1977 DATSUN PICK-UP check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 121 of 537

When
throttle
valve
is
opened
fur
ther
locking
arm
is
detached
from
secondary
throttle
arm
permitting
see
ondary
system
to
start
operation
Linkage
between
primary
and
see
ondary
throttles
will
function
properly
if
distance
between
throttle
valve
and
inner
wall
of
throttle
chamber
is
74
mm
0
291
in
Adjustment
is
made
by
bending
connecting
link
I
L
l
1
4
CAl
Secondary
prm
ary
I
Jl
I
7
t
@
1
Roller
4
Adjust
plate
2
Connecting
lever
5
Throttle
c
amber
3
Return
plate
6
Throttle
valve
Fig
EF
48
Adjusting
interlock
opening
DASH
POT
1
Idling
speed
of
engine
and
mix
ture
must
be
well
tuned
up
and
engine
sufficiently
warm
2
Turn
throttle
valve
by
hand
and
read
engine
speed
when
dash
pot
just
touches
stopper
lever
3
Adjust
position
of
dash
pot
by
turning
nut
until
engine
speed
is
in
the
specified
range
Specified
engine
speed
Manual
transmission
1
900
to
2
100
rpm
Automatic
transmission
1
650
to
1
850
rpm
4
Tighten
lock
nuts
5
Make
sure
that
engine
speed
drops
smoothly
from
2
000
to
1
000
rpm
in
about
three
seconds
Engine
Fuel
Fig
EF
49
Adjusting
dash
pot
ACCELERATING
PUMP
I
Visually
inspect
accelerating
pump
cover
for
any
sign
of
fuel
leaks
2
If
fuel
leaks
are
found
check
gasket
and
replace
if
necessary
ANTI
DIESELING
SOLENOID
VALVE
If
engine
does
not
stop
when
igni
tion
switch
is
turned
off
this
indicates
that
a
striking
closed
solenoid
valve
is
shutting
off
supply
of
fuel
to
engine
If
harness
is
in
good
condition
replace
solencid
valve
as
a
unit
Notes
a
Tightening
torque
is
1
8
to
3
5
kg
m
13
to
25
ft
Ib
b
After
replacement
star
engine
and
check
to
be
sure
that
fuel
is
not
leaking
and
that
anti
dieseling
sol
noid
is
in
good
condition
B
C
D
D
CIRCUIT
WITH
FUNCTION
TEST
CONNECTOR
Caution
Do
not
attach
test
leads
of
a
circuit
tester
to
those
other
than
designated
Refer
to
Figure
EF
50
Menuel
trensmlsslon
models
I
Check
for
continuity
between
A
and
B
when
vehicle
is
brought
to
a
complete
stop
Refer
to
Figure
EF
50
B
C
D
D
circuit
is
functioning
properly
if
continuity
exists
and
volt
meter
reading
is
0
volt
d
c
in
step
2
below
If
continuity
does
not
exist
check
for
disconnected
connector
and
or
faulty
amplifier
speed
detecting
switch
or
B
C
D
D
solenoid
valve
2
Check
for
presence
of
voltage
across
A
and
B
at
a
speed
of
more
than
16
km
h
10
MPH
Refer
to
Figure
EF
50
Conduct
this
test
by
one
of
the
following
two
methods
I
Raising
up
rear
axle
housing
with
stand
2
Chassis
dynamometer
test
If
voltmeter
reading
is
0
volt
at
a
speed
of
more
than
16
km
h
10
MPH
circuit
is
functioning
prop
erly
If
voltmeter
reading
is
not
0
volt
check
for
disconnected
connector
burned
fuse
faulty
amplifier
B
C
D
D
solenoid
valve
or
speed
detecting
switch
3
If
by
above
checks
faulty
part
or
unit
is
located
it
should
be
removed
and
tested
again
If
necessary
replace
1
P4
11
0
8
l
1
Ignition
Icey
2
Fuse
3
Amplifier
4
Speed
detecting
switch
Above
10
mph
OFF
Below
10
mph
ON
5
Function
test
connector
6
B
C
D
D
solenoid
valve
EF711
Fig
EF
50
Checking
B
C
D
D
circuit
with
function
test
connector
for
manual
transmission
EF
25
Page 122 of 537

AUtomatic
trailamlsalon
modela
I
With
inhibitor
switch
ON
UN
or
P
position
check
for
presence
of
voltage
across
A
and
B
Refer
to
Figure
EF
51
If
voltmeter
ading
is
12
volts
d
c
B
C
D
O
circuit
is
func
tioning
properly
If
vol
tmeter
ading
is
zero
check
for
disconnected
connector
faulty
solenoid
valve
m
inhibitor
switch
2
With
inhibitor
switch
OFF
HI
2
IY
or
oR
position
Engine
Fuel
check
for
resistance
between
A
and
B
Refer
to
Figure
EF
51
If
ohmmeter
reading
is
25
ohms
or
below
circuit
is
functioning
prop
erly
If
ohmmeter
reading
is
32
ohms
or
above
check
for
poor
connection
of
connec
or
faulty
B
C
D
D
sole
noid
valve
or
inhibitor
relay
3
If
by
above
checks
faulty
part
or
unit
is
located
it
should
be
moved
and
tested
again
If
necessary
replace
yu
@
@
1
Ignition
key
2
Inhibit
T
switch
N
P
positions
ON
I
2
D
R
positions
OFF
3
D
C
D
D
solenoid
valve
4
Function
test
connector
5
Inhibitor
relay
EF712
Fig
EF
51
Checking
B
C
D
D
circuit
with
unction
t
st
connector
for
automatic
transmi
sion
Set
pressure
of
Boost
Controlled
Deceleration
Device
B
C
D
O
Generally
it
is
unnecessary
to
ad
just
the
B
CD
D
however
if
it
should
become
necessary
to
adjust
it
the
procedure
is
3S
follows
Prepare
the
foUowing
tool
I
Tachometer
to
measure
the
en
gine
speed
while
idling
and
a
screw
driver
2
A
vacuum
gauge
and
connecting
pipe
Note
A
quick
response
type
hoost
gauge
such
as
Bourdon
s
type
is
recommended
a
mercury
type
manometer
should
not
be
used
To
properly
set
the
B
C
D
D
set
pressure
proceed
as
follows
I
Remove
the
harness
of
solenoid
valve
To
B
D
D
solenoid
valve
1
B
C
D
D
olenoid
valve
harness
EF262
Fig
EF
52
Removing
harness
of
solenoid
valve
2
Connect
rubber
hose
between
vacuum
gauge
and
intake
manifold
as
shown
Fig
EF
53
Connecting
vacuum
gauge
EF
26
3
Warm
up
the
engine
until
it
is
heated
to
operating
temperature
Then
adjust
the
engine
at
nunnal
idling
setting
Refer
to
the
item
Idling
Adjustmenl
in
page
EF
21
Idling
engine
speed
Manual
transmission
750
rpm
Automatic
transmission
in
D
position
650
rpm
4
Run
the
engine
under
no
load
Increase
engine
speed
to
3
000
to
3
500
rpm
then
quickly
close
throttle
valve
5
At
the
time
the
manifold
vacuum
p
ssure
increases
abruptly
to
600
mmHg
23
62
inHg
or
above
and
then
graduaUy
decreases
to
the
level
set
at
idling
6
Check
that
the
B
C
D
D
set
pres
sure
is
within
the
specified
pressure
Specified
pressure
0
m
sea
level
and
760
mmHg
30
inHg
atmos
pheric
pressu
Manual
transmission
510
to
550
mmHg
20
1
to
21
7
inHg
Automatic
transmission
490
to
530
mmHg
19Tto
20
9
inHg
Notes
a
When
atmospheric
pressure
is
known
operating
pressure
will
be
found
by
tracing
the
arrow
line
A
See
Figure
EF
56
When
alti
tude
is
known
operating
pressure
will
be
found
by
tracing
the
arrow
line
B
See
Figu
EF
56
b
When
checking
the
set
pressu
of
B
CD
D
find
the
specified
set
pressu
in
Figure
EF
56
from
the
atmospheric
pressure
and
altitude
of
the
given
location
For
example
if
an
automatic
trans
mission
model
vehicle
is
located
at
an
altitude
of
1
000
m
3
280
ft
the
specified
set
p
ssu
for
B
C
D
D
is
445
mmHg
17
5
inHg
7
If
it
is
higher
than
the
set
level
turn
the
adjusting
screw
or
nut
until
correct
adjustment
is
made
Page 123 of 537
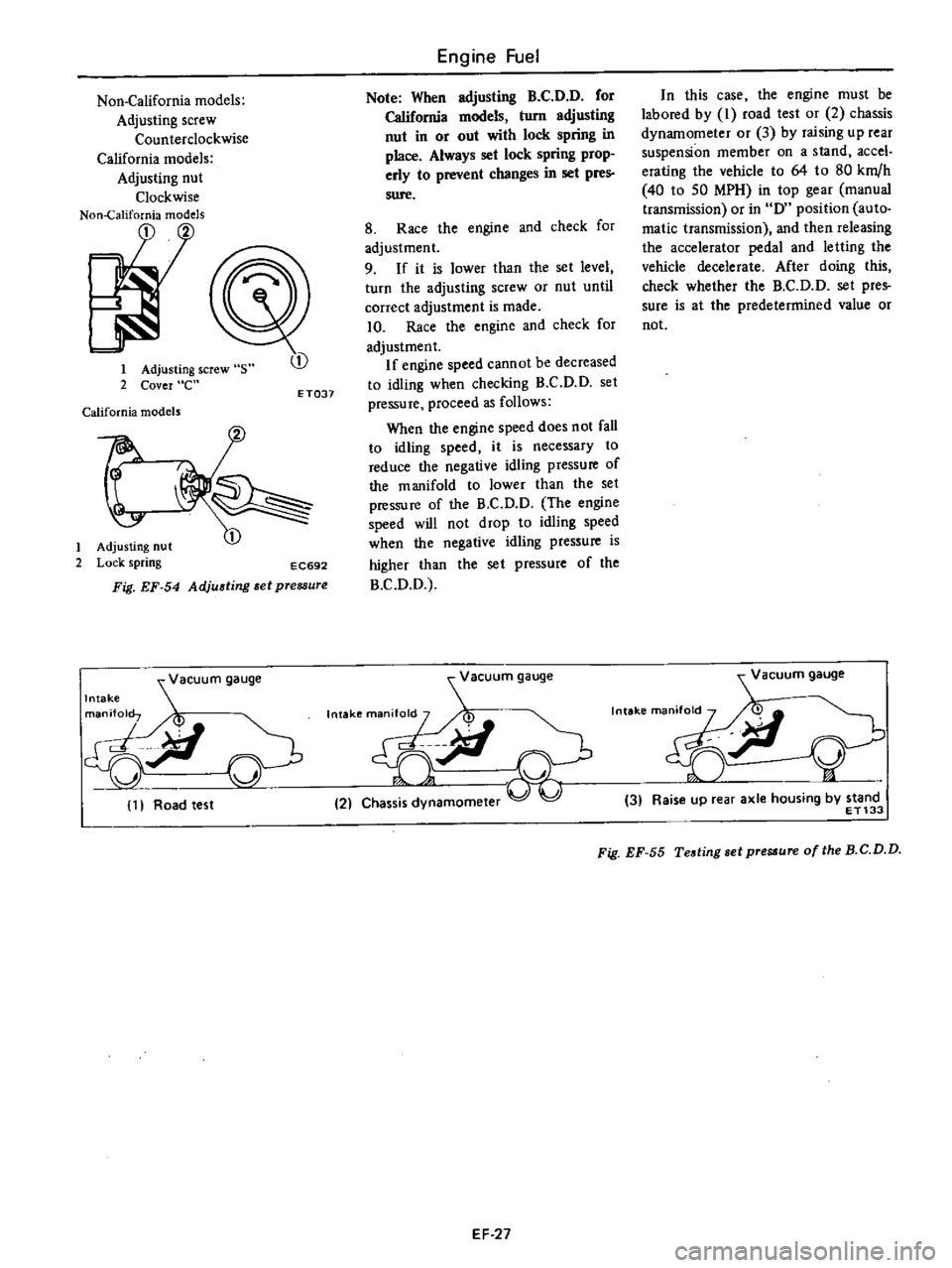
Non
California
models
Adjusting
screw
Counterclockwise
California
models
Adjusting
nut
Clockwise
Non
California
models
1
2
1
Adjusting
screw
s
2
Cover
e
California
models
t
1
Adjusting
nut
2
Lock
spring
EC692
Fig
EF
54
Adjusting
et
pressure
vacuum
gauge
Intake
gjl
11
Road
test
CD
ET037
Engine
Fuel
Note
When
adjusting
B
C
D
D
for
California
models
turn
adjusting
nut
in
or
out
with
lock
spring
in
place
Always
set
lock
spring
prop
erly
to
prevent
changes
in
set
pres
sure
8
Race
the
engine
and
check
for
adjustment
9
If
it
is
lower
than
the
set
level
turn
the
adjusting
screw
or
nut
until
correct
adjustment
is
made
10
Race
the
engine
and
check
for
adjustment
If
engine
speed
cannot
be
decreased
to
idling
when
checking
B
C
D
D
set
pressure
proceed
as
follows
When
the
engine
speed
does
not
fall
to
idling
speed
it
is
necessary
to
reduce
the
negative
idling
pressure
of
the
manifold
to
lower
than
the
set
pressure
of
the
B
C
D
O
The
engine
speed
will
not
drop
to
idling
speed
when
the
negative
idling
pressure
is
higher
Ihan
the
sel
pressure
of
the
B
C
O
O
acuum
gauge
Intakema
M
V
9iI
21
Chas
amomeler
In
this
case
the
engine
must
be
labored
by
I
road
test
or
2
chassis
dynamometer
or
3
by
raising
up
rear
suspension
member
on
a
stand
accel
erating
the
vehicle
to
64
to
80
km
h
40
10
50
MPH
in
top
gear
manual
transmission
or
in
0
position
auto
matic
transmission
and
then
releasing
the
accelerator
pedal
and
letting
the
vehicle
decelerate
After
doing
this
check
whether
the
B
C
O
D
set
pres
sure
is
at
the
predetermined
value
or
not
Vacuum
gauge
n
i
Y
3
Raise
up
rear
axle
housing
by
stand
ET133
Fig
EF
55
Testing
sel
pre
ure
of
the
B
C
D
D
EF
27
Page 124 of 537

300
n
o
o
B
C
D
D
solenoid
valve
I
Turn
on
engine
key
Do
not
start
engine
Ensure
that
solenoid
valve
clicks
when
intermittently
electrified
as
shown
in
Figure
EF
57
1
000
2
000
3
000
4
000
5
000
0
5
1
0
6
000
ft
Altitude
km
1
5
2
0
EF558
Fig
EF
56
Changes
in
set
pres
ure
versus
changes
in
atmospheric
pressure
and
altitude
EF262
Fig
EF
57
Checking
solenoid
valve
EF
28
3
If
a
dick
is
heard
solenoid
valve
is
normal
4
I
f
a
dick
is
not
heard
ar
all
check
for
continuity
with
a
circuit
tester
If
discontinuity
is
detected
replace
sole
noid
valve
Amplifier
Manual
transmIssIon
models
The
amplifier
is
installed
at
the
rear
of
the
speedometer
To
check
proceed
as
follows
Page 125 of 537

I
Set
circuit
tester
in
d
c
ampere
range
IA
min
fuU
scale
connect
test
probes
of
tester
as
shown
in
Figure
EF
58
Do
not
confuse
positive
line
with
negative
line
2
Turn
ignition
key
to
ON
posi
tion
I
t
EF264
1
Ignition
key
2
Amplifier
3
Speed
detecting
switch
4
B
C
D
D
solenoid
valve
Inhibitor
switch
Automatic
transmission
models
Refer
to
the
AT
section
Inhibitor
relay
Automatic
transmission
models
Inhibitor
relay
EF724
Fig
EF
59
Location
of
inhibitor
relay
2
Make
an
inhibitor
relay
check
as
shown
in
Figure
EF
60
Apply
12
volts
d
c
across
termi
nals
1
and
4
to
ensure
that
continuity
exists
between
terminals
2
and
3
Check
that
continuity
does
not
exist
between
terminals
2
and
3
when
no
voltage
is
applied
across
them
Engine
Fuel
3
Ensure
that
tester
pointer
deflects
when
ignition
key
is
turned
on
4
If
tester
pointer
does
not
deflect
when
solenoid
valve
and
speed
detect
ing
switch
circuits
are
functioning
properly
amplifier
is
faulty
Fig
EF
58
Checking
amplifier
If
results
satisfy
the
above
inhi
bitor
relay
is
functioning
properly
if
not
replace
inhibitor
relay
it
@
j
l
j
4
L
I
44
11
oJ
EF287
Fig
EF
60
Checking
inhibitor
relay
ALTITUDE
COMPENSATOR
California
models
Make
sure
that
altitude
com
pensator
to
carburetor
hoses
are
con
nected
properly
and
that
they
are
not
cracked
and
obstructed
2
Check
that
altitude
compensator
is
properly
set
At
low
altitudes
At
high
altitudes
Notes
a
The
idle
Pm
and
CO
vary
accord
ing
to
the
altitude
Therefore
they
should
be
properly
adjusted
when
the
position
of
the
H
L
lever
is
changed
Close
Open
EF
29
b
Counties
1
219
m
4
000
ft
or
more
above
sea
level
have
been
designated
by
law
as
High
Altitude
Counties
For
further
details
refer
to
1977
DATSUN
PICK
UP
Service
BuUetin
Pub
No
257
Q0
1
v
EF733
Fig
EF
61
Checking
altitude
compensator
MAJOR
SERVICE
OPERATION
The
perfectly
adjusted
carburetor
delivers
the
proper
fuel
and
air
ratios
at
all
speeds
for
the
particular
engine
for
which
it
was
designed
By
com
pletely
disassembling
which
will
allow
deaning
of
all
parts
and
passages
the
carburetor
can
be
maintained
its
origi
nal
condition
and
will
continue
to
deliver
the
proper
ratios
To
maintain
accurate
carburetion
of
passages
and
discharge
holes
ex
treme
care
must
be
taken
in
cleaning
Use
only
carburetor
solvent
and
compressed
air
to
clean
all
passages
and
discharge
holes
Never
use
wire
or
other
pointed
instrument
to
clean
or
carburetor
calibration
will
be
affected
REMOVAL
Remove
carburetor
from
engine
taking
sufficient
care
to
the
following
Precautions
a
When
disconnecting
fuel
lines
do
not
spill
fuel
from
fuel
pipe
b
When
removing
carburetor
do
not
drop
any
nut
or
bolt
into
intake
manifold
c
Be
careful
not
to
bend
or
scratch
any
part
Page 129 of 537

Engine
Fuel
Throttle
chamber
parts
I
Idle
limiter
cap
2
Idle
adjust
screw
3
Idle
adjust
screw
sprinl
4
Throttle
adjust
screw
5
Throttle
adjust
screw
sprini
6
Primary
and
secondary
throttle
valves
7
Nut
Notc
Do
not
remove
the
parlS
marked
with
an
asterisk
@ff
EF827
Fig
EF
66
Removing
throttle
chamlHr
parta
Assembly
To
assemble
reverse
the
disassem
bly
procedcre
taking
care
to
the
following
I
Thoroughly
wash
all
the
parts
before
assembling
2
Inspect
gaskets
to
see
if
they
appear
hard
or
brittle
or
if
edges
are
torn
or
distorted
If
any
of
such
undesirable
condi
tions
is
noted
they
must
be
replaced
3
Install
jet
and
air
bleed
having
the
same
size
number
as
that
of
original
one
4
After
reassembling
carburetor
check
each
rotating
portion
or
sliding
portion
for
smooth
operation
EF
33
Page 130 of 537

CLEANING
AND
INSPECTION
Dirt
gum
wuler
or
l
arbon
con
taminatiun
in
or
on
exterior
moving
parts
of
a
arburctor
arc
often
respon
sihk
for
unsatisfactory
performance
For
this
reason
efficient
carbutetioll
dcpends
upon
careful
cleaning
and
inspection
while
servicing
I
Blow
all
passages
and
castings
with
compressed
air
and
blow
off
all
parts
until
dry
Note
Do
not
pass
drills
or
wires
through
calibrated
jet
or
passaaa
as
this
may
enlarge
orirlce
and
seriously
affect
carburetor
calibrs
lion
2
Check
all
parts
for
wear
If
wear
is
noted
damaged
parts
must
be
re
placed
Note
especially
the
following
Engine
Fuel
I
Check
float
needle
and
seat
for
wear
If
wear
is
noted
assembly
must
be
replaced
2
Check
throule
and
choke
shaft
bores
in
throtlle
chamber
and
choice
chamber
for
wear
or
out
of
roundness
3
Inspect
idle
adjusting
needle
for
burrs
or
ridges
Such
a
condition
re
quires
replacemen
1
3
Inspect
gaskets
0
see
if
they
appear
hard
or
briUle
or
if
edges
are
torn
or
distorted
If
any
such
condi
tion
i
noted
they
must
be
replaced
4
Check
filter
screen
for
dirt
or
lint
Clean
and
if
screen
is
distorted
or
remain
plugged
replace
5
Check
linkage
for
operating
condition
6
Inspect
operation
of
accelerating
pump
Pour
f
el
into
jloat
chamber
and
make
throtlle
lever
operate
Check
condition
of
fuel
injection
from
the
EF
34
accelerating
nowe
7
Push
connecting
rod
of
dia
phragm
chamber
and
block
passage
of
vacuum
with
finger
When
connecting
rod
becomes
free
check
for
leakage
of
air
or
damage
to
diaphragm
Jets
Carburetor
performance
depends
on
jet
and
air
bleed
That
is
why
these
components
must
be
fabricated
with
utmost
care
To
clean
them
use
cleaning
solvent
and
blow
air
on
them
Larger
inner
numbers
tamped
on
the
jet
indicate
larger
diameters
Ac
cordingly
main
and
slow
jets
with
lalger
nUmbers
provide
richer
mixture
the
smaller
the
numbers
the
leaner
the
mixture
Conversely
the
main
and
slow
air
bleeds
through
which
air
to
passes
through
make
the
fueLleaner
if
they
bear
larger
numbers
the
smaller
the
numbers
the
richer
the
fuel
Page 132 of 537

Engine
Fuel
toms
and
causes
of
carburetor
troubles
and
remedies
for
them
are
listed
to
facilitate
quick
repairs
There
are
various
causes
of
engine
malfunctions
It
sometimes
happens
that
a
carburetor
which
has
no
fault
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
In
the
following
table
the
syml
Condition
Probable
cause
Overflow
Dirt
accumulated
on
needle
valve
Fuel
pump
pressure
too
high
Needle
valve
improperly
seated
Excessive
fuel
consumption
Fuel
overflow
Slow
jet
too
large
on
each
main
jet
Main
air
bleed
clogged
Choke
valve
does
not
open
fully
Outlet
valve
seat
of
accelerator
pump
improper
Linked
opening
of
secondary
throttle
valve
opens
too
early
Power
shortage
Main
jets
clogged
Every
throttle
valve
does
not
open
fully
Idling
adjustment
incorrect
FIICI
tr
clogged
Vacuum
jet
clogged
Air
c1eane
clogged
Diaphragm
damaged
Power
valve
operating
improperly
Altitude
compensator
setting
incorrect
Cali
fornia
models
Improper
idling
Slow
jet
clogged
Every
throttle
valve
does
not
close
Secondary
throttle
valve
operating
im
properly
Throttle
valve
shafts
worn
Packing
between
manifold
carburetor
fauJiy
Manifold
carburetor
tightening
improper
Fuel
overflow
B
C
D
D
adjustment
incorrect
Vacuum
control
solenoid
damaged
Stuck
anti
stall
dash
pot
EF
36
appears
to
have
some
problems
when
actually
the
electric
system
is
at
fault
Therefore
whenever
the
engine
is
mal
functioning
the
electrical
system
should
be
checked
rust
before
adjust
ing
carburetor
Corrective
action
Clean
needle
valve
Repair
pump
Re
place
See
condition
overflow
Replace
Clean
Adjust
Lap
Adjust
Clean
Adjust
AdjusL
pa
ir
Clean
Clean
Replace
Adjust
Correct
H
L
lever
position
Clean
Adjust
Overhaul
and
clean
Replace
Replace
packing
Correct
tightening
See
l
ondition
ov
rl1ow
Adjust
Replace
Replace