1967 CHEVROLET CAMARO ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 211 of 659

REAR SUSPENSION AND DRIVE LINE 4-21
Fig.
54—Marking Camber Cam and Bracket (Corvette)
bracket, so they may be reassembled in same loca-
tion (fig. 54).
5.
Loosen camber bolt and nut. Remove four bolts se-
curing strut rod bracket to carrier and lower
bracket.
6. Remove cam bolt nut and cam and bolt assembly.
Pull strut down out of bracket and remove bushing
caps.
7.
Inspect strut rod bushings for wear and replace
where necessary. Replace strut rod if it is bent or
damaged in any way.
Repairs
1.
With strut rod bushing centered over Tool J-7877-2
and with strut rod supported horizontally, press or
drive bushing from rod, using Tools J-7877-i and
J-7079-2 as shown in Figure 55.
2.
With strut rod end centered over Tool J-7877-2 and
rod supported horizontally, press or drive bushing
into arm using Tools J-7877-3 and J-7079-2 as
shown in Figure 55. Tool J-7877-3 should bottom
on strut rod when bushing is fully installed.
Installation
1.
Place bushing caps over inboard bushing and slide
rod into bracket. Install cam and bolt assembly and
adjust cam to line up with mark on bracket. Tighten
nut but do not torque at this point.
SPRING
LINK BOLT
SPRING
CUSHION
SPRING
CUSHION
CENTER
CLAMP
PLATE
J-7877-3
J-7877-1
STRUT ROD 11 s* ^#3 STRUT ROD
BUSHING
Fig.
56—Spring Mounting (Corvette)
2.
Raise bracket and assemble to carrier lower mount-
ing surface. Torque bolts to specifications.
3.
Raise outboard end of strut rod into spindle support
fork and insert strut rod shaft into fork so that flat
on shaft lines up with corresponding flat in spindle
fork. Install retaining nut, but do not torque.
4.
Place shock absorber lower eye and bushing over
strut shaft, install washer and nut and torque to
specifications.
5.
Lower vehicle to floor and torque camber cam nut
and strut rod shaft nut to specifications. Then in-
stall cotter pin through rod bolt.
6. Check rear wheel camber and adjust where
necessary.
SPRING (Fig. 56)
Removal
1.
Raise rear of vehicle and support on frame slightly
forward of torque control arm pivot points. Remove
wheels and tires.
Fig.
55—Strut Rod Bushing Replacement
Fig.
57—Chain Installation (Corvette)
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 264 of 659

BRAKES
5-31
POWER BRAKES
INDEX
General Description 5-31
Maintenance
and"
Adjustments 5-31
Inspection . ... 5_31
Lubrication 5-31
Bleeding Instructions . . . 5.31
Air Cleaner Service . . . , 5.31
Page
Component Replacement 5-31
Power Brake Cylinder ......* 5-31
Removal . . 5-31
Disassembly and Assembly See Overhaul Manual
Installation . . . . 5-31
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Power Brake Unit is a self-contained hydraulic
and vacuum unit, utilizing manifold vacuum and atmos-
phere pressure for its power.
This unit permits the use of a low brake pedal as well
as less pedal effort than is required with the conventional
(nonpower) hydraulic brake system. Only two external
line connections are necessary -
one
a vacuum connection
from manifold to check valve located on front shell; the
other, a hydraulic connection from the main cylinder
outlet directly into the hydraulic system. The unit is
mounted on the engine side of the fire wall and directly
connected to the brake pedal.
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
INSPECTIONS
1.
Check vacuum line and vacuum line connections as
well as vacuum check valve in front shell of power
unit for possible vacuum loss.
2.
Inspect all hydraulic lines and connections at the
wheel cylinders and main cylinder for possible
hydraulic leaks.
3.
Check brake assemblies for scored drums, grease
or brake fluid on linings, worn or glazed linings,
and make necessary adjustments.
4.
Check brake fluid level in the hydraulic reser-
voirs.
The reservoirs should be filled to the levels
shown in Figure 8.
5. Check for loose mounting bolts at main cylinder and
at power section.
6. Check air cleaner filter in power piston extension
and replace filter if necessary.
7. Check brake pedal for binding and misalignment
between pedal
-and
push rod.
LUBRICATION
The power brake unit is lubricated at assembly and
needs no further lubrication other than maintaining
normal reservoir fluid level. The reservoir should be
filled as described in this section.
BLEEDING INSTRUCTIONS
The power system may be bled manually or with a
pressure bleeder as outlined in this section. Use only
GM
Supreme 11 Brake Fluid or equivalent. Do not use the
power assist while bleeding. The engine should not be
running and the vacuum reserve should be reduced to
zero by applying the brake several times before starting
the bleeding procedure.
AIR CLEANER SERVICE
Servicing of the air cleaner is recommended and the
element replaced when restriction becomes severe
enough to affect power brake response. At any other
time, if cleaning of the filter is felt necessary, it should
be shaken free of dirt or washed in soap and water and
thoroughly dried.
COMPONENT REPLACEMENT
POWER BRAKE CYLINDER
Removal
1.
Remove vacuum hose from vacuum check valve.
2.
Disconnect hydraulic lines at main cylinder.
Disconnect push rod at brake pedal assembly.
Remove nuts and lock washers securing power unit
to fire wall, and remove power unit from engine
compartment.
3.
4.
NOTE:
Chevy
to fire wall.
has a three stud attachment
Repair procedures for the power cylinder are outlined
in the Brake Section of the Overhaul Manual-for service
of the main cylinder refer to applicable portion of
"Standard Brakes" in this manual.
Installation
1.
Mount the power brake assembly in place and install
the attaching nuts and lock washers.
2.
Attach vacuum line to check valve.
3.
Secure hydraulic lines to main cylinder.
4.
Attach push rod to brake pedal assembly, and check
operation of stop light.
5. Bleed brakes as outlined in this section.
CAUTION: After replacing the unit on the vehi-
cle,
start the engine and allow vacuum to build
up before applying the brake.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE
Page 267 of 659

ENGINE 6-2
remotely at the starter, with a special jumper
cable or other means, the primary distributor
lead must be disconnected from the negative
post on the coil and the ignition switch must be
in the "ON" position. Failure to do this will
result in a damaged grounding circuit in the
ignition switch.
3.
Crank engine through at least four compression
strokes to obtain highest possible reading.
4.
Check and record compression of each cylinder.
5.
If one or more cylinders read low tor uneven, inject
about a tablespoon of engine oil on top of pistons
in low reading cylinders (through spark plug
port).
Crank engine several times and recheck
compression.
• If compression comes up but does not necessarily
reach normal, rings are worn.
• If compression does not improve, valves are
burnt, sticking or not seating properly.
• If two adjacent cylinders indicate low compres-
sion and injecting oil does not increase compres-
sion, the cause may be a head gasket leak between
the cylinders. Engine coolant and/or oil in cylin-
ders could result from this defect.
NOTE: If a weak cylinder cannot be located
with the compression check, see "Cylinder Bal-
ance Test" under "Additional Checks and Adjust-
ments" in this section.
Service and Install Spark Plugs (Fig. 2)
1.
Inspect each plug individually for badly worn elec-
trodes,
glazed, broken or blistered porcelains and
replace plugs where necessary. Refer to spark plug
diagnosis information presented in Section 6Y for an
analysis of plug conditions.
2.
Clean serviceable spark plugs thoroughly, using an
abrasive-type cleaner such as sand blast. File the
center electrode flat.
3.
Inspect each spark plug for make and heat range. All
plugs must be of the same make and number.
4.
Adjust spark plug gaps to specifications using a
round feeler gauge.
PORCELAIN
INSULATOR
INSULATOR CRACKS
OFTEN OCCUR HERE
CENTER ELECTRODE
[FILE FLAT WHEN
ADJUSTING GAP-
[DO NOT BEND!
(PROPER GAP)
(BEND TO ADJUST GAP)
CAUTION:
adjust gap.
Fig.
2 - Spark Plug Detail
Never bend the center electrode to
Always adjust by bending ground or
side electrode.
If available, test plugs with a spark plug tester.
Inspect spark plug hole threads and clean before in-
stalling plugs. Corrosion deposits can be removed
with a 14 mm. x 1.25 SAE spark plug tap (available
through local jobbers) or by using a small wire brush
in an electric drill. (Use grease on tap to catch
chips.)
ADJUST DWELL
ANGLE SETTING OR
POINT OPENING
Fig.
1 - Checking Compression
Fig.
3 - Distributor (In Line)
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 313 of 659

ENGINE FUEL 6M-5
3.
Disconnect choke rod or choke cable.
4.
Disconnect accelerator linkage.
5.
If equipped with Automatic transmission, discon-
nect TV linkage.
6. Remove carburetor attaching nuts and/or bolts and
remove carburetor.
Test Before Installation -
It is good shop practice to fill the carburetor bowl
before installing the carburetor. This reduces the strain
on the starting motor and battery and reduces the pos-
sibility of backfiring while attempting to start the engine.
A fuel pump clamped to the bench, a small supply of fuel
and the necessary fittings enable the carburetor to be
filled1 and the operation of the float and'intake needle and
seat to be checked. Operate the throttle several times
and check the discharge from the pump jets before in-
stalling the carburetor.
Installation
1.
Be certain throttle body and intake manifold sealing
surfaces are clean.
2.
Install new carburetor to manifold flange gasket (if
required).
3.
Install carburetor over manifold studs.
4.
Start vacuum and fuel lines at carburetor.
5.
Install attaching nuts and/or bolts and tighten
securely.
6. Tighten fuel and vacuum lines.
7.
Connect and adjust accelerator and TV linkage.
8. Connect choke tube or choke rod.
9. Adjust idle speed and mixture, then install air
cleaner. #
Fuel Filter Maintenance
1.
Disconnect fuel line connection at inlet fuel filter
nut.
2.
Remove inlet fuel filter nut from carburetor with a
1"
box wrench or socket.
3.
Remove filter element and spring (fig. 4c).
Fig. 5C-Choke Coil-L6 Engine
4.
Fig. 4C-Fuel Filter
Check element for restriction by blowing on cone
end, element should allow air to pass freely.
5.
Clean element by washing in solvent and blowing out.
Blow in opposite direction of fuel flow.
NOTE: Element should be replaced if plugged
or if flooding ocpurs. A plugged filter will
result in a loss of engine power or rough (pul-
sating) engine feel, especially at high engine
speeds.
6. Install element spring, then install element in car-
buretor so small section of cone faces out.
7.
Install new gasket on inlet fitting nut then install
nut in carburetor and tighten securely.
8. Install fuel line and tighten connector.
Choke Coil Replacement
L6 Engines (Fig. 5c)
1.
Remove air cleaner then disconnect choke rod upper
clip.
2.
Remove bolts attaching choke coil to manifold, then
remove choke coil and choke rod as an assembly.
3.
Disconnect choke rod from choke coil.
4.
Connect choke rod to new choke coil and install as-
sembly on manifold.
5.
Install bolts and tighten securely.
6. Adjust and connect choke rod as outlined.
7.
Start and warm-up the engine then check operation
of choke and install air cleaner.
V8 Engines (Fig. 6c)
1.
Remove air cleaner then disconnect choke rod upper
clip.
2.
Remove choke coil as follows:
WITH ROCHESTER 2GV CARBURETOR
• Remove the choke coil shield by prying with a
screw driver in the cut out provided then re-
move the choke rod.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 323 of 659
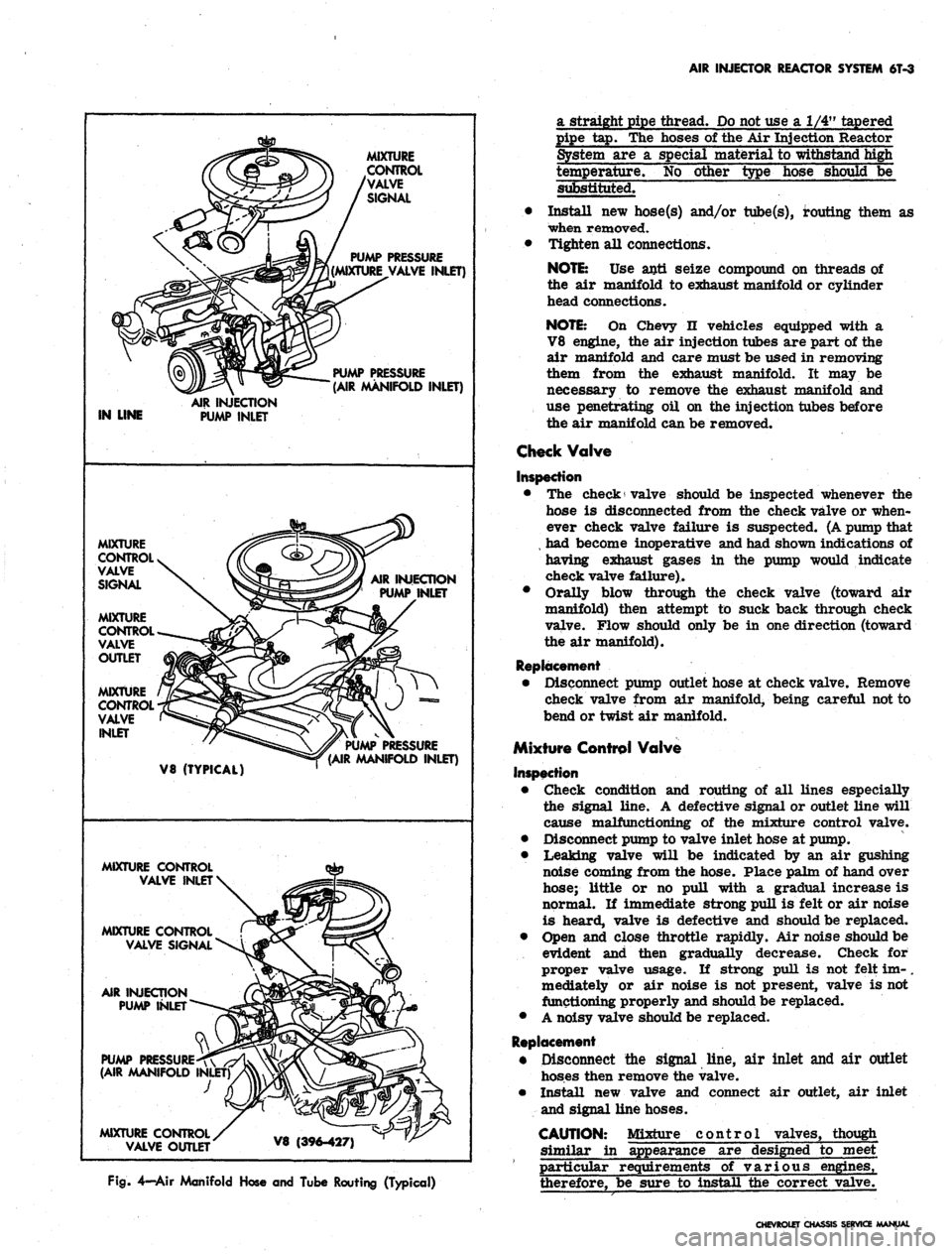
AIR INJECTOR REACTOR SYSTEM
6T-3
MIXTURE
CONTROL
VALVE
SIGNAL
PUMP PRESSURE
(MIXTURE VALVE INLET)
PUMP PRESSURE
(AIR MANIFOLD INLET)
IN LINE
AIR INJECTION
PUMP INLET
MIXTURE
CONTROL
VALVE
SIGNAL
MIXTURE
CONTROL
VALVE
OUTLET
MIXTURE
CONTROL
VALVE
INLET
AIR INJECTION
PUMP INLET
V8 (TYPICAL)
PUMP PRESSURE
(AIR MANIFOLD INLET)
MIXTURE CONTROL
VALVE INLET
MIXTURE CONTROL
VALVE SIGNAL
AIR INJECTION
PUMP INLET
PUMP PRESSURE^
(AIR MANIFOLD
J
MIXTURE CONTROL
VALVE OUTLET
V8 (396-427)
Fig.
4—Air Manifold Hose and Tube Routing (Typical)
a straight pipe thread.
Do
not use
a 1/4"
tapered
pipe
tap. The
hoses
of
the
Air
Injection Reactor
System
are a
special material
to
withstand high
temperature.
No
other type hose should
be
substituted.
• Install
new
hose(s) and/or tube(s), routing them
as
when removed.
• Tighten
all
connections.
NOTE:
Use
anti seize compound
on
threads
of
the
air
manifold
to
exhaust manifold
or
cylinder
head connections.
NOTE:
On
Chevy
n
vehicles equipped with
a
V8 engine,
the air
injection tubes
are
part
of the
air manifold
and
care must
be
used
in
removing
them from
the
exhaust manifold.
It may be
necessary
to
remove
the
exhaust manifold
and
use penetrating
oil on the
injection tubes before
the
air
manifold can
be
removed.
Check Valve
Inspection
•
The
check valve should
be
inspected whenever
the
hose
is
disconnected from
the
check valve
or
when-
ever check valve failure
is
suspected. (A pump that
,
had
become inoperative and had shown indications
of
having exhaust gases
in the
pump would indicate
check valve failure)..
• Orally blow through
the
check valve (toward
air
manifold) then attempt
to
suck back through check
valve. Flow should only
be in one
direction (toward
the
air
manifold).
Replacement
• Disconnect pump outlet hose
at
check valve. Remove
check valve from
air
manifold, being careful not
to
bend
or
twist
air
manifold.
Mixture Control Valve
Inspection
• Check condition
and
routing
of all
lines especially
the signal line.
A
defective signal
or
outlet line will
cause malfunctioning
of the
mixture control valve.
• Disconnect pump
to
valve inlet hose
at
pump.
• Leaking valve will
be
indicated
by an air
gushing
noise coming from
the
hose. Place palm
of
hand over
hose; little
or no
pull with
a
gradual increase
is
normal.
If
immediate strong pull
is
felt
or air
noise
is heard, valve
is
defective
and
should
be
replaced.
• Open
and
close throttle rapidly.
Air
noise should
be
evident
and
then gradually decrease. Check
for
proper valve usage.
If
strong pull
is not
felt
im-.
mediately
or air
noise
is not
present, valve
is not
functioning properly and should be replaced.
•
A
noisy valve should be replaced.
Replacement
• Disconnect
the
signal line,
air
inlet
and air
outlet
hoses then remove
the
valve.
• Install
new
valve
and
connect
air
outlet,
air
inlet
and signal line hoses.
CAUTION: Mixture control valves, though
similar
in
appearance
are
designed
to
meet
particular requirements
of
various engines,
therefore,
be
sure
to
install
the
correct valve.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 331 of 659

ENGINE-ELECTRICAL 6Y-6
DO NOT SUCK
IN TOO MUCH
ELECTROLYTE
FLOAT MUST
BE FREE
TAKE READING
AT EYE LEVEL
• Be sure there are not foreign objects in the carrier,
so that the new Battery will rest properly in the
bottom of the carrier.
• Tighten the hold-down evenly until snug (60-80 in.
lbs.).
Do not draw down tight enough to distort or
crack the case or cover.
• Be sure the cables are in good condition and the
terminal clamps are clean and tight. Make sure the
ground cable is clean and tight at engine block or
frame.
• Check polarity to be sure the Battery is not reversed
with respect to the generating system.
Fig.
7b—Testing Specific Gravity
Fig.
8b--Battery Installation (Corvette Shown)
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 353 of 659

ENGINE-ELECTRICAL 6Y-28
terminals on eoil. On Corvettes equipped with radio,
remove bolts securing ignition shield over distribu-
tor and coil.
2.
Pull high tension wire from center terminal of coil.
3.
Remove the two coil support mounting bolts or loosen
friction clamp screw and remove coil.
4.
Place new coil in position and install attaching bolts
or tighten clamp screw.
5.
Place high tension lead securely in center terminal
of coil and connect ignition switch and distributor
primary leads to terminals on coil. Replace ignition
shield on Corvettes.
6. Start engine and test coil operation.
IGNITION PULSE AMPLIFIER
DISASSEMBLY
To check the amplifier for defective components, pro-
ceed as follows:
1.
Remove the bottom plate from the amplifier.
2.
To aid in reassembly, note the locations of the lead
connections to the panel board.
3.
Remove the three panel board attaching screws, and
lift the assembly from the housing.
4.
To aid in reassembly, note any identifying markings
on the two transistors and their respective locations
on the panel board and heat sink assembly.
5.
Note the insulators between the transistors.and the
heat sink, and the insulators separating the heat sink
from the panel board.
6. Remove the transistor attaching screws, and sepa-
rate the two transistors and heat sink from the panel
board.
7.
Carefully examine the panel board for evidence of
damage.
MOUNTING
SCREW
RESISTOR R5 jgSfe. / DIODE Dl
TRANSISTOR TR2
(UNDERNEATH)
1H L >©V
[So
To
I
/'%**jt\
\
TRANSISTC>R"""
1 X ^^w^ X \ (UNDERNEATH)
9^ESISTORR^^^H|^^^^^H
^B
RESISTOR
R4
^HPH^^H
WM'
RESISTOR
R3
I^B^^^^I^U
N .6 ®
mm
N%|/MOUNTING
• tr^i^w ^\ vjR SCREW
CAPACITOR
Cl\
pNkj^^A^
\
RESISTOR
Rl
MOUNTING ^55S^^ \ CAPACITOR C3
SCREW I RESISTOR R6 CAPACITOR C2
TRANSISTOR TR3
COMPONENT CHECKS (Figs. \7\ and 18i)
With the two transistors separated from the assembly,
an ohmmeter may be used to check the transistors and
components on the panel board for defects. An ohmmeter
having a 1-1/2 volt cell, which is the type usually found
in service stations, is recommended. The low range
scale on the ohmmeter should be used except where
specified otherwise.
A 25 watt soldering gun is recommended, and a 60% tin
40%
lead solder should be used when re-soldering. Avoid
excessive heat which may damage the panel board. Chip
away any epoxy involved, and apply new epoxy which is
commercially available.
In order to check the panel board assembly, it is
necessary to unsolder at the locations indicated in Fig-
ure 18i the two capacitors C2 and C3. In all of the fol-
lowing checks, connect the ohmmeter as shown and then
reverse the ohmmeter leads to obtain two readings. The
amplifier circuitry is shown in Figure 19i.
1.
Transistors TR1 and TR2: Check each transistor by
referring to Figure 20i. If both readings in Step 1
are zero, the transistor is shorted. If both readings
in Step 2 are zero, the transistor is shorted; and if
both readings are infinite, the transistor is open.
Interpret Step 3 the same as Step 2.
2.
Trigger Transistor TR3:
11
both readings in Step 1
are zero, the transistor is shorted. If both readings
in Step 2 are zero, the transistor is shorted; and if
both readings are infinite, the transistor is open.
Interpret Step 3 the same as Step 2.
3.
Diode Dl: 11 both readings are zero, the diode is
shorted; and if both readings are infinite, the diode
is open.
4.
Capacitor Cl: If both readings are zero, the capaci-
tor is shorted.
5.
Capacitors C2 and C3: Connect the ohmmeter across
CHECKING
RESISTOR Rl
UNSOLDER
I
CHECKING TRIGGER
TRANSISTOR TR3
CHECKING
CAPACITOR C
Fig.
171—Pulse Amplifier Panel Board
Fig.
18i—Pulse
Amplifier
Component
Checks
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 360 of 659

SECTION 7
CLUTCH AND TRANSMISSIONS
CONTENTS OF THIS SECTION
Clutch
Three-Speed . . .
Overdrive
Three-Speed, (Warner T-16)
Four-Speed (Muncie) . . . .
Page
7-1
7-6
7-9
7-14
7-16
CLUTCH
Page
Four-Speed (Saginaw) 7-20
Powerglide 7-23
Turbo Hydra-Matic 7-36
Special Tools 7-43
INDEX
General Description
Maintenance and Adjustments
Linkage Inspection
Clutch Linkage Adjustment
Component Parts Replacement
Clutch Assembly ......
Removal from Vehicle .
Page
7-1
7-1
7-1
7-2
7-3
7-3
7-3
Installation in Vehicle
Clutch Pedal ..'....,
Clutch Cross Shaft . . .
Removal.......
Repairs
Installation .....
Page
7-4
7-4
7-4
7-4
7-4
7-4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
A diaphragm spring-type clutch assembly is used with
manual transmissions.
The clutch assembly is enclosed in a 360° bell housing
which must be removed to gain access to the clutch.
V-8 engines (equipped with a 4 speed transmission)
use a bent-finger, centrifugal diaphragm type clutch as-
sembly. All its integral release fingers are bent back to
gain a centrifugal boost and to insure quick re engagement
at high engine speeds.
This type of clutch has the advantages of increasing
pressure plate load as the driven plate wears, and of low
pedal effort with high plate loads without requiring over-
center booster springs on the clutch linkage.
The pressure plate is a high tensile strength iron de-
signed for maximum speed conditions.
The clutch release bearing (fig. 4), used with the bent
finger diaphragm clutch, has an overall length of approxi-
mately
1-1/4".
The longer bearing, used with the straight
diaphragm, will cause inability to obtain free pedal travel,
especially as the clutch wears, resulting in slippage and
rapid wear.
DO
NOT INTERCHANGE!
The clutch is operated by conventional linkage consist-
ing of two groups, upper linkage and lower linkage.
The return spring pre-loads clutch linkage, removing
looseness due to wear. The clutch free pedal travel,
therefore, will increase with linkage wear and decrease
with driven disc wear, and free travel felt at pedal is
throwout bearing lash.
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
LINKAGE INSPECTION
There are several things which affect good clutch op-
eration. Therefore, it is necessary, before performing
any major clutch operations, to make preliminary in-
spections to determine whether trouble is actually in the
clutch.
Check the clutch linkage to be sure the clutch releases
fully as follows:
1.
With engine running, hold the clutch pedal approxi-
mately 1/2" from floor mat and move shift lever be-
tween first and reverse several times. If this can be
done smoothly, the clutch is fully releasing. If shift
is not smooth, clutch is not fully releasing and ad-
justment is necessary.
2.
Check clutch pedal bushings for sticking or excessive
wear.
3.
Check fork for proper installation on ball stud. Lack
of lubrication on fork can cause fork to be pulled off
the ball.
4.
Check for bent, cracked or damaged cross shaft
levers or support bracket.
5.
Loose or damaged engine mounts may aUiow the en-
gine to shift its position causing a bind on clutch
linkage at the cross shaft. Check to be sure there is
Fig.
1 - Chevrolet Clutch Pedal Free Travel Adjustment
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL