2015 KIA Soul EV torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 94 of 407

Features of your vehicle
24
4
Electric power steering (EPS)
The power steering uses a motor to
assist you in steering the vehicle. If the
vehicle is in not the ready ( ) mode
or if the power steering system
becomes inoperative, the vehicle may
still be steered, but it will require
increased steering effort.
The motor driven power steering is
controlled by a power steering con-
trol unit which senses the steering
wheel torque and vehicle speed to
command the motor.
The steering becomes heavier as
the vehicle’s speed increases and
becomes lighter as the vehicle’s
speed decreases for optimum steer-
ing control.
Should you notice any change in the
effort required to steer during normal
vehicle operation, have the power
steering checked by an authorized
Kia dealer. If the Electric Power Steering
System does not operate normally,
the warning light will illuminate on
the instrument cluster. The steering
wheel may require increased
steering effort. Take your vehicle to
an authorized Kia dealer and have
the vehicle checked as soon as
possible.
When you operate the steering wheel in low temperature, noise
may occur. If temperature rises, the
noise will likely disappear. This is a
normal condition.
When the vehicle is stationary, when the steering wheel is turned
all the way to the left or right con-
tinuously, the steering wheel
becomes harder to turn. The power
assist is limited to protect the
motor from overheating.
As time passes, the steering wheel
return to its normal condition.
✽ ✽ NOTICE
The following symptoms may occur
during normal vehicle operation:
• The EPS warning light does not
illuminate.
• The steering gets heavy immedi- ately after turning the POWER
button on. This happens as the
system performs the EPS system
diagnostics. When the diagnostics
are completed, the steering wheel
will return to its normal condition.
• A click noise may be heard from the EPS relay after the POWER
button is turned to the ON or OFF
position.
• A motor noise may be heard when the vehicle is at a stop or at a low
driving speed.
• If the Electric Power Steering System does not operate normally,
the warning light will illuminate on
the instrument cluster. The steer-
ing wheel may become difficult to
control or operate abnormally.
Take your vehicle to an authorized
Kia dealer and have the vehicle
checked as soon as possible. (Continued)
STEERING WHEEL
Page 282 of 407
719
Maintenance
EXPLANATION OF SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE ITEMS
Cooling system
Check the cooling system compo-
nents, such as the radiator, coolant
reservoir, hoses and connections ,
coolant 3way valve, chiller for leak-
age and damage. Replace any dam-
aged parts.
Coolant
The coolant should be changed at
the intervals specified in the mainte-
nance schedule.
Brake hoses and lines
Visually check for proper installation,
chafing, cracks, deterioration and
any leakage. Replace any deteriorat-
ed or damaged parts immediately.
Brake fluid
Check the brake fluid level in the
brake fluid reservoir. The level should
be between “MIN” and “MAX” marks
on the side of the reservoir. Use only
hydraulic brake fluid conforming to
DOT 3 or DOT 4 specification.
Brake discs, pads, calipers
and rotors
Check the pads for excessive wear,
discs for run out and wear, and
calipers for fluid leakage.
For more information on checking the
pads or lining wear limit, we recom-
mend you to refer to the Kia website.
(http://www
.kiatechinfo.com)
Suspension mounting bolts
Check the suspension connections
for looseness or damage. Retighten
to the specified torque.
Steering gear box, linkage &
boots/lower arm ball joint
With the vehicle stopped and off,
check for excessive free-play in the
steering wheel.
Check the linkage for bends or dam-
age. Check the dust boots and ball
joints for deterioration, cracks, or dam-
age. Replace any damaged parts.
Drive shafts and boots
Check the drive shafts, boots and
clamps for cracks, deterioration, or
damage. Replace any damaged
parts and, if necessary, repack the
grease.
Air conditioning refrigerant
Check the air conditioning lines and
connections for leakage and dam-
age.
Page 339 of 407
Specifications & Consumer information
28
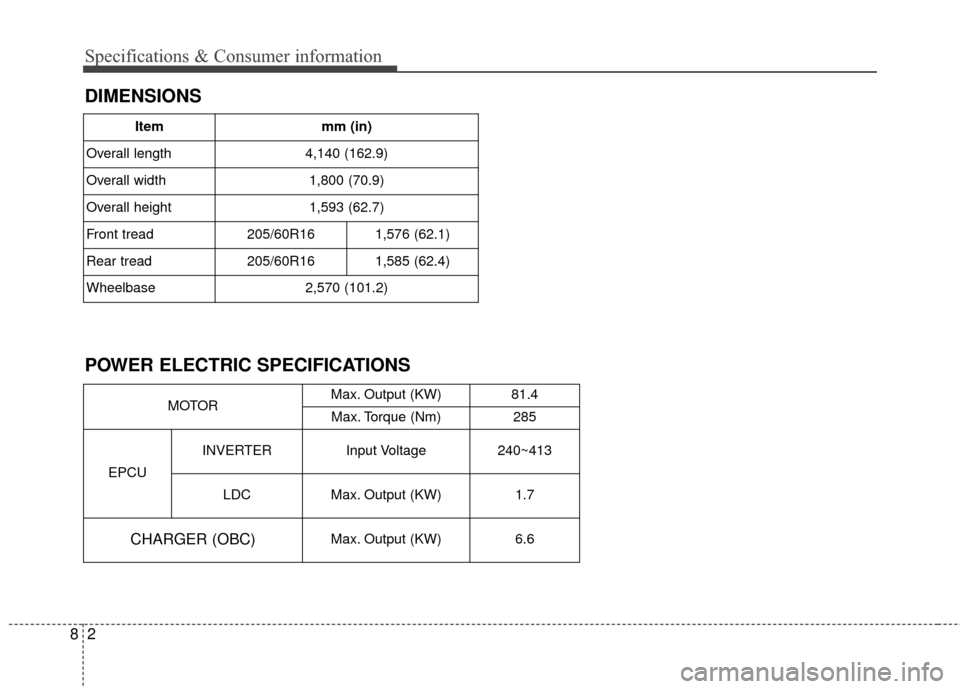
DIMENSIONS
POWER ELECTRIC SPECIFICATIONS
Itemmm (in)
Overall length
4,140 (162.9)
Overall width
1,800 (70.9)
Overall height
1,593 (62.7)
Front tread
205/60R161,576 (62.1)
Rear tread
205/60R161,585 (62.4)
Wheelbase
2,570 (101.2)
MOTOR Max. Output (KW)
81.4
Max. Torque (Nm) 285
EPCU INVERTER
Input Voltage 240~413
LDC Max. Output (KW) 1.7
CHARGER (OBC)Max. Output (KW)6.6
Page 342 of 407
85
Specifications & Consumer information
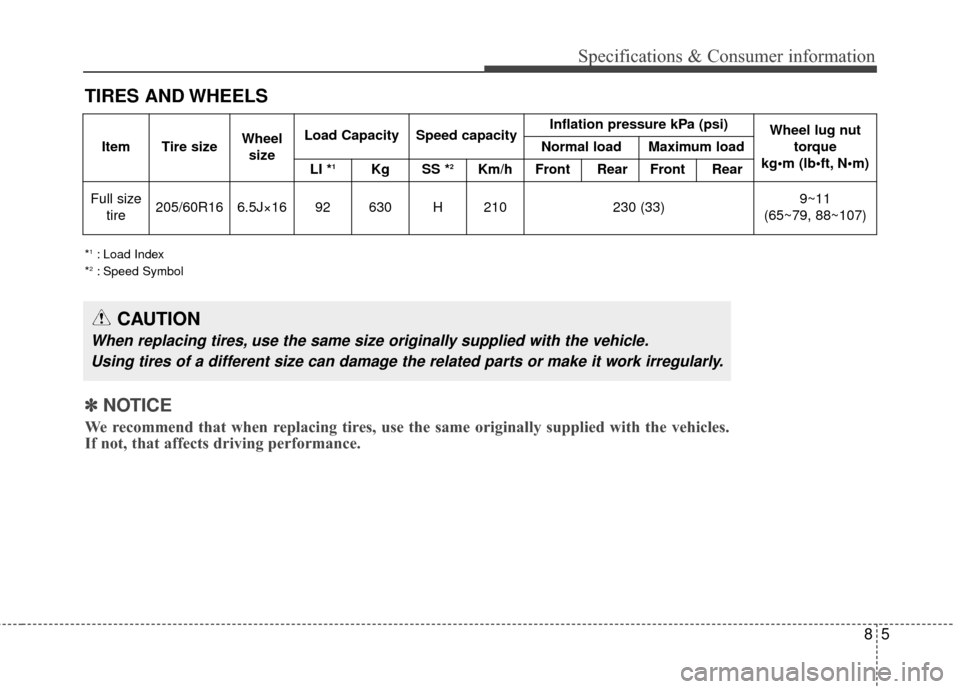
TIRES AND WHEELS
*1: Load Index
*2: Speed Symbol
ItemTire sizeWheel sizeLoad CapacitySpeed capacityInflation pressure kPa (psi)Wheel lug nut torque
kg•m (lb N
Normal loadMaximum load
LI *1KgSS *2Km/hFrontRear FrontRear
Full size tire205/60R166.5J×1692630H210230 (33)9~11
(65~79, 88~107)
CAUTION
When replacing tires, use the same size originally supplied with the vehicle.
Using tires of a different size can damage the related parts or make it work irregularly.
✽
✽ NOTICE
We recommend that when replacing tires, use the same originally supplied with the vehicles.
If not, that affects driving performance.
Page 347 of 407
2
An electric vehicle is driven using a
battery and an electric motor. While
general vehicles use an internal
combustion engine and gasoline as
fuel, electric vehicles use electrical
energy that is stored inside the high
voltage battery. As a result, electric
vehicles are eco-friendly in that they
do not require fuel and do not emit
exhaust gases.1. It is driven using the electrical ener-
gy that is stored inside the high
voltage battery. This method pre-
vents air pollution since fuel, like
gasoline, is not required, negating
the emission of exhaust gases.
2. A high performance motor is used in the vehicle as well. Compared
to standard, internal combustion
engine vehicles, engine noise and
vibrations are much more minimal
when driving.
3. When decelerating or driving down- hill, regenerative braking is utilized
to charge the high voltage battery.
This minimizes energy loss and
increases the distance to empty.
4. When the battery charge is not sufficient, normal charge, quick
charge and trickle charge are
available. (Refer to “Charge Types
for Electric Vehicle” for details.)
REVIEW OF ELECTRIC VEHICLE
Review of Electric Vehicle Characteristics of Electric
Vehicles
What does regenerative braking
do?
It uses an electric motor when
decelerating and braking and
transforms kinetic energy to elec-
trical energy in order to charge the
high voltage battery. (Torque is
applied in the opposite direction
when decelerating to generate
braking force and electric energy.)
Note
Page 349 of 407
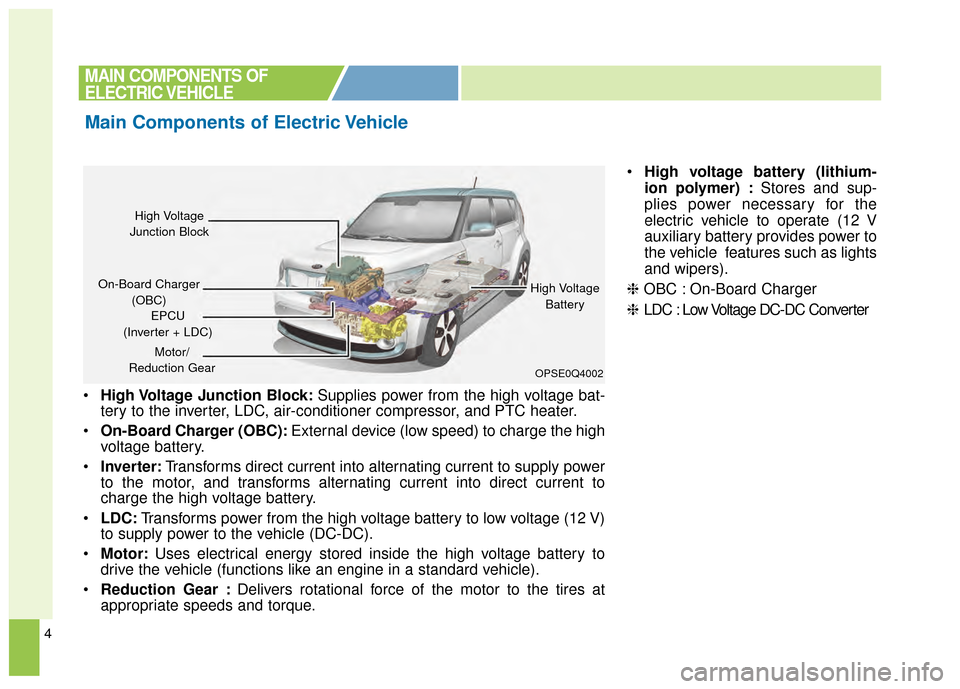
4
High Voltage Junction Block: Supplies power from the high voltage bat-
tery to the inverter, LDC, air-conditioner compressor, and PTC heater.
On-Board Charger (OBC): External device (low speed) to charge the high
voltage battery.
Inverter: Transforms direct current into alternating current to supply power
to the motor, and transforms alternating current into direct current to
charge the high voltage battery.
LDC: Transforms power from the high voltage battery to low voltage (12 V)
to supply power to the vehicle (DC-DC).
Motor: Uses electrical energy stored inside the high voltage battery to
drive the vehicle (functions like an engine in a standard vehicle).
Reduction Gear : Delivers rotational force of the motor to the tires at
appropriate speeds and torque.
High voltage battery (lithium-
ion polymer) : Stores and sup-
plies power necessary for the
electric vehicle to operate (12 V
auxiliary battery provides power to
the vehicle features such as lights
and wipers).
❈ OBC : On-Board Charger
❈ LDC : Low Voltage DC-DC Converter
MAIN COMPONENTS OF
ELECTRIC VEHICLE
Main Components of Electric Vehicle
OPSE0Q4002
High Voltage
Junction Block
On-Board Charger (OBC) High Voltage
Battery
EPCU
(Inverter + LDC)
Motor/
Reduction Gear