2023 FORD F650/750 radiator
[x] Cancel search: radiatorPage 14 of 378

• The gearshift lever must be in P (Park)
or N (Neutral) in order for the starter
to operate.
• Try operating the starter switch several
times. This operation may clean
potentially corroded contacts or make
the switch temporarily operable until
you can reach the dealer.
• If all electrical connections are tight
and you need assistance to start, See
Jump Starting the Vehicle (page 190).
If engine cranks but won’t start
Prolonged starter cranking (in excess of 10
seconds) could cause damage to the
starter motor or the high-pressure fuel
pump.
• Check the fuel gauge. You may be out
of fuel. If the gauge shows that there
is fuel in the tank, the trouble may be
in the electrical system or the fuel
system. If equipped with an auxiliary
tank, be sure that the tank control
switch is set for the tank with fuel and
not on an empty tank.
• Leaving your ignition key turned to on
for over two minutes without starting
may make starting difficult because
the glow plugs will cease activation.
Reset the system by turning the ignition
key to off and then back to on again.
Note:If the system is out of fuel and the
engine will not start, do not continue
cranking the engine. Continued cranking can
damage the high-pressure fuel pump.
If the engine runs hot
The following could cause the engine to
overheat:
• Lack of coolant
• Dirty cooling system.
• Plugged radiator fins, A/C condenser
and/or oil cooler
• Malfunctioning fan drive• Driving with frozen coolant
• Sticking thermostat
• Overloading or pulling heavy trailers
during hot weather
• Grill or radiator air blockage
• Slipping or missing drive belt
• Plugged or very dirty air filter
If fuses burn out
WARNING: Replacement fuses and
circuit breakers must always be the
same rating as the original equipment
shown. Never replace a fuse or circuit
breaker with one of a higher rating.
Higher rated fuses or circuit breakers
could allow circuit overloading in the
event of a circuit malfunction, resulting
in severe vehicle damage or personal
injury due to fire.
Burned-out or blown fuses usually indicate
an electrical short-circuit, although a fuse
may occasionally burn out from vibration.
Insert a second fuse. If this fuse
immediately burns out and you cannot
locate the cause, return your vehicle to
your dealer for a circuit check. See
Changing a Fuse (page 208).
Selective catalytic reduction system
speed limit and Idle-only modes
If the vehicle’s speed is limited or in an
idle-only mode, the selective catalytic
reduction system may be limiting the
vehicle’s functions due to low or
contaminated DEF. Check the DEF. See
Selective Catalytic Reductant System
(page 118).
SYMBOLS GLOSSARY
These are some of the symbols you may
see on your vehicle.
10
Introduction
Page 25 of 378

PROTECTING THE
ENVIRONMENT
Sustainability is a priority at Ford. We are
constantly looking for ways to reduce our
impact on the planet while providing
customers with great products and
delivering a strong business. You should
play your part in protecting the
environment. Correct vehicle usage and
the authorized disposal of waste, cleaning
and lubrication materials are significant
steps toward this aim.
For additional information about our
sustainability progress and initiatives, visit
www
.sustainability.ford.com.
NOISE POLLUTION CONTROL
In order to keep to the federal exterior
noise regulations, your vehicle may be
equipped with noise emission items.
Depending on your vehicle configuration,
it may have all or some of the following
items:
Air Intake System
Inspect the air cleaner. Do not alter its
location. Do not alter inlet and outlet
piping.
Body
Inspect wheel well splash shields, cab
shields and under hood insulation for
deterioration, dislocation and orientation.
Cooling System
• Inspect the fan for blade damage. If
you find any damage, replace with the
recommended parts. Inspect for
fan-to-shroud interference and any
damage to shroud, such as cracks and
holes.
• Do not change fan ratio or alter fan
spacer dimensions and positions.
• Inspect fan clutch for proper operation.
Make sure the fan is disengaged when
cooling of the engine is not required.
• Inspect radiator shutters (if equipped)
for proper operation. The shutters
should be open during normal
operating temperatures.
Engine
Valve covers and block covers damp-out
engine mechanical noise. If they need
replacing, make sure to replace them with
the recommended parts. Check for
mechanical isolations.
Transmission Enclosure
Inspect for cracks, holes and tears. Clean
any deposits, such as oil, dirt and stones.
Exhaust System
• Inspect for leaks at various joint
connections and loose clamps.
• Perform a visual inspection for cracks
or holes in the muffler and tail pipe.
• Always use the recommended
replacement parts.
21
Environment
Page 137 of 378

Note:Do not rock your vehicle for more
than a minute or damage to the
transmission and tires could occur, or the
engine could overheat.
If your vehicle is stuck in mud or snow, you
could rock it out by shifting between
forward and reverse gears, stopping
between shifts in a steady pattern. Press
lightly on the accelerator in each gear.
POWER TAKE-OFF (IF EQUIPPED)
Auxiliary equipment called power take-off,
or PTO, is often added to the engine or
transmission to operate utility equipment.
Examples include a wheel-lift for tow
trucks, cranes, tools for construction or tire
service and pumping fluids. PTO
applications draw auxiliary horsepower
from the powertrain, often while the
vehicle is stationary or mobile. In the
stationary condition, there is limited
cooling air flow through the radiator and
around the vehicle that normally occurs
when a vehicle is moving. The aftermarket
PTO system installer, having the most
knowledge of the final application, is
responsible for determining whether
additional chassis heat protection or
powertrain cooling is required and alerting
the user to the safe and proper operation.
Your vehicle is approved for use as a
Stationary Mode, SplitShaft Mode or
Mobile Mode power source within the limits
and operating guidelines detailed in the
Ford Truck Body Builders Layout Book,
found at https://fordbbas.com/home and
through the Ford Truck Body Builders
Advisory Service. The transmission power
source modes are engine specific.
133
Transmission
Page 238 of 378

Note: Do not use stop leak pellets, cooling
system sealants, or non-specified additives
as they can cause damage to the engine
cooling or heating systems. Resulting
component damage may not be covered by
the vehicle Warranty.
It is very important to use prediluted
coolant approved to the correct
specification in order to avoid plugging the
small passageways in the engine cooling
system. See Cooling System Capacity
and Specification (page 297). Do not mix
different colors or types of coolant in your
vehicle. Mixing of engine coolants or using
an incorrect coolant may harm the engine
or cooling system components and may
not be covered by the vehicle Warranty.
Note: Coolants marketed for all makes and
models may not be approved to Ford
specifications and may cause damage to
the cooling system. Resulting component
damage may not be covered by the vehicle
Warranty.
If the coolant level is at or below the
minimum mark, add prediluted coolant
immediately.
For vehicles with overflow coolant systems
with a non-pressurized cap on the coolant
recovery system, add coolant to the
coolant recovery reservoir when the engine
is cool. Add prediluted coolant to the
maximum level. For all vehicles which have
a coolant degas system with a pressurized
cap, or if it is necessary to remove the
coolant pressure relief cap on the radiator,
follow these steps to add engine coolant:
1. Turn the engine off and let it cool.
2. Unscrew the cap slowly. Any pressure
escapes as you unscrew the cap.
3. Fill the coolant reservoir slowly with
prediluted engine coolant to within the
minimum and maximum range on the
engine coolant reservoir. If you
removed the radiator cap in an
overflow system, fill the radiator untilthe coolant is visible and the radiator
is almost full. If coolant is added to
bring the level within the minimum and
maximum range when the engine is not
cold, the system may remain under
filled.
4. Replace the coolant reservoir cap, turn
it clockwise until you feel a strong
resistance.
5. Check the coolant level in the coolant
reservoir the next few times you drive
your vehicle. If necessary, add enough
prediluted engine coolant to bring the
coolant level to the proper level.
Note:If prediluted coolant is not available,
use the approved antifreeze concentrate
diluting it to 50/50 with distilled water. See
Cooling System Capacity and
Specification (page 297). Using water that
has not been deionized may contribute to
deposit formation, corrosion or plugging of
the small cooling system passageways.
If you have to add more than 1.1 qt (1 L) of
engine coolant per month, have your
vehicle checked as soon as possible.
Operating an engine with a low level of
coolant can result in engine overheating
and possible engine damage.
Note:During normal vehicle operation, the
coolant may change color from orange to
pink or light red. As long as the coolant is
clear and uncontaminated, this color change
does not indicate the coolant has degraded
nor does it require the coolant to be drained,
the system to be flushed, or the coolant to
be replaced.
In case of emergency, you can add a large
amount of water without prediluted
coolant in order to reach a vehicle service
location. On arrival do the following:
1. Drain the cooling system.
2. Chemically clean the cooling system.
We recommend Motorcraft Premium
Cooling System Flush.
234
Maintenance
Page 239 of 378

3. Refill with prediluted coolant as soon
as possible.
Water alone, without prediluted coolant,
can cause engine damage from corrosion,
overheating or freezing.
Do not use the following as a coolant
substitute:
• Alcohol.
• Methanol.
• Brine.
• Any coolant mixed with alcohol or
methanol antifreeze.
Alcohol and other liquids can cause engine
damage from overheating or freezing.
Do not add extra inhibitors or non-specified
additives to the coolant. These can be
harmful and compromise the corrosion
protection of the coolant.
Engine and Secondary Cooling
System Refill Procedure
The following procedure should be used
when refilling the engine or secondary
cooling systems after it has been drained
or become extremely low:
1. Before you remove the cap, turn the
engine off and let it cool.
2. When the engine is cool, wrap a thick
cloth around the cap. Slowly turn cap
counterclockwise until pressure begins
to release.
3. Step back when the pressure releases.
4. When you are sure that all the pressure
has been released, use the cloth to turn
the cap counterclockwise and then
remove it.
5. Slowly add prediluted engine coolant
to the coolant reservoir until the
coolant level is within the minimum
and maximum range as listed on the
reservoir.
6. Reinstall the pressure relief cap.7. Start and run the engine at 2000 rpm
for 2 minutes.
8. Shut engine off, and remove the
pressure relief cap as previously
outlined.
9. If required, add prediluted engine
coolant to the coolant reservoir until
the coolant level is within the minimum
and maximum range as listed on the
reservoir.
10. Engine cooling system: Repeat steps
5 through 9 until the coolant level has
stabilized (is no longer dropping after
each step) and the upper radiator
hose at the radiator is warm to the
touch (indicating that the engine
thermostat is open and coolant is
flowing through the radiator).
11. Check the secondary cooling system.
Repeat steps 1 through 10 until the
coolant level has stabilized (is no
longer dropping after each step) and
the lower passenger side of the
secondary radiator is warm to the
touch (indicating secondary
thermostat is open and coolant is
flowing through the entire system).
12. Check the coolant level in both
systems before you drive your vehicle
the next few times.
13. If necessary, add prediluted engine
coolant to the coolant reservoirs until
the coolant level is within the
minimum and maximum range as
listed on the reservoir. After any
coolant has been added, check the
coolant concentration.
Recycled Coolant
We do not recommend the use of recycled
coolant as an approved recycling process
is not yet available.
235
Maintenance
Page 243 of 378

It is very important to use prediluted
coolant approved to the correct
specification in order to avoid plugging the
small passageways in the engine cooling
system. See Cooling System Capacity
and Specification (page 298). Do not mix
different colors or types of coolant in your
vehicle. Mixing of engine coolants or using
an incorrect coolant may harm the engine
or cooling system components and may
not be covered by the vehicle Warranty.
Note: Coolants marketed for all makes and
models may not be approved to our
specifications and may cause damage to
the cooling system. Resulting component
damage may not be covered by the vehicle
Warranty.
If the coolant level is at or below the
minimum mark, add prediluted coolant
immediately.
For vehicles with overflow coolant systems
with a non-pressurized cap on the coolant
recovery system, add coolant to the
coolant recovery reservoir when the engine
is cool. Add prediluted coolant to the
maximum level. For all vehicles which have
a coolant degas system with a pressurized
cap, or if it is necessary to remove the
coolant pressure relief cap on the radiator,
follow these steps to add engine coolant:
1. Turn the engine off and let it cool.
2. Unscrew the cap slowly. Any pressure
escapes as you unscrew the cap.
3. Fill the coolant reservoir slowly with
prediluted engine coolant to within the
minimum and maximum range on the
engine coolant reservoir. If you
removed the radiator cap in an
overflow system, fill the radiator until
the coolant is visible and the radiator
is almost full. If coolant is added to
bring the level within the minimum and
maximum range when the engine is not
cold, the system may remain
underfilled.4. Replace the coolant reservoir cap. Turn
the cap clockwise until it contacts the
hard stop.
5. Check the coolant level in the coolant
reservoir the next few times you drive
your vehicle. If necessary, add enough
prediluted engine coolant to bring the
coolant level to the proper level.
Note:If prediluted coolant is not available,
use the approved antifreeze concentrate
diluting it to 50/50 with distilled water. See
Cooling System Capacity and
Specification (page 298). Using water that
has not been deionized may contribute to
deposit formation, corrosion or plugging of
the small cooling system passageways.
If you have to add more than 1.1 qt (1 L) of
engine coolant per month, have your
vehicle checked as soon as possible.
Operating an engine with a low level of
coolant can result in engine overheating
and possible engine damage.
Note:During normal vehicle operation, the
coolant may change color from orange to
pink or light red. As long as the coolant is
clear and uncontaminated, this color change
does not indicate the coolant has degraded
nor does it require the coolant to be drained,
the system to be flushed, or the coolant to
be replaced.
Note:In case of emergency, you can add a
large amount of water without coolant in
order to reach a vehicle service location.
Water alone, without coolant, can cause
engine damage from corrosion, overheating
or freezing. When you reach a service
location, you must have the cooling system
drained, flushed and refilled using the
correct specification prediluted coolant or
antifreeze concentrate. See Cooling
System Capacity and Specification (page
298).
239
Maintenance
Page 327 of 378
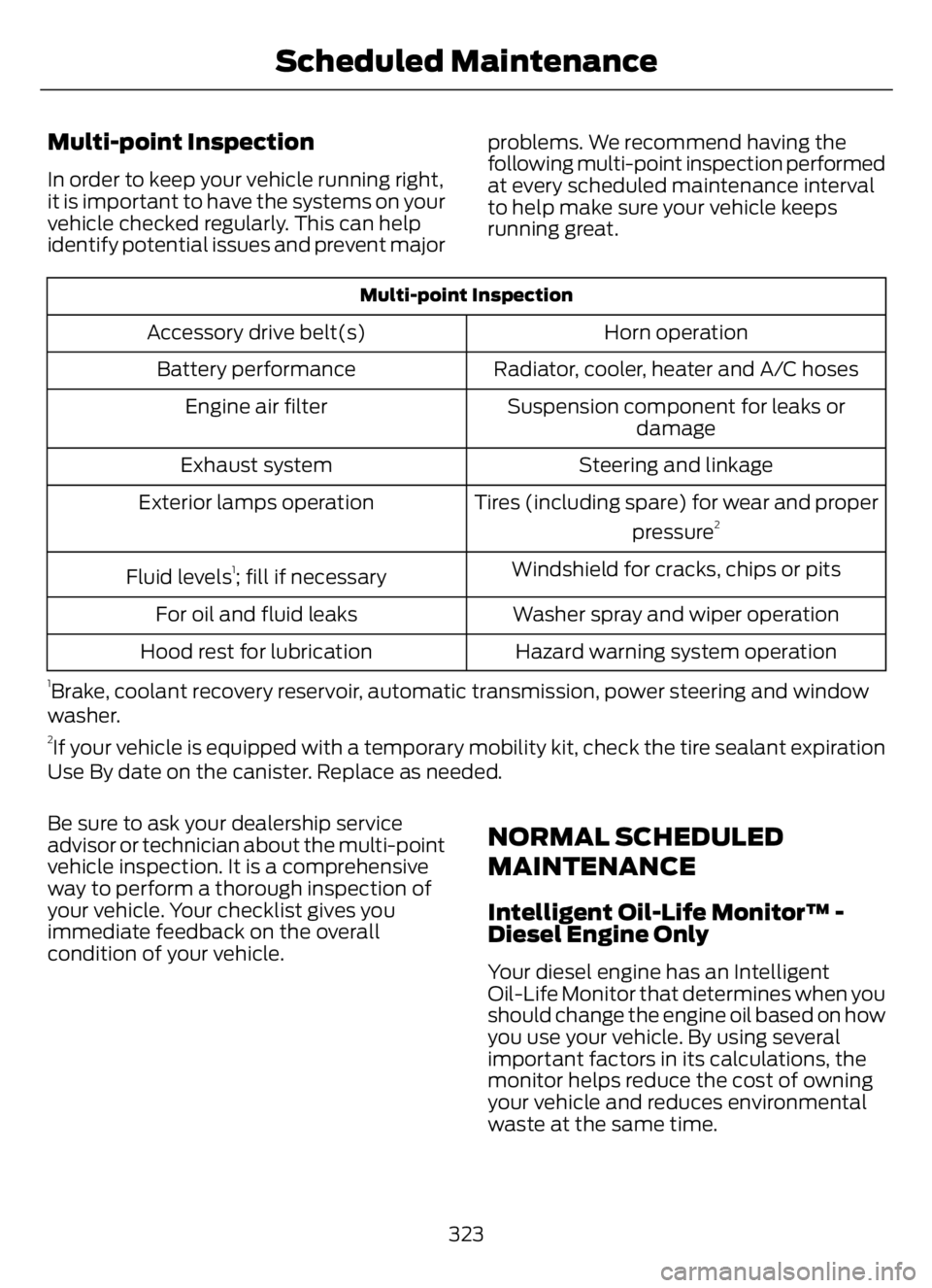
Multi-point Inspection
In order to keep your vehicle running right,
it is important to have the systems on your
vehicle checked regularly. This can help
identify potential issues and prevent majorproblems. We recommend having the
following multi-point inspection performed
at every scheduled maintenance interval
to help make sure your vehicle keeps
running great.
Multi-point Inspection
Horn operation Accessory drive belt(s)
Radiator, cooler, heater and A/C hoses Battery performance
Suspension component for leaks or
damage Engine air filter
Steering and linkage Exhaust system
Tires (including spare) for wear and proper
pressure
2Exterior lamps operation
Windshield for cracks, chips or pits
Fluid levels
1; fill if necessary
Washer spray and wiper operation For oil and fluid leaks
Hazard warning system operation Hood rest for lubrication
1Brake, coolant recovery reservoir, automatic transmission, power steering and window
washer.
2If your vehicle is equipped with a temporary mobility kit, check the tire sealant expiration
Use By date on the canister. Replace as needed.
Be sure to ask your dealership service
advisor or technician about the multi-point
vehicle inspection. It is a comprehensive
way to perform a thorough inspection of
your vehicle. Your checklist gives you
immediate feedback on the overall
condition of your vehicle.
NORMAL SCHEDULED
MAINTENANCE
Intelligent Oil-Life Monitor™ -
Diesel Engine Only
Your diesel engine has an Intelligent
Oil-Life Monitor that determines when you
should change the engine oil based on how
you use your vehicle. By using several
important factors in its calculations, the
monitor helps reduce the cost of owning
your vehicle and reduces environmental
waste at the same time.
323
Scheduled Maintenance