2015 SKODA SUPERB warning light
[x] Cancel search: warning lightPage 163 of 276

Fig. 197
Segment display: Examples of status displays the CCS
Read and observe
on page 160 first.
CCS status displays » Fig. 196 , » Fig. 197
Speed is set, control is inactive (in the colour display the digits of speed
limits is shown in grey).
Control active (in the colour display the digits of the speed limits are high-
lighted).
No speed set.
System fault - seek assistance from a specialist garage immediately.
Basic requirements for start of control The CCS is activated.
On vehicles with a manual transmission , the second gear or higher is en-
gaged.
On vehicles with an automatic transmission , the selector lever is in the
D/S position or in the Tiptronic position.
The current speed is higher than approx. 20 km/h.
This is only possible within the range which is permitted by the power output and braking power of the engine.
WARNINGIf the engine power and engine braking effect is insufficient to maintain
the set speed, vehicle operation must be taken over!Operating DescriptionFig. 198
Cruise control system controls
Read and observe on page 160 first.
Overview of the CCS controls » Fig. 198ADeactivate CCS (delete set speed) Interrupt control (sprung position) Activate CCS (regulation deactivated)BTake control again a)
/ Increase speedCLaunch control / reduce speedDSwitching between CCS and speed limiter » page 162a)
If no speed is set the current speed is adopted.
At the start of the regulation the CCS regulates the vehicle to the current
speed, and this speed is shown on the instrument cluster display. The warning
light illuminates in the instrument cluster.
Automatic control interruption
Automatic control interruption occurs if any of the following conditions are
met.
▶ The brake pedal is operated.
▶ When one of the brake assist systems (e.g. ESC) intervenes.
▶ Through an airbag deployment.
▶ By pressing the button
D
» Fig. 198 .
WARNING■
Always deactivate the cruise control system after use to prevent the sys-
tem being switched on unintentionally.■
Control may only be resumed if the set speed is not too high for the cur-
rent traffic conditions.
161Assist systems
Page 164 of 276

Note■During control, speed can be increased by pressing the accelerator pedal. Re-
leasing the accelerator pedal will cause the speed to drop again to the set
speed.■
By pressing the button
D
» Fig. 198 during the regulation this is cancelled
and the Speed Limiter is activated.
Speed Limiter
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Operation
162
Operation description
163
The Speed Limiter limits the maximum driving speed to the set speed limit.
This limit can only be exceeded by depressing the accelerator pedal fully.
The condition in which the Speed Limiter monitors a potential set speed limit
excess is referred to as Regulation.
WARNINGThe general information relating to the use of assistance systems must be
observed » page 142, in section Introduction .
Operation
Fig. 199
MAXI DOT display (monochrome): Examples of Speed Limiter sta-
tus displays
Fig. 200
Segment display: Examples of Speed Limiter status displays
Read and observe
on page 162 first.
Status display of the Speed Limiter » Fig. 199, » Fig. 200
Speed limit is set, control is inactive (in the colour display the digits of
speed limits is shown in grey).
Control active (in the colour display the digits of the speed limits are high-
lighted).
No speed limit set.
System fault - seek assistance from a specialist garage immediately.
Basic requirements for start of control The Speed Limiter is activated.
The current speed is higher than approx. 30 km/h.
162Driving
Page 165 of 276
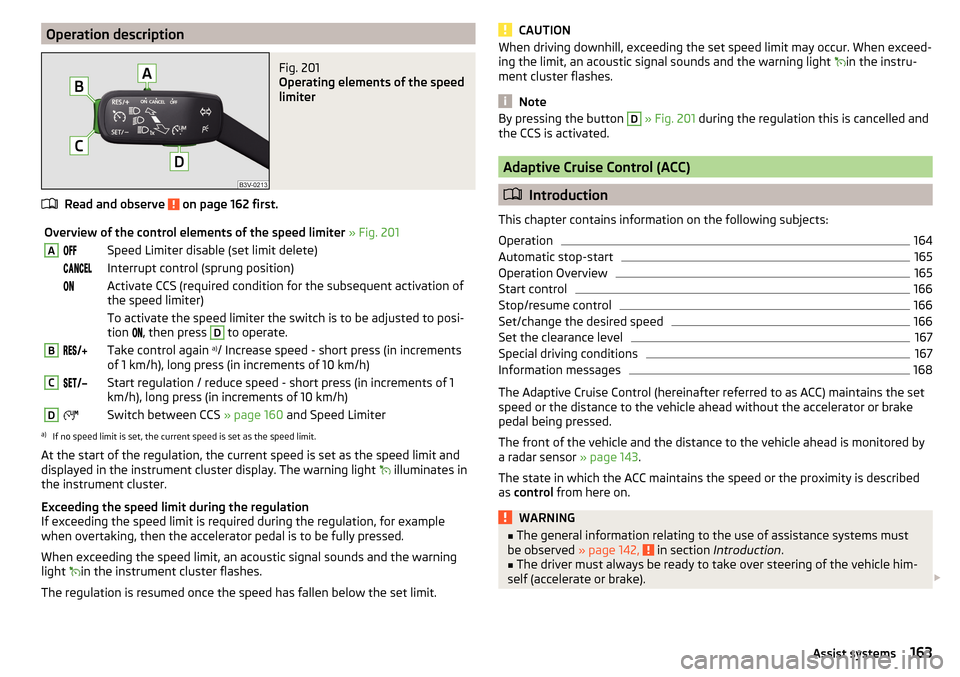
Operation descriptionFig. 201
Operating elements of the speed
limiter
Read and observe on page 162 first.
Overview of the control elements of the speed limiter » Fig. 201ASpeed Limiter disable (set limit delete) Interrupt control (sprung position) Activate CCS (required condition for the subsequent activation of
the speed limiter) To activate the speed limiter the switch is to be adjusted to posi-
tion
, then press D
to operate.
BTake control again a)
/ Increase speed - short press (in increments
of 1 km/h), long press (in increments of 10 km/h)CStart regulation / reduce speed - short press (in increments of 1
km/h), long press (in increments of 10 km/h)DSwitch between CCS » page 160 and Speed Limitera)
If no speed limit is set, the current speed is set as the speed limit.
At the start of the regulation, the current speed is set as the speed limit and
displayed in the instrument cluster display. The warning light illuminates in
the instrument cluster.
Exceeding the speed limit during the regulation
If exceeding the speed limit is required during the regulation, for example
when overtaking, then the accelerator pedal is to be fully pressed.
When exceeding the speed limit, an acoustic signal sounds and the warning
light in the instrument cluster flashes.
The regulation is resumed once the speed has fallen below the set limit.
CAUTIONWhen driving downhill, exceeding the set speed limit may occur. When exceed-
ing the limit, an acoustic signal sounds and the warning light in the instru-
ment cluster flashes.
Note
By pressing the button D » Fig. 201 during the regulation this is cancelled and
the CCS is activated.
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC)
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Operation
164
Automatic stop-start
165
Operation Overview
165
Start control
166
Stop/resume control
166
Set/change the desired speed
166
Set the clearance level
167
Special driving conditions
167
Information messages
168
The Adaptive Cruise Control (hereinafter referred to as ACC) maintains the set
speed or the distance to the vehicle ahead without the accelerator or brake
pedal being pressed.
The front of the vehicle and the distance to the vehicle ahead is monitored by
a radar sensor » page 143.
The state in which the ACC maintains the speed or the proximity is described
as control from here on.
WARNING■
The general information relating to the use of assistance systems must
be observed » page 142, in section Introduction .■
The driver must always be ready to take over steering of the vehicle him-
self (accelerate or brake).
163Assist systems
Page 166 of 276

WARNING (Continued)■The ACC does not react when approaching a stationary obstacle, such as
traffic jams, vehicle breakdowns or vehicles waiting at a traffic light.■
The ACC does not respond to crossing or oncoming objects.
■
If the ACC does not decelerate fast enough, immediately apply the vehi-
cle's foot brake.
WARNINGFor safety reasons, do not use the ACC under the following conditions.■When driving in turning lanes, motorway exits or construction sites, to
avoid an unwanted acceleration to the stored speed.■
When visibility is poor, (e.g. fog, heavy rain, thick snowfall).
■
When road conditions are poor (e.g. ice, slippery road, gravel, dirt road).
■
When driving around “sharp” bends.
■
When riding on a steep gradient / high slope.
■
When driving through places where metal objects (such as metal build-
ings, railway tracks, etc.) can be found.
■
When driving through very divided and enclosed spaces (such as large-ca-
pacity garages, car ferries, tunnels and the like.).
Note
■ The ACC is designed primarily for use on motorways.■The ACC reduces the speed by automatically releasing the accelerator or by
means of a braking procedure as appropriate. If the brakes are used for an au-
tomatic speed reduction at any moments, then the brake light illuminates.■
In case of failure of more than one brake light on the vehicle or on the con-
nected trailer, the ACC becomes unavailable.
■
The control automatically cancels the engagement of the brake supportive
assistance systems (e.g. ESC) or when the maximum permitted engine speed is
exceeded.
OperationFig. 202
Instrument cluster display: Examples of ACC displays
Fig. 203
Instrument cluster display: Examples of ACC status displays
Read and observe
on page 163 first.
The ACC allows you to set a speed of 30 - 160 or 210 km / h (depending on
equipment) and the distance to the vehicle ahead in the range of a very short
to a very long distance.
The ACC adjusts the set speed with respect to the detected vehicle ahead,
thus maintaining the selected proximity.
The ACC can detect a vehicle that is up to approx. 150 m ahead using the radar
sensor.
ACC display » Fig. 202
Vehicle detected (control active).
Line showing the displacement of the distance when setting » page 167,
Set the clearance level .
12164Driving
Page 167 of 276

Set distance to the vehicle ahead.
Vehicle detected (control deactivated).
ACC status indications » Fig. 203
Regulation is inactive (in the colour display the digits of speed limits is
shown in grey).
Regulation active - no vehicle detected (in the colour display the digits of
the speed limits are highlighted).
Regulation deactivated - no speed stored.
Regulation active - vehicle detected (in the colour display the digits of the
speed limits are highlighted).
Note to reduce speed
If the delay of the ACC is insufficient in relation to the vehicle in front, in the instrument cluster, the warning light lights up and the display shows the
following message.Apply the brake!
Regulation according to the vehicle in the adjacent lane
During regulation your vehicle may be regulated according to the vehicle in the adjacent lane.
This could occur at speeds above about 80 km / h when your vehicle is moving
faster than the vehicle in the adjacent lane on the driver's side. The display
shows the detected vehicle is in the adjacent lane.
Note
Some ACC notifications in the display of the instrument cluster may be hidden
by notifications for other functions. An ACC notification automatically appears
for a brief moment when there is a change in status of the ACC.
Automatic stop-start
Read and observe
on page 163 first.
Vehicles with an automatic transmission can decelerate to a standstill and
start moving again using the ACC.
Decelerate to a standstill
If a vehicle ahead decelerates to a standstill, the ACC will also decelerate your
vehicle to a standstill.
34Starting to drive again after a holding period
As soon as the vehicle ahead starts moving again after a holding period, your
vehicle will also move and the speed will continue to be regulated.
If the preceding vehicle starts moving again after a long break, then to contin-
ue the regulation press the accelerator pedal or lever to position
ad-
just » page 165 , Operation Overview .
Operation Overview
Fig. 204
Operating lever
Read and observe
on page 163 first.
Overview of ACC functions operated with the lever » Fig. 2041Activate ACC (regulation deactivated)2Start control (resume) / increase speed by 1 km/h at a time
(sprung position)3Interrupt control (sprung position)4Deactivate ACC5 Increase speed by 10 km/h at a time6 Decrease speed by 10 km/h at a timeA Set proximity levelBStart control (adopt current speed) / Reduce speed by 1 km/h at
a time
Note
If the lever is set » Fig. 204 from the position directly into the sprung posi-
tion, the current speed is stored and the control process is started.165Assist systems
Page 168 of 276

Start controlRead and observe
on page 163 first.
Basic requirements for start of control The ACC is activated.
The TCS is activated » page 143, Braking and stabilisation systems .
On vehicles with a manual transmission , the second gear or higher must
be engaged.
On vehicles with an automatic transmission , the selector lever must be in
the D/S position or in the Tiptronic position.
On vehicles with a manual transmission , the current speed must be higher
than approx. 25 km/h.
The control be started with the key or by adjusting the lever
» Fig. 204 on page 165 into the sprung position.
Button
›
Press the button .
The ACC will adopt the current speed and execute control.
Lever position
›
Set the lever into the sprung position Set.
The ACC will adopt the current speed and execute control. Should the speed be stored already, the ACC adopts this speed and executes control.
The warning light illuminates in the instrument cluster when the regulation
is switched on.
Note
■ If control is started at a speed of less than 30 km/h on vehicles with an auto-
matic transmission, the speed of 30 km/h is stored. The speed increases auto-
matically to 30 km/h or is regulated with respect to the speed of the vehicle
ahead.■
When TCS is disabled, it will be activated automatically upon starting control.
■
If the TCS is deactivated during control, control is stopped automatically.
Stop/resume control
Read and observe
on page 163 first.
Stop control
›
Set the lever into the sprung position
» Fig. 204 on page 165 Set.
Or
›
Apply the brake.
Control stops, the speed remains stored.
Resume control
›
Start control » page 166.
WARNINGControl may only be resumed if the stored speed is not too high for the cur-
rent traffic conditions.
Note
Regulation is also stopped when the clutch is held down for longer than 30 s.
Set/change the desired speed
Read and observe
on page 163 first.
The desired speed can be set or changed using the control lever » Fig. 204 on
page 165 .
The set speed is stored upon releasing the lever or the button on the button
on the lever.
Setting/changing the speed by 10 km/h at a time (
) - requirements
The ACC is activated.
Increasing the speed by 1 km/h at a time (
) - requirements
The ACC is activated.
The vehicle is controlled.
Decreasing the speed by 1 km/h at a time (
) - requirements
The ACC is activated.
The vehicle is controlled.
166Driving
Page 171 of 276

The Front Assist (hereinafter referred to as the system) warns you of the dan-
ger of a collision with a vehicle or another obstacle in front of the vehicle, and
tries to avoid a collision or mitigate its consequences by automatically applying
the brakes where necessary.
The area in front of the vehicle is monitored by a radar sensor » page 143.WARNING■
Please take note of the general points relating to the use of assistance
systems » page 142, in section Introduction .■
The system does not respond to crossing or oncoming objects.
CAUTION
In case of failure of more than one brake light on the vehicle or on the electri-
cally connected trailer, the system becomes unavailable.
Operation
Read and observe
and on page 169 first.
The system support is provided in the following manner.▶ Alerts you about a dangerous proximity to the vehicle ahead.
▶ Warns you of an impending collision.
▶ Prepares the brakes for emergency braking prior to a detected danger.
▶ Assists with a brake action triggered by the driver.
▶ If the driver fails to respond to a detected danger, an automatic braking ac-
tion is performed.
The system can work only if the following basic conditions are met. The system is activated.
The TCS is activated » page 143, Braking and stabilisation systems .
The vehicle is moving forwards at a speed of more than approx. 5 km/h.
Note
The system can be impaired or may not be available, for example when driving
in “sharp ”curves or with an ESC engagement » page 144.Distance warning (dangerous distance)Fig. 207
Symbols in the instrument cluster: Note (dangerous
proximity)
Read and observe and on page 169 first.
The display of the distance warning is for vehicles with MAXI DOT display.
If a safe interval to the vehicle ahead falls below a minimum the display of the
instrument cluster shows the symbol
» Fig. 207 .
Immediately increase the proximity if the current traffic situation allows you
to do so!
The proximity at which the warning is displayed depends on the current speed.
The warning may occur when driving between about 60 km/h and 210 km/h.
Warning and automatic braking
Fig. 208
Symbols in the instrument cluster: Warning or emer-
gency braking at low speed
Read and observe and on page 169 first.
Emergency braking at low speed
In a driving speed range of about 5 km/h to about 30 km/h the automatic brak- ing action is not preceded by a warning. With an immediate impact hazard au-
tomatic braking is done with the breaking force increasing in stages.
169Assist systems
Page 177 of 276

When the vehicle approaches a detected line between lanes, the system
makes a light movement of the steering wheel in the opposite direction to the
boundary line. This corrective steering intervention can be manually overrid-
den at any time.WARNING■ Please take note of the general points relating to the use of assistance
systems » page 142, in section Introduction .■
Lane Assist can help you keep the vehicle within the lane. However, it
does not steer the vehicle for you. The driver retains full responsibility for
steering at all times.
■
Some objects on the road may be incorrectly detected as lines. As a re-
sult, an incorrect steering intervention may take place.
WARNINGThe detection capability of the camera may be limited by various external
influences. In such cases, the assistant may not detect the line between
two lanes at all or not properly. The detection capability of the camera may
be restricted in the following situations, for example.■
When visibility is poor, (e.g. fog, heavy rain, thick snowfall).
■
When driving around “sharp” bends.
■
The camera is blinded by the sun.
■
The camera is blinded by the oncoming traffic.
■
The viewing range of the camera is impeded by a vehicle travelling ahead.
■
The camera viewing range is obstructed by an obstacle.
CAUTION
Do not attach any stickers or similar objects to the windscreen to avoid impair-
ing the functions of the systems.
Note
■ The system is designed for driving on motorways and roads with adequate
longitudinal markings.■
The system can detect both continuous and broken lines.
OperationFig. 212
Monochromatic display of the instrument cluster: Examples of
system indications
Fig. 213
Colour display of the instrument cluster: Examples of system in-
dications
Read and observe
and on page 175 first.
System Indicators » Fig. 212 and » Fig. 213
The system is active, but not ready to intervene.
The system is active and ready to intervene.
The system intervenes when approaching the right-hand boundary lane.
Adaptive lane assist ensues (boundary lines on both sides of the vehicle
detected).
175Assist systems