1953 JEEP CJ fuel filter
[x] Cancel search: fuel filterPage 78 of 376
01
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
14358
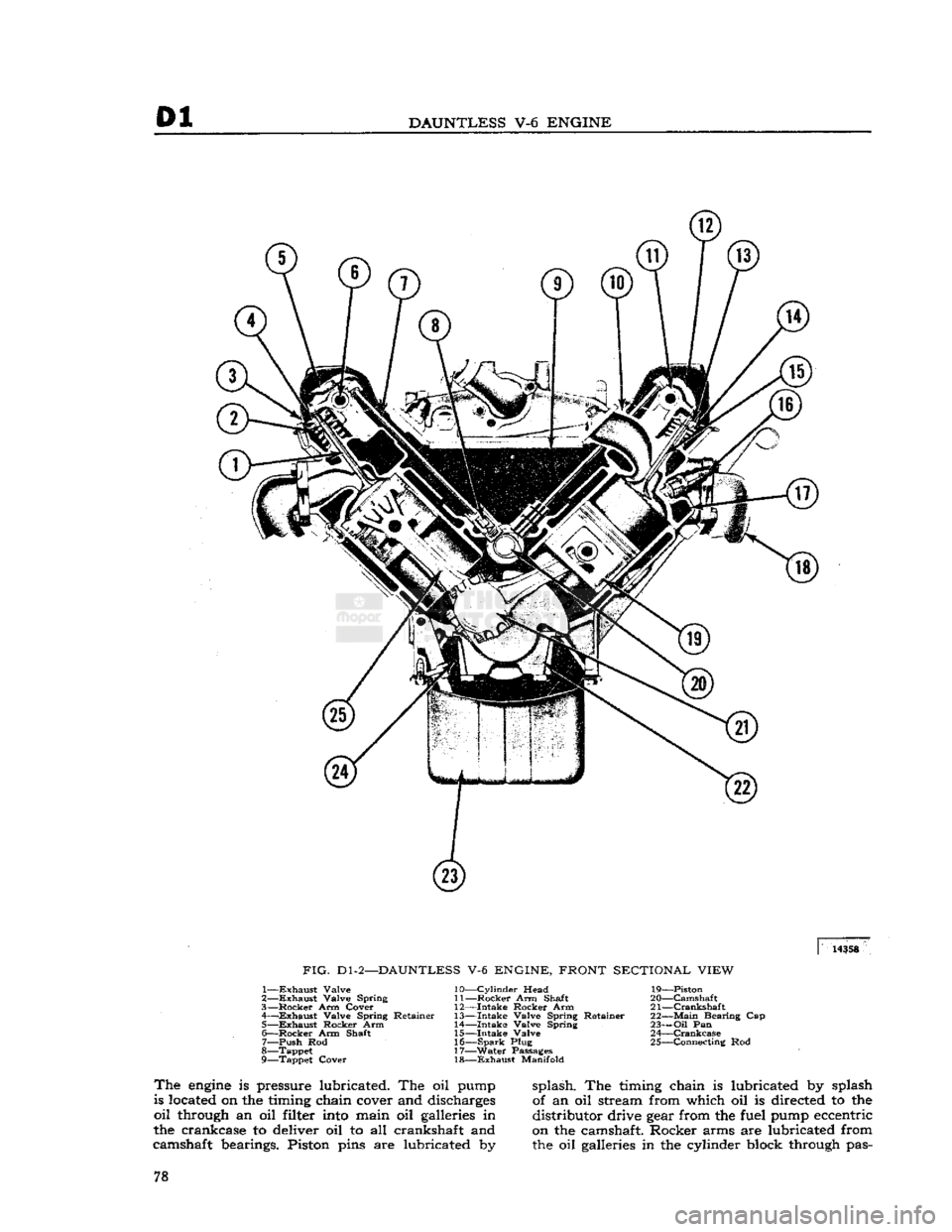
FIG.
Dl-2—DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE, FRONT SECTIONAL VIEW
1—
Exhaust
Valve
2—
Exhaust
Valve Spring
3—
Rocker
Arm Cover
4—
—Exhaust
Valve Spring Retainer 5—
Exhaust
Rocker Arm
6—
Rocker
Arm Shaft 7— push Rod
8— Tappet
9— Tappet Cover 10—
Cylinder
Head
11—
Rocker
Arm Shaft
12—
Intake
Rocker Arm
13—
Intake
Valve Spring Retainer
14—
Intake
Valve Spring
15—
Intake
Valve 16—
Spark
Plug
17—
Water
Passages 18—
Exhaust
Manifold 19— Piston
20—
Camshaft
21—
Crankshaft
22—
Main
Bearing Cap
23—
Oil
Pan
24—
Crankcase
25— Connecting Rod
The
engine
is pressure lubricated. The oil pump
is located on the timing chain cover and discharges
oil
through an oil filter
into
main oil galleries in
the crankcase to deliver oil to all crankshaft and
camshaft bearings. Piston pins are lubricated by- splash. The timing chain is lubricated by splash
of an oil stream from which oil is directed to the
distributor drive gear from the fuel pump eccentric
on the camshaft. Rocker arms are lubricated from
the oil galleries in the cylinder block through pas- 78
Page 80 of 376
Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
In
addition to the instructions covering operations
for disassembling the
engine
out of the vehicle, special instructions are given to cover different
operations required when disassembly is
done
with
the
engine
installed.
During
disassembly operations, the
engine
should be mounted in a suitable
engine
repair stand.
Where
practicable, modify or adapt an existing re
pair
stand as necessary to accommodate the
engine.
If
an
engine
repair stand is not used, take care to
perform
disassembly operations in a manner that
will
protect personnel against an accident and the
engine
and its parts against damage.
Dl-6.
Mounting Engine
On
Engine Stand
Refer
to Fig. Dl-4.
a.
With
the
engine
supported by a hoist, remove
the clutch housing and clutch. Match
mark
the flywheel and the clutch cover before disassembly to assure proper reassembly.
b. Position the
engine
on the
engine
stand.
c. Release
some
tension of the hoist cables and secure
engine
to stand.
d.
Make sure the position lock on the
engine
stand
is tight to prevent the
engine
from accidentally
inverting.
e.
Release the hoist cables.
FIG.
D1
-4—ENGINE
MOUNTED
ON
STAND
1—
Spacer
J-8690-6
A—Bolt,
i/2-NC
x 3i/2"
2—
Bolt,
3/a-NC
x 4*/2" 5—Adapter 21316-J 3—
Engine
Mounting Stand
Dl-7.
Remove Intake Manifold
and
Carburetor Assembly
Disconnect crankcase vent
hose,
distributor vacuum
hose,
and fuel line from carburetor. Disconnect two distributor leads from ignition coil. Disconnect
wiring
harness from coolant temperature sending
unit.
Remove ten cap
bolts
which attach intake
manifold to cylinder heads. Remove intake mani
fold assembly and gaskets from
engine.
Dl-8. Remove Exhaust Manifold
The
engine
has two exhaust manifolds. Remove five attaching screws, one nut, and exhaust mani
fold from each cylinder head.
Dl-9.
Remove Distributor
Disconnect vacuum
hose
and wiring harness from
distributor.
Disconnect spark plug cables from
spark
plugs. Remove sparks plugs from
engine.
Pull
spark
plug cable retainers from brackets on rocker
arm
covers. Remove mounting screw, retainer
bracket,
and distributor from timing chain cover.
If
timing chain and sprockets are not to be re
moved from
engine,
note
position of distributor
rotor so that it can be installed in identical position.
Dl-10. Remove
Fuel Pump
Disconnect output fuel line from fuel pump. Re
move
two mounting bolts, fuel pump, and gasket
from
timing chain cover.
Dl-11.
Remove Alternator
and Fan
Belt
Disconnect wiring harness from alternator. Remove nut and flat washer which fasten alternator to
adjustment bracket. Pivot alternator
inward,
to
ward
engine
cylinder block, to relieve fan belt
tension. Remove fan belt from pulleys. Remove
two attaching screws, mounting bracket, and alter nator from right cylinder head of
engine.
Dl-12.
Remove Cooling
Fan and
Water Pump
Refer
to Fig. Dl-5.
Remove four cap screws, lock washers, cooling fan,
fan
hub, and fan drive pulley from flange of water
pump shaft. Remove nine attaching screws, water
pump, alternator adjustment bracket, and water pump from timing chain cover.
Dl-13.
Remove
Oil
Filter
Unscrew
oil filter from
engine
oil pump.
Dl-14.
Remove Starter Motor
Disconnect wiring harness from starter motor and
solenoid. Remove two attaching screws, starter motor, solenoid, and motor attaching bracket from
engine
flywheel housing and cylinder block.
Dl-15.
Remove
Oil
Pressure Sending Unit
Disconnect wiring harness from oil pressure send
ing unit. Remove oil pressure sending unit from
engine
cylinder block.
Dl-16.
Remove
Oil
Dipstick
Withdraw
and remove oil level dipstick and dip
stick
tube
from
engine
cylinder block.
Dl-17.
Remove Crankshaft Pulley
Remove six attaching screws and crankshaft pulley
from
crankshaft vibration damper. 80
Page 102 of 376
![JEEP CJ 1953 Service Manual
Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
FIG.
Dl-41—WATER
PUMP
AND
TIMING CHAIN COVER BOLT LOCATION
Cover
Bolts
alternately and evenly 8 to 12 lb-ft. [1,10 a 1,66
kg-m.].
Dl-88.
Install
Cranksh JEEP CJ 1953 Service Manual
Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
FIG.
Dl-41—WATER
PUMP
AND
TIMING CHAIN COVER BOLT LOCATION
Cover
Bolts
alternately and evenly 8 to 12 lb-ft. [1,10 a 1,66
kg-m.].
Dl-88.
Install
Cranksh](/manual-img/16/57040/w960_57040-101.png)
Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
FIG.
Dl-41—WATER
PUMP
AND
TIMING CHAIN COVER BOLT LOCATION
Cover
Bolts
alternately and evenly 8 to 12 lb-ft. [1,10 a 1,66
kg-m.].
Dl-88.
Install
Crankshaft
Vibration
Damper
a.
Lubricate
the vibration damper hub
before
in
stallation to prevent
damage
to the crankshaft
front oil seal during installation and when the
engine
is first started.
b.
Install
the vibration damper on the crankshaft.
Secure it with its attaching flat washer and screw.
Torque
the screw to a minimum of 140 lb-ft.
[19,35
kg-m.].
Dl-89.
Install
Crankshaft Pulley
Secure the crankshaft pulley to the crankshaft
vibration
damper with six screws. Torque screws 18 to 25 lb-ft. [2,5 a 3,4 kg-m.].
Dl-90.
Install
Oil
Level
Dipstick
Insert
oil level dipstick
into
the dipstick tube.
Dl-91.
Install
Oil
Pressure Sending Unit
Install
oil pressure sending unit in cylinder block.
Connect electrical wiring harness to unit.
Dl-92.
Install Starting Motor
Secure starting motor and
solenoid
assembly to
the flywheel housing and cylinder block with two attaching screws. Torque screw, which attaches this
assembly to the flywheel housing, 30 to 40 lb-ft. [4,1 a 5,5 kg-m.]. Torque screw, which attaches
bracket
to cylinder block, 10 to 12 lb-ft. [1,4 a 1,7 kg-m.].
Dl-93.
Install
Oil
Filter
Install
a new oil filter
element
at oil filter nipple,
at
left
side
of timing chain cover. Torque 10 to 15 lb-ft. [1,38 a 2,07 kg-m.].
D1-94. Install Water Pump
Be
certain that mating surfaces of the water pump
and
timing chain cover are clean.
Install
a new
gasket
on the pump flange. Secure the pump and
alternator adjustment bracket to the cover with
nine attaching bolts. Torque
bolts
6 to 8 lb-ft. [0,83 a 1,10 kg-m.]. Refer to Fig. Dl-41.
D1-9S.
Install
Cooling Fan
Secure the cooling fan, fan hub, and fan drive
pulley to the water pump shaft
flange
with four
attaching screws. Torque screws 17 to 23 lb-ft. [2,35 a 3,18 kg-m.].
Dl-96.
Install
Alternator
and Fan
Belt
Mount the alternator and bracket assembly on
right
cylinder head with two attaching screws.
Torque
screws 30 to 40 lb-ft. [4,1 a 5,5 kg-m.].
Fasten
the alternator
loosely
to its adjustment
bracket
with attaching flat washer and nut.
Install
the fan
belt
on its pulleys. Pivot the alternator
outward,
away from cylinder block, to apply fan
belt
tension. Adjust fan
belt
tension to 80 lb. [36,2 kg.];
tighten
alternator-to-adjustment bracket
nut to secure adjustment
setting.
Connect wiring
harness to alternator.
Dl-97.
Install
Fuel Pump
Install
two mounting
bolts
and new
gasket
on
flange
of fuel pump. Secure pump to timing chain cover with screws; torque screws 17 to 23 lb-ft. [2,35 a 3,8 kg-m.]. Connect
output
fuel line to
pump.
Dl-98.
Install Exhaust Manifold
Secure each of two exhaust manifolds to corre
sponding cylinder head with five attaching screws,
and
one nut. Torque screws and nut 15 to 20 lb-ft. [2,07 a 2,8 kg-m.]. See Fig. Dl-42.
Dl-99.
Install Distributor
Insert
distributor drive gear
into
distributor mount-
FIG.
Dl-42—EXHAUST
MANIFOLD INSTALLATION
1—Torque
Bolts—15
to 20
lb-ft.
[2,07 a 2,8
kg-m.]
102
Page 109 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
E
FUEL
SYSTEM
Contents
SUBJECT
PAR.
GENERAL
E-1 Dash
FUEL
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION
?*^r
CONTROL SYSTEM
..E-2
Canister
.E-3 . Demand Valve E-4
Fuel
Tank.
.E-5
Inspection Test. E-8
Sealed Gas Cap. E-7
Servicing
System E-9
Vapor
Separator or Expansion
Tank
E-6
CARBURETOR
—
HURRICANE F4 ENGINE.
. .
......
..... ,. . .E-10 Accelerating Pump System.............. .E-19 Accelerating Pump Maintenance E-20
Carburetor
Reassembly
E-2
2
Carburetor
Disassembly E-21
Choke
System E-17
Dash
Pot Adjustment E-44
Fast
Idle Adjustment E-18
Float
Adjustment E-12
Float
System. E-ll
High-Speed System . .E-15
Idle
Adjustment .E-14
Low-Speed
System . E-13
Metering Rod Adjustment E-16
CARBURETOR
~r
DAUNTLESS V-6 ENGINE
.E-25
Accelerator Pump Adjustment E-41 Accelerator Pump System. . E-30
Air
Horn Body Assembly E-39
Air
Horn Body Removal and Disassembly.
E-33
Carburetor
Cleaning and Inspection E-36
Carburetor
Removal E-32
Choke
System E-31
Curb-Idle
Speed and Mixture Adjustment. .E-42
E-1. GENERAL
The
fuel system of the Jeep Universal vehicle,
whether equipped with a Hurricane F4 or Daunt
less
V-6 Engine,
consists
of the fuel tank, fuel lines, fuel pump, carburetor and
air
cleaner.
Fig. E-1, E-2.
Vehicles equipped with a
Fuel
Evaporative
Emis
sion Control System
also
include a
non-vent
pressure and vacuum
sensitive
gas cap, a liquid
expansion and vapor separator tank, a carbon filled vapor
storage
canister, and a vapor purge line. Service information pertaining to the
Fuel
Evap
orative Emission Control System is outlined in
Par.
E-2 through
E-9.
Refer to Figs. E-3 and E-4.
The
most
important
attention
necessary to the fuel
system is to
keep
it clean and free from water. It should be periodically inspected for leaks.
CAUTION—Whenever
a vehicle is to be stored for
an
extended
period, the fuel system should be com
pletely
drained, the
engine
started and allowed to
run
until the carburetor is emptied.
This
will
avoid
oxidization of the fuel, resulting in the formation of
SUBJECT
PAR.
Pot Adjustment .E-44
nal
Carburetor Adjustments.........E-40
Idle
Adjustment
.
E-43 System . . .E-26
Bowl
Body Assembly E-38
Fuel
Bowl Body Disassembly E-34
Idle
System E-27
Main
Metering System E-28
Power System . E-29
Throttle
Body Assembly .E-37
Throttle
Body Removal, and Disassembly. .E-35
FUEL
PUMP
—
HURRICANE F4 ENGINE.
E-45, 54, 60
Cleaning
and Inspection.............
.E-57,
63 Disassembly E-46, 56, 62
Installation E-59, 65
Reassembly
.E-47,
58, 64
Removal
E-55, 61
Testing.
E-49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 66
Vacuum
Pump E-48
FUEL
PUMP
—
DAUNTLESS V-6 ENGINE
E-67
Removal
E-68
AIR CLEANER
—
CARBURETOR
E-69
ACCELERATOR
LINKAGE
.E-70
FUEL
TANK
AND
LINES
E-71
Float
Unit . .E-76
Fuel
Lines E-77
Fuel
Tank
. . .E-72
Fuel
Tank
Cap E-75
Fuel
Tank
Installation. E-74
Fuel
Tank
Removal E-73
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS
E-78
SPECIFICATIONS.
E-79
gum in the units of the fuel system. Gum formation
is similar to hard varnish and may cause the fuel
pump valves or the carburetor
float
valve to be
come
stuck or the filter screen blocked. Acetone or commercial fuel system cleaners
will
dissolve
gum formation. In
extreme
cases
it
will
be necessary
to dissassemble and clean the fuel system. In
most
cases, however, a
good
commercial fuel system sol
vent
used in accordance with the manufacturer's
instructions or one pint [0,6 ltr.] of
acetone
placed
in
the fuel tank with
about
one gallon [4,5 ltr.]
of
gasoline
will
dissolve
any
deposits
as it
passes
through the system with the
gasoline.
E-2.
FUEL
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
Description and Operation
•
Refer to Figs. E-3 and E-4.
The
Fuel
Evaporative Emission Control System
is
designed
to reduce fuel vapor emission that 109
Page 111 of 376
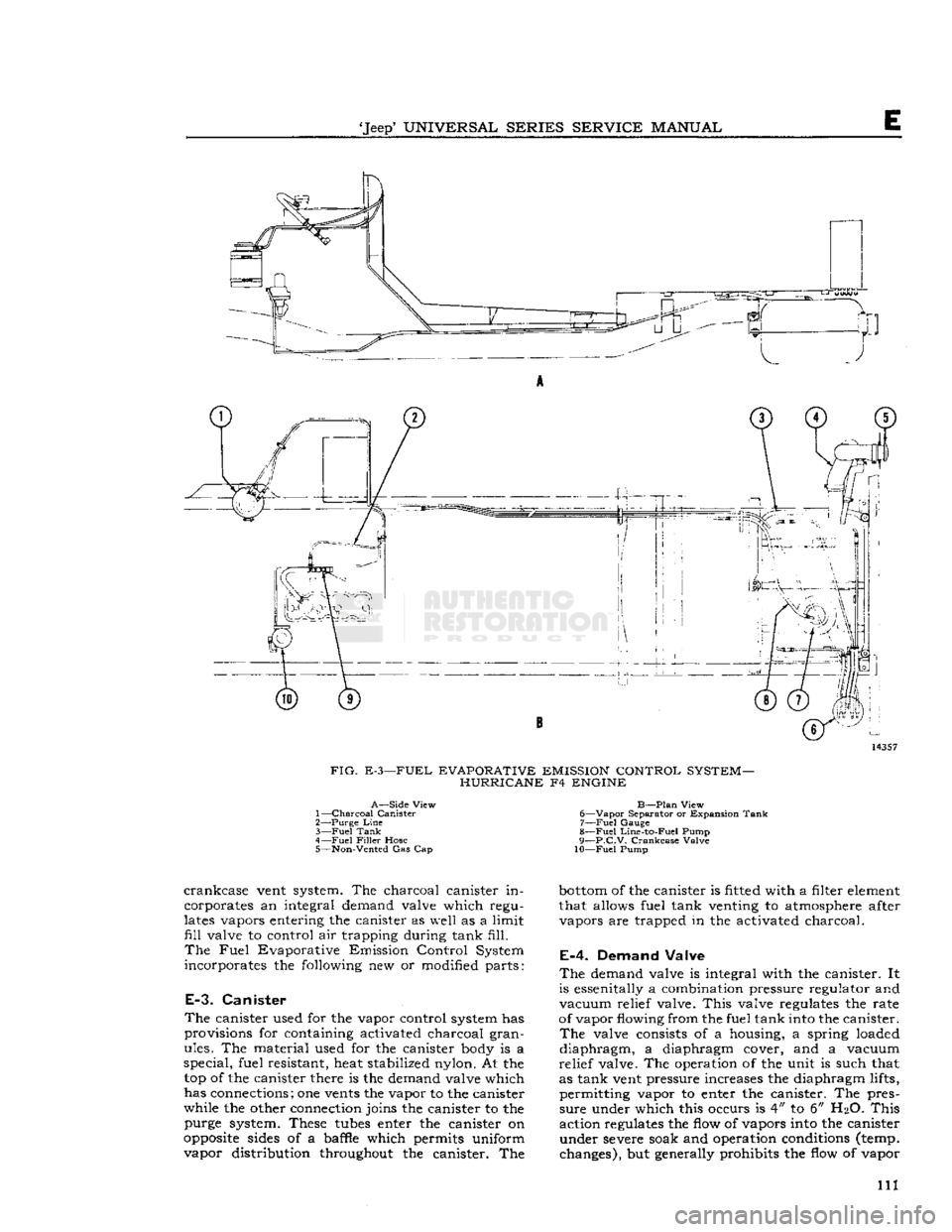
'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
E
FIG.
E-3—FUEL EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM- HURRICANE F4 ENGINE
A—Side
View
1—
Charcoal Canister
2— Purge
Line
3—
Fuel
Tank
4—
Fuel
Filler
Hose 5—
Non-Vented
Gas Cap
B—Plan
View
6—
Vapor
Separator
or Expansion Tank 7—
Fuel
Gauge
8—
Fuel
Line-to-Fuel Pump
9—
p.C.V.
Crankcase
Valve
10—Fuel
Pump
crankcase
vent system. The charcoal canister in
corporates an integral demand valve
which
regu
lates
vapors entering the canister as
well
as a
limit
fill
valve
to control air trapping during tank
fill.
The
Fuel
Evaporative Emission Control System
incorporates the following new or modified parts:
E-3.
Canister
The canister used for the vapor control system has
provisions for containing activated charcoal gran ules. The material used for the canister body is a
special,
fuel resistant, heat stabilized nylon. At the top of the canister there is the demand valve which
has connections; one vents the vapor to the canister
while the other connection joins the canister to the purge system. These
tubes
enter the canister on
opposite
sides of a baffle which permits uniform
vapor distribution throughout the canister. The
bottom
of the canister is fitted with a filter element
that allows fuel tank venting to atmosphere after vapors are trapped in the activated charcoal.
E-4.
Demand Valve
The
demand valve is integral with the canister. It
is essenitally a combination pressure regulator and
vacuum
relief valve.
This
valve regulates the rate
of vapor
flowing
from the fuel tank into the canister.
The
valve consists of a housing, a spring loaded
diaphragm,
a diaphragm cover, and a vacuum
relief
valve. The operation of the unit is such that
as tank vent pressure increases the diaphragm lifts,
permitting vapor to enter the canister. The pres
sure
under which this occurs is 4" to 6"
H2O.
This
action regulates the flow of vapors into the canister
under severe soak and operation conditions (temp, changes), but generally prohibits the flow of vapor 111
Page 113 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
E
there is a relief valve that
opens
to reduce high
(dangerous) pressures in the fuel tank. In con
junction
with the pressure relief valve there is a
vacuum
relief valve to
stop
collapse of the fuel
tank
in case of a plugged system or failure of the demand valve. When replacing the gas cap, the
same type must be used as originally installed.
E-8.
System Inspection Test
The
fuel emission vent system should be checked
carefully
to ensure the absence of any leaks to the
atmosphere of either liquid or vapor which might
affect the accuracy, safety, or performance of the control system.
To
assure that the sealed system has been properly
installed,
the following
test
procedure has been
developed.
Disconnect the vent line from the fuel tank system
to the activated charcoal canister, induce l/i p.s.i.
air
pressure. If this pressure can be maintained for
a
few seconds the vent system is assured to be sealed. DO NOT add air pressure to the canister
because damage can occur to the demand valve if
care
is not taken.
E-9.
Servicing the System
Periodic
Maintenance — Replace carbon canister filter at
12,000
miles
[19,200
km.] or 12 month intervals (more
often
for operation in dusty areas).
This
is the only regular maintenance service
required.
Canister
Filter
Replacement — Disconnect
hoses
from
top of canister, remove canister from mount
-
t
FIG.
E-5—CARBURETOR—
F4 ENGINE,
EARLY
MODEL
1—
Choke
Clamp
Bracket
2—
Choke
Shaft and
Lever
Assembly
3—
Fuel
Inlet
Elbow
4—
Bowl
Vent Tube 5—
Idle
Air Adjusting
Needle
6—
Throttle
Lever
and Shaft Assembly
7—
Idle
Speed Adjusting Screw
8—
Fast
Idle Connector Rod ing bracket. Remove cover from
bottom
of canister
by pulling it down to
disengage
clips. Remove and
discard
polyurethane filter element
(squeeze
ele
ment out from under retainer bar).
Install
new
filter by squeezing element under retainer bar and positioning it evenly around entire
bottom
of
canister with
edges
tucked under canister lip, snap
bottom
cover in place, reinstall canister on bracket
and
reconnect
hoses.
Vapor
line
hoses
used in this system are made of
special
rubber material.
Bulk
hoses
are available for
parts
service.
Ordinary
rubber
hose
should not be
used to service vapor lines as they are subject to deterioration and may clog the system.
Liquid
vapor separators or expansion tanks and canisters
are
serviced as complete units only.
Canister
air filters, however, are serviced separately.
E-10.
CARBURETOR
—
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
A
single-barrel manual choke, down-draft carbure
tor (Fig. E-6) is used on the
Hurricane
F4 engine.
The
carburetor is internally vented by a tube
opening located in the air horn body of the
car
buretor.
This
opening is connected by a rubber
tube to the air
outlet
horn of the air cleaner thus
allowing only filtered atmospheric pressure air
to enter the float chamber for balance pressure
of the carburetor fuel.
Note:
A carburetor with a specific flow character
istic
is used for exhaust emission control. The
carburetor
is identified by a number, and the correct
carburetor
must be used, when replacement is
necessary.
Early
production models
CJ-3B,
CJ-5,
CJ-5A,
CJ-6,
and
CJ-6A
have a
Carter
YF-938SD
carbure
tor superseding the earlier
YF-938SC,
YF-938SA,
or
YF-938S
models.
Note."
Conversion kits for changing earlier models
to SD models are available. See Par E-23. It is recommended that when a carburetor is converted
that a tag be fashioned stamped with the new model number and installed under one of the air
horn
screws.
Look
for such a tag to determine if
the carburetor has previously been converted.
Carburetors
listed above are all in the same YF
series and have only minor differences. Descriptions
and
repair procedures given in the following
para
graphs apply equally to all
YF-series
carburetors.
YF-series
carburetors employ manual and vacuum
control of the metering rod and accelerator pump.
The
carburetor controls and vaporizes the fuel
through five separate systems: float system, low-
speed system, high-speed system, choke system,
and
accelerating-pump system. A description of the function and operation of each system provides an over all description of the carburetor.
For
identification, the series designation is stamped
on the body under the name
Carter
and the model
designation is stamped on a flange protruding
from
the body.
Note:
When checking for carburetor icing causes,
also check the vacuum-pump-to-manifold vacuum
line connector. 113
Page 123 of 376

'Jeep9
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
E
exterior moving parts of a carburetor are
often
responsible for unsatisfactory performance.
For
this
reason,
efficient carburetion depends upon careful cleaning and inspection while servicing.
a.
Thoroughly clean carburetor castings and metal
parts
in carburetor cleaning solvent.
Caution:
Accelerator pump plunger and any fiber
or
rubber parts should never be immersed in
car
buretor
cleaner. Wash pump plunger in cleaning
solvent.
b.
Blow out all passages in the castings with com
pressed air. Dry all parts with compressed air.
Make
sure all jets and passages are clean. Do
not use wire to clean fuel passages or air bleeds.
c.
Check
inlet valve
needle
and seat for wear. If
wear
is noted, the assembly must be replaced.
d.
Check
float hinge pin for wear and check float
for damage.
e.
Check
throttle and choke shaft bores for wear
and
out-of-round.
f. Inspect idle mixture adjustment
needles
for
burrs
or
grooves; replace if damaged.
g. Inspect cup of accelerator pump plunger; re
place if damaged, worn, or hardened. Inspect pump
well
in bowl for wear or scoring.
h.
Check
filter screens for
dirt
or lint.
Clean,
and
if
they remain
clogged,
replace.
i.
If for any reason parts have
become
loose
or
damaged in the cluster assembly, the assembly
must be replaced.
Note:
Use ijew gaskets whenever the carburetor
is disassembled.
E-37.
Throttle Body Assembly
a.
Install
idle mixture adjustment
needles
and
springs in throttle body. Tighten finger-tight, then
unthread
one
turn
as a preliminary adjustment
setting.
Caution:
Do not force idle mixture adjustment
needles
against
seats
or damage may result.
b.
Invert
fuel bowl body and place new throttle
body gasket on bowl. Fasten throttle body to bowl
body with three screws and lockwashers; tighten
securely.
E-38.
Fuel
Bowl Body Assembly
a.
Drop steel discharge check
tall
of accelerator
pump into discharge hole.
Install
pump discharge
spring
and T-shaped retainer. Stake retainer in
place.
Note:
Top of retainer must be flush with flat
surface
of fuel bowl body.
b.
Install
two inserts in main well. Align surface
on lip of insert with flat surface in recess on top
of main well.
Install
venturi cluster with gasket,
and
tighten mounting screws evenly and securely.
Be
certain that center screw is fitted with fiber gasket, and that a special smooth shank screw is
used.
c.
Install
two main metering jets, power valve
gasket and power valve.
d.
Install
small aluminum inlet check
ball
in ac
celerator
pump inlet at
bottom
of pump well. In
sert
pump return spring into well, and center by
pressing spring downward with finger.
e.
Install
pump inlet screen in
bottom
of fuel
bowl.
E-39.
Air
Horn Body
Assembly
a.
Install
choke lever and collar on choke shaft.
Prong
on choke lever must face away from air
horn
body and be on top of choke trip lever.
b.
Install
choke shaft and lever assembly into the
air
horn. Choke rod
hole
in the choke lever must
face fuel inlet side of carburetor.
c.
Install
choke valve plate in choke shaft so that
letters RP
will
face upward in finished carburetor.
Install
two new valve plate attaching screws, but
do not tighten securely until valve plate is centered.
To
center choke valve plate on choke shaft, hold
choke valve tightly closed, then slide choke shaft
inward
to obtain approximately .020" [0,508 mm.]
clearance
between
choke trip lever and choke lever
and
collar assembly. Tighten choke valve screws
securely,
and stake lightly in place. Choke valve
will
be perfectly free in all positions when installed
correctly.
d.
Insert
outer accelerator pump lever and shaft as sembly into air horn body, with lever pointing to
ward
choke shaft.
Install
inner pump arm, with plunger
hole
inward,
and tighten set screw securely.
Position pump plunger assembly on inner pump
arm,
with pump shaft pointing
inward,
and install
retainer.
e.
Install
needle
seat screen on inlet valve seat. In
stall
seat and gasket in air horn body. Tighten seat
securely with a wide-blade screwdriver.
f.
Install
power piston into vacuum cavity.
Lightly
stake piston retainer washer in place. Piston should
travel
freely in cavity.
g.
Install
air horn gasket on air horn body, fitting
gasket over guide pin.
h.
Attach inlet valve
needle
to float.
Carefully
position float and insert float hinge pin. Drop tang
at
rear
of float arm downward toward air horn.
i.
Install
fuel inlet fitting, if removed.
j.
With
air horn assembly inverted, measure the distance from the air horn gasket to top of float
at toe \%£f [27,78 mm.] for standard carburetors
and
\%i [29,36 mm.] for exhaust emission control
equipped carburetors, as shown in Fig. E-23. Use
float level
gauge
J-5127-2. Bend float arm as re
quired
to adjust float level.
k.
With
air horn body held upright, measure dis
tance from gasket to
bottom
of float
pontoon
at outer end. Use a l7/s" [47,625 mm.] float drop
gauge.
Bend float tang, as required, to adjust float
drop.
See Fig. E-24.
I.
Carefully
place air horn body on fuel bowl
body, making certain that the accelerator pump
plunger is properly positioned in the pump well.
Lower
the cover gently, straight down; install air 123
Page 126 of 376

FUEL
SYSTEM
|
11893
FIG.
E-29—FUEL
AND
VACUUM
PUMP—F4
ENGINE,
EARLY
MODELS
1—
Cover
Screw
2—
Lockwasher
3—
Diaphragm
Spring
4—
Spring
Seat 5—
Diaphragm
and Rod
6—
Oil
Seal 7—
Valve
Assembly
8— Body
9—
Rocker
Arm Pin Spring
10—
Fuel
Diaphragm
11—
Oil
Seal Retainer
12—
Diaphragm
and Rod 13—
Valve
Retainer
14—
Cover
15—
Gasket
16—
Screen
17—
Bow!
18—
Bail
19—
Gasket
20—
Screw
21—
Rocker
Arm Spring
22—
Link
Spacer
23—
Rocker
Arm
24—
Washer
25—
Body
fuel. The diaphragm can start and
stop
many
times
in
each mile of vehicle operation, but the pump
actuating lihkage is always in operation while the
engine
is running. The fuel pump incorporates a
pulsator and pulsator chamber to dampen the
effect
of pump pressure pulsations on the carburetor
needle
valve.
This
prevents high fuel level in the
reservoir
that would result from the
needle
being
jarred
away from its seat. Also, operating
economy
would be affected because a high fuel level usually results in an over-rich mixture.
The
actuating linkage has its own spring to ensure
continuous contact of the lever to the camshaft
eccentric.
This
fuel pump has a sediment bowl and filtering
screen which is attached to the top of the pump by
a
wire clamp and thumb nut. The screen and sedi
ment bowl should be cleaned at least twice yearly
to prevent trouble due to a blocked screen or water
freezing. The bowl should be washed and wiped
dry
and the screen dried and then cleaned with a
stiff
brush.
When reassembling the bowl make cer
tain
that the cork gasket is not broken; reverse it
and
position it flat on the seat, then install the
bowl and tighten the thumb nut securely. After
cleaning, start the
engine
and carefully inspect the
bowl for leakage.
E-46.
Disassembly
Remove the cover plate, gasket, and screen or
bowl clamp, sediment bowl, gasket and screen if so equipped.
Mark
the two castings with a file to
ensure positioning in the same relation upon
assembly. Remove the screws attaching the fuel cover to the pump body. Remove the cover,
diaphragm,
and spring. Remove rocker arm pin,
rocker
arm, and rocker arm spring. Remove the
valve plate screw and separate the valve plate
retainer,
valve gaskets, and valves.
Clean
all parts in cleaning solvent and blow out
with
compressed air. Valves should not be removed
from
the valve housing assembly.
Check
all parts
to see that
they
have not
been
cracked or broken
and
that screw threads have not
been
stripped or
cross threaded. Refer to Par. E-49 for fuel pump
testing. 126