1969 FORD MUSTANG checking oil
[x] Cancel search: checking oilPage 245 of 413
04-05-04
Specifications
04-05-04
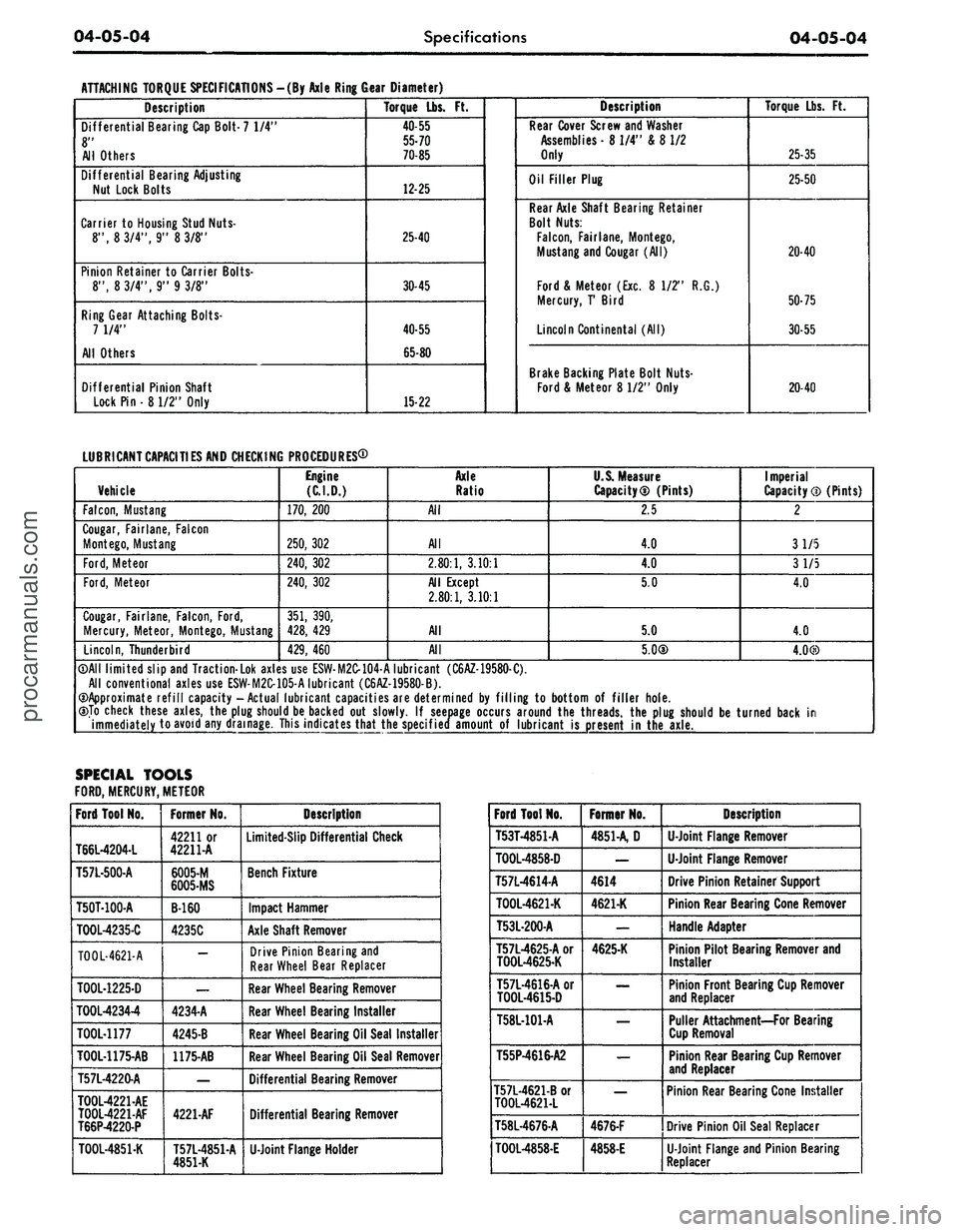
ATTACHING TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS -(By Axle Ring Gear Diameter)
Description
Differential Bearing Cap Bolt- 7 1/4"
8"
All Others
Differential Bearing Adjusting
Nut Lock Bolts
Carrier
to
Housing Stud Nuts-
8", 8 3/4", 9" 8 3/8"
Pinion Retainer
to
Carrier Bolts-
8", 8 3/4", 9" 9 3/8"
Ring Gear Attaching Bolts-
7 1/4"
All Others
Differential Pinion Shaft
Lock Pin
•
8 1/2" Only
Torque Lbs.
Ft.
40-55
55-70
70-85
12-25
25-40
30-45
40-55
65-80
15-22
Description
Rear Cover Screw and Washer
Assemblies
-8
1/4" &
8
1/2
Only
Oil Filler Plug
Rear Axle Shaft Bearing Retainer
Bolt Nuts:
Falcon,
Fairlane, Montego,
Mustang and Cougar (All)
Ford & Meteor (Exc.
8 1/2" R.G.)
Mercury,
T
Bird
Lincoln Continental (All)
Brake Backing Plate Bolt Nuts-
Ford & Meteor
8
1/2" Only
Torque Lbs.
Ft.
25-35
25-50
20-40
50-75
30-55
20-40
LUBRICANT
CAPACITIES
AND CHECKING PROCEDURES®
Vehicle
Falcon,
Mustang
Cougar, Fairlane, Falcon
Montego, Mustang
Ford,
Meteor
Ford,
Meteor
Cougar, Fairlane, Falcon, Ford,
Mercury, Meteor, Montego, Mustang
Lincoln,
Thunderbird
Engine
(C.I.D.)
170,
200
250,
302
240,
302
240,
302
351,
390,
428,
429
429,
460
Axle
Ratio
All
All
2.80:1,
3.10:1
All Except
2.80:1,
3.10:1
All
All
U.S. Measure
Capacity® (Pints)
2.5
4.0
4.0
5.0
5.0
5.0©
Imperial
Capacity
CD
(Pints)
2
31/5
3 1/5
4.0
4.0
4.0©
©All limited slip and Traction-Lok axles use ESW-M2C-104-A lubricant (C6AZ-19580-C).
All conventional axles use ESW-M2C-105-A lubricant (C6AZ-19580-B).
©Approximate refill capacity-Actual lubricant capacities are determined
by
filling
to
bottom
of
filler hole.
©To check these axles, the plug should be backed
out
slowly.
If
seepage occurs around the threads, the plug should
be
turned back
in
immediately to avoid any drainage. This indicates that the specified amount
of
lubricant
is
present
in
the axle.
SPECIAL TOOLS
FORD,
MERCURY, METEOR
Ford Tool No.
T66L-4204-L
T57L-500-A
T50T-100-A
TOOL-4235-C
T00L-4621-A
TOOL-1225-D
T00L42344
TOOL-1177
TOOL-U75-AB
T57L4220-A
T00L4221-AE
T00L-4221-AF
T66P-4220-P
TOOL-4851-K
Former No.
42211 or
42211-A
6005-M
6005-MS
B-160
4235C
—
—
4234-A
4245-B
1175-AB
—
4221-AF
T57L-4851-A
4851-K
Description
Limited-Slip Differential Check
Bench Fixture
Impact Hammer
Axle Shaft Remover
Drive Pinion Bearing and
Rear Wheel Bear Replacer
Rear Wheel Bearing Remover
Rear Wheel Bearing Installer
Rear Wheel Bearing Oil Seal Installer
Rear Wheel Bearing Oil Seal Remover
Differential Bearing Remover
Differential Bearing Remover
U-Joint
Flange Holder
Ford Tool No.
T53T4851-A
T00L4858-D
T57L4614-A
T00L4621-K
T53L-200-A
T57L-4625-A or
T00L4625-K
T57L4616-A or
T00L4615-D
T58L-101-A
T55P4616-A2
T57L4621-B or
T00L4621-L
T58L4676-A
T00L4858-E
Former No.
4851-A, D
—
4614
4621-K
—
4625-K
—
—
—
—
4676-F
4858-E
Description
U-Joint
Flange Remover
U-Joint
Flange Remover
Drive Pinion Retainer Support
Pinion Rear Bearing Cone Remover
Handle Adapter
Pinion Pilot Bearing Remover and
Installer
Pinion Front Bearing Cup Remover
and Replacer
Puller Attachment—For Bearing
Cup Removal
Pinion Rear Bearing Cup Remover
and Replacer
Pinion Rear Bearing Cone Installer
Drive Pinion Oil Seal Replacer
U-Joint
Flange and Pinion Bearing
Replacerprocarmanuals.com
Page 295 of 413

07-01-04
General Transmission Service
07-01-04
taching bolts to the proper torque. If
necessary, replace the gasket.
Check the fluid filler tube connec-
tion at the transmission case or pan.
If leakage is found here, install a new
O-ring or tighten the fitting to the
specified torque.
Check the fluid lines and fittings
between the transmission and the
cooler in the radiator tank for loose-
ness,
wear, or damage. If leakage can-
not be stopped by tightening a fitting,
replace the damaged parts.
Check the engine coolant in the ra-
diator. If transmission fluid is present
in the coolant, the cooler in the radia-
tor is probably leaking.
The cooler can be further checked
for leaks by disconnecting the lines
from the cooler fittings and applying
50-75 psi air pressure to the fittings.
Remove the radiator cap to relieve the
pressure build at the exterior of the oil
cooler tank. If the cooler is leaking
and will not hold this pressure the
cooler must be replaced. Cooler re-
placement is described in the Cooling
System Section of Group 11.
If leakage is found at either the
downshift control lever shaft or the
manual lever shaft, replace either or
both seals.
Inspect the pipe plug on the left
side of the transmission case at the
front. If the plug shows leakage, tor-
que the plug to specifications. If tight-
ening does not stop the leaks, replace
the plug. On a C6 transmission, a TV
pressure plug is also provided on the
right rear side of the case.
When converter drain plugs leak,
remove drain plugs with a six-point
wrench. Coat the threads with FoMo-
Co Perfect Seal Sealing Compound or
its equivalent, and install the plugs.
Torque the drain plugs to specifica-
tion. Fluid leakage from the converter
housing may be caused by engine oil
leaking past the rear main bearing or
from oil gallery plugs, or power steer-
ing oil leakage from steering system.
Be sure to determine the exact cause
of the leak before repair procedures
are started.
Oil-soluble aniline or fluorescent dyes
premixed at the rate of 1/2 teaspoon
of dye powder to 1/2 pint of transmis-
sion fluid have proved helpful in locat-
ing the source of the fluid leakage.
Such dyes may be used to determine
whether an engine oil or transmission
fluid leak is present or if the fluid in
the oil cooler leaks into the engine
coolant system. A black light, how-
ever, must be used with the fluorescent
dye solution.
DISHED OR
FLAT WASHER
" O.D.,
a" STEEL PLATE
5/8"X \W,
DRILL TO SUIT
HEX. HEAD SCREW
3/8"-24 X Vl
HEX. NUT W—
24
WELD
TOGETHER
WING
NUT
>/2"_13
THREAD
CHAIN,
10"
LONG
RUBBER PLUG
1
Vi" DIA. X 2"
LONG Vl"
HOLE THRU
APPROXIMATELY
40 DUROMETER
FLAT WASHER
Vs" O.D.
PLUG
VALVE
STANDARD BOLT
W-13
X 4Vl"
LONG SQUARE
THREAD
END
REMOVE HEAD
AND WELD
TO
WASHER
STANDARD 1/8" FITTING-87971-S FOR
RETAPPED DRAIN PLUG THREADS-USE
1/4" OVERSIZE FITTING-87973-S
D 1067-B
WELD TOGETHER
SECURELY—MUST
NOT LEAK
FIG. 2—Converter Leak Checking Tool
CONVERTER LEAKAGE
CHECK
If there are indications that the
welds on the torque converter are
leaking, the converter will have to be
removed and the following check
made before the unit is replaced.
A leak checking tool (Fig. 2) can be
made from standard parts. The tool
can be used to check all converters.
1.
Install the plug in the converter
(Fig. 3) and expand it by tightening
the wing nut. Attach the safety chains.
2.
Install the air valve in one of the
drain plug holes.
3.
Introduce air pressure into the
converter. Check the pressure with a
tire gauge and adjust it to 20 psi.
4.
Place the converter in a tank of
water. Observe the weld areas for
bubbles. If no bubbles are observed, it
may be assumed that the welds are
not leaking.
ENGINE IDLE SPEED CHECK
Check and, if necessary, adjust the
engine idle speed, using the procedure
given in Group 10.
If the idle speed is too low, the en-
gine will run roughly. An idle speed
that is too high will cause the vehicle
to creep, have harsh engagements and
harsh closed-throttle downshifts.
ANTI-STALL DASHPOT
CLEARANCE CHECK
After the engine idle speed has been
properly adjusted, check the anti-stall
dashpot clearance. Follow the proce-
dure given in Group 10 for checking
and adjusting this clearance.
MANUAL LINKAGE CHECKS
Correct manual linkage adjustment
is necessary to position the manual
valve for proper fluid pressure direc-
tion to the different transmission com-
ponents. Improperly adjusted manual
Tire Pressure Gauge
D1921-A
FIG. 3—Converter Leak Checking
Tool Installationprocarmanuals.com
Page 297 of 413

07-01-06
General Transmission Service
07-01-06
MAKE MARK HERE
BELLOWS INTACT
BELLOWS FAILED
FIG. 9—Checking Vacuum Unit Bellows
tester equipped with a vacuum pump
(Fig. 8). Set the regulator knob so
that the vacuum gauge reads 18 inches
with the end of the vacuum hose
blocked off.
Then connect the vacuum hose to
the transmission vacuum unit. If the
gauge still reads 18 inches, the vacuT
urn unit diaphragm is not leaking. As
the hose is removed from the trans-
mission vacuum unit, hold a finger
over the end of the control rod. When
the hose is removed, the internal
spring of the vacuum unit should push
the control rod outward.
ALTITUDE
COMPENSATING-TYPE
The vacuum diaphragm should be
checked for ruptured or damaged bel-
lows.
Check the diaphragm assembly
as follows:
1.
Remove the diaphragm and
throttle valve rod from the transmis-
sion.
2.
Insert a rod into the diaphragm,
making sure that the rod is buttonec
in the hole. Make a reference mark on
the rod where it enters the diaphragm
hole.
3.
Hold the assembly in such a way
that the end of the rod is resting on
the weighing surface of a scale (Fig.
9).
4.
Gradually press down on the dia-
phragm assembly until the rod is
pressed into the diaphragm body. If
the reference mark on the rod is still
visible with 12 pounds of force regis-
tered on the scale, the bellows are in-
tact. If the mark disappears before 4
pounds of force is exerted, the bellows
have failed and the diaphragm must
be replaced. If the bellows are intact,
then perform various pressure checks.
SHIFT POINT CHECKS
Check the minimum throttle up-
shifts in D. The transmission should
start in first gear, shift to second, and
then shift to third, within the shift
points specified in the specification
section.
While the transmission is in third
gear, depress the accelerator pedal
through the detent (to the floor). The
transmission should shift from third to
second or third to first, depending on
the vehicle speed.
Check the closed throttle downshift
from third to first by coasting down
from about 30 mph in third gear. The
shift should occur within the limits
specified in the specification section.
When the selector lever is at 2, the
transmission can operate only in sec-
ond gear.
With the transmission in third gear
and road speed over 30 mph, the
transmission should shift to second
gear when the selector lever is moved
from D to 2 to 1. The transmission
will downshift from second or third to
first gear when this same manual shift
is made below approximately 25 mph
with a C4 transmission, 30 mph with
D 1791.A
a C6 transmission or 35 mph with an
FMX transmission. This check will
determine if the governor pressure and
shift control valves are functioning
properly.
During the shift point check opera-
tion, if the transmission does not shift
within specifications or certain gear
ratios cannot be obtained, refer to the
Ford Car and Truck Diagnosis Manu-
al to resolve the problem.
AIR PRESSURE CHECKS
A NO DRIVE condition can exist,
even with correct transmission fluid
pressure, because of inoperative
clutches or bands. Erratic shifts could
be caused by a stuck governor valve.
The inoperative units can be located
through a series of checks by subst-
ituting air pressure for the fluid pres-
sure to determine the location of the
malfunction.
To make the air pressure checks,
drain the transmission fluid and re-
move the oil pan and the control valve
body assembly. The inoperative units
can be located by introducing air pres-
sure into the transmission case passa-
ges leading to the clutches, servos, and
governor (Figs. 10, 11 or 12).
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM BENCH
TESTS (FMX TRANSMISSION)
After the transmission has been as-
sembled and is ready for installationprocarmanuals.com
Page 303 of 413
07-01-12
General Transmission Service
07-01-12
the transmission,
any
metal particles
or clutch plate
or
band material that
may have been carried into
the
cooler
should
be
removed from
the
system
by
flushing
the
cooler
and
lines before
the transmission
is put
back into serv-
ice.
In no
case should
an
automatic
transmission having
a
clutch
or
band
failure
or
other internal trouble result-
ing
in
fluid contamination,
be put
back into service without first flushing
the transmission
oil
cooler.
To flush
the oil
cooler, follow
the
instruct!
on >
provided with
the
Rotun-
da Automatic Transmission Torque
Converter
and
Cooler Cleaner
LRE-
60081.
INSPECTION
TURBINE
AND
STATOR
END
PLAY CHECK
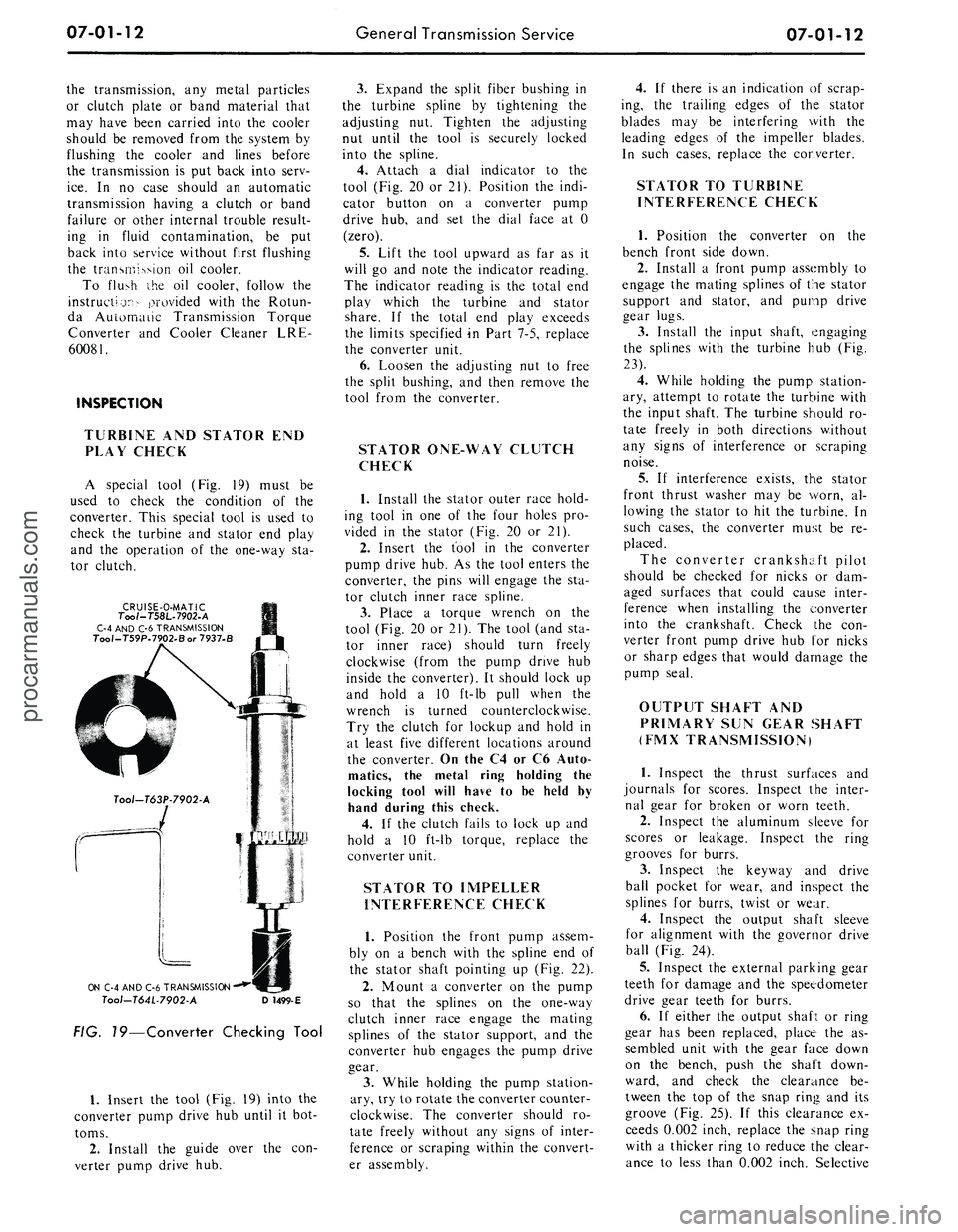
A special tool
(Fig. 19)
must
be
used
to
check
the
condition
of the
converter. This special tool
is
used
to
check
the
turbine
and
stator
end
play
and
the
operation
of the
one-way
sta-
tor clutch.
CRUISE-O-MATIC
Too/-T58L-7902-A
C-4 AND C-6 TRANSMISSION
Tool-T59P.7902.Bor 7937-B
ON C-4 AND C-6 TRANSMISSION
Tool-T64L-7902-A
D
1499-E
FIG. 19—Converter Checking Tool
1.
Insert
the
tool (Fig.
19)
into
the
converter pump drive
hub
until
it
bot-
toms.
2.
Install
the
guide over
the con-
verter pump drive
hub.
3.
Expand
the
split fiber bushing
in
the turbine spline
by
tightening
the
adjusting
nut.
Tighten
the
adjusting
nut until
the
tool
is
securely locked
into
the
spline.
4.
Attach
a
dial indicator
to the
tool (Fig.
20 or
21). Position
the
indi-
cator button
on a
converter pump
drive
hub, and set the
dial face
at 0
(zero).
5.
Lift
the
tool upward
as far as it
will
go and
note
the
indicator reading.
The indicator reading
is the
total
end
play which
the
turbine
and
stator
share.
If the
total
end
play exceeds
the limits specified
in
Part 7-5, replace
the converter unit.
6. Loosen
the
adjusting
nut to
free
the split bushing,
and
then remove
the
tool from
the
converter.
STATOR ONE-WAY CLUTCH
CHECK
1.
Install
the
stator outer race hold-
ing tool
in one of the
four holes
pro-
vided
in the
stator (Fig.
20 or 21).
2.
Insert
the
tool
in the
converter
pump drive hub.
As the
tool enters
the
converter,
the
pins will engage
the sta-
tor clutch inner race spline.
3.
Place
a
torque wrench
on the
tool (Fig.
20 or
21).
The
tool (and
sta-
tor inner race) should turn freely
clockwise (from
the
pump drive
hub
inside
the
converter).
It
should lock
up
and hold
a 10
ft-lb pull when
the
wrench
is
turned counterclockwise.
Try
the
clutch
for
lockup
and
hold
in
at least five different locations around
the converter.
On
the
C4
or C6
Auto-
matics,
the
metal ring holding
the
locking tool will have
to be
held
by
hand during this check.
4.
If the
clutch fails
to
lock
up and
hold
a 10
ft-lb torque, replace
the
converter unit.
STATOR
TO
IMPELLER
INTERFERENCE CHECK
1.
Position
the
front pump assem-
bly
on a
bench with
the
spline
end of
the stator shaft pointing
up
(Fig.
22).
2.
Mount
a
converter
on the
pump
so that
the
splines
on the
one-way
clutch inner race engage
the
mating
splines
of the
stator support,
and the
converter
hub
engages
the
pump drive
gear.
3.
While holding
the
pump station-
ary, try
to
rotate the converter counter-
clockwise.
The
converter should
ro-
tate freely without
any
signs
of
inter-
ference
or
scraping within
the
convert-
er assembly.
4.
If
there
is an
indication
of
scrap-
ing,
the
trailing edges
of the
stator
blades
may be
interfering with
the
leading edges
of the
impeller blades.
In such cases, replace
the
converter.
STATOR
TO
TURBINE
INTERFERENCE CHECK
1.
Position
the
converter
on the
bench front side down.
2.
Install
a
front pump assembly
to
engage
the
mating splines
of
the
stator
support
and
stator,
and
pump drive
gear lugs.
3.
Install
the
input shaft, engaging
the splines with
the
turbine
hub (Fig.
23).
4.
While holding
the
pump station-
ary, attempt
to
rotate
the
turbine with
the input shaft.
The
turbine should
ro-
tate freely
in
both directions without
any signs
of
interference
or
scraping
noise.
5.
If
interference exists,
the
stator
front thrust washer
may be
worn,
al-
lowing
the
stator
to hit the
turbine.
In
such cases,
the
converter must
be re-
placed.
The converter crankshaft pilot
should
be
checked
for
nicks
or dam-
aged surfaces that could cause inter-
ference when installing
the
converter
into
the
crankshaft. Check
the con-
verter front pump drive
hub for
nicks
or sharp edges that would damage
the
pump seal.
OUTPUT SHAFT
AND
PRIMARY
SUN
GEAR SHAFT
(FMX TRANSMISSION)
1.
Inspect
the
thrust surfaces
and
journals
for
scores. Inspect
the
inter-
nal gear
for
broken
or
worn teeth.
2.
Inspect
the
aluminum sleeve
for
scores
or
leakage. Inspect
the
ring
grooves
for
burrs.
3.
Inspect
the
keyway
and
drive
ball pocket
for
wear,
and
inspect
the
splines
for
burrs, twist
or
wear.
4.
Inspect
the
output shaft sleeve
for alignment with
the
governor drive
ball (Fig.
24).
5.
Inspect
the
external parking gear
teeth
for
damage
and the
speedometer
drive gear teeth
for
burrs.
6.
If
either
the
output shaft
or
ring
gear
has
been replaced, place
the as-
sembled unit with
the
gear face down
on
the
bench, push
the
shaft down-
ward,
and
check
the
clearance
be-
tween
the top of the
snap ring
and its
groove
(Fig. 25).
If
this clearance
ex-
ceeds 0.002 inch, replace
the
snap ring
with
a
thicker ring
to
reduce
the
clear-
ance
to
less than 0.002 inch. Selectiveprocarmanuals.com
Page 320 of 413

07-02-12
C4 Automatic Transmission
07-02-12
MAJOR REPAIR OPERATIONS
Before removing
any of the sub-
assemblies, thoroughly clean
the out-
side
of the
transmission
to
prevent dirt
from entering
the
mechanical parts.
During
the
repair operations, refer
to
Part 7-1
for
common adjustments
and
repairs
or
cleaning
and
inspection
pro-
cedures.
During
the
transmission disassem-
bly
or
assembly operations,
ten
thrust
washers located between
the sub-
assemblies must
be
removed
and in-
stalled.
It is
important that each
thrust washer
be in the
correct posi-
tion during
the
assembly operation.
To properly locate
and
identify
the
thrust washers,
the
various positions
of
the
thrust washers
are
shown
in the
illustrations
and are
numbered
1
through
10. No. 1 is at the
first thrust
washer located
at the
front pump.
The
last thrust washer,
No. 10, is
located
at
the
parking pawl ring gear.
DISASSEMBLY
OF
TRANSMISSION
1.
Remove
the
converter from
the
transmission front pump
and
convert-
er housing.
2.
Remove
the
transmission vacuum
unit with
the
tool shown
in Fig. 22.
Remove
the
vacuum unit gasket and
the control
rod.
GRIND OFF
SHADED AREA
TO DIMENSION SHOWN L .
SNAP-ON
Tool-FCO-24
(Reworked)
D1380-A
FIG. 22—Removing Vacuum Unit
3.
Remove
the
primary throttle
valve (Fig.
23)
from
the
opening
at the
rear
of the
case.
4.
Remove
the two
extension
housing-to-case bolts shown
in Fig. 24
and mount
the
transmission
in the
holding fixture.
5.
Remove
the
transmission
pan at-
taching bolts,
pan and
gasket.
6. Remove
the
control valve body
attaching bolts (Fig.
25).
Remove
the
control valve body from
the
case.
7.
Loosen
the
intermediate band
adjusting screw
(Fig. 26) and
remove
the intermediate band struts from
the
case.
Loosen
the
low-reverse band
ad-
justing screw
and
remove
the low-
reverse band struts.
TRANSMISSION END
PLAY CHECK
1.
To
keep
the
output shaft
in
alignment during
the end
play check,
install
the
extension housing
oil
seal
replacer tool
or a
front universal
D1861-A
FIG. 23—Removing
or
Installing
Primary Throttle Valve
Tool-T57L-500-A
or 6005-M or 6005-MS
D1862-A
joint yoke in the extension housing.
2.
Remove
one of the
converter
housing-to-case attaching bolts
and
mount
the
dial indicator
as
shown
in
Fig. 27.
3.
The
input shaft
is a
loose part
and
has to be
properly engaged with
the spline
of the
forward clutch
hub
during
the end
play checking proce-
dure.
Move
the
input shaft
and
gear
train toward
the
rear
of the
transmis-
sion case.
V*
- 20 x
V/7 INCH
V*
- 20 x 1
INCH
V*
- 20 x 1
INCH
D1863-A
FIG. 25—Control Valve Body
Attaching Bolts
INTERMEDIATE
BAND STRUTS
INTERMEDIATE BAND
ADJUSTING SCREW
I
LOW-REVERSE BAND
ADJUSTING SCREW
LOW-REVERSE
BAND STRUTS
D
1384-B
FIG.
24—Transmission
Mounted
in Holding Fixture
FIG. 26—Band Adjusting Screws
and Struts—Typicalprocarmanuals.com
Page 342 of 413

07-03-02
FMX Transmission
07-03-02
COMPONENT INDEX
OIL PAN
Assembly
Removal and Installation
OUTPUT SHAFT
Assembly
Inspection
OUTPUT SHAFT BUSHING
Disassembly and Overhaul
PARKING PAWL
Removal and Installation
PRESSURE REGULATOR
Assembly
Disassembly and Overhaul
Inspection
Removal and Installation
PRIMARY SUN GEAR SHAFT
Disassembly and Overhaul
Inspection
REAR BRAKE DRUM SUPPORT BUSHING
Disassembly and Overhaul
REAR CLUTCH
Assembly
Disassembly and Overhaul
Inspection
Page
03-29
03-11
03-26
01-11
03-17
03-13
03-28
03-21
01-16
03-12
03-18
01-11
03-17
03-26
03-18
01-15
REAR SERVO
Assembly
Disassembly and Overhaul
Inspection
Removal and Installation
REAR SUPPORT
Assembly
Inspection
REAR SUPPORT BUSHING
Disassembly and Overhaul
SELECTOR LEVER-CONSOLE SHIFT
Removal and Installation
THROTTLE LINKAGE
Adjustment
Parts Repair or Replacement
TRANSMISSION (Complete)
Removal and Installation
TRANSMISSION CASE BUSHING
Parts Repair or Replacement
TRANSMISSION CASE LINKAGE
Parts Repair or Replacement
VACUUM DIAPHRAGM UNIT
Assembly
Adjustment
Checking
Page
03-28
03-24
01-16
03-12
03-28
03-15
03-21
03-08
03-05
03-05
03-14
03-26
03-25
03-29
01-07
01-04
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
Figure 1 shows the location of the
converter, front pump, clutches,
bands,
gear train and most of the in-
ternal parts used in the FMX Trans-
mission
The identification tag (Fig. 2) on an
FMX transmission is attached under
the oil pan by a pan to case bolt. The
tag includes the model prefix and suf-
fix, assembly part number and the
build date code.
The service identification number
indicates changes to service details
which affect interchangeability when
the transmission model is not
changed. For interpretation of this
number, see the Master Parts Catal-
og-
The tag must be kept with the indi-
vidual transmission it was originally
installed on. If the tag was removed
during disassembly, reinstall it on the
same unit.
The FMX transmission is a three
speed unit capable of providing auto-
matic upshifts and downshifts through
the three forward gear ratios, and also
capable of providing manual selection
of first and second gears.
The transmission consists essentially
of a torque converter, planetary gear
train, two multiple disc clutches and a
hydraulic control system (Fig. 3).
procarmanuals.com