking, renewal and
tensioning
Part D: Heater unit later models
Heater unit - removal and refitting
Heater unit - dismantling and reassembly
Fuel and exhaust systems............................................................... 9
Part A: General
Unleaded fuel
Air cleaner modified types
Fuel pump (999 cc engine) - description, removal and
refitting
Fuel tank (999 cc engine)
Part B: Carburettor models
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF) - description
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF) - idle speed and mixture
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF) - removal and refitting
Carburettor (Weber 32 TLF) - overhaul
Carburettor (Weber 30/32 DMTE) - general
Carburettor (Weber 30/32 DMTE) - overhaul
Carburettor (Weber 32 ICEV 61/250 and DMTE 30/32,
DMTE 30/150) - general
Carburettor (Solex C 30/32-CIC 8) - description
Part C: Bosch LE-2 Jetronic fuel injection system
Description
Maintenance
Fuel filter - renewal
Air cleaner element - renewal
Idle speed and mixture - adjustment
Fuel injection system - electrical tests
Fuel injection system - mechanical tests
Fuel injection system components - removal and
refitting
Throttle control linkage - general
Fuel tank - general
Part D: Bosch Mono-Jetronic fuel injection system
Description
Maintenance
Fuel filter - renewal
Air cleaner element - renewal
Idle speed and mixture adjustment
Accelerator control system - check and adjustment
Fuel system - depressurisation
Fuel pump and supply - system checks
Fuel pump - removal and refitting
Injector unit - removal and refitting
Intake air temperature sensor - removal and refitting
Fuel injector - removal and refitting
Electronic control unit (ECU) - removal and refitting
Inlet manifold - removal and refitting
Exhaust manifold - removal and refitting
Catalytic converter - general information
Fuel evaporation control system - generalPart E: Bosch L3.1/2 Jetronic fuel injection systems
Description
Fuel system - depressurisation
Maintenance
Fuel filter - renewal
Air cleaner element - renewal
Checks and adjustments
Injection system components - removal and refitting
Part G: Turbocharger system
Description
Precautions
Turbocharger (1301 cc ie engine) - removal and refitting
Turbocharger (1372 cc ie engine) - removal and refitting
Intercooler - removal and refitting
Injector cooling fan - removal and refitting
Fault finding - fuel injection system
Fault finding - turbocharger system
Ignition system................................................................................. 10
General
Ignition timing (all later models)
Breakerless ignition system - description
Distributor (breakerless type) - removal and refitting
Distributor (breakerless type) - overhaul
Breakerless ignition system components - testing
Microplex ignition system - description
Distributor (Microplex) - removal and refitting
Microplex ignition system components - testing
Digiplex 2 ignition system - description
Distributor (Digiplex 2) - removal and refitting
Spark plugs and HT leads - general
Fault finding - Microplex ignition system
Clutch................................................................................................ 11
Clutch pedal adjustment (cable clutch)
Hydraulic clutch - description
Maintenance (hydraulic clutch)
Clutch master cylinder - removal, overhaul and
refitting
Clutch operating cylinder - removal, overhaul and
refitting
Clutch hydraulic system - bleeding
Transmission.................................................................................... 12
Part A: 1301 cc Turbo ie engine
Description
Gearchange linkage - removal and refitting
Gearchange linkage (Antiskid models) - general
Final drive output shafts - description and oil seal
renewal
Part B: 1372 cc ie and 1372 cc Turbo ie engines
Description
Maintenance
Oil level - checking
Oil - renewal
Gearlever and linkages - general
Transmission - removal and refitting
Part C: 999 and 1108 cc with C514 type transmission
Description
Maintenance
Driveshafts........................................................................................ 13
Inboard joint boots (non-Turbo models, September 1987 on) -
modification
Intermediate driveshaft (Turbo ie models)
Inboard CV joints (Turbo ie models - overhaul
Right-hand driveshaft damper weight (1108 and 1372 cc
models) - removal and refitting
13•2 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
Page 147 of 303

lubrication pipe (prise the oil feed stub out
with a screwdriver), unscrew the remaining
bolts and take off the bearing caps (photos).
24Lift the camshaft carefully from the
cylinder head, checking that the valve
clearance shims and cam followers are not
withdrawn by the adhesion of the oil (photo).
25If the shims and cam followers are to be
removed, keep them in their originally fitted
order (photos).
26Refitting is a reversal of removal but use a
new camshaft oil seal and camshaft cover
gasket. Oil the camshaft bearings (photos).
27Make sure that the timing belt is
reconnected and tensioned as described
previously.
28Check the valve clearances.
29Tighten all nuts and bolts to the specified
torque.
Cylinder head -
removal and refitting#
Warning: Refer to the beginning
of Section 9 before starting any
work.
Note: The cylinder head should be removed
cold.
30Drain the cooling system.
31Remove the air cleaner.
32Disconnect the throttle and choke
connections from the carburettor (photo).
33On carburettor models, disconnect the
fuel hoses from the fuel pump and the
carburettor. On fuel injection models,
13•22 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
5B.26B Camshaft cover gasket5B.26A Camshaft oil seal5B.25B Removing a cam follower (tappet)
with shim
2B.25A Valve clearance shim showing
thickness mark5B.24 Removing the camshaft
5B.23D Camshaft bearing cap showing
short and long positioning dowels for
correct fitting5B.23C Camshaft lubrication pipe
5B.23B Unscrewing the camshaft
bearing/banjo union bolt5B.23A Prising out the camshaft oil feed
pipe stub5B.22C Camshaft sprocket showing
integral key (arrowed)
Page 149 of 303
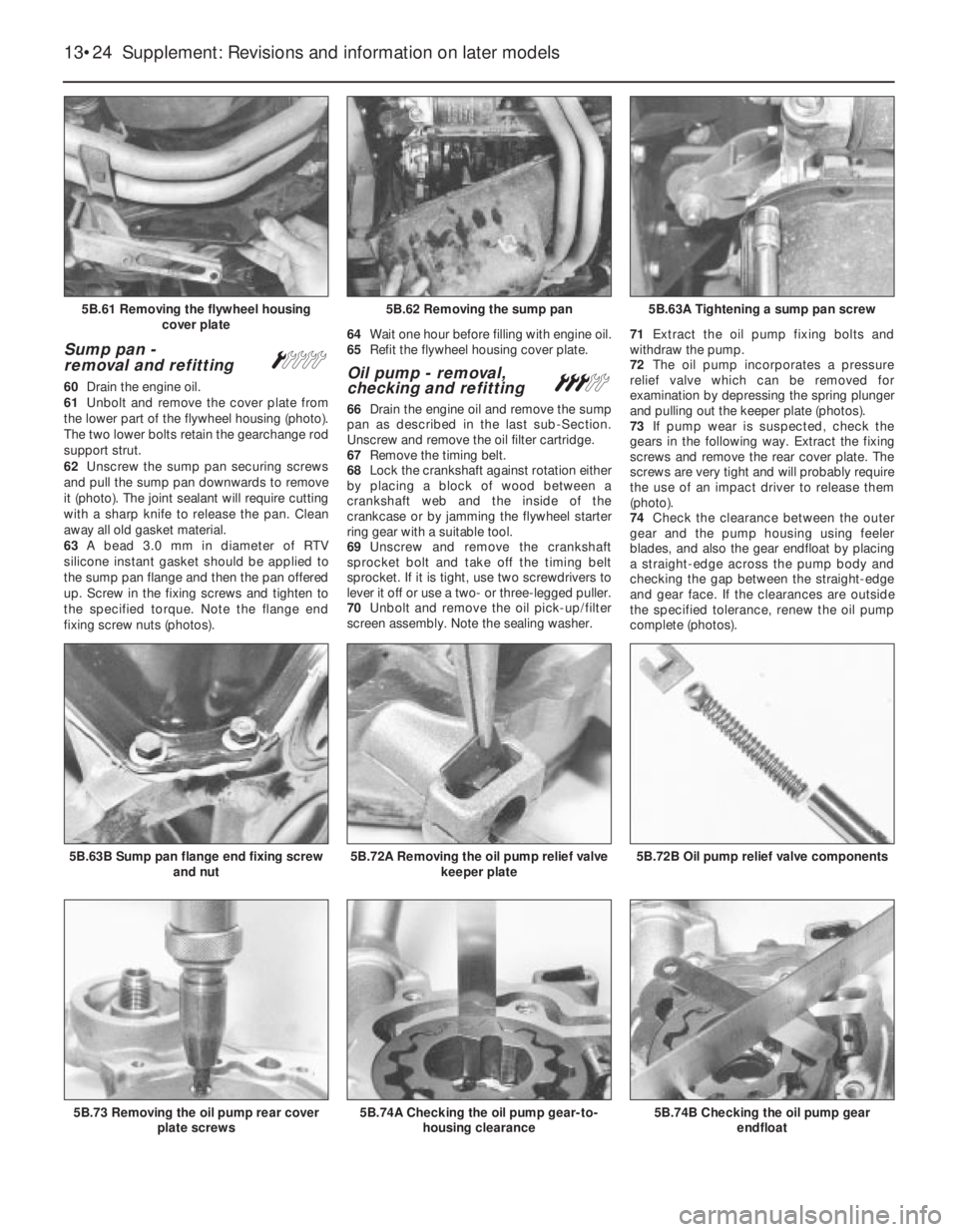
Sump pan -
removal and refitting Á
60Drain the engine oil.
61Unbolt and remove the cover plate from
the lower part of the flywheel housing (photo).
The two lower bolts retain the gearchange rod
support strut.
62Unscrew the sump pan securing screws
and pull the sump pan downwards to remove
it (photo). The joint sealant will require cutting
with a sharp knife to release the pan. Clean
away all old gasket material.
63A bead 3.0 mm in diameter of RTV
silicone instant gasket should be applied to
the sump pan flange and then the pan offered
up. Screw in the fixing screws and tighten to
the specified torque. Note the flange end
fixing screw nuts (photos).64Wait one hour before filling with engine oil.
65Refit the flywheel housing cover plate.Oil pump - removal,
checking and refitting#
66Drain the engine oil and remove the sump
pan as described in the last sub-Section.
Unscrew and remove the oil filter cartridge.
67Remove the timing belt.
68Lock the crankshaft against rotation either
by placing a block of wood between a
crankshaft web and the inside of the
crankcase or by jamming the flywheel starter
ring gear with a suitable tool.
69Unscrew and remove the crankshaft
sprocket bolt and take off the timing belt
sprocket. If it is tight, use two screwdrivers to
lever it off or use a two- or three-legged puller.
70Unbolt and remove the oil pick-up/filter
screen assembly. Note the sealing washer.71Extract the oil pump fixing bolts and
withdraw the pump.
72The oil pump incorporates a pressure
relief valve which can be removed for
examination by depressing the spring plunger
and pulling out the keeper plate (photos).
73If pump wear is suspected, check the
gears in the following way. Extract the fixing
screws and remove the rear cover plate. The
screws are very tight and will probably require
the use of an impact driver to release them
(photo).
74Check the clearance between the outer
gear and the pump housing using feeler
blades, and also the gear endfloat by placing
a straight-edge across the pump body and
checking the gap between the straight-edge
and gear face. If the clearances are outside
the specified tolerance, renew the oil pump
complete (photos).
13•24 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
5B.74B Checking the oil pump gear
endfloat5B.74A Checking the oil pump gear-to-
housing clearance5B.73 Removing the oil pump rear cover
plate screws
5B.72B Oil pump relief valve components5B.72A Removing the oil pump relief valve
keeper plate5B.63B Sump pan flange end fixing screw
and nut
5B.63A Tightening a sump pan screw5B.62 Removing the sump pan5B.61 Removing the flywheel housing
cover plate
Page 155 of 303
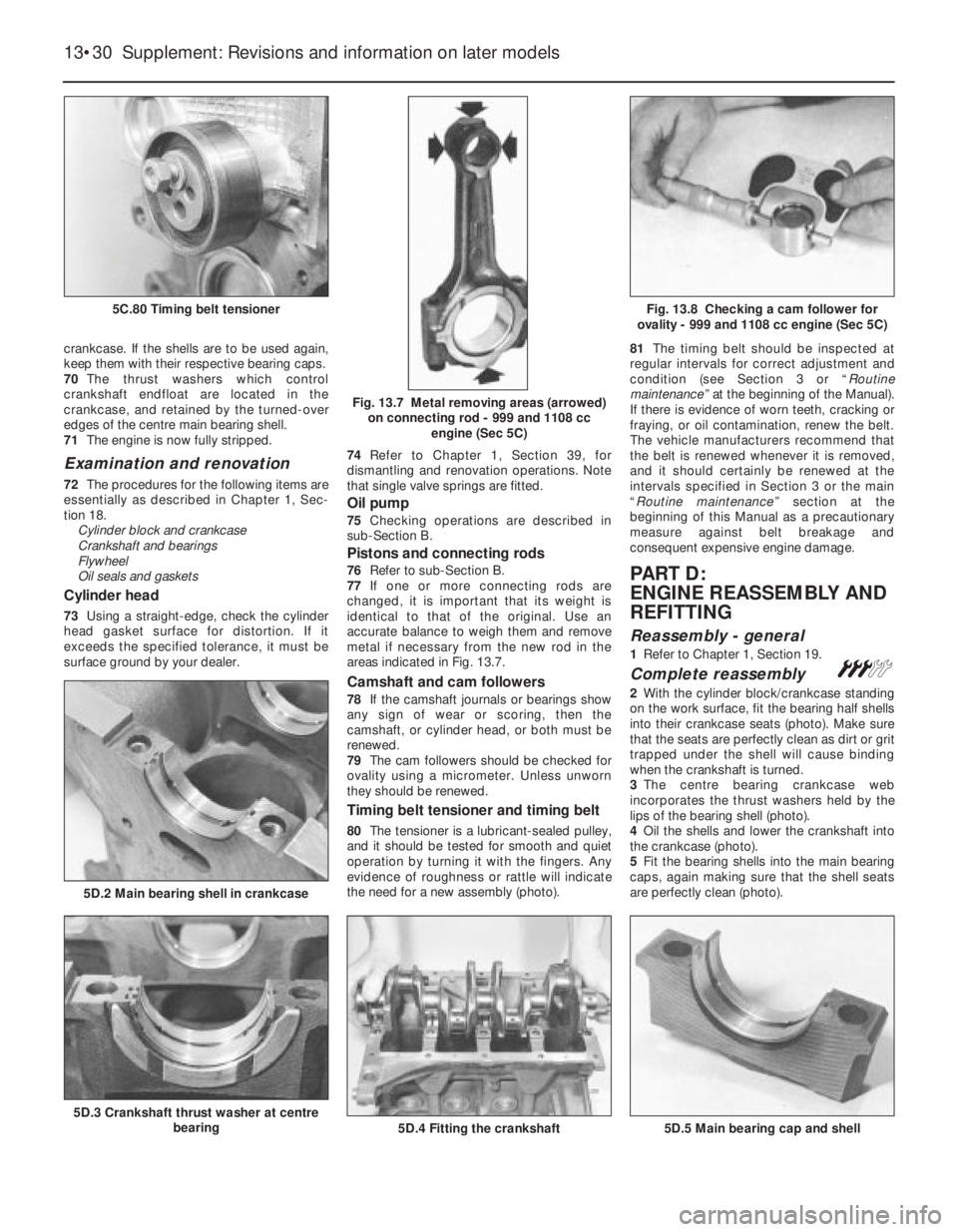
crankcase. If the shells are to be used again,
keep them with their respective bearing caps.
70The thrust washers which control
crankshaft endfloat are located in the
crankcase, and retained by the turned-over
edges of the centre main bearing shell.
71The engine is now fully stripped.
Examination and renovation
72The procedures for the following items are
essentially as described in Chapter 1, Sec-
tion 18.
Cylinder block and crankcase
Crankshaft and bearings
Flywheel
Oil seals and gaskets
Cylinder head
73Using a straight-edge, check the cylinder
head gasket surface for distortion. If it
exceeds the specified tolerance, it must be
surface ground by your dealer.74Refer to Chapter 1, Section 39, for
dismantling and renovation operations. Note
that single valve springs are fitted.
Oil pump
75Checking operations are described in
sub-Section B.
Pistons and connecting rods
76Refer to sub-Section B.
77If one or more connecting rods are
changed, it is important that its weight is
identical to that of the original. Use an
accurate balance to weigh them and remove
metal if necessary from the new rod in the
areas indicated in Fig. 13.7.
Camshaft and cam followers
78If the camshaft journals or bearings show
any sign of wear or scoring, then the
camshaft, or cylinder head, or both must be
renewed.
79The cam followers should be checked for
ovality using a micrometer. Unless unworn
they should be renewed.
Timing belt tensioner and timing belt
80The tensioner is a lubricant-sealed pulley,
and it should be tested for smooth and quiet
operation by turning it with the fingers. Any
evidence of roughness or rattle will indicate
the need for a new assembly (photo).81The timing belt should be inspected at
regular intervals for correct adjustment and
condition (see Section 3 or “Routine
maintenance” at the beginning of the Manual).
If there is evidence of worn teeth, cracking or
fraying, or oil contamination, renew the belt.
The vehicle manufacturers recommend that
the belt is renewed whenever it is removed,
and it should certainly be renewed at the
intervals specified in Section 3 or the main
“Routine maintenance” section at the
beginning of this Manual as a precautionary
measure against belt breakage and
consequent expensive engine damage.
PART D:
ENGINE REASSEMBLY AND
REFITTING
Reassembly - general
1Refer to Chapter 1, Section 19.
Complete reassembly#
2With the cylinder block/crankcase standing
on the work surface, fit the bearing half shells
into their crankcase seats (photo). Make sure
that the seats are perfectly clean as dirt or grit
trapped under the shell will cause binding
when the crankshaft is turned.
3The centre bearing crankcase web
incorporates the thrust washers held by the
lips of the bearing shell (photo).
4Oil the shells and lower the crankshaft into
the crankcase (photo).
5Fit the bearing shells into the main bearing
caps, again making sure that the shell seats
are perfectly clean (photo).
13•30 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
5D.5 Main bearing cap and shell5D.4 Fitting the crankshaft5D.3 Crankshaft thrust washer at centre
bearing
5D.2 Main bearing shell in crankcase
Fig. 13.8 Checking a cam follower for
ovality - 999 and 1108 cc engine (Sec 5C)
Fig. 13.7 Metal removing areas (arrowed)
on connecting rod - 999 and 1108 cc
engine (Sec 5C)
5C.80 Timing belt tensioner
Page 156 of 303

6Fit the main bearing caps in their numbered
sequence and the correct way round (photo).
7Clean the threads of the main bearing cap
bolts, lightly oil them and screw them in
finger-tight. Tighten all bolts progressively to
the specified torque, then check that the
crankshaft turns smoothly and evenly
(photos).
8Now check the crankshaft endfloat. Do this
using a dial gauge or feeler blades inserted
between the machined shoulder of a journal
and the side of the bearing cap (photo). Move
the crankshaft fully in one direction and then
the other to ensure that full movement is
obtained. If the endfloat is outside the
specified tolerance and new bearing shellshave been fitted, then a fault must have
occurred during crankshaft regrinding.
9Fit a new oil seal to the crankshaft rear oil
seal retainer. Apply grease to the seal lips. A
conventional gasket is not used at the oil seal
joint face but a 3.0 mm diameter bead of RTV
silicone instant gasket must be applied
to a clean surface as shown in Fig. 13.9
(photo).
10Bolt the retainer into position. One hour at
least must be allowed for the RTV to cure
before oil contacts it.
11Turn the engine on its side and fit the
piston/connecting rods as described in
sub-Section B.
12Fit a new oil seal to the oil pump, oil theseal lips and bolt on the pump using a new
joint gasket (photos).
13Use a new sealing washer and fit the oil
pick-up/filter screen assembly.
14Fit the engine rear plate and then the
flywheel on its mounting flange. Apply
thread-locking fluid to (clean) bolt threads and
screw in the bolts to the specified torque
(photo). Hold the flywheel against rotation by
locking the starter ring gear with a suitable
tool.
15Fit the sump pan as described in
sub-Section B.
16Fit the crankshaft sprocket so that the
timing mark is visible. Lock the flywheel
starter ring gear teeth, and screw in and
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•31
5D.7B Angle-tightening a main bearing cap
bolt5D.7A Initial tightening of a main bearing
cap bolt5D.6 Fitting a main bearing cap
5D.14 Tightening a flywheel bolt5D.12B Tightening an oil pump bolt5D.12A Oil pump gasket
5D.9 Fitting crankshaft rear oil seal
retainerFig. 13.9 Application area for silicone
gasket on crankshaft rear oil seal retainer
(Sec 5D)5D.8 Checking crankshaft endfloat using a
dial gauge
13
Page 162 of 303

Initial start-up after major
overhaul
28Refer to Chapter 1, Section 45, but note
that an oil pressure gauge is fitted to indicate
oil pressure.
29Check the ignition static timing as
described in Section 10.
30Check the engine idle speed and CO level
as described in Section 9.
7 Engine-
1372 cc ie and 1372 cc
Turbo ie
PART A: GENERAL
Description
1The 1372 cc engine is similar in design to
the OHC engine fitted to the FIAT Tipo
variants. The engine is of four-cylinder, in-line,
overhead camshaft type, mounted
transversely at the front of the vehicle.
2The crankshaft runs in five main bearings.
Thrustwashers are fitted to the rear (flywheel
end) main bearing in order to control
crankshaft endfloat.
3The connecting rods are attached to the
crankshaft by horizontally split shell-type
big-end bearings. The pistons are attached to
the connecting rods by fully-floating gudgeon
pins which are secured by circlips. The
aluminium alloy pistons are fitted with three
piston rings: two compression rings and an oil
control ring.
4The camshaft is driven by a toothed belt
and operates the valves via bucket and shim
type cam followers. The camshaft is located in
a separate housing on top of the cylinder
head.
5The inlet and exhaust valves are each
closed by double valve springs, and operate
in guides pressed into the cylinder head.
6The auxiliary shaft, which is also driven by
the toothed belt, drives the oil pump.
7Lubrication is by means of a gear type
pump which draws oil through a strainer
located in the sump, and forces it through a
full-flow filter into the engine oil galleries fromwhere it is distributed to the crankshaft,
camshaft and auxiliary shaft. The big-end
bearings are supplied with oil via internal
drillings in the crankshaft. The undersides of
the pistons are cooled by oil spray nozzles
located in each main bearing location in the
crankcase.
8A crankcase ventilation system is
employed, whereby piston blow-by gases are
drawn via an oil separator into the air cleaner,
from where they are drawn into the inlet
manifold and re-burnt with fresh air/fuel
mixture.
9The 1372 cc ie engine is fitted with a Bosch
Mono-Jetronic single point fuel injection (SPi)
system. Whilst the higher performance
1372 cc Turbo ie engine is fitted with a Bosch
L3.1 (L3.2 from 1992) Jetronic multi-point
injection (MPi) system and turbocharger with
intercooler and oil cooling. The L3.2 system
models are fitted with catalytic converters.
Maintenanceª
10At the intervals specified in Section 3 or
“Routine maintenance” at the beginning of
this Manual, carry out the following tasks.
11Check the engine oil level as follows. With
the vehicle parked on level ground, and with
the engine having been stopped for a few
minutes, withdraw the oil level dipstick, wipe it
on a clean rag, and re-insert it fully. Withdraw
the dipstick again and read off the oil level
relative to the MAX and MIN marks. The oil
level should be between the marks. If the level
is at or below the MIN mark, top up through
the filler on the camshaft cover without delay
(photo). The quantity of oil required to raise
the level from MIN to MAX on the dipstick is
approximately 1.0 litre (1.8 pints). Do not
overfill.
12Renew the engine oil and filter as
described in Section 2 of Chapter 1 (photos).
13Check and if necessary adjust the valve
clearances as described in Part B of this
Section.
14Inspect the engine for signs of oil, coolant
or fuel leaks and rectify as necessary.
15Inspect the crankcase ventilation hose for
blockage or damage. Clean or renew as
necessary.
16Check the condition and tension of thetiming belt as described in Part B of this
Section.
17Renew the timing belt as described in
Part B of this Section.
PART B:
OPERATIONS POSSlBLE
WITH ENGINE IN CAR
Valve clearances -
checking and adjustment#
1It is important to ensure that the valve
clearances are set correctly, as incorrect
clearances will result in incorrect valve timing
thus affecting engine performance.
2The clearances must be checked and
adjusted with the engine cold.
3On the ie engine, refer to Section 9 in this
Chapter for details and remove the air cleaner
unit.
4On the ie engine disconnect the crankcase
ventilation hose from the injector unit and
position the hose out of the way.
5On Turbo ie engines, loosen off the clips
and remove the air hose to the inlet manifold
(above the camshaft cover).
6On Turbo ie engines, disconnect the
accelerator cable from the throttle housing
and the support bracket on the camshaft
cover.
7Unscrew the securing nuts and washers
and remove the camshaft cover, noting that
on later models two of the nuts also secure
the hose clip assembly. Recover the gasket.
8Numbering from the front (timing belt) end
of the engine, the exhaust valves are 1, 4, 5
and 8, and the inlet valves are 2, 3, 6 and 7.
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•37
7A.12B Engine oil filter removal using a
strap wrench - 1372 cc engine7A.12A Engine sump drain plug - 1372 cc
engine7A.11 Topping up the engine oil level -
1372 cc engine
Fig. 13.15 Engine oil level dipstick location
and level markings on the 1372 cc ie and
Turbo ie engines (Sec 7A)
13
Page 171 of 303

new oil seal, ensuring that it is correctly
orientated, and drive it squarely into position.
149Refit all disturbed components.
Flywheel - removal,
inspection and refitting#
150If not already done, remove the clutch as
described in Chapter 5.
151Prevent the flywheel from turning by
jamming the ring gear teeth, or by bolting a
strap between the flywheel and the cylinder
block.
152Make alignment marks on the flywheel
and the end of the crankshaft, so that the
flywheel can be refitted in its original position.
153Unscrew the securing bolts and remove
the washer plate, then withdraw the flywheel.
Do not drop it, it is very heavy.
154With the flywheel removed, the ring gear
can be examined for wear and damage.
155If the ring gear is badly worn or has
missing teeth it should be renewed. The old
ring gear can be removed from the flywheel by
cutting a notch between two teeth with a
hacksaw and then splitting it with a cold
chisel. Wear eye protection when doing this.
156Fitting of a new ring gear requires heating
the ring to a temperature of 80ºC (176ºF). Do
not overheat, or the hard-wearing properties
will be lost. The gear has a chamfered inner
edge which should fit against the shoulder on
the flywheel. When hot enough, place the gear
in position quickly, tapping it home ifnecessary, and let it cool naturally without
quenching in any way.
157Ensure that the mating faces are clean,
then locate the flywheel on the rear of the
crankshaft, aligning the previously made
marks on the flywheel and crankshaft.
158Fit the washer plate, and insert the
securing bolts, then prevent the flywheel from
turning as described in paragraph 151 whilst
the bolts are tightened progressively to the
specified torque setting in a diagonal
sequence (photos).
159If applicable, refit the clutch as described
in Chapter 5.
Sump -
removal and refittingÁ
160Drain the engine oil from the sump as
described in Chapter 1.
161Disconnect the lead from the engine oil
level sensor in the sump.
162Unscrew and remove the bolts retaining the
gear linkage mounting bracket (where applicable)
and the clutch housing lower cover bolts.
Remove the cover from the clutch housing.
163Unscrew and remove the sump retaining
bolts and nuts and lower the sump from the
crankcase. Recover the gasket.
164Clean all traces of old gasket from the
sump, crankcase and both oil seal housing
mating surfaces.
165Commence reassembly by applying
sealing compound (FIAT No. 5882442 orequivalent) to the joints between the
crankshaft front and rear oil seal housings and
the mating face of the crankcase (photo).
166Locate the new gasket in position on the
crankcase then fit the sump. As it is fitted it
will need to be twisted to avoid fouling the oil
pump unit. Refit the retaining bolts and nuts
and tighten them to the specified torque
(photos).
167Check that the sump drain plug is refitted
and fully tightened. If the engine is in the car,
top up the engine oil level.
Oil pump - removal,
checking and refittingª
168Drain the engine oil and remove the
sump as described in the previous
sub-Section.
169Unscrew the retaining bolts then
withdraw the oil pump and intake pipe/filter
from its location within the crankcase.
Remove the gasket.
170If oil pump wear is suspected, first check
the cost and availability of new parts and the
cost of a new pump. Then examine the pump
as described below and decide whether
renewal or repair is the best course of action.
171Unscrew the three securing bolts and
remove the oil pump cover (photo). Note that
as the cover is removed, the oil pressure relief
valve components will be released.
172Recover the oil pressure relief valve,
spring and spring seat.
13•46 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
7B.166C . . . and insert the retaining bolts7B.166B . . . refit the sump . . .7B.166A Locate the new gasket . . .
7B.165 Apply sealant to the front oil seal
housing/cylinder block joint7B.158B . . . tighten the bolts to the
specified torque7B.158A Locate the flywheel, washer plate
and bolts . . .
Page 172 of 303
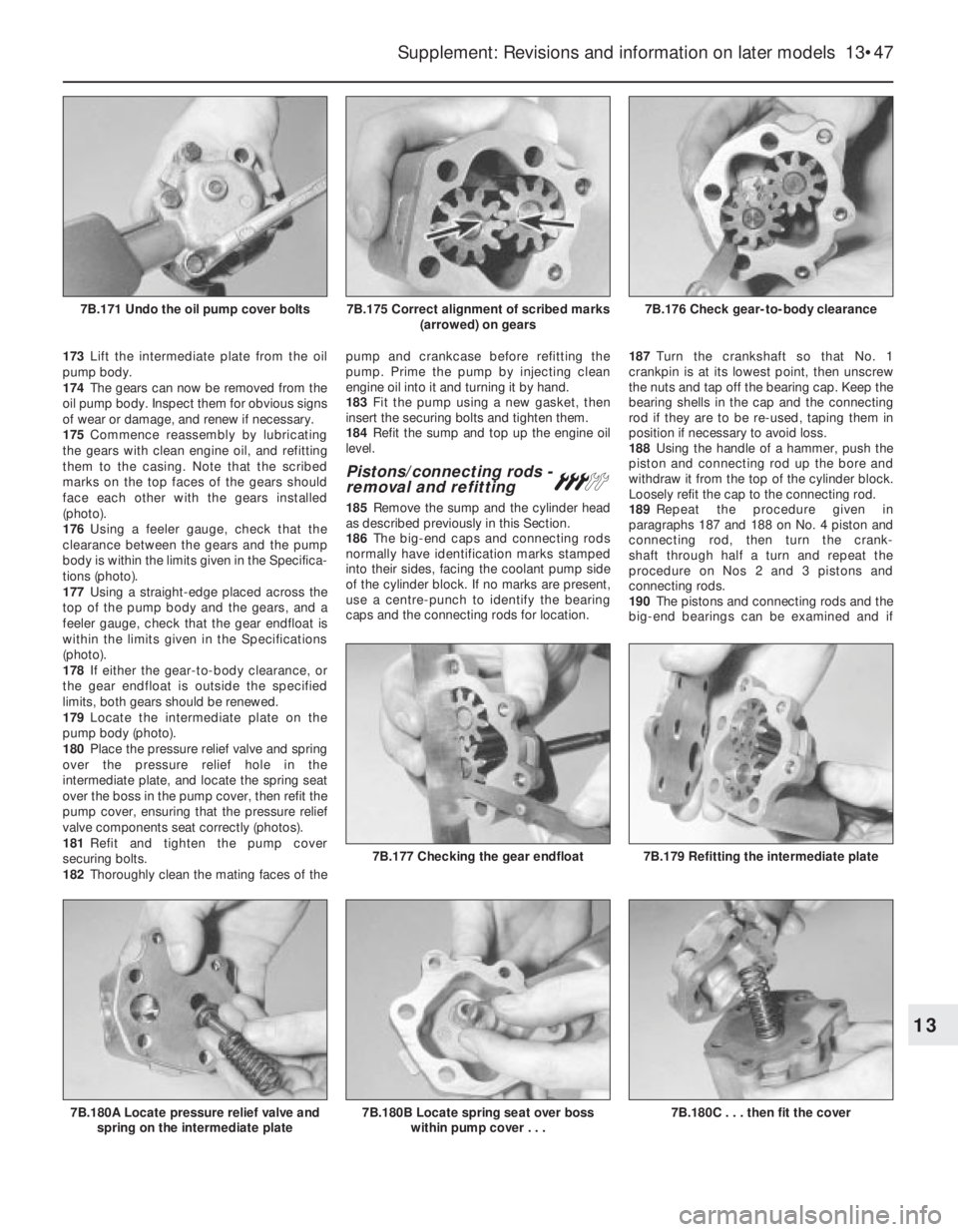
173Lift the intermediate plate from the oil
pump body.
174The gears can now be removed from the
oil pump body. Inspect them for obvious signs
of wear or damage, and renew if necessary.
175Commence reassembly by lubricating
the gears with clean engine oil, and refitting
them to the casing. Note that the scribed
marks on the top faces of the gears should
face each other with the gears installed
(photo).
176Using a feeler gauge, check that the
clearance between the gears and the pump
body is within the limits given in the Specifica-
tions (photo).
177Using a straight-edge placed across the
top of the pump body and the gears, and a
feeler gauge, check that the gear endfloat is
within the limits given in the Specifications
(photo).
178If either the gear-to-body clearance, or
the gear endfloat is outside the specified
limits, both gears should be renewed.
179Locate the intermediate plate on the
pump body (photo).
180Place the pressure relief valve and spring
over the pressure relief hole in the
intermediate plate, and locate the spring seat
over the boss in the pump cover, then refit the
pump cover, ensuring that the pressure relief
valve components seat correctly (photos).
181Refit and tighten the pump cover
securing bolts.
182Thoroughly clean the mating faces of thepump and crankcase before refitting the
pump. Prime the pump by injecting clean
engine oil into it and turning it by hand.
183Fit the pump using a new gasket, then
insert the securing bolts and tighten them.
184Refit the sump and top up the engine oil
level.
Pistons/connecting rods -
removal and refitting#
185Remove the sump and the cylinder head
as described previously in this Section.
186The big-end caps and connecting rods
normally have identification marks stamped
into their sides, facing the coolant pump side
of the cylinder block. If no marks are present,
use a centre-punch to identify the bearing
caps and the connecting rods for location.187Turn the crankshaft so that No. 1
crankpin is at its lowest point, then unscrew
the nuts and tap off the bearing cap. Keep the
bearing shells in the cap and the connecting
rod if they are to be re-used, taping them in
position if necessary to avoid loss.
188Using the handle of a hammer, push the
piston and connecting rod up the bore and
withdraw it from the top of the cylinder block.
Loosely refit the cap to the connecting rod.
189Repeat the procedure given in
paragraphs 187 and 188 on No. 4 piston and
connecting rod, then turn the crank-
shaft through half a turn and repeat the
procedure on Nos 2 and 3 pistons and
connecting rods.
190The pistons and connecting rods and the
big-end bearings can be examined and if
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•47
7B.176 Check gear-to-body clearance7B.175 Correct alignment of scribed marks
(arrowed) on gears7B.171 Undo the oil pump cover bolts
7B.180C . . . then fit the cover7B.180B Locate spring seat over boss
within pump cover . . .
7B.179 Refitting the intermediate plate7B.177 Checking the gear endfloat
7B.180A Locate pressure relief valve and
spring on the intermediate plate
13