2018 Alfa Romeo Giulietta esp
[x] Cancel search: espPage 35 of 216

Turning off
Mover the lever 1 fig. 33 to the "Natural"
position;
TURNING“All Weather” MODE ON/OFF
Activation
Move lever 1 fig. 33 downwards (to the
letter “a”) and hold in this position for
0.5 seconds until the corresponding LED
lights up or the word “All Weather”
appears on the display.
Deactivation
Mover the lever 1 fig. 33 to the "Natural"
position;
IMPORTANT
9)"VELOCE" VERSION: Considering the high
levels of vehicle performance, it is
recommended to not use the "Dynamic"
mode when driving the first kilometres with
the vehicle in order to provide the
mechanical components with the necessary
running-in period.
VERSION WITH LPGSYSTEM
19) 21)10) 11) 12) 13) 14) 16)
INTRODUCTION
The LPG version features two fuel supply
systems: one for petrol and one for LPG.
PASSIVE SAFETY/ACTIVE SAFETY
Although the LPG system has numerous
safety features, it is advisable to proceed
as follows every time the vehicle is not in
use for a long period or moved in an
emergency as a result of a breakdown or
accident:
unscrew the fixing devices 1 fig. 34,
then remove the cover 2;
Close the LPG cock rotating the ring 1
fig. 35clockwise.
refit the cover and retighten the
fastening devices.
LPG TANK
The car has a (pressurised) tank A for
storing LPG in a liquid state. It is toroidal
and is located in the spare wheel
compartment with suitable protection.
LPG tank certification
The LPG tank is certified in accordance
with the regulations in force.
In Italy, the tank has a life of 10 years
starting from the car registration date. If
the vehicle has been registered in a
country other than Italy, the duration and
the testing/inspection procedures of the
LPG tank can vary depending on the
national provisions in force in that
country. In any case, when the time limit
in the individual country has run out, go to
an Alfa Romeo Dealership to have the
tank replaced.
34A0K0322C
35A0K0323C
33
Page 42 of 216

DISPLAY
The car is equipped with a reconfigurable
multifunction display that, according to
the previously applied settings, will show
useful driving information.
With the ignition key removed, the
display lights up and shows the time and
total odometer reading (in km or miles)
for a few seconds when a door is
opened/closed.
RECONFIGURABLE MULTIFUNCTION
DISPLAY
The following information is shown on the
display (example given in fig. 38 ):
1: Time
2: Area reserved for messages
(information, settings, etc)
3: Milometer (total distance covered
in km or miles).4: Car status indications (e.g. doors open,
possible ice on road, etc.)/Start&Stop
function indication (for versions/
markets, where provided)/Gear Shift
Indicator (for versions/markets, where
provided)
5: Headlight alignment position (only with
dipped beam headlights on)
6: External temperature
The turbocharger pressure will appear on
some versions when “DYNAMIC” driving
mode is selected (see “Alfa DNA system”
in this chapter).GEAR SHIFT INDICATOR
The GSI (Gear Shift Indicator) system
advises the driver to change gear through
a special indication on the display.
Through the GSI, the driver is notified
that the gear change will allow a
reduction in fuel consumption.
Therefore, for driving oriented towards
reducing fuel consumption, it is advisable
to stick to “Natural” or “All Weather”
mode and to follow the suggestions of
the Gear Shift Indicator, where traffic
conditions permit.
When the SHIFT UP icon
is shown on
the display the GSI suggests the driver to
up-shift, whereas if the SHIFT DOWN
icon
is displayed, the driver is advised
to down-shift.
The indication in the instrument panel
remains on until the driver shifts gear or
the driving conditions go back to a
situation where gearshifting is not
required to improve consumption.
CONTROL BUTTONS
fig. 39: to scroll up the screen and
the respective items or to increase the
displayed value.
SET ESC: Press to access the menu
and/or go to the next screen or confirm
your choice. Hold down to go back to the
standard screen.
: to scroll through the screen and
the options downwards or to decrease
the value displayed.38A0K0600C
39A0K0541C
40
KNOWING THE INSTRUMENT PANEL
Page 62 of 216

ACTIVE SAFETYSYSTEMS
ABS SYSTEM
This system, which is an integral part of
the braking system, prevents one or more
wheels from locking and slipping in all
road surface conditions, irrespective of
the intensity of the braking action,
ensuring that the vehicle can be
controlled even during emergency
braking and optimising stopping
distances.
System intervention
The driver can feel that the ABS system
has come into action because the brake
pedal pulsates slightly and the system
gets noisier: this is entirely normal with
the system operating.
33) 34) 35) 36) 37) 38) 39)
ASR (AntiSlip Regulation)SYSTEM
40) 41) 42)
This is an integral part of the ESC system
and automatically operates in the event
of one or both drive wheels slipping, loss
of grip on wet roads (aquaplaning) and
acceleration on slippery, snowy or icy
roads, etc.System intervention
The system operates on the engine
power and brakes.
This is indicated by the flashing of the
warning light
on the instrument panel,
to inform the driver that the car is in
critical stability and grip conditions.
MSR (Motor Schleppmoment
Regelung)SYSTEM
The system prevents the drive wheels
from possibly locking, which could
happen, for example, if the accelerator
pedal is released suddenly or in the case
of a sudden downshifting in conditions of
poor grip.
In this conditions, the engine braking
effect could cause the drive wheels to
slip, resulting in a loss of vehicle stability.
In these situations, the system
intervenes, restoring torque to the
engine in order to conserve vehicle
stability and increase vehicle safety.
HBA (Hydraulic Brake Assist)SYSTEM
43) 44) 45)
The HBA system is designed to improve
the car’s braking capacity during
emergency braking: the HBA system
therefore completes the ABS system.
Maximum assistance from the HBA
system is obtained by continuously
pressing the brake pedal very quickly.
DST SYSTEM (Dynamic Steering
Torque)
46)
The DST function uses the integration of
the ESC system with the electric power
steering to increase the safety level of
the whole vehicle.
In critical situations (braking on surfaces
with different grip conditions), through
the DST function the ESC system
controls the steering to implement an
additional torque contribution on the
steering wheel, to suggest the most
correct manoeuvre to the driver.
The coordinated action of the brakes and
steering increases the sensation of
safety and control of the vehicle.
EBD SYSTEM
The EBD system is an integral part of the
ESC system and intervenes during
braking, distributing the brake force
optimally between front and rear wheels.
This guarantees greater braking stability
for the car, preventing sudden locking of
the rear wheels and the consequent
instability of the car.
ESC SYSTEM
The ESC system improves the directional
control and stability of the car in various
driving conditions.
60
SAFETY
Page 63 of 216

The ESC system corrects the car’s
understeer and oversteer, distributing
the brake force on the appropriate
wheels. The torque supplied by the
engine can also be reduced in order to
maintain control of the vehicle.
28) 29) 30) 31) 32)
The ESC system comprises the active
safety systems such as: ABS, EBD, ASR,
HILL HOLDER, etc.
The ESC system switches on
automatically when the engine is started
and cannot be switched off.
System intervention
This is indicated by the flashing of the
warning light
on the instrument panel,
to inform the driver that the car is in
critical stability and grip conditions.
CBC (Cornering Brake Control)SYSTEM
This system acts when braking on
corners, optimising the distribution of
brake pressure on the four wheels: the
system prevents the wheels on the inside
of the corner (less affected by the weight
of the car) from locking, ensuring better
stability and direction for the car.
HILL HOLDERSYSTEM
This is an integral part of the ESC system
and facilitates starting on uphill or
downhill slopes by operating the brakes:
IMPORTANT The Hill Holder system is
not a parking brake; therefore, never
leave the car without having engaged the
handbrake, turned the engine off and
engaged first gear, so that it is parked in
safe conditions (for further information
read the "Parking" paragraph in the
"Starting and driving" chapter).
IMPORTANT There may be situations on
small gradients (less than 8%), with car
laden, in which the Hill Holder system
may not activate, causing a slight
reversing motion and increasing the risk
of collision with another vehicle or object.
The driver is, in any case, responsible for
safe driving.
“ELECTRONIC Q2”SYSTEM (“E-Q2”)
The "Electronic Q2" system intervenes
during acceleration on corners, braking
the inner drive wheel and thus increasing
the traction of the outer wheel (which
bears more of the car’s weight): the
torque is thus distributed optimally
between the drive wheels in accordance
with the driving conditions and road
surface, permitting particularly effective,
sporty driving.
"PRE-FILL"SYSTEM (RAB - Ready Alert
Brake)
(only with 'Dynamic" mode activated)
This function activates automatically if
the accelerator pedal is released rapidly,
reducing the brake pad travel (both at
front and back), with the aim of preparing
the braking system and enhancing its
responsiveness, thus reducing the
stopping distance in the event of
subsequent braking.
WARNING
28)The ESC system cannot alter the natural
laws of physics, and cannot increase grip,
which depends on the condition of the road.
29)The ESC system cannot prevent
accidents, including those due to excessive
speed on corners, driving on low-grip
surfaces or aquaplaning.
30)The capability of the ESC system must
never be tested irresponsibly and
dangerously, in such a way as to compromise
personal safety and the safety of others.
31)For the correct operation of the ASR
system, the tyres must of necessity be the
same make and type on all wheels, in perfect
condition and, above all, of the prescribed
type and dimensions.
32)Do not take unnecessary risks, even if
your vehicle is fitted with the ESC and ASR
systems. Your driving style must always be
suited to the road conditions, visibility and
traffic. The driver is always responsible for
road safety.
61
Page 64 of 216

33)When the ABS intervenes and you feel
the brake pedal pulsating, do not reduce the
pressure, but hold it down firmly and
confidently; in doing so you will brake in the
shortest distance possible, depending on the
current road conditions.
34)To obtain the maximum efficiency of the
braking system, a bedding-in period of about
500 km is needed: during this period it is
better to avoid sharp, repeated and
prolonged braking.
35)If the ABS intervenes, this indicates that
the grip of the tyres on the road is nearing its
limit: you must slow down to a speed
compatible with the available grip.
36)The ABS cannot overrule the natural
laws of physics, and cannot increase the grip
available according to the condition of the
road.
37)The ABS cannot prevent accidents,
including those due to excessive speed on
corners, driving on low-grip surfaces or
aquaplaning.
38)The capability of the ABS must never be
tested irresponsibly and dangerously, in
such a way as to compromise personal
safety and the safety of others.
39)For the correct operation of the ABS, the
tyres must of necessity be the same make
and type on all wheels, in perfect condition
and, above all, of the prescribed type and
dimensions.
40)The ASR cannot overrule the natural
laws of physics, and cannot increase the grip
available according to the condition of the
road.
41)The ASR system cannot prevent
accidents, including those due to excessive
speed on corners, driving on low-grip
surfaces or aquaplaning.42)The capability of the ASR must never be
tested irresponsibly and dangerously, in
such a way as to compromise personal
safety and the safety of others.
43)The HBA system can’t overrule the
natural laws of physics, and can’t increase
the grip available according to the condition
of the road.
44)The HBA system cannot prevent
accidents, including those due to excessive
speed on corners, driving on low-grip
surfaces or aquaplaning.
45)The features of the HBA system must
never be tested in imprudent or dangerous
ways, with the possibility of putting the
safety of the driver, occupants or other road
users at risk.
46)DST is an aid for driving and does not
relieve the driver of responsibility for driving
the vehicle.iTPMS System (indirect Tyre
Pressure Monitoring System)
(for versions/markets, where provided)
DESCRIPTION
The car can be equipped with the iTPMS
(indirect Tyre Pressure Monitoring
System) which monitors the tyre inflation
status thanks to wheel speed sensors.
The system warns the driver if one or
more tyres are flat by the dedicated
warning light
continuously on and a
warning message on the display.
If one tyre only is flat, the system can
indicate its position: it is in any case
recommended to check the pressure on
all four tyres.
This indication is displayed also when
turning the engine off and on again until
the RESET procedure is carried out.
RESET PROCEDURE
The iTPMS needs an initial "self-learning"
phase (with length depending on the
driving style and road conditions: optimal
conditions being driving on a straight
road at 80 km/h for at least 20 minutes)
which starts when the RESET procedure
is carried out.
The Reset procedure must be carried out:
each time tyre pressure is modified;
when even only one tyre is changed;
when tyres are rotated/inverted;
62
SAFETY
Page 68 of 216

After about 30 seconds from the last
indication, the warning lights for rear
seats will switch off, irrespective of the
belt conditions (red or green).
IMPORTANT NOTES
All warning lights will remain off if all the
seat belts (front and rear) are already
fastened when the key it turned to MAR.
All the warning lights will come on when
at least one belt changes from fastened
to unfastened status or vice versa.PRE-TENSIONERS
56) 57)
The vehicle is equipped with front seat
belt pretensioners, which draw back the
seat belts by several centimetres in the
event of a strong frontal impact. This
guarantees the perfect adherence of the
seat belts to the occupant's bodies
before the retention action begins.
It is evident that the pretensioners have
operated when the belt withdraws
toward the retractor.
This car is also equipped with a second
pretensioner (fitted in the kick plate
area). Its activation is signalled by the
shortening of the metal cable.
A slight discharge of smoke may be
produced during the activation of the
pretensioner which is not harmful and
does not involve any fire hazard.
IMPORTANT To obtain the highest
degree of protection from the action of
the pretensioner, wear the seat belt tight
to the chest and pelvis.
The pretensioner does not require any
maintenance or lubrication: any changes
to its original conditions will invalidate its
efficiency. If, due to unusual natural
events (floods, sea storms, etc.), the
device has been affected by water and/or
mud, contact an Alfa Romeo Dealership
to have it replaced.
LOAD LIMITERS
To increase passenger safety, the front
seat belt reels contain a load limiter
which allows the force acting on the chest
and shoulders to be modulated during the
belt restraining action in the event of a
frontal impact.
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR USING
THE SEAT BELTS
Respect and ensure that all the other
occupants of the vehicle comply with the
local laws in force regarding the use of
seat belts. Always fasten the seat belts
before starting off.
58) 59)
Seat belts must also be worn by pregnant
women: the risk of injury in the event of
an accident is reduced for them and the
unborn child if they are wearing a seat
belt.
Pregnant women must position the lower
part of the belt very low down so that it
passes over the pelvis and under the
abdomen fig. 45.
66
SAFETY
Page 71 of 216
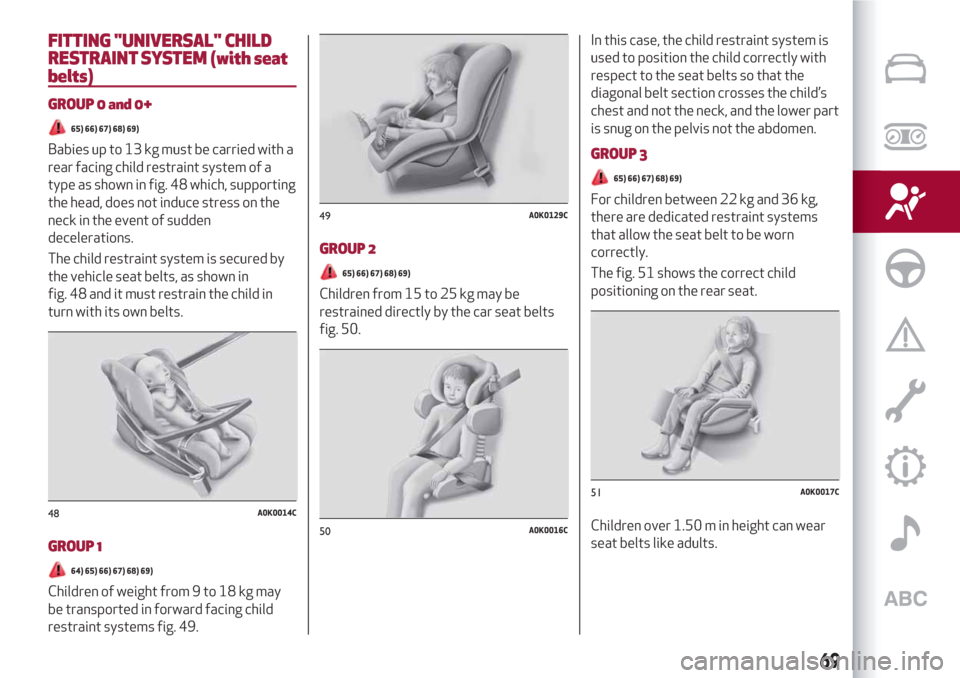
FITTING "UNIVERSAL" CHILD
RESTRAINTSYSTEM (with seat
belts)
GROUP 0 and 0+
65) 66) 67) 68) 69)
Babies up to 13 kg must be carried with a
rear facing child restraint system of a
type as shown in fig. 48 which, supporting
the head, does not induce stress on the
neck in the event of sudden
decelerations.
The child restraint system is secured by
the vehicle seat belts, as shown in
fig. 48 and it must restrain the child in
turn with its own belts.
GROUP 1
64) 65) 66) 67) 68) 69)
Children of weight from 9 to 18 kg may
be transported in forward facing child
restraint systems fig. 49.
GROUP 2
65) 66) 67) 68) 69)
Children from 15 to 25 kg may be
restrained directly by the car seat belts
fig. 50.In this case, the child restraint system is
used to position the child correctly with
respect to the seat belts so that the
diagonal belt section crosses the child’s
chest and not the neck, and the lower part
is snug on the pelvis not the abdomen.
GROUP 3
65) 66) 67) 68) 69)
For children between 22 kg and 36 kg,
there are dedicated restraint systems
that allow the seat belt to be worn
correctly.
The fig. 51 shows the correct child
positioning on the rear seat.
Children over 1.50 m in height can wear
seat belts like adults.
48A0K0014C
49A0K0129C
50A0K0016C
51A0K0017C
69
Page 79 of 216
FRONT AIRBAGS
“SMART BAG”SYSTEM (MULTISTAGE
FRONT AIRBAGS)
The car features multistage front airbags
(“Smart bag”) for driver and passenger.
The front driver/passenger airbags are
designed to protect occupants in the
event of frontal impacts of medium-high
severity, by placing the bag between the
occupant and the steering wheel or
dashboard.
Therefore non-activation in other types
of collisions (side collisions, rear shunts,
roll-overs, etc.) is not a system
malfunction.
Airbags are not a replacement of but
complementary to the seat belts, which
you are recommended to always wear. In
the event of impact, those not wearing a
seat belt are projected forwards and may
come into contact with the bag which is
still inflating. The protection offered by
the bag is compromised in these
circumstances.
74) 75) 77)
Front airbags may not activate in the
following situations:
frontal impacts against highly
deformable objects not involving the
front surface of the car (e.g. wing collision
against guard rail, etc.);
jamming of the car underneath other
vehicles or protective barriers (e.g.
underneath a truck or a guard rail) as, in
this case, the bags would offer no
additional protection with respect to the
seat belt and their deployment would be
inappropriate. Failure to activate in the
conditions described above is due to the
fact that they may not provide any
additional protection compared with seat
belts, so their activation would be
inappropriate. In these cases,
non-deployment does not indicate a
system malfunction.
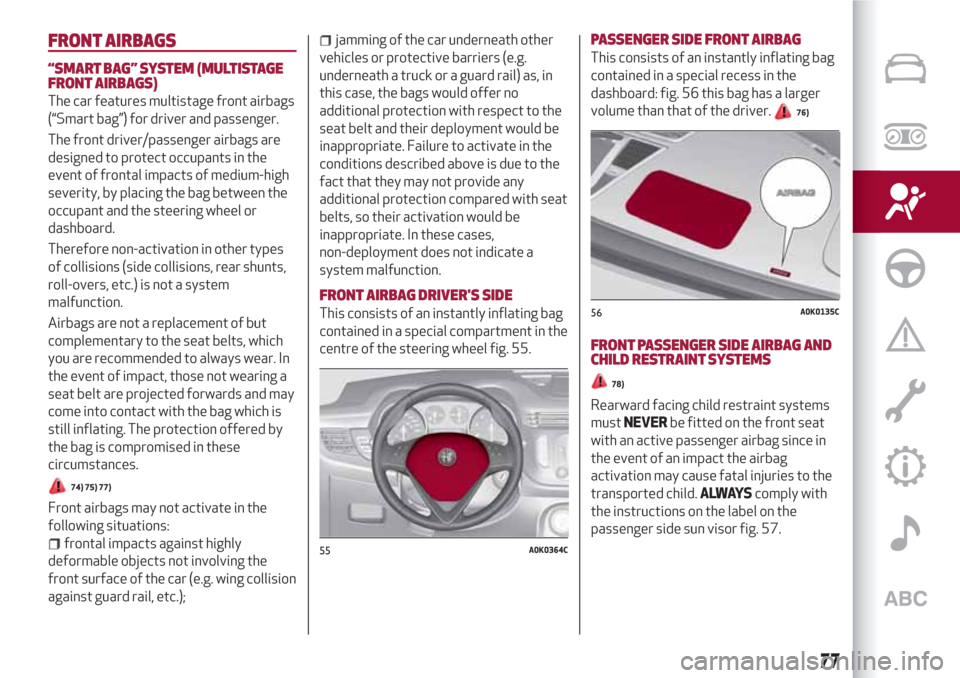
FRONT AIRBAG DRIVER'S SIDE
This consists of an instantly inflating bag
contained in a special compartment in the
centre of the steering wheel fig. 55.
PASSENGER SIDE FRONT AIRBAG
This consists of an instantly inflating bag
contained in a special recess in the
dashboard: fig. 56 this bag has a larger
volume than that of the driver.
76)
FRONT PASSENGER SIDE AIRBAG AND
CHILD RESTRAINTSYSTEMS
78)
Rearward facing child restraint systems
mustNEVERbe fitted on the front seat
with an active passenger airbag since in
the event of an impact the airbag
activation may cause fatal injuries to the
transported child.ALWAYScomply with
the instructions on the label on the
passenger side sun visor fig. 57.
55A0K0364C
56A0K0135C
77