1983 FIAT UNO ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 96 of 303

the tyres correctly inflated and square to a
wall, at a distance of 10.0 m (32.8 ft) from it.
4Mark the wall to correspond with the
centres of the headlamps.
5Switch to dipped beams when the brightest
parts of the light pattern should be below the
marks on the wall by an amount equal to one
tenth of the distance between the floor and
the mark on the wall.
6Adjust the beams as necessary by turning
the adjuster screws (A) vertical or (B) hori-
zontal, which are located at the rear of the
headlamp.
18 Headlamp-
removal and refitting
1
1Open the bonnet and extract the two
headlamp mounting screws from the top rail
(photo).
2Pull the headlamp unit forward off its
ballstud and then disconnect the wiring plug
(photo).
3Refitting is a reversal of removal.
19 Exterior lamps-
bulb renewal
1
Front parking lamp
1The bulbholder is located in the headlamp
reflector. 2Open the bonnet, push and twist the
bulbholder from its location (photo).
3The wedge base type bulb is simply pulled
from its holder.
Front direction indicator lamp
4Extract the screws and remove the lens
(photo).
5Depress and twist the bayonet fitting type
bulb from its holder.
Side repeater lamp
6This bulb may be renewed in one of two
ways. Either partially remove the underwing
protective shield and reach up under the front
wing and pull the holder out of the lamp body
or depress the lamp retaining tab and
withdraw the lamp from outside the wing. The
tab is very brittle (photo). 7Remove the bulb from the holder.
Rear lamp cluster
8Open the tailgate.
9Gently prise up the clips on the top surface of
the lens. Pull the upper part of the lens outwards
and release it from the lower fixings (photo).
10The individual lamp bulbs may be
renewed, all of them being of bayonet fitting
type (photo).
Rear number plate lamp
11Insert a screwdriver blade in the lens slot
and prise it from the bulb holder. Withdraw
the bulb.
12If preferred, the complete lamp may be
removed from the bumper by reaching up
under the bumper and squeezing the lamp
retaining tabs (photo).
Electrical system 9•7
19.2 Front parking lamp bulb18.2 Withdrawing headlamp18.1 Headlamp upper fixing screw
19.12 Rear number plate lamp withdrawn
19.10 Rear lamp bulbs
19.6 Side repeater lamp19.4 Front direction indicator lamp lens
and bulb
19.9 Rear lamp lens upper clip
9
A Direction indicator
B ReversingC Stop E Fog
D Tail
Page 99 of 303

27 Tailgate wiper motor-
removal and refitting
1
1Remove the blade and arm as previously
described. Unscrew the drive spindle bezel
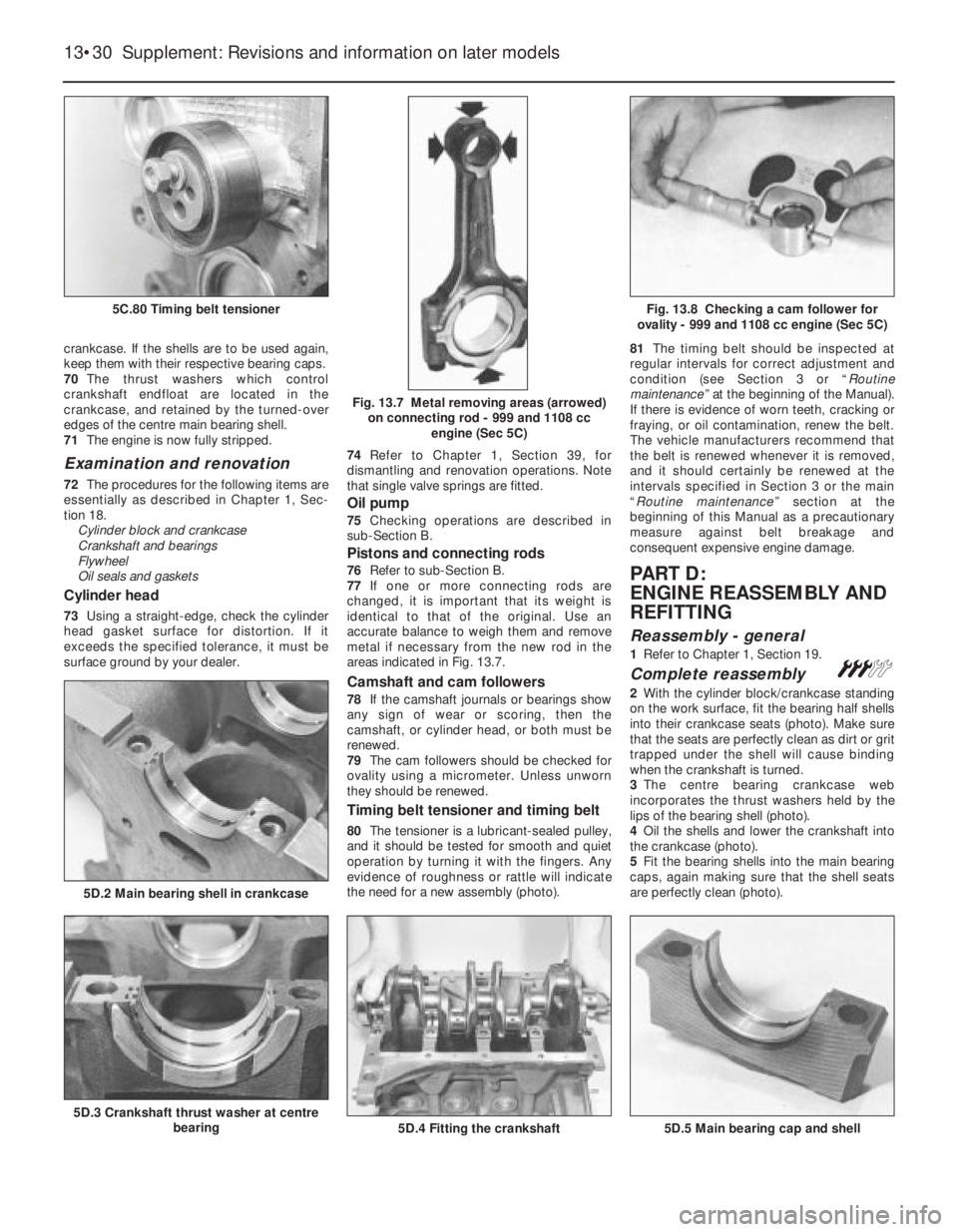
nut.
2Open the tailgate fully.
3Unclip and remove the wiper motor cover.
4Unscrew the mounting screws, withdraw
the motor and disconnect the wiring plug
(photo).
5Refitting is a reversal of removal.
28 Washer system
1
1The washer system for the windscreen and
the tailgate operates from a bag type fluid
reservoir within the engine compartment
(photo).
2The reservoir bag is fitted with two pumps,
one for each system (photo).
3Use screen cleaning fluid mixed in the
recommended proportion in the washer fluid
reservoir and in very cold weather add a small
quantity of methylated spirit.
4To clear a blocked washer jet nozzle or to
adjust the wash jet glass-striking pattern,
insert a pin part way into the jet nozzle.
29 Heated tailgate window-
precautions and repair
2
1The heater element inside the tailgate glass
should be treated with care.
2Clean only with a damp cloth and wipe in
the direction in which the filaments run. Avoid
scratching with rings on the fingers, or by
allowing luggage to rub on the glass. Never
stick adhesive labels over the heater element.
3Should one of the heater filaments be
broken it can be repaired using one of the
special silver paints available, but follow the
manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
30 Radio/cassette- fitting
2
1In-car entertainment equipment is not
provided as standard on the models covered
by this Manual.
2However, the centre console is designed to
receive a radio set after removing the blanking
plate behind which a power lead is already
provided.
3The ignition system and other electrical
components are suppressed during
production of the car and further suppression
should not be required other than earthing the
wiper motor.
Receiver
4Fit the radio/cassette using the installation
kit supplied with the equipment.
5On Comfort models, fit an in-line fuse in the
power feed. On Super models the radio
supply is protected by fuse number 12.
6Make sure that the radio is well earthed to a
metal body component.
Aerial
7The recommended locations for the aerial
are towards the rear of the right-hand front
wing or on the windscreen pillar.
8Fitting instructions for Fiat aerials are
supplied with them, but the following general
advice will help if using non-Fiat equipment.9Motorised automatic aerials rise when the
equipment is switched on and retract at
switch-off. They require more fitting space
and supply leads, and can be a source of
trouble.
10There is no merit in choosing a very long
aerial as, for example, the type about three
metres in length which hooks or clips on to
the rear of the car, since part of this aerial will
inevitably be located in an interference field.
For VHF/FM radios the best length of aerial is
about one metre. Active aerials have a
transistor amplifier mounted at the base and
this serves to boost the received signal. The
aerial rod is sometimes rather shorter than
normal passive types.
11A large loss of signal can occur in the
aerial feeder cable, especially over the Very
High Frequency (VHF) bands. The design of
feeder cable is invariably in the co-axial form,
ie a centre conductor surrounded by a flexible
copper braid forming the outer (earth)
conductor. Between the inner and outer
conductors is an insulator material which can
be in solid or stranded form. Apart from
insulation, its purpose is to maintain the
correct spacing and concentricity. Loss of
signal occurs in this insulator, the loss usually
being greater in a poor quality cable. The
quality of cable used is reflected in the price
of the aerial with the attached feeder cable.
12The capacitance of the feeder should be
within the range 65 to 75 picofarads (pF)
approximately (95 to 100 pF for Japanese and
American equipment), otherwise the
adjustment of the car radio aerial trimmer may
not be possible. An extension cable is
necessary for a long run between aerial and
receiver. If this adds capacitance in excess of
the above limits, a connector containing a
series capacitor will be required, or an
extension which is labelled as
“capacity-compensated”.
13Fitting the aerial will normally involve
making a 7/8 in (22 mm) diameter hole in the
bodywork, but read the instructions that come
with the aerial kit. Once the hole position has
been selected, use a centre punch to guide
the drill. Use sticky masking tape around the
area for this helps with marking out and drill
location, and gives protection to the
9•10 Electrical system
Fig. 9.8 Radio housing and power lead (A)
(Sec 30)
28.2 Washer pumps28.1 Washer fluid reservoir27.4 Tailgate wiper motor
Page 103 of 303

9•14 Electrical system
Fault finding - electrical system
No voltage at starter motor
m mBattery discharged
m mBattery defective internally
m mBattery terminals loose or earth lead not securely attached to body
m mLoose or broken connections in starter motor circuit
m mStarter motor switch or solenoid faulty
Voltage at starter motor - faulty motor
m
mStarter brushes badly worn, sticking, or brush wires loose
m mCommutator dirty, worn or burnt
m mStarter motor armature faulty
m mField coils earthed
Starter motor noisy or rough in engagement
m
mPinion or flywheel gear teeth broken or worn
m mStarter drive main spring broken
m mStarter motor retaining bolts loose
Alternator not charging*
m
mDrivebelt loose and slipping, or broken
m mBrushes worn, sticking, broken or dirty
m mBrush springs weak or broken
* If all appears to be well but the alternator is still not charging, take the
car to an automobile electrician for checking of the alternator
Ignition light fails to go out, battery runs flat in a
few days
m mDrivebelt loose and slipping, or broken
m mAlternator faulty
Battery will not hold charge for more than a few
days
m mBattery defective internally
m mElectrolyte level too low or electrolyte too weak due to leakage
m mPlate separators no longer fully effective
m mBattery plates severely sulphated
m mDrivebelt slipping
m mBattery terminal connections loose or corroded
m mAlternator not charging properly
m mShort in lighting circuit causing continual battery drain
Fuel gauge gives no reading
m
mFuel tank empty!
m mElectric cable between tank sender unit and gauge earthed or loose
m mFuel gauge case not earthed
m mFuel gauge supply cable interrupted
m mFuel gauge unit broken
Fuel gauge registers full all the time
m
mElectric cable between tank unit and gauge broken or disconnected
Horn operates all the time
m
mHorn push either earthed or stuck down
m mHorn cable to horn push earthed
Horn fails to operate
m
mBlown fuse
m mCable or cable connection loose, broken or disconnected
m mHorn has an internal fault
Horn emits intermittent or unsatisfactory noise
m
mCable connections loose
m mHorn incorrectly adjusted
Lights do not come on
m
mIf engine not running, battery discharged
m mLight bulb filament burnt out or bulbs broken
m mWire connections loose, disconnected or broken
m mLight switch shorting or otherwise faulty
Lights come on but fade out
m
mIf engine not running, battery discharged
Lights give very poor illumination
m
mLamp glasses dirty
m mReflector tarnished or dirty
m mLamps badly out of adjustment
m mIncorrect bulb with too low wattage fitted
m mExisting bulbs old and badly discoloured
m mElectrical wiring too thin not allowing full current to pass
Lights work erratically, flashing on and off,
especially over bumps
m mBattery terminals or earth connections loose
m mLights not earthing properly
m mContacts in light switch faulty
Wiper motor fails to work
m
mBlown fuse
m mWire connections loose, disconnected or broken
m mBrushes badly worn
m mArmature worn or faulty
m mField coils faulty
Wiper motor works very slowly and takes
excessive current
m mCommutator dirty, greasy or burnt
m mDrive spindle binding or damaged
m mArmature bearings dry or unaligned
m mArmature badly worn or faulty
Wiper motor works slowly and takes little current
m
mBrushes badly worn
m mCommutator dirty, greasy or burnt
m mArmature badly worn or faulty
Wiper motor works but wiper blade remains static
m
mDrive spindle damaged or worn
m mWiper motor gearbox parts badly worn
Page 115 of 303

can be drained out (photos). Brightwork
should be treated in the same way as
paintwork. Windscreens and windows can be
kept clear of the smeary film which often
appears, by the use of proprietary glass
cleaner. Never use any form of wax or other
body or chromium polish on glass.
3 Maintenance-
upholstery and carpets
1
Mats and carpets should be brushed or
vacuum-cleaned regularly, to keep them free
of grit. If they are badly stained, remove them
from the vehicle for scrubbing or sponging,
and make quite sure they are dry before
refitting. Seats and interior trim panels can be
kept clean by wiping with a damp cloth. If they
do become stained (which can be more
apparent on light-coloured upholstery), use a
little liquid detergent and a soft nail brush to
scour the grime out of the grain of the
material. Do not forget to keep the headlining
clean in the same way as the upholstery.
When using liquid cleaners inside the vehicle,
do not over-wet the surfaces being cleaned.
Excessive damp could get into the seams and
padded interior, causing stains, offensive
odours or even rot.
4 Minor body damage-
repair
3
Note:For more detailed information about
bodywork repair, Haynes Publishing produce
a book by Lindsay Porter called “The Car
Bodywork Repair Manual”. This incorporates
information on such aspects as rust treatment,
painting and glass-fibre repairs, as well asdetails on more ambitious repairs involving
welding and panel beating.
Repairs of minor scratches in
bodywork
If the scratch is very superficial, and does
not penetrate to the metal of the bodywork,
repair is very simple. Lightly rub the area of
the scratch with a paintwork renovator, or a
very fine cutting paste, to remove loose paint
from the scratch, and to clear the surrounding
bodywork of wax polish. Rinse the area with
clean water.
Apply touch-up paint to the scratch using a
fine paint brush; continue to apply fine layers
of paint until the surface of the paint in the
scratch is level with the surrounding
paintwork. Allow the new paint at least two
weeks to harden, then blend it into the
surrounding paintwork by rubbing the scratch
area with a paintwork renovator or a very fine
cutting paste. Finally, apply wax polish.
Where the scratch has penetrated right
through to the metal of the bodywork, causing
the metal to rust, a different repair technique
is required. Remove any loose rust from the
bottom of the scratch with a penknife, then
apply rust-inhibiting paint to prevent the
formation of rust in the future. Using a rubber
or nylon applicator, fill the scratch with
bodystopper paste. If required, this paste can
be mixed with cellulose thinners to provide a
very thin paste which is ideal for filling narrow
scratches. Before the stopper-paste in the
scratch hardens, wrap a piece of smooth
cotton rag around the top of a finger. Dip the
finger in cellulose thinners, and quickly sweep
it across the surface of the stopper-paste in
the scratch; this will ensure that the surface of
the stopper-paste is slightly hollowed. The
scratch can now be painted over as described
earlier in this Section.
Repairs of dents in bodywork
When deep denting of the vehicle’s
bodywork has taken place, the first task is to
pull the dent out, until the affected bodywork
almost attains its original shape. There is little
point in trying to restore the original shape
completely, as the metal in the damaged area
will have stretched on impact, and cannot be
reshaped fully to its original contour. It isbetter to bring the level of the dent up to a
point which is about 3 mm below the level of
the surrounding bodywork. In cases where the
dent is very shallow anyway, it is not worth
trying to pull it out at all. If the underside of the
dent is accessible, it can be hammered out
gently from behind, using a mallet with a
wooden or plastic head. Whilst doing this,
hold a suitable block of wood firmly against
the outside of the panel, to absorb the impact
from the hammer blows and thus prevent a
large area of the bodywork from being
“belled-out”.
Should the dent be in a section of the
bodywork which has a double skin, or some
other factor making it inaccessible from
behind, a different technique is called for. Drill
several small holes through the metal inside
the area - particularly in the deeper section.
Then screw long self-tapping screws into the
holes, just sufficiently for them to gain a good
purchase in the metal. Now the dent can be
pulled out by pulling on the protruding heads
of the screws with a pair of pliers.
The next stage of the repair is the removal
of the paint from the damaged area, and from
an inch or so of the surrounding “sound”
bodywork. This is accomplished most easily
by using a wire brush or abrasive pad on a
power drill, although it can be done just as
effectively by hand, using sheets of abrasive
paper. To complete the preparation for filling,
score the surface of the bare metal with a
screwdriver or the tang of a file, or
alternatively, drill small holes in the affected
area. This will provide a really good “key” for
the filler paste.
To complete the repair, see the Section on
filling and respraying.
Repairs of rust holes or gashes
in bodywork
Remove all paint from the affected area,
and from an inch or so of the surrounding
“sound” bodywork, using an abrasive pad or a
wire brush on a power drill. If these are not
available, a few sheets of abrasive paper will
do the job most effectively. With the paint
removed, you will be able to judge the severity
of the corrosion, and therefore decide
whether to renew the whole panel (if this is
possible) or to repair the affected area. New
body panels are not as expensive as most
people think, and it is often quicker and more
satisfactory to fit a new panel than to attempt
to repair large areas of corrosion.
Remove all fittings from the affected area,
except those which will act as a guide to the
original shape of the damaged bodywork (eg
headlight shells etc). Then, using tin snips or a
hacksaw blade, remove all loose metal and
any other metal badly affected by corrosion.
Hammer the edges of the hole inwards, in
order to create a slight depression for the filler
paste.
Wire-brush the affected area to remove the
powdery rust from the
surface of the remaining metal. Paint the
12•2 Bodywork
2.4B Sill drain with non-return valve2.4A Door drain hole
If the inside of the vehicle
gets wet accidentally, it is
worthwhile taking some
trouble to dry it out properly,
particularly where carpets are involved.
Do not leave oil or electric heaters
inside the vehicle for this purpose.
Page 116 of 303

affected area with rust-inhibiting paint, if the
back of the rusted area is accessible, treat
this also.
Before filling can take place, it will be
necessary to block the hole in some way. This
can be achieved by the use of aluminium or
plastic mesh, or aluminium tape.
Aluminium or plastic mesh, or glass-fibre
matting, is probably the best material to use
for a large hole. Cut a piece to the
approximate size and shape of the hole to be
filled, then position it in the hole so that its
edges are below the level of the surrounding
bodywork. It can be retained in position by
several blobs of filler paste around its
periphery.
Aluminium tape should be used for small or
very narrow holes. Pull a piece off the roll, trim
it to the approximate size and shape required,
then pull off the backing paper (if used) and
stick the tape over the hole; it can be
overlapped if the thickness of one piece is
insufficient. Burnish down the edges of the
tape with the handle of a screwdriver or
similar, to ensure that the tape is securely
attached to the metal underneath.
Bodywork repairs - filling and
respraying
Before using this Section, see the Sections
on dent, deep scratch, rust holes and gash
repairs.
Many types of bodyfiller are available, but
generally speaking, those proprietary kits
which contain a tin of filler paste and a tube of
resin hardener are best for this type of repair. A
wide, flexible plastic or nylon applicator will be
found invaluable for imparting a smooth and
well-contoured finish to the surface of the filler.
Mix up a little filler on a clean piece of card
or board - measure the hardener carefully
(follow the maker’s instructions on the pack),
otherwise the filler will set too rapidly or too
slowly. Using the applicator, apply the filler
paste to the prepared area; draw the
applicator across the surface of the filler to
achieve the correct contour and to level the
surface. As soon as a contour that
approximates to the correct one is achieved,
stop working the paste - if you carry on too
long, the paste will become sticky and begin
to “pick-up” on the applicator. Continue to
add thin layers of filler paste at 20-minute
intervals, until the level of the filler is just
proud of the surrounding bodywork.
Once the filler has hardened, the excess
can be removed using a metal plane or file.
From then on, progressively-finer grades of
abrasive paper should be used, starting with a
40-grade production paper, and finishing with
a 400-grade wet-and-dry paper. Always wrap
the abrasive paper around a flat rubber, cork,
or wooden block - otherwise the surface of
the filler will not be completely flat. During the
smoothing of the filler surface, the wet-and-
dry paper should be periodically rinsed in
water. This will ensure that a very smooth
finish is imparted to the filler at the final stage.At this stage, the “dent” should be
surrounded by a ring of bare metal, which in
turn should be encircled by the finely
“feathered” edge of the good paintwork.
Rinse the repair area with clean water, until all
of the dust produced by the rubbing-down
operation has gone.
Spray the whole area with a light coat of
primer - this will show up any imperfections in
the surface of the filler. Repair these
imperfections with fresh filler paste or
bodystopper, and once more smooth the
surface with abrasive paper. Repeat this
spray-and-repair procedure until you are
satisfied that the surface of the filler, and the
feathered edge of the paintwork, are perfect.
Clean the repair area with clean water, and
allow to dry fully.
The repair area is now ready for final
spraying. Paint spraying must be carried out
in a warm, dry, windless and dust-free
atmosphere. This condition can be created
artificially if you have access to a large indoor
working area, but if you are forced to work in
the open, you will have to pick your day very
carefully. If you are working indoors, dousing
the floor in the work area with water will help
to settle the dust which would otherwise be in
the atmosphere. If the repair area is confined
to one body panel, mask off the surrounding
panels; this will help to minimise the effects of
a slight mis-match in paint colours. Bodywork
fittings (eg chrome strips, door handles etc)
will also need to be masked off. Use genuine
masking tape, and several thicknesses of
newspaper, for the masking operations.
Before commencing to spray, agitate the
aerosol can thoroughly, then spray a test area
(an old tin, or similar) until the technique is
mastered. Cover the repair area with a thick
coat of primer; the thickness should be built
up using several thin layers of paint, rather
than one thick one. Using 400-grade wet-and-
dry paper, rub down the surface of the primer
until it is really smooth. While doing this, the
work area should be thoroughly doused withwater, and the wet-and-dry paper periodically
rinsed in water. Allow to dry before spraying
on more paint.
Spray on the top coat, again building up the
thickness by using several thin layers of paint.
Start spraying at one edge of the repair area,
and then, using a side-to-side motion, work
until the whole repair area and about 2 inches
of the surrounding original paintwork is
covered. Remove all masking material 10 to 15
minutes after spraying on the final coat of
paint.
Allow the new paint at least two weeks to
harden, then, using a paintwork renovator, or
a very fine cutting paste, blend the edges of
the paint into the existing paintwork. Finally,
apply wax polish.
5 Major body damage-
repair
5
1Major repair to the body should be left to
your Fiat dealer or specialist body repairer.
2Special jigs and alignment gauges are
required without which steering and
suspension characteristics may be incorrect
after the repairs are completed.
6 Radiator grille-
removal and refitting
1
1Open the bonnet.
2Extract the single fixing screw from the
centre of the grille slats (photo).
3Release the retaining clips and withdraw
the grille upwards from its lower spigot holes
(photo).
4Refitting is a reversal of removal.
7 Bonnet-
removal and refitting
1
1Open the bonnet and support it on its stay.
2Pencil around the hinges on the underside
Bodywork 12•3
12
If bodystopper is used, it can
be mixed with cellulose
thinners to form a really thin
paste which is ideal for
filling small holes
6.3 Grille clip6.2 Grille screw
Page 150 of 303

75If the pump is unworn, refit the rear cover
plate and tighten the screws fully.
76Apply air pressure from a tyre pump to the
oil pump oil ducts to clear any sludge or other
material and then prime the pump by pouring
clean engine oil into its intake duct at the
same time turning the oil pump inner gear with
the fingers.
77Lever out the oil seal and drive a new one
squarely into the oil pump casing (photos).
Lubricate the oil seal lips.
78Bolt the pump into position using a new
joint gasket. Note one bolt is longer than the
others (photo).
79Bolt on the oil pick-up assembly using a
new sealing washer.
80Fit the crankshaft sprocket and tighten the
bolt to specified torque.
81Fit and tension the timing belt.
82Fit the sump pan. Screw on a new oil filter
cartridge. Wait for the specified period of time
(one hour) and then fill the engine with oil.
83Run the engine for a few minutes, then
check and top up the oil level.
Pistons/connecting rods -
removal and refitting#
84Remove the sump pan.
85Unbolt and remove the oil pump
pick-up/filter screen assembly.
86The big-end bearing shells can be
renewed without having to remove the
cylinder head if the caps are unbolted and the
piston/connecting rod pushed gently about
one inch up the bore (the crankpin being at its
lowest point). If these shells are worn,however, the main bearing shells will almost
certainly be worn as well, necessitating a
complete overhaul, including crankshaft
removal.
87To remove the piston/connecting rods,
the cylinder head must be removed.
88The big-end caps and their connecting
rods are numbered 1, 2, 3 and 4 from the
timing cover end of the engine. The numbers
are located either side of the rod/cap joint on
the engine oil dipstick tube side (photo).
89Turn the crankshaft as necessary to bring
the first connecting rod big-end crankpin to its
lowest point, then unscrew the cap bolts and
remove the cap and shell bearing.
90Push the connecting rod/piston assembly
up the bore and out of the cylinder block.
There is one reservation; if a wear ridge has
developed at the top of the bores, remove this
by careful scraping before trying to remove
the piston/rod assemblies. The ridge will
otherwise prevent removal, or break the
piston rings during the attempt.
91Remove the remaining piston/connecting
rods in a similar way. If the bearing shells are
to be used again, tape them to their
respective caps or rods.
92Removal of the piston rings and
separation of the piston from the connecting
rod is covered in the next sub-Section.
93Fit the bearing shells into the connecting
rods and caps, ensuring that the recesses into
which the shells seat are clean and dry.
94Check that the piston ring gaps are evenly
spaced at 120º intervals. Liberally oil the rings
and the cylinder bores.95Fit a piston ring clamp to compress the
rings, oiling the rings and the clamp interior
surfaces liberally.
96Insert the first piston/connecting rod into
its cylinder bore. Make sure that the assembly
is the correct one for its particular bore. The
cap and rod matching numbers must be
towards the engine oil dipstick guide tube and
the arrow on the piston crown towards the
timing belt (photo).
97Push the piston into the bore until the
piston ring clamp is against the cylinder block
and then tap the crown of the piston lightly to
push it out of the ring clamp and into the bore
(photo).
98Oil the crankshaft journal and fit the
big-end of the connecting rod to the journal.
Check that the bearing shells are still in
position, then fit the big-end cap and bolts;
check that the cap is the right way round
(photo).
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•25
5B.78 Fitting the oil pump5B.77B Using a socket to fit the new oil
pump oil seal5B.77A Removing the oil pump seal
5B.98 Fitting a big-end bearing cap
5B.88 Connecting rod and cap numbers
5B.97 Fitting a piston/connecting rod5B.96 Piston directional arrow
13
Page 155 of 303
crankcase. If the shells are to be used again,
keep them with their respective bearing caps.
70The thrust washers which control
crankshaft endfloat are located in the
crankcase, and retained by the turned-over
edges of the centre main bearing shell.
71The engine is now fully stripped.
Examination and renovation
72The procedures for the following items are
essentially as described in Chapter 1, Sec-
tion 18.
Cylinder block and crankcase
Crankshaft and bearings
Flywheel
Oil seals and gaskets
Cylinder head
73Using a straight-edge, check the cylinder
head gasket surface for distortion. If it
exceeds the specified tolerance, it must be
surface ground by your dealer.74Refer to Chapter 1, Section 39, for
dismantling and renovation operations. Note
that single valve springs are fitted.
Oil pump
75Checking operations are described in
sub-Section B.
Pistons and connecting rods
76Refer to sub-Section B.
77If one or more connecting rods are
changed, it is important that its weight is
identical to that of the original. Use an
accurate balance to weigh them and remove
metal if necessary from the new rod in the
areas indicated in Fig. 13.7.
Camshaft and cam followers
78If the camshaft journals or bearings show
any sign of wear or scoring, then the
camshaft, or cylinder head, or both must be
renewed.
79The cam followers should be checked for
ovality using a micrometer. Unless unworn
they should be renewed.
Timing belt tensioner and timing belt
80The tensioner is a lubricant-sealed pulley,
and it should be tested for smooth and quiet
operation by turning it with the fingers. Any
evidence of roughness or rattle will indicate
the need for a new assembly (photo).81The timing belt should be inspected at
regular intervals for correct adjustment and
condition (see Section 3 or “Routine
maintenance” at the beginning of the Manual).
If there is evidence of worn teeth, cracking or
fraying, or oil contamination, renew the belt.
The vehicle manufacturers recommend that
the belt is renewed whenever it is removed,
and it should certainly be renewed at the
intervals specified in Section 3 or the main
“Routine maintenance” section at the
beginning of this Manual as a precautionary
measure against belt breakage and
consequent expensive engine damage.
PART D:
ENGINE REASSEMBLY AND
REFITTING
Reassembly - general
1Refer to Chapter 1, Section 19.
Complete reassembly#
2With the cylinder block/crankcase standing
on the work surface, fit the bearing half shells
into their crankcase seats (photo). Make sure
that the seats are perfectly clean as dirt or grit
trapped under the shell will cause binding
when the crankshaft is turned.
3The centre bearing crankcase web
incorporates the thrust washers held by the
lips of the bearing shell (photo).
4Oil the shells and lower the crankshaft into
the crankcase (photo).
5Fit the bearing shells into the main bearing
caps, again making sure that the shell seats
are perfectly clean (photo).
13•30 Supplement: Revisions and information on later models
5D.5 Main bearing cap and shell5D.4 Fitting the crankshaft5D.3 Crankshaft thrust washer at centre
bearing
5D.2 Main bearing shell in crankcase
Fig. 13.8 Checking a cam follower for
ovality - 999 and 1108 cc engine (Sec 5C)
Fig. 13.7 Metal removing areas (arrowed)
on connecting rod - 999 and 1108 cc
engine (Sec 5C)
5C.80 Timing belt tensioner
Page 158 of 303

32Fit the hot air collector plate for the air
cleaner (photo).
33Refer to Section 10 and fit the distributor.
34Bolt on the timing belt cover.
35Fit the camshaft cover, using a new
gasket unless the original one is in perfect
condition.
Engine/transmission -
reconnection and refitting#
36Locate the engine in an upright position
on wooden blocks to allow for the greater
depth of the transmission flywheel housing
when it is joined to the engine.
37Make sure that the clutch driven plate has
been centralised, offer the transmission to the
engine and locate the flywheel housing on the
single stud and dowels.
38Tighten the connecting bolts to specifiedtorque, having located the lifting eye (photo).
39Bolt on the starter motor.
40Refit the cover plate to the flywheel
housing, but do not insert the lower bolts at
this stage as they retain the support bracket
for the gearchange rod.
41The engine and transmission are now
ready for refitting. The operations are a direct
reversal of the operations described earlier,
but observe the following points.
42Have the engine/transmission perfectly
horizontal and suspended on the hoist.
43Lower it into position very slowly until it is
possible to engage the driveshaft inboard
joints with the transmission.
44Continue lowering until the driveshafts
can be fully engaged and the mountings
reconnected. Remove the hoist.
45Tighten all nuts and bolts to the specifiedtorque. Note the method shown for
connecting the gearchange rod ball socket
using pliers (photo).
46Refill the engine with oil and coolant and
replenish the transmission oil.
Initial start-up after major
overhaul
47Refer to Chapter 1, Section 45.
6 Engine-
1301 cc Turbo ie
PART A: GENERAL
Description
1This engine is similar in design to the
1301 cc engine described in Chapter 1, but
the fuel and ignition systems are different, and
a turbocharger, oil cooler and intercooler are
fitted.
2Many dimensions and tolerances have
been altered for this engine, and reference
should be made to the Specifications at the
beginning of this Supplement.
3Operations which differ from those
described in Chapter 1 are given in the
following sub-Sections.
Lubrication system - description
4The lubrication system differs from the
non-Turbo 1301 cc engine in the following
respects.
5An oil cooler is fitted, which comprises a
matrix with inlet and outlet hoses connected
to the oil filter cartridge mounting base.
6A thermostatic control switch is fitted,
which diverts the oil flow through the matrix
only at oil temperatures above 84ºC (183ºF).
Note that a faulty switch will require renewal
of the complete oil filter mounting base.
7Special oil spray nozzles are located in the
crankcase main bearing webs, to cool the
underside of the pistons.
8The ball-type valves in the nozzles open
when the engine oil pressure reaches 1.2 bars
(17.4 lbf/in
2).
9An oil pressure sender unit is screwed into
Supplement: Revisions and information on later models 13•33
5D.45 Connecting ball socket type
gearchange rod5D.38 Lifting eye on flywheel housing
flange5D.32 Air cleaner hot air collector plate
Fig. 13.10 Cutaway view of the 1301 cc Turbo ie engine (Sec 6A)
13