2019 VOLKSWAGEN T-ROC 0A and 11
[x] Cancel search: 0A and 11Page 59 of 502
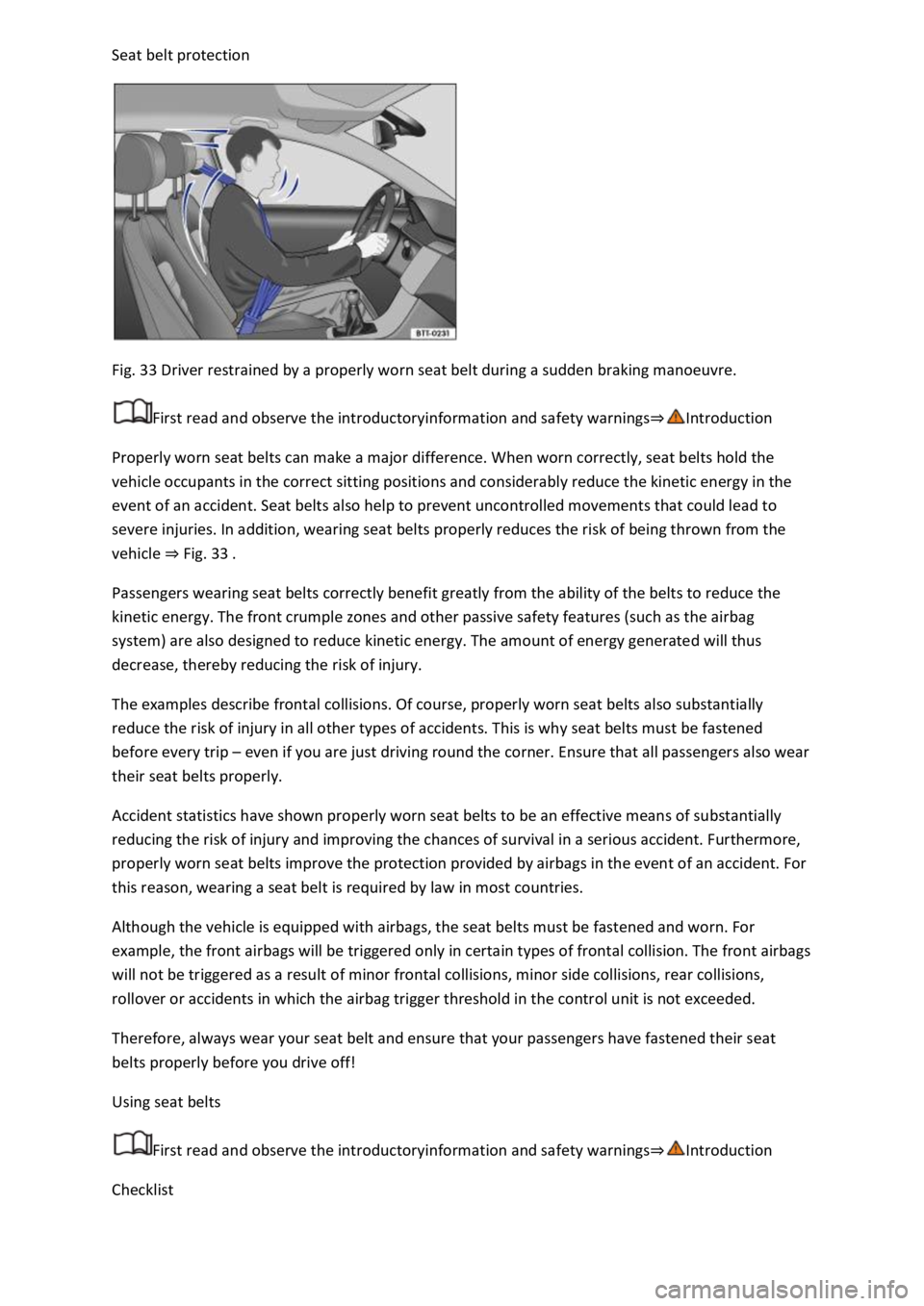
Fig. 33 Driver restrained by a properly worn seat belt during a sudden braking manoeuvre.
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings
Properly worn seat belts can make a major difference. When worn correctly, seat belts hold the
vehicle occupants in the correct sitting positions and considerably reduce the kinetic energy in the
event of an accident. Seat belts also help to prevent uncontrolled movements that could lead to
severe injuries. In addition, wearing seat belts properly reduces the risk of being thrown from the
vehicle Fig. 33
Passengers wearing seat belts correctly benefit greatly from the ability of the belts to reduce the
kinetic energy. The front crumple zones and other passive safety features (such as the airbag
system) are also designed to reduce kinetic energy. The amount of energy generated will thus
decrease, thereby reducing the risk of injury.
The examples describe frontal collisions. Of course, properly worn seat belts also substantially
reduce the risk of injury in all other types of accidents. This is why seat belts must be fastened
before every trip even if you are just driving round the corner. Ensure that all passengers also wear
their seat belts properly.
Accident statistics have shown properly worn seat belts to be an effective means of substantially
reducing the risk of injury and improving the chances of survival in a serious accident. Furthermore,
properly worn seat belts improve the protection provided by airbags in the event of an accident. For
this reason, wearing a seat belt is required by law in most countries.
Although the vehicle is equipped with airbags, the seat belts must be fastened and worn. For
example, the front airbags will be triggered only in certain types of frontal collision. The front airbags
will not be triggered as a result of minor frontal collisions, minor side collisions, rear collisions,
rollover or accidents in which the airbag trigger threshold in the control unit is not exceeded.
Therefore, always wear your seat belt and ensure that your passengers have fastened their seat
belts properly before you drive off!
Using seat belts
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings
Checklist
Page 60 of 502

Regularly check the condition of all seat belts.
Keep the seat belts clean.
Avoid allowing any foreign bodies or fluids to get on to the seat belt or latch plate or into the slot for
the seat belt buckle.
Do not trap or damage the seat belt and latch plate, for example when closing the door.
Never remove, modify or repair the seat belt or belt anchorage elements.
Always fasten the seat belt correctly before any journey and wear it properly while the vehicle is in
motion.
Twisted seat belt
If it is difficult to pull the seat belt out of the belt guide, the seat belt may have become twisted in
the side trim as a result of being retracted too quickly when unfastened:
Take hold of the latch plate, then slowly and carefully pull out the seat belt fully.
Untwist the seat belt and guide it back slowly by hand.
Fasten the seat belt even if you are unable to undo the twist. However, the twist should not be in
part of the seat belt which comes into direct contact with the body. The twist should be corrected
immediately by a qualified workshop.
WARNING
Using seat belts incorrectly increases the risk of severe or fatal injuries.
Regularly check to ensure that the seat belt and its related parts are in perfect condition.
Always keep the seat belt clean.
Do not allow the belt webbing to become jammed, damaged or to rub on any sharp edges.
Always keep the latch plate and slot in the buckle free from foreign bodies and liquids.
Fastening and unfastening seat belts
Page 61 of 502
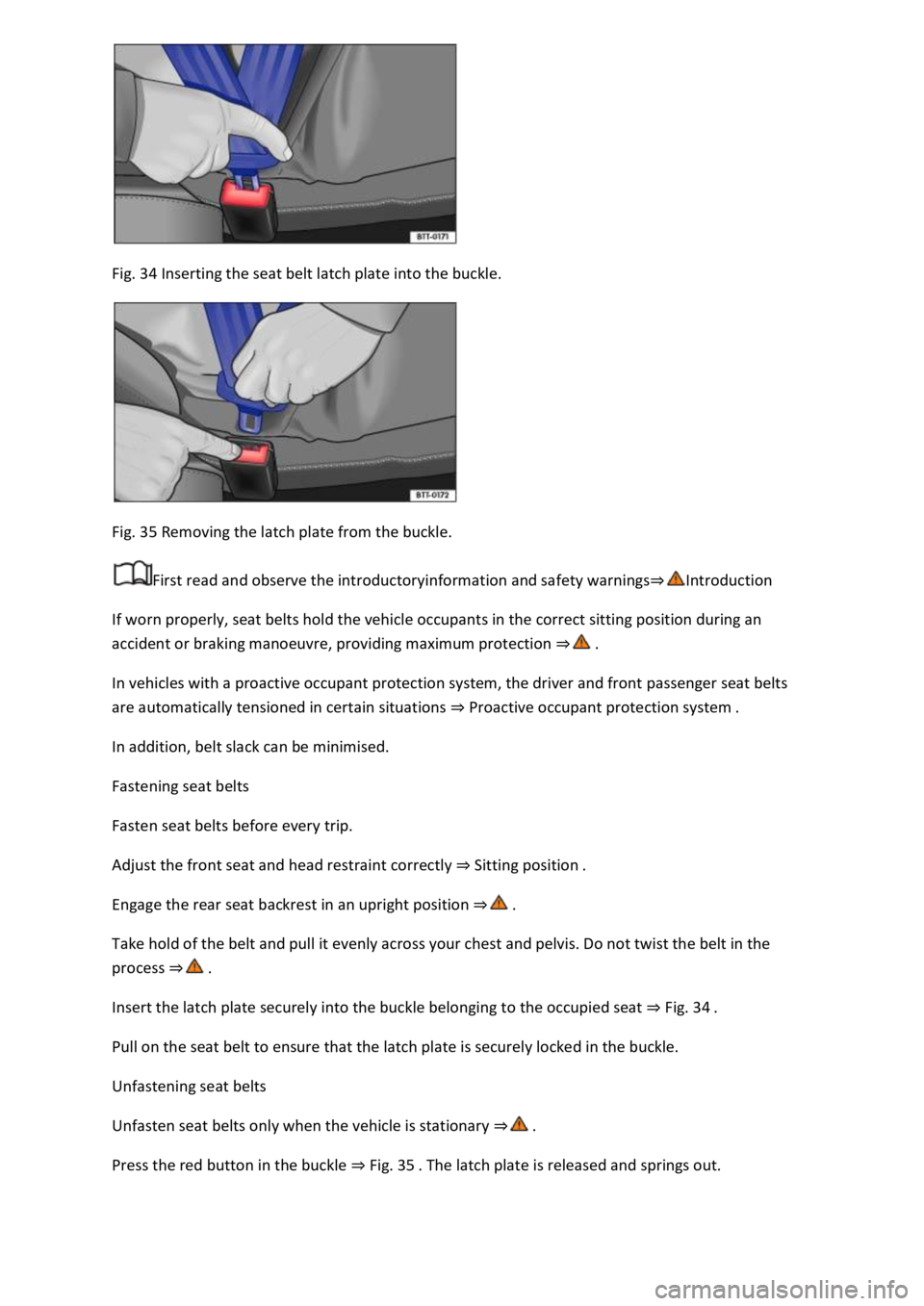
Fig. 34 Inserting the seat belt latch plate into the buckle.
Fig. 35 Removing the latch plate from the buckle.
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings
If worn properly, seat belts hold the vehicle occupants in the correct sitting position during an
accident or braking manoeuvre, providing maximum protection
In vehicles with a proactive occupant protection system, the driver and front passenger seat belts
are automatically tensioned in certain situations Proactive occupant protection system
In addition, belt slack can be minimised.
Fastening seat belts
Fasten seat belts before every trip.
Adjust the front seat and head restraint correctly Sitting position
Engage the rear seat backrest in an upright position
Take hold of the belt and pull it evenly across your chest and pelvis. Do not twist the belt in the
process
Insert the latch plate securely into the buckle belonging to the occupied seat Fig. 34
Pull on the seat belt to ensure that the latch plate is securely locked in the buckle.
Unfastening seat belts
Unfasten seat belts only when the vehicle is stationary
Press the red button in the buckle Fig. 35 latch plate is released and springs out.
Page 62 of 502
damaging the trim.
WARNING
Incorrect seat belt routing can cause severe or fatal injuries in the event of an accident.
The seat belts offer best protection only when the backrests are in an upright position and the seat
belts have been fastened properly according to the occupant's size.
Unfastening seat belts while the vehicle is in motion can lead to severe or fatal injuries in the event
of an accident or sudden braking manoeuvre.
Seat belt routing
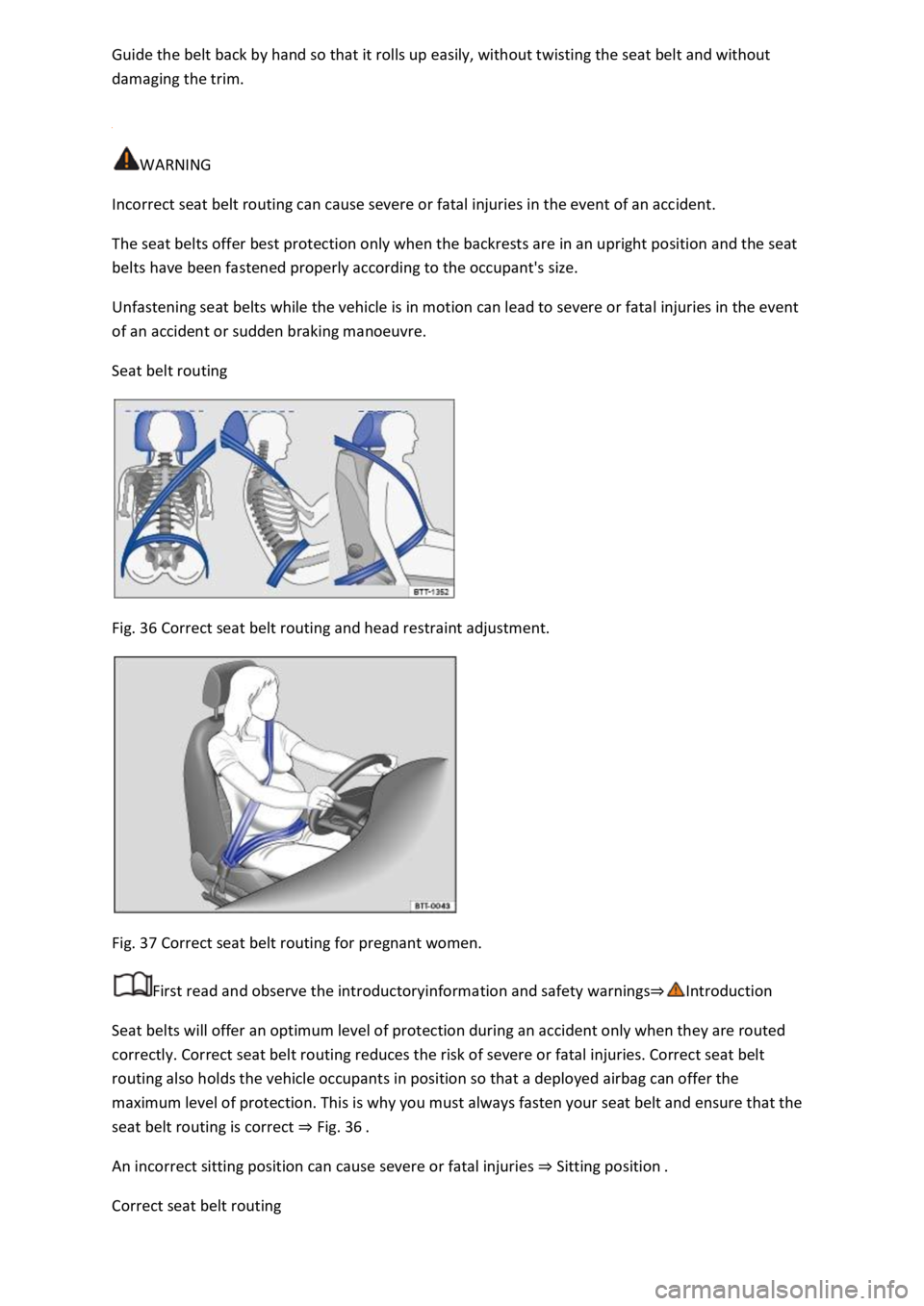
Fig. 36 Correct seat belt routing and head restraint adjustment.
Fig. 37 Correct seat belt routing for pregnant women.
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings
Seat belts will offer an optimum level of protection during an accident only when they are routed
correctly. Correct seat belt routing reduces the risk of severe or fatal injuries. Correct seat belt
routing also holds the vehicle occupants in position so that a deployed airbag can offer the
maximum level of protection. This is why you must always fasten your seat belt and ensure that the
seat belt routing is correct Fig. 36
An incorrect sitting position can cause severe or fatal injuries
Correct seat belt routing
Page 63 of 502

neck, over or under the arm or behind the back.
The lap part of the seat belt must always lie across the pelvis, never across the stomach.
The seat belt must always lie flat and snugly on the body. Tighten the belt slightly if necessary.
For pregnant women, the seat belt must be positioned evenly over the chest and as low as possible
over the pelvis. It must also lie flat so that no pressure is exerted on the abdomen this applies in
every stage of pregnancy Fig. 37
Adjusting seat belt routing to body size
The following equipment can be used to adjust the seat belt routing:
Seat belt height adjuster for the front seats Seat belt height adjuster
Height-adjustable front seats Sitting position
WARNING
Incorrect seat belt routing can cause severe injuries in the event of an accident or a sudden braking
or driving manoeuvre.
The seat belts offer best protection only when the backrests are in an upright position and the seat
belts have been fastened properly.
The seat belt itself or a loose seat belt can cause serious injuries if the seat belt shifts from harder
body parts in the direction of softer body parts (e.g. stomach).
The shoulder part of the seat belt must lie on the centre of the shoulder and never under the arm or
across the neck.
The seat belt must lie flat and snugly on the upper body.
The lap part of the seat belt must lie across the pelvis and never across the stomach. The seat belt
must lie flat and snugly on the pelvis. Tighten the belt slightly if necessary.
For pregnant women, the lap part of the seat belt must be as low as possible over the pelvis and lie
flat around the round stomach.
Do not twist the belt webbing while the seat belt is being worn.
Never hold the seat belt away from the body by hand.
The belt webbing should not lie over hard or fragile objects, such as glasses, pens or keys.
Never use seat belt clips, retaining rings or similar items to alter the seat belt routing.
If a person's physical build prevents them from routing the seat belt properly, contact a qualified
workshop to find out about any special modifications so that the seat belts and airbags can provide
Page 64 of 502
purpose.
Seat belt height adjuster
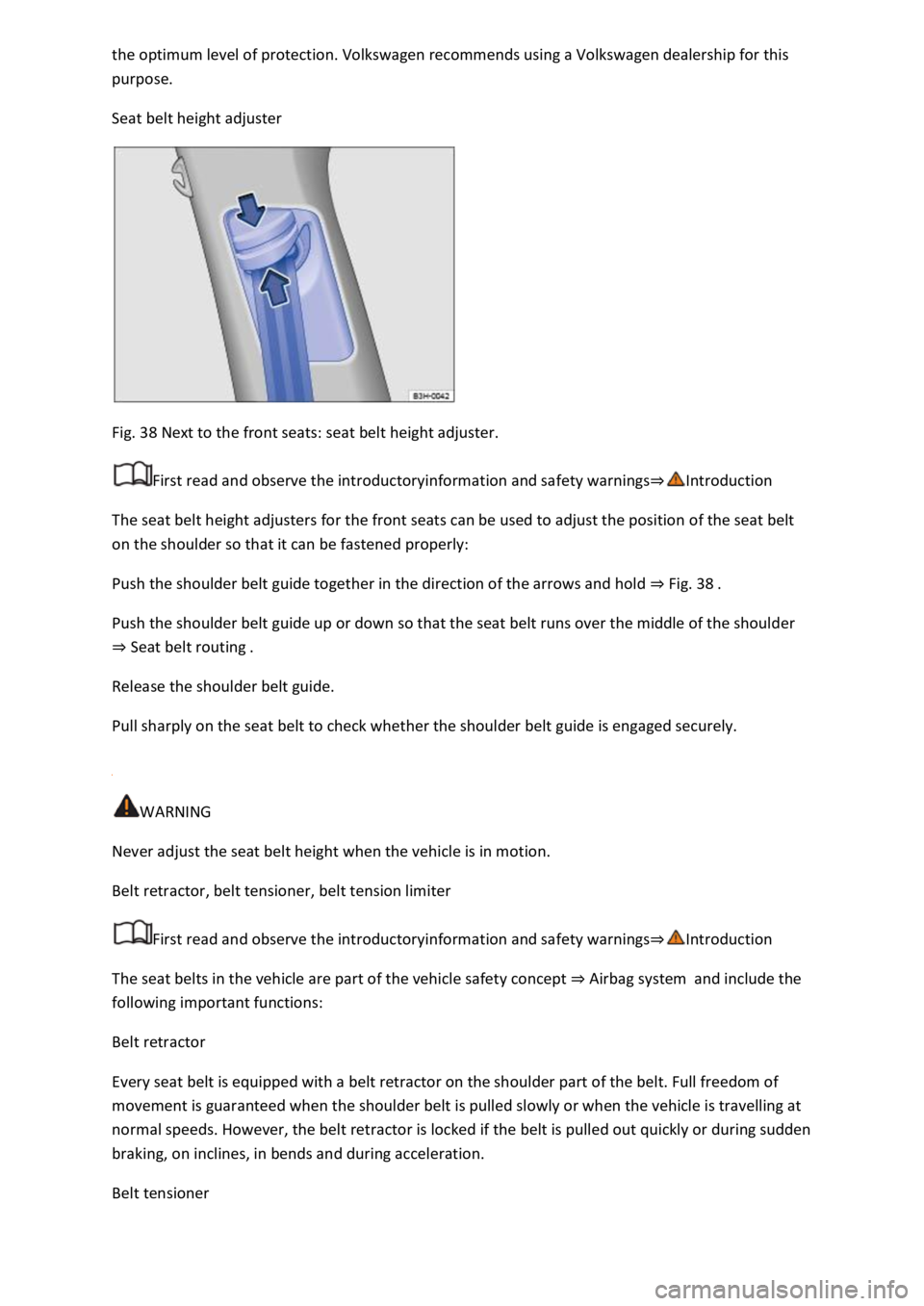
Fig. 38 Next to the front seats: seat belt height adjuster.
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings
The seat belt height adjusters for the front seats can be used to adjust the position of the seat belt
on the shoulder so that it can be fastened properly:
Push the shoulder belt guide together in the direction of the arrows and hold Fig. 3
Push the shoulder belt guide up or down so that the seat belt runs over the middle of the shoulder
Seat belt routing
Release the shoulder belt guide.
Pull sharply on the seat belt to check whether the shoulder belt guide is engaged securely.
WARNING
Never adjust the seat belt height when the vehicle is in motion.
Belt retractor, belt tensioner, belt tension limiter
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings
The seat belts in the vehicle are part of the vehicle safety concept Airbag systemand include the
following important functions:
Belt retractor
Every seat belt is equipped with a belt retractor on the shoulder part of the belt. Full freedom of
movement is guaranteed when the shoulder belt is pulled slowly or when the vehicle is travelling at
normal speeds. However, the belt retractor is locked if the belt is pulled out quickly or during sudden
braking, on inclines, in bends and during acceleration.
Belt tensioner
Page 65 of 502

They tighten the seat belts against the direction in which they are pulled. Any slack in the seat belt is
retracted, which can reduce the forward movement of the vehicle occupants and their movement in
the direction of the impact. The belt tensioner works together with the airbag system. If the vehicle
rolls over, the belt tensioners will not be activated if the side airbags are not triggered.
Fine dust may be produced when belt tensioners are triggered. This is quite normal and does not
mean there is a fire in the vehicle.
Belt tension limiter
The belt tension limiter reduces the pressure exerted by the seat belt on the body in an accident.
All safety regulations must be observed when the vehicle or components of the system are
scrapped. Qualified workshops are familiar with these regulations Service and disposal of belt
tensioners
Service and disposal of belt tensioners
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings
Seat belts may become damaged during any work on the belt tensioners or while removing or
refitting any vehicle parts in conjunction with any other repair work. This damage will not always be
noticeable. The consequence may be that the belt tensioners could function incorrectly, or not
function at all, in the event of an accident.
Regulations must be observed to ensure that the effectiveness of the belt tensioner is not reduced
and that removed parts do not cause any injuries or environmental pollution. Qualified workshops
are familiar with these regulations.
WARNING
The risk of severe or fatal injuries may be increased if the seat belts, belt retractors and belt
tensioners are not used correctly or if they are repaired by a non-professional. As a result, the belt
tensioners may not be triggered when they should be, or they may be triggered unexpectedly.
Any repairs, adjustments or removal and refitting of parts in the belt tensioners or seat belts should
always be carried out by a qualified workshop and never by yourself Accessories, modifications,
Belt tensioners and belt retractors cannot be repaired. They must be replaced.
The airbag modules and belt tensioners may contain perchlorate. Observe the applicable legislation
regarding disposal.
Proactive occupant protection system
Page 66 of 502

The proactive occupant protection system is an assistance system that initiates measures to protect
vehicle occupants in dangerous situations. However, the system cannot prevent a collision.
The full range of functions of the proactive occupant protection system will be available only if the
function has been activated in the Infotainment system, no special driving profile has been selected
and there are no malfunctions Driving profile selecFunction
limitations
Basic functions
Depending on country-specific legal requirements and also on the vehicle equipment, the following
functions may be initiated, either individually or jointly, in critical situations (e.g. emergency braking
or in the case of oversteering or understeering) as of a speed of approximately 30 km/h (19 mph):
Reversible tensioning of the fastened front seat belts.
Depending on the critical driving situation, the seat belts can be tensioned separately or together.
Additional information for vehicles with an area monitoring system (Front Assist)
In vehicles fitted with the area monitoring system (Front Assist) Area monitoring system (Front
Assist)
limits. The system can trigger the proactive occupant protection system if it detects a probable
collision or initiates strong braking.
Function limitations
The proactive occupant protection system will not be available, or will be available only to a limited
extent, in the following situations:
If there is a fault in the ESC, belt tensioner Seat beltsor airbag control unit Airbag system
WARNING
The intelligent technology of the proactive occupant protection system cannot overcome the laws of
physics, and functions only within the limits of the system. Never let the extra convenience afforded
by the proactive occupant protection system tempt you into taking any risks when driving. The
system cannot prevent a collision. The system is not a substitute for the full concentration of the
driver.
Adapt your speed and distance from the vehicles ahead to suit visibility, weather, road and traffic
conditions.
The system cannot detect objects in all situations.
The proactive occupant protection system does not react to people, animals, objects crossing in
front of the vehicle, or objects which are hard to detect.