2021 AUDI Q2 airbag
[x] Cancel search: airbagPage 276 of 364

Safe driving
positioning, move the front passenger's seat as
far upwards as possibLe using the seat's height
adjustment. After installing the child seat on the
front passenger's seat, move the front passen
ger's backrest forward until it makes contact
with the child seat.
A WARNING
- Please refer to the important safety notes
•=>
A in Safety notes for using child seats on
page 268,
•=>
A in Child seat categories on
page 269 and the instructions provided by
the child seat manufacturer.
- Never install
a
rearward-facing child seat on
the front passenger's seat unless the front
passenger's airbag has been deactivated -
this can result in potentially fatal injuries to
the
child.
Pedal area
Pedals
The
pedals must always be free to move and
must never be obstructed by floor mats or any
objects in the footwell.
•
Make sure that none of the pedals is obstructed
and all of the pedals can be pressed all the way
down to the floor.
•
Make sure that all pedals are able to return
freely to their original positions.
Only use floor mats which Leave the pedal area
free and can be securely fastened in the footwell.
If one of the brake circuits should
fail,
increased
brake pedal travel will be required to bring the
vehicle safely to a stop.
A WARNING
Any obstructions that restrict pedal travel can
cause loss of vehicLe control and lead to
criti
cal traffic situations.
- Never place objects in the driver's footwell.
Such objects could move under the pedals
and interfere with their proper function. In
the event of sudden braking or
a
change of
direction,
you would not be able to use the
pedals. This could result in a loss of control
and possibly cause an accident.
Floor mats on the driver's side
Use
only floor mats which can be securely fas
tened in the footwell and do not obstruct the
pedals.
•
Make sure that floor mats are securely fastened
and cannot interfere with the pedals
o /\.
Use only floor mats that leave the pedal area un
obstructed and are firmly secured to prevent
them from slipping. You can obtain suitable floor
mats from your dealer or a specialist retailer.
A WARNING
Any obstructions that restrict pedal travel can
cause Loss of vehicle control and increase the
risk of serious personal injury.
- Always make sure that floor mats are prop
erly secured.
- Never lay or
instaLl
additional floor mats or
other floor coverings over the existing floor
mats;
this would restrict the pedal area and
possibly obstruct the pedals, which could
cause an accident.
Stowing Luggage
safely
Luggage compartment
Fig.
214 Heavy items should be placed as far forwards as
possible (example).
All Luggage and other objects must be safely se
cured in the Luggage compartment. To maintain
safe handling on the
road,
please observe the
fol
lowing points: •
272
Page 279 of 364

Seat belts
CO
< o rN
iv
rN
t-H
o < 00
Seat belts
Why is it so important to
use seat belts?
Seat belts provide effective protection
The common belief that passengers can brace
their weight with their hands in a minor collision
is false.
Fig.
215 Driver with correctly positioned seat belt - good
protection if the brakes are applied suddenly
It is an established fact that seat belts provide
good protection in accidents. Therefore wearing
a seat belt is required by law in most countries.
When worn correctly, seat belts hold the occu
pants in the best position for maximum protec
tion
^>Fig.
215. The seat belts are capable of ab
sorbing much of the kinetic energy which is
gen
erated in a collision. They also help to prevent
uncontrolled movements which could Lead to se
vere injuries
^>page
275, Important safety
notes when using seat belts.
If they wear the seat belts correctly, the passen
gers benefit greatly from the ability of the belts
to reduce the kinetic energy gradually. The front
crumple zones and other passive safety features
(such as the airbag system) are also designed to
absorb the kinetic energy generated in a
colli
sion.
Taken together, all these features reduce
the forces acting on the occupants and conse
quently the risk of injury.
Although these examples are based on a frontal
collision,
the physical principles involved are the
same in other types of accidents. This is why it is
so important to put on the seat belts before ev
ery trip - even when "just driving around the cor
ner". Ensure that your passengers wear their seat
belts as well
^A-
Seat belts worn correctly have been shown to be
an effective means of reducing the potential for
injury and improving the chances of survival in a
serious accident
^>page
276, Forces acting in a
collision.
For information on how children can travel safely
in the car refer to
^>page
267, Child seats.
A WARNING
- Seat belts must be put on before every trip -
even when driving in town. This also applies
to the rear passengers - risk of injury!
- During pregnancy, women should always
ensure they wear a seat belt. The best way
to protect the unborn child is to protect the
mother
^>page
278, Wearing and adjust
ing the seat belts during pregnancy.
Important safety notes when using seat
belts
There are a number of safety points concerning
the seat belts which you should remember. This
will help to reduce the risk of injury in an
acci
dent.
A WARNING
- The seat belts can only provide maximum
protection if the seats are adjusted properly
^>page
58, Front seats.
- To ensure proper protection, it is important
to wear the seat belts in the correct position
^>page
277, How to wear seat belts prop
erly.
Ensure that the seat belts are worn ex
actly as recommended in this chapter. Belts
which are
not
worn properly can increase
the risk of injury in accidents considerably.
- Do not allow the seat belt to become twis
ted or jammed, or to rub on any sharp
edges.
- Never allow two passengers (even children)
to share the same seat belt. It is especially
dangerous to place a seat belt over a child
sitting on your lap.
275
Page 285 of 364

Airbag system
Airbag system
Description of airbag
system
General notes on airbag system
The airbag is an integral part of the car's passive
safety system.
In conjunction with the three-point seat belts,
the airbag system gives the front occupants
addi
tional protection for the head and chest in the
event of a severe frontal collision.
In a severe side collision the side airbags and the
head-protection airbags reduce the risk of injury
to the occupants
•=>
A-
In addition to their normal function of protecting
the occupants in a collision, the seat belts also
hold them in a position where the airbags can in
flate properly and provide maximum protection.
The airbag system will only work with the
igni
tion on. The airbag system is monitored electron
ically; the airbag warning lamp indicates whether
the system is functioning properly.
The main parts of the airbag system are:
-The electronic monitoring system (control unit
and sensors)
- The two front airbags
- The front side airbags
-The head-protection airbags
- The indicator Lamp
Q
in the instrument cluster
There is a fault in the airbag system if the
warning lamp
- does not come on when the ignition is switched
on.
- does not go out about 4 seconds after the
igni
tion is switched on.
- goes out and then comes on again after the ig
nition is switched on.
- comes on or flickers while the car is moving.
CO
< o rN
iv
rN
t-H
o <
A WARNING
- The airbags are not a substitute for the seat
belts;
they are an integral part of the car's
overall passive safety system. The airbags
can only offer effective protection if the oc
cupants are wearing their seat belts. For
this reason it is very important to wear the
seat belts at all times
^>page
275, Why is it
so important to use seat belts?.
The seat belts and airbags can only provide
maximum protection if the occupants are
seated correctly
^>page
58, Front seats.
•
If you do not wear a seat belt, if you lean
forward,
or are not seated correctly while
the vehicle is in motion, you are at greater
risk of injury should the airbag system be
triggered in an accident.
Components of the airbag system are loca
ted in various parts of the vehicLe. If repairs
to other vehicle components make it neces
sary to perform work on the airbag system
or to remove or install parts of the airbag
system,
this may cause damage to the air-
bag system. As a result, the airbags may not
inflate correctly or may not be triggered at
all in an accident situation. For this reason,
you should always have the work carried out
by a qualified workshop.
If a fault should occur in the airbag system,
have the system checked immediately by a
qualified workshop. Otherwise the system
may fail to trigger in an accident.
Do not attempt to modify components of
the airbag system in
anyway.
Never make any alterations to the front
bumper
or
the body.
Do not remove the front seats.
The airbag system can only be activated
once;
if the airbag has been triggered, the
system must be replaced. Should the airbag
system or airbag modules have to be re
placed,
the qualified workshop carrying out
the replacement will document all details.
•
If any repair work is required
or
the airbag
and restraint systems have to be replaced,
have the work carried out by your authorised
Audi dealer or a qualified workshop which
adheres to the Audi factory standards. This
will minimise the risk of injury.
If you sell the vehicle, remember to pass on
the complete Service Wallet to the new
owner. If any of the airbags have been
281
Page 286 of 364

Airbag system
deactivated, it is important that the new
owner is also given the relevant documents.
- The relevant safety requirements must be
observed when the vehicLe or components
of the airbag or belt tensioner systems are
scrapped.
When are the airbags triggered?
One or more airbag systems are triggered in se
vere collisions, depending on the circumstances.
Factors determining the triggering response
It is not possible to define the exact triggering
response of the airbag system in all possible sit
uations, since the circumstances in different
types of accident will vary considerably. Impor
tant factors include, for example, the nature
(hard or soft) of the object which the car hits, the
angle of impact, vehicle speed and so on.
Whether the airbags are triggered depends
pri
marily on the vehicle deceleration rate resulting
from the collision. By processing the signals from
the sensors Located in the vehicLe, the electronic
control unit is immediately able to evaluate the
severity of the collision and activate the restraint
systems accordingly. If the deceleration rate is
below the predefined reference value in the
con
trol unit the airbags will not be triggered, even
though the accident may cause extensive damage
to the car. In these situations, the occupants are
protected by wearing the seat belts.
©
Note
The airbag may release a fine dust when it in
flates.
This is quite normal and does not
mean there is a fire in the vehicle.
Front airbags
Important notes on front passenger's
airbag
AIRBAG
B
1<&
W
\fiS
cm
Fig.
226 Version 1, passenger's sun visor: Airbag sticker
AIRBAG
m
S
Fig.
227 Version 2, passenger's sun visor: Airbag sticker
A
sticker1)
with important information about the
front passenger's airbag is provided on the front
passenger's sun visor. Please refer to the safety
notes in the following chapters:
- Child seats and front passenger's airbag
^page
267, Safety notes for using child seats
- Safe distance from front passenger's airbag
tapage
284, Important safety notes on the
front airbag system
- Objects between front passenger and front pas
senger's airbag
•=>page
284, Important safety
notes on the front airbag system
x)
Not available in all export vehicles.
282
Page 287 of 364
Airbag system
Description of front airbags How the
front
airbags work
CO
â
rN
IV
rN
•-i
§
•H
00
The
airbag system is not a substitute for the seat
belts.
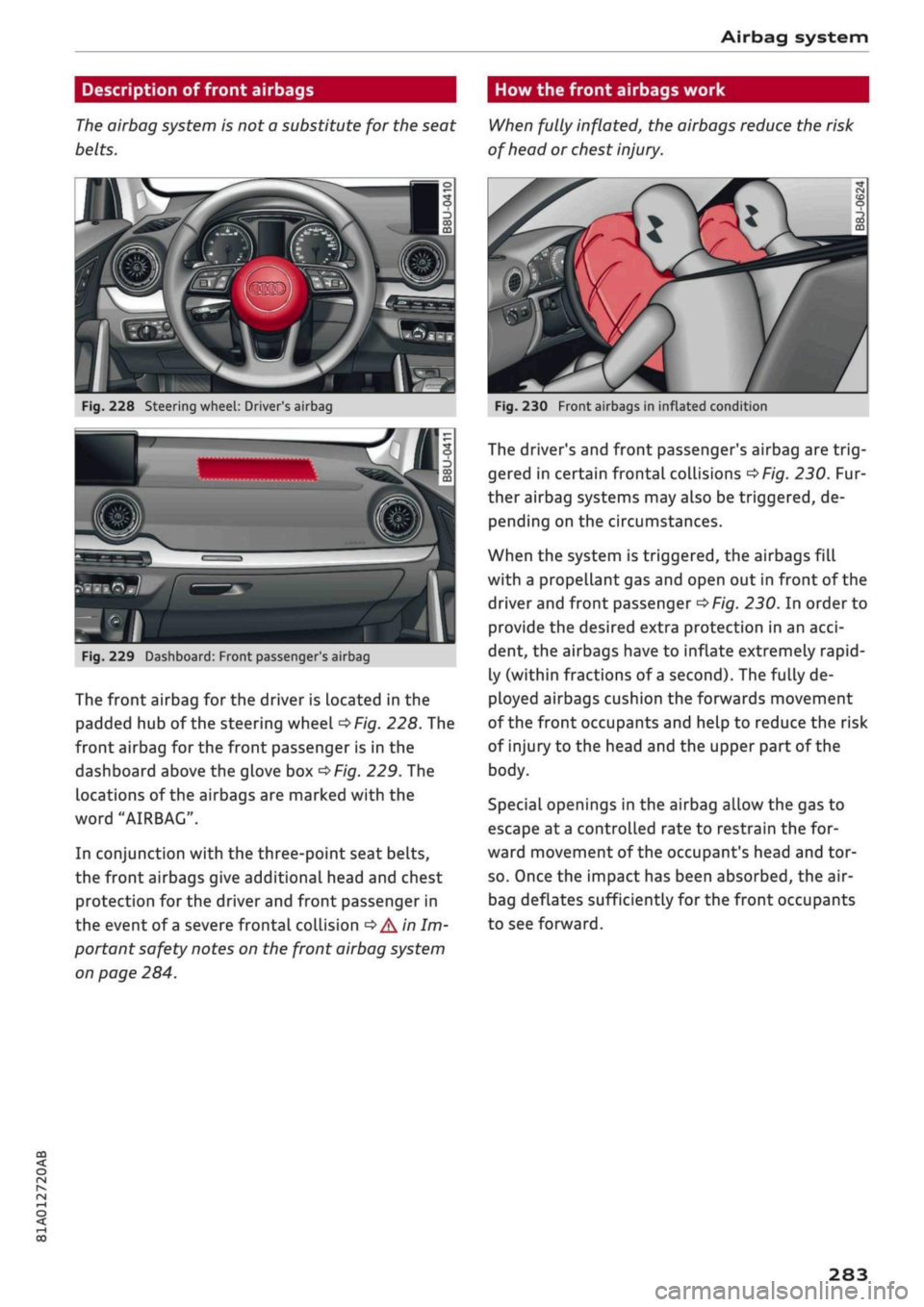
When fully inflated, the airbags reduce the risk
of head or chest
injury.
Fig.
228 Steering wheel: Driver's airbag
SiMlP
Fig.
229 Dashboard: Front passenger
s
airbag
The front airbag for the driver is Located in the
padded hub of the steering wheel
^Fig.
228. The
front airbag for the front passenger is in the
dashboard above the glove box
^Fig.
229. The
locations of the airbags are marked with the
word "AIRBAG".
In conjunction with the three-point seat belts,
the front airbags give additional head and chest
protection for the driver and front passenger in
the event of
a
severe frontal collision
•=>
A'n
Im
portant safety notes on the front airbag system
on page 284.
Fig.
230 Front airbags in inflated condition
The driver's and front passenger's airbag are
trig
gered in certain frontal collisions
^>Fig.
230. Fur
ther airbag systems may also be triggered, de
pending on the circumstances.
When the system is triggered, the airbags fill
with a propellant gas and open out in front of the
driver and front passenger
^>Fig.
230. In order to
provide the desired extra protection in an
acci
dent, the airbags have to inflate extremely rapid
ly (within fractions of
a
second). The fully de
ployed airbags cushion the forwards movement
of the front occupants and help to reduce the risk
of injury to the head and the upper part of the
body.
Special openings in the airbag allow the gas to
escape at
a
controlled rate to restrain the for
ward movement of the occupant's head and tor
so.
Once the impact has been absorbed, the air-
bag deflates sufficiently for the front occupants
to see forward.
283
Page 288 of 364

Airbag system
Important safety notes on the front airbag
system
There are a number of safety points concerning
the airbag system which you should remember.
This will help to reduce the risk of injury in an ac
cident.
25cm
Fig.
231 Minimum distance from steering wheel
A WARNING
- It is important for the driver and front pas
senger to maintain a distance of at least
25 cm from the steering wheel or dash
board
oFig.
231. The airbag system will not
be able to give the required protection if you
sit too close to the steering wheel or dash
board.
There is also a risk of injury if the air-
bags are inflated. The front seats and head
restraints must always be positioned cor
rectly for the height of the occupant.
- If you do not wear a seat belt, if you lean
forward or to the side, or are not seated cor
rectly while the vehicle is in motion, you are
at greater risk of injury. Should the airbag
system be triggered in an accident there is
an even greater risk of injury.
- Never let a child travel on the front seat
without an appropriate restraint system. If
the airbag is triggered in an accident, the
child could sustain serious or fatal injuries
^>page
267, Child seats.
- Child seats in which the child faces the rear
of the car are located directly in the path of
the front passenger's airbag if it inflates. In
this case, the child could sustain serious or
fatal injuries if the airbag were to be de
ployed.
- Applies to vehicles on which the front pas
senger's airbag cannot be deactivated: Do
NOT use a rearward-facing child seat on
the front passenger's seat.
- Applies to vehicles with key-operated
switch for deactivating the front passeng
er's airbag: Do NOT use a rearward-facing
child seat on the front passenger's seat
while the front passenger's airbag is ac
tive.
If you have no alternative but to use a
rearward-facing child seat on the front
passenger's seat, the front passenger's
airbag must be deactivated beforehand via
the key-operated switch*
^>page
288.
Make sure that the front passenger's air-
bag is reactivated by means of the key-op
erated switch* as soon as the child seat is
no longer needed on the front passenger's
seat.
- Occupants sitting in the front of the car
must never carry any objects or pets in the
space between them and the airbags, or al
low children or other passengers to travel in
this position.
- Do not cover or stick anything on the steer
ing wheel hub or the soft plastic surface of
the airbag unit on the passenger's side of
the dashboard, and do not obstruct or modi
fy them in any way. These parts should only
be cleaned with a dry cloth (or with a cloth
moistened with plain water). It is also im
portant not to attach any objects such as
cup holders or telephone mountings to the
surfaces covering the airbag units.
- Any work on the airbag system or removal
and installation of the airbag components
for other repairs (such as repairs to the
steering wheel or removal of seats) must be
performed by a qualified workshop.
284
Page 289 of 364

Airbag system
CO
< o rN
iv
rN
•-i
•H
00
Side airbags
Description of side airbags
The
airbag system is not a substitute for the seat
belts.
Fig.
232 Side airbags: Location in driver's seat (example)
The side airbags are located in the backrest
pad
ding of the front seats.
In conjunction with the three-point seat belts,
the side airbags give the occupants additional
protection for the whole upper part of the body
(i.e.
the chest, stomach and pelvis) in the event
of
a
severe side collision
•=> A
in Important safety
notes on the side airbag system on page 285.
In a side collision the side airbags reduce the risk
of injury to the areas of the body facing the im
pact.
How the side airbags work
When fully inflated, the side airbags reduce the
risk of injuries to the upper part of the
body.
Fig.
233 Side airbags in inflated condition
In certain types of side collision, the side airbag
(front) is triggered on the impact side of the
vehi
cle
^Fig.
233. Further airbag systems may also
be triggered, depending on the circumstances.
When the system is triggered, the airbag is filled
with propellant gas.
In order to provide the desired extra protection in
an accident, the airbags have to inflate extremely
rapidly (within fractions of
a
second).
The fully deployed airbags cushion the impact for
the occupants and help to reduce the risk of in
jury to the upper part of the body on the side fac
ing the door.
Important safety notes on the side airbag
system
There
are a number of safety points concerning
the airbag system which you should remember.
This will help to reduce the risk of injury in an ac
cident.
WARNING
-If
you
do
not
wear
a
seat belt, if
you
Lean
forward,
or are not seated correctly while
the vehicle is in motion, you are at greater
risk of injury should the side airbags be
trig
gered in an accident. This applies particular
ly to children if they are not properly protec
ted by
a
child restraint system.
- If children are not seated correctly, they are
at greater risk of injury should the airbag
system be triggered in an accident. This is
particularly the case if the child is travelling
on the front passenger's seat and the airbag
system is triggered in an accident. This
could result in serious or potentially fatal in
jury
^>page
267, Child seats.
- It is important not to attach any accessories
(such as cup holders) to the doors. This
would impair the protection offered by the
front side airbags.
- The sensors for the airbags are located in
the front doors. You must therefore not
make any modifications to the doors or door
trim (e.g. retrofitting loudspeakers),
as
this
could impair the function of the side air-
bags.
Any damage to the front doors could
285
Page 290 of 364

Airbag system
lead to faults in the system. Repairs or any
other work on the front doors must there
fore always be carried out by
a
qualified
workshop.
- The built-in coat hooks* should only be used
for lightweight clothing. Do not leave any
heavy or sharp-edged objects in the pockets.
- Do not apply excessive force to the sides of
the backrests (such as hard knocks or kicks),
as this could damage parts of the system.
The side airbags could then fail to operate
when required.
- If
you
intend to fit protective covers over
the seats, these must be of the specific type
approved for use on Audi seats with side air-
bags.
Conventional seat covers would ob
struct the side airbag when it inflates out of
the backrest, and seriously reduce the air-
bag's effectiveness.
- Any damage to the original seat upholstery
or around the seams of the side airbag units
must be repaired immediately by a qualified
workshop.
- Any work involving the side airbag system or
removal and installation of the airbag com
ponents for other repairs (such as repairs to
the seats) must always be performed by a
qualified workshop. Otherwise the airbag
system may fail to work properly.
© Note
All the other airbags in the car will remain
functional if the front passenger's airbag has
been deactivated.
Head-protection airbags
Description of head-protection airbags
Fig.
234 Location of head-protection airbags above the
doors (example)
The head-protection airbags are located above
the doors on the left and right sides of the
vehi
cle.
The locations of the airbags are marked with
the word "AIRBAG".
In conjunction with the three-point seat belts
and side airbags, the head-protection airbags
give the occupants additional protection against
head and neck injuries in a severe side collision
•=>
A in Important safety notes on the head-pro
tection airbags on page 287.
Together with other design features (including
cross-braces in the seats and the overall strength
of the body structure), the head-protection and
side airbag system offers an effective further im
provement to occupant protection in side im
pacts.
How the head-protection airbags work
When fully inflated, the airbags reduce the risk
of head or chest injury in a side collision.
jfW
Fig.
235 Head-protection airbags in inflated condition (ex
ample) •
286