2014 SUBARU TRIBECA tire size
[x] Cancel search: tire sizePage 317 of 426

9-10In case of emergency
holder.
Refer to“Spare tire”F9-2 for its location,instructions and precautions.
CAUTION
.When stowing a flat tire in thespare tire holder, turn the hoistshaft end only slowly. If it isturned quickly, the wheel disc ofthe flat tire could be damaged.
.Afull-sizeflattireshouldbestowed in the spare tire holderin an emergency only. After hav-ing the flat tire repaired, immedi-ately swap it with the temporaryspare tire.
.Remember that the tread width ofa flat tire is wider than that of thetemporary spare tire. When car-rying a flat tire stowed in thespare tire holder, make sure thetire does not touch any obsta-cles.
WARNING
Never place a tire or tire changingtools in the passenger compartmentafter changing wheels. In a suddenstop or collisions, loose equipment
could strike occupants and causeinjury. Store the tire and all tools inthe proper place.
&Tire pressure monitoring
system (TPMS)
The tire pressure monitoring system pro-vides the driver with the warning messageindicated by sending a signal from asensor that is installed in each wheelwhen tire pressure is severely low.
The tire pressure monitoring system willactivate only when the vehicle is driven.Also, this system may not react immedi-ately to a sudden drop in tire pressure (forexample, a blow-out caused running overa sharp object).
WARNING
If the low tire pressure warning lightilluminates while driving, neverbrake suddenly and keep drivingstraight ahead while gradually redu-cing speed. Then slowly pull off theroad to a safe place. Otherwise anaccident involving serious vehicledamageand serious personal injurycould occur.
Check the pressure for all four tiresand adjust the pressure to the COLDtire pressure shown on the vehicleplacard on the door pillar on thedriver’s side. If this light still illumi-nates while driving after adjustingthe tire pressure, a tire may havesignificant damage and a fast leakthat causes the tire to lose airrapidly. If you have a flat tire, replaceit with a spare tire as soon aspossible.
When a spare tire is mounted or awheel rim is replaced without theoriginal pressure sensor/transmitterbeing transferred, the low tire pres-sure warning light will illuminatesteadily afterblinking for approxi-mately one minute. This indicatesthe TPMS is unable to monitor allfour road wheels. Contact your
Page 359 of 426
11-26Maintenance and service
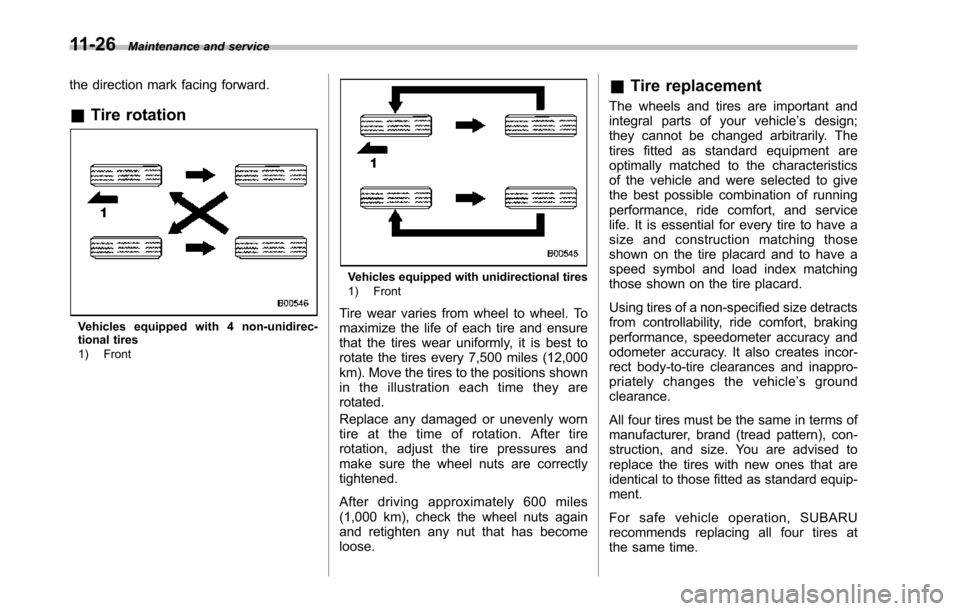
the direction mark facing forward.
&Tire rotation
Vehicles equipped with 4 non-unidirec-tional tires1) Front
Vehicles equipped with unidirectional tires1) Front
Tire wear varies from wheel to wheel. Tomaximize the life of each tire and ensurethat the tires wear uniformly, it is best torotate the tires every 7,500 miles (12,000km). Move the tires to the positions shownin the illustration each time they arerotated.
Replace any damaged or unevenly worntire at the time of rotation. After tirerotation, adjust the tire pressures andmake sure the wheel nuts are correctlytightened.
After driving approximately 600 miles(1,000 km), check the wheel nuts againand retighten any nut that has becomeloose.
&Tire replacement
The wheels and tires are important andintegral parts of your vehicle’s design;they cannot be changed arbitrarily. Thetires fitted as standard equipment areoptimally matched to the characteristicsof the vehicle and were selected to givethe best possible combination of runningperformance, ride comfort, and servicelife. It is essential for every tire to have asize and construction matching thoseshown on the tire placard and to have aspeed symbol and load index matchingthose shown on the tire placard.
Usingtires of a non-specified size detractsfrom controllability, ride comfort, brakingperformance, speedometer accuracy andodometer accuracy. It also creates incor-rect body-to-tire clearances and inappro-priately changes the vehicle’sgroundclearance.
All four tires must be the same in terms ofmanufacturer, brand (tread pattern), con-struction, and size. You are advised toreplace the tires with new ones that areidentical to those fitted as standard equip-ment.
For safe vehicle operation, SUBARUrecommends replacing all four tires atthe same time.
Page 360 of 426

WARNING
.When replacing a tire, you mustuse a tire that is of the same size,circumference, speed symboland load index as the originaltires listed on the tire placard.Using tires of other sizes, cir-cumferences or constructionsmay result in severe mechanicaldamage to the drive train of yourvehicle and may affect ride,handling, braking, speedometer/odometer calibration, and clear-ance betweenthe body and tires.It also may be dangerous andlead to loss of vehicle control.
.You must install four tires that areof the same size, circumference,construction, manufacturer,brand(tread pattern), degree ofwear, speed symbol and loadindex. Mixing tires of differenttypes, sizes or degrees of wearcan result in damage to thevehicle’spowertrain.Useofdifferent types or sizes of tirescan also dangerously reducecontrollability and braking per-formance and can lead to anaccident.
.Use only radial tires. Do not use
radial tires together with beltedbias tires and/or bias-ply tires.Doing so can dangerously re-duce controllability, resulting inan accident.
&Wheel replacement
When replacing wheels due, for example,to damage, make sure the replacementwheels match the specifications of thewheels that are fitted as standard equip-ment. Replacement wheels are availablefrom SUBARUdealers.
WARNING
Use only those wheels that arespecified for your vehicle. Wheelsnot meeting specifications couldinterfere with brake caliper opera-tion and may cause the tires to rubagainst the wheel well housing dur-ing turns. The resulting loss ofvehicle control could lead to anaccident.
Aluminum wheels
.Aluminum wheels can be scratchedand damaged easily. Handle them care-fully to maintain their appearance, perfor-mance, and safety.
.When any of the wheels are removedand replaced for tire rotation or to changea flat tire, always check the tightness ofthe wheel nuts after driving approximately600 miles (1,000 km). If any nut is loose,tighten it to the specified torque.–For the wheel nut tightening torque,refer to“Tires”F12-8.–For the wheel nut tightening proce-dure, refer to“Changing a flat tire”F9-6..Never apply oil to the threaded parts,wheel nuts, or tapered surface of thewheel.
.Never let the wheel rub against sharpprotrusions or curbs.
.When wheel nuts, balance weights, orthe center cap is replaced, be sure toreplace them with genuine SUBARU partsdesigned for the specific wheel.
Maintenance and service11-27
Page 385 of 426
12-8Specifications
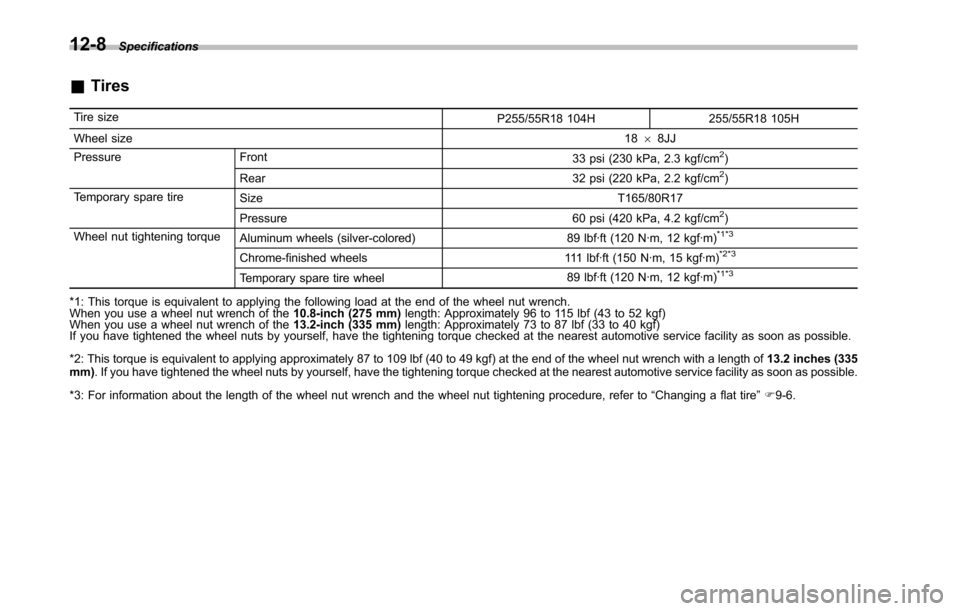
&Tires
Tire sizeP255/55R18 104H 255/55R18 105H
Wheel size1868JJ
Pressure Front33 psi (230 kPa, 2.3 kgf/cm2)
Rear 32 psi (220 kPa, 2.2 kgf/cm2)
Temporary spare tireSize T165/80R17
Pressure 60 psi (420 kPa, 4.2 kgf/cm2)
Wheel nut tightening torqueAluminum wheels (silver-colored) 89 lbf·ft (120 N·m, 12 kgf·m)*1*3
Chrome-finished wheels 111 lbf·ft (150 N·m, 15 kgf·m)*2*3
Temporary spare tire wheel89 lbf·ft (120 N·m, 12 kgf·m)*1*3
*1: This torque is equivalent to applying the following load at the end of the wheel nut wrench.When you use a wheel nut wrench of the10.8-inch (275 mm)length: Approximately 96 to 115 lbf (43 to 52 kgf)When you use a wheel nut wrench of the13.2-inch (335 mm)length: Approximately 73 to 87 lbf (33 to 40 kgf)If you have tightened the wheel nuts by yourself, have the tightening torque checked at the nearest automotive service facility as soon as possible.
*2: This torque is equivalent to applying approximately 87 to 109 lbf (40 to 49 kgf) at the end of the wheel nut wrench with a length of13.2 inches (335mm). If you have tightened the wheel nuts by yourself, have the tightening torque checked at the nearest automotive service facility as soon as possible.
*3: For informationabout the length of the wheelnut wrenchand the wheel nut tightening procedure, refer to“Changinga flat tire”F9-6.
Page 395 of 426
13-2Consumer information and Reporting safety defects
For U.S.A.
The following information has been
compiled according to Code of
Federal Regulations“Title 49, Part
575”.
Tire information
&Tire labeling
Many markings (e.g. Tire size, Tire
Identification Number or TIN) are
placed on the sidewall of a tire by
tire manufacturers. These markings
can provide you with useful infor-
mation on the tire.
!Tire size
Your vehicle comes equipped with
P-Metric tire size. It is important to
understand the sizing system in
selecting the proper tire for your
vehicle. Here is a brief review of the
tire sizing system with a breakdown
of its individual elements.
!P Metric
With the P-Metric system, Section
Width is measured in millimeters.
To convert millimeters into inches,
divide by 25.4. The Aspect Ratio
(Section Height divided by Section
Width) helps provide more dimen-
sional information about the tire
size.
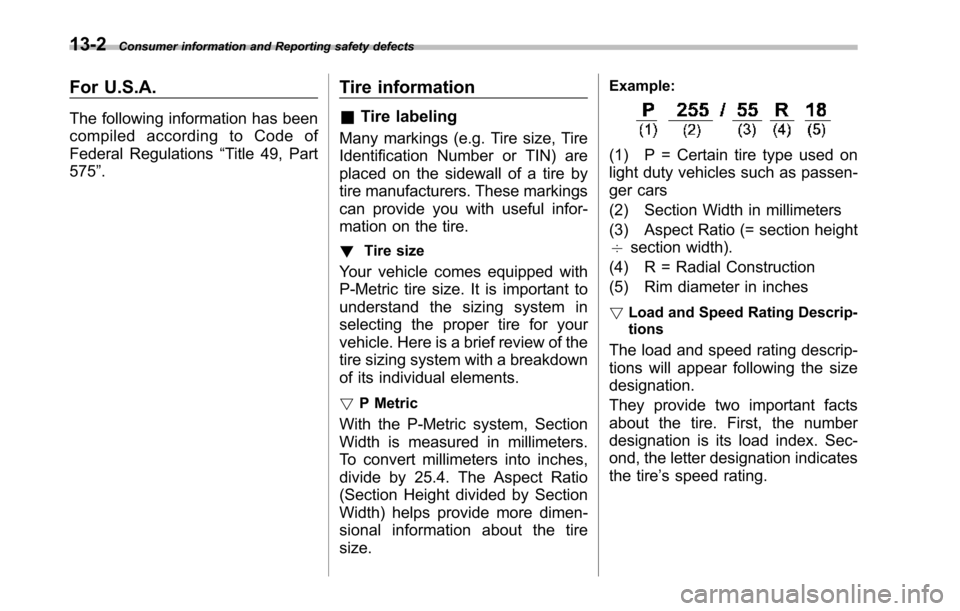
Example:
(1) P = Certain tire type used on
light duty vehicles such as passen-
ger cars
(2) Section Width in millimeters
(3) Aspect Ratio (= section height
7section width).
(4) R = Radial Construction
(5) Rim diameter in inches
!Load and Speed Rating Descrip-
tions
The load and speed rating descrip-
tions will appear following the size
designation.
They provide two important facts
about the tire. First, the number
designation is its load index. Sec-
ond, the letter designation indicates
the tire’s speed rating.
Page 396 of 426

Example:
(6) Load Index: A numerical code
which specifies the maximum load
atirecancarryatthespeed
indicated by its speed symbol, at
maximum inflation pressure.
For example,“104”means 1,984
lbs (900 kg),“100”means 1,764 lbs
(800 kg),“90”means 1,323 lbs (600
kg).
WARNING
Load indices apply only to the
tire, not to the vehicle. Putting
a load rated tire on any vehicle
does not mean the vehicle can
be loaded up to the tire’s rated
load.
(7) Speed Rating: An alphabetical
system describing a tire’s capability
to travel at established and prede-
termined speeds.
For example,“H”means 130 mph
(210 km/h).
WARNING
.Speed ratings apply only to
the tire, not to the vehicle.
Putting a speed rated tire on
any vehicle does not mean
the vehicle can be operated
at the tire’s rated speed.
.The speed rating is void if
the tires are worn out, da-
maged, repaired, retreaded,
or otherwise altered from
their original condition. If
tires are repaired, re-
treaded, or otherwise al-
tered, they may not be sui-
table for original equipment
tire designed loads and
speeds.
!Tire Identification Number (TIN)
Tire Identification Number (TIN) is
marked on the intended outboard
sidewall. The TIN is composed of
four groups. Here is a brief review
of the TIN with a breakdown of its
individual elements.
(1) Manufacturer’sIdentification
Mark
(2) Tire Size
(3) Tire Type Code
(4) Date of Manufacture
The first two figures identify the
week, starting with“01”to represent
the first full week of the calendar
year; the second two figures repre-
sent the year. For example, 0101
means the 1st week of 2001.
!Other markings
The following makings are also
placed on the sidewall.
!Maximum permissible inflation
pressure
The maximum cold inflation pres-
sure to which this tire may be
inflated. For example,“300 kPa
(44 PSI) MAX. PRESS”.
Consumer information and Reporting safety defects13-3
–CONTINUED–
Page 398 of 426

Example:
The vehicle placard shows original
tire size, recommended cold tire
inflation pressure on each tire at
maximum loaded vehicle weight,
seating capacity and loading infor-
mation.
!Adverse safety consequences
of under-inflation
Driving at high speeds with exces-
sively low tire pressures can cause
the tires to flex severely and to
rapidly become hot. A sharp in-
crease in temperature could cause
tread separation, and failure of the
tire(s). Possible resulting loss of
vehicle control could lead to an
accident.
!Measuring and adjusting air
pressure to achieve proper in-
flation
Check and, if necessary, adjust the
pressure of each tire (including the
spare) at least once a month and
before any long journey. Check the
tire pressures when the tires are
cold. Use a pressure gauge to
adjust the tire pressures to the
specific values. Driving even a
short distance warms up the tires
and increases the tire pressures.
Also, the tire pressures are affected
by the outside temperature. It is
best to check tire pressure out-
doors before driving the vehicle.
When a tire becomes warm, the air
inside it expands, causing the tire
pressure to increase. Be careful not
to mistakenly release air from a
warm tire to reduce its pressure.
&Glossary of tire terminology
.Accessory weight
The combined weight (in excess of
those standard items which may be
replaced) of automatic transmis-
sion, power steering, power brakes,
power windows, power seats, radio,
and heater, to the extent that these
items are available as factory-in-
stalled equipment (whether in-
stalled or not).
.Bead
The part of the tire that is made of
steel wires, wrapped or reinforced
by ply cords and that is shaped to fit
the rim.
.Bead separation
A breakdown of the bond between
components in the bead.
.Bias ply tire
A pneumatic tire in which the ply
cords that extend to the beads are
laid at alternate angles substantially
less than 90 degrees to the center-
line of the tread.
.Carcass
The tire structure, except tread and
Consumer information and Reporting safety defects13-5
–CONTINUED–
Page 400 of 426
.Measuring rim
The rim on which a tire is fitted for
physical dimension requirements.
.Normal occupant weight
150 lbs (68 kg) times the number of
occupants specified in the second
column of Table 1 that is appended
to the end of this section.
.Occupant distribution
Distribution of occupants in a vehi-
cle as specified in the third column
of Table 1 that is appended to the
end of this section.
.Open splice
Any parting at any junction of tread,
sidewall, or innerliner that extends
to cord material.
.Outer diameter
The overall diameter of an inflated
new tire.
.Overall width
The linear distance between the
exteriors of the sidewalls of an
inflated tire, including elevations
due to labeling, decorations, or
protective bands or ribs.
.Passenger car tire
A tire intended for use on passen-
ger cars, multipurpose passenger
vehicles, and trucks, that have a
gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR)
of 10,000 lbs (4,535 kg) or less.
.Ply
A layer of rubber-coated parallel
cords.
.Ply separation
Apartingofrubbercompound
between adjacent plies.
.Pneumatic tire
A mechanical device made of rub-
ber, chemicals, fabric and steel or
other materials, that, when
mounted on an automotive wheel,
provides the traction and contains
the gas or fluid that sustains the
load.
.Production options weight
The combined weight of those
installed regular production options
weighing over 5.1 lbs (2.3 kg) in
excess of those standard items
which they replace, not previously
considered in curb weight or acces-
sory weight, including heavy duty
brakes, ride levelers, roof rack,
heavy duty battery, and special
trim.
.Radial ply tire
A pneumatic tire in which the ply
cords that extend to the beads are
laid at substantially 90 degrees to
the centerline of the tread.
.Recommended inflation pres-
sure
The cold inflation pressure recom-
mended by a vehicle manufacturer.
.Reinforced tire
A tire designed to operate at higher
loads and at higher inflation pres-
sures than the corresponding stan-
dard tire.
.Rim
A metal support for a tire or a tire
and tube assembly upon which the
tire beads are seated.
.Rim diameter
Nominal diameter of the bead seat.
.Rim size designation
Rim diameter and width.
Consumer information and Reporting safety defects13-7
–CONTINUED–